IJCRR - 3(8), August, 2011
Pages: 101-109
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
SELECTIVE GENE SILENCING BY SMART DELIVERY OF NEWLY DESIGNED RNAI MATERIALS
Author: Yasuko Kitagishi, Hitomi Yoshida, Naoko Okumura, Mutsumi Murakami, Yuri Nishimura, Satoru Matsuda
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:The development of effective therapies for lethal diseases is highly desired. RNA interference (RNAi) is a
post-transcriptional gene silencing mechanism preserved during evolution. Intriguing aspect of the RNAi
is its attractive potential therapeutic value, because of their ability to target any disease for which the
genetic basis is known. As the use of RNAi for gene manipulation-tool has been extensively studied,
RNAi technology has not only become a powerful tool for functional molecular biology, but also
represents a promising novel therapeutic option for treating deseases. In this review, we will describe
these studies that demonstrate the feasibility of using RNAi and discuss potential strategies for improving
gene silencing. We will also discuss the recent consideration and challenges of using RNAi based
technologies.
Keywords: RNA interference, gene silencing, gene delivery, gene therapy
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION RNA
interference (RNAi) has emerged as an effective method of silencing gene expression in a variety of organisms. This method become a powerful tool of studying the function of genes. The RNAi pathway is mediated through small non-coding double stranded RNA, termed small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). An RNase III like enzyme known as Dicer processes double strand RNA into the siRNAs (1-3). The siRNA binds to homologous target mRNA, resulting in mRNA cleavage by RNA induced silencing complex (RISC). Due to the specificity of siRNAmediated mRNA cleavage, gene silencing via the RNAi pathway has also become an attractive method to target diseases (4). This is revolutionizing therapeutic target validation efforts. RNAi based therapy for cancer is one of the most progressing applications (5). Experimentally tested, effective targets are oncogenes or mutated anti-oncogenes, which are involved in cancer associated cellular pathways. Pathogenic viruses are also targets for RNAi, because they are unique in the host as exogenous sequences. Targeted gene silencing and virusspecific immunity against challenge with viruses have been obtained in shrimp by injection of long dsRNAs corresponding to sequences encoding viral structural proteins (6, 7). Successful use of an RNAi technique for gene knockdown in the symbiotic sea anemone has also been reported (8). Other therapeutically relevant fields are neurogenerative disease, metabolic disease, autoimmune diseases and dominant genetic disorders in a lot of species. The efficacy has highlighted a new therapeutic potential for various diseases. Actually, RNAi can be induced essentially by the following methods (Figure 1): i) cytoplasmic delivery of siRNA, which is chemically synthesized or in vitro transcribed; ii) nuclear delivery of gene expression vector that express short hairpin RNA (shRNA) driven by RNA polymerase III promoter, including U6, H1, 7SK, and tRNA promoters (9-11), or a pol II promoter such as cytomegalovirus; Viral delivery of the siRNA expression vector. However, widespread use of such beautiful approach is contingent on establishing appropriate systems to achieve clinically safe and efficiency. Now, there are many barriers to the ideal therapeutics.
What are obstacles along the way?
A major obstacle to applying RNAi in the clinic is the delivery. Administered siRNAs must get contact with the appropriate cells and following internalization, gain access to the cytosol where the RNAi machinery resides. This must be achieved so that silencing is effectively maximized, while minimizing any undesirable off-target effects (12, 13). Accordingly, siRNAs must be formulated so that they remain available for cellular uptake. In addition, they must be designed to resist degradation by nucleases. Naked siRNA is highly vulnerable to nucleases that render it ineffective. As an siRNA must circumvent such a large and diverse set of obstacles, the delivery system and siRNA formulation are very critical in the efficacy of RNAi based therapeutics. Effective in vivo delivery of siRNA has been therefore difficult. The transfer of DNA in gene therapy can also be achieved through viral systems, which show high efficacy, but have major limitations with regard to immunogenicity, risk of mutagenesis, large scale production and poor pharmacokinetics. However, systemic applications of virally delivered siRNA and related RNAi products are unlikely to be viable in the future, because of host immune responses on repeated delivery and ineffective targeting. Anyway, successful gene therapy requires safe and efficient delivery systems. Nonviral delivery systems are safe and easy to apply, but suffer from low transfection efficiency and transient gene expression (14). Although methods such as cationic polymers could enhance the gene transfection in vitro, the results of in vivo studies were still not so satisfactory. Targeting vectors have to overcome chemical and structural barriers to reach cells. Advanced targeted delivery as administration of antibody-based therapy results in hepatic sequestration of the antibody so that very little reaches the target tissues. Saturation of the RNAi machinery can also mediate unwanted effects. Overexpression of shRNA in mouse hepatocytes following intravenous infusion resulted in liver injury. High concentrations of siRNAs can disturb miRNA function (15). Furthermore, injection of multiple siRNAs can lead to competition for RISC resulting in less efficient silencing of one of the targeted genes (16). The duration of the response to treatment with siRNA will also have to be determined. In vitro, inactive nondividing cell siRNA treatment can have an effect that lasts up to 2 weeks, but in rapidly dividing cells, this effect may be as short as 24 to 48 h in duration. Nonviral vectors for delivering nucleic acid have improved dramatically in the last decade. Their activity is comparable with that of viral vectors in many cases. Their clinical development has also been accelerated recently. However, cationic lipids (Figure 2) and polymers induce a rapid increase in cellular reactive oxygen species (17, 18). Then, macrophages and other innate immune cells secrete inflammatory cytokines. In addition, siRNA often leads to off-target effects, a kind of unwanted toxicity (19).
Figuring out some way for improved gene delivery and RNAi materials Gene delivery
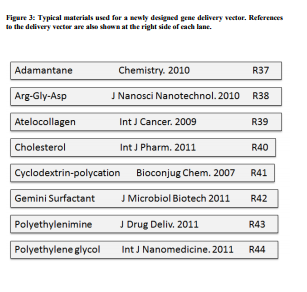
Gene silencing requires efficient uptake of siRNAs. Direct delivery of siRNAs critically relies on the protection of the instable siRNAs against degradation, efficient cellular internalization and correct subcellular localization and release of the siRNA from its formulation. Various systems for the delivery of unmodified or chemically modified siRNA molecules in vivo have been described. In a recent study, nanoparticles were synthesized to release siRNAs over several weeks (20, 21). These systems include the covalent conjugation to lipids, the covalent conjugation to peptides, aptamers or antibodies, the encapsulation in lipids, the complex formation with liposomes or the complex formation with cationic polymers. In addition to effective bioactivity, the absence of cytotoxicity is of major importance. Furthermore, siRNA formulations need to be highly biocompatible and must exhibit favourable profiles regarding pharmacokinetics. As the lipid reagent used in previous studies displayed some toxicity, an alternative method to deliver the siRNAs was needed. Naked siRNAs require chemical stabilization for in vivo use (22), have nonspecific biodistributions and require repeated dosages for more efficacy. It has been reported that siRNA uptake and gene-specific silencing at mucosal surface and lung occur by using unmodified siRNAs formulated in saline, delivered intranasally (23, 24). Modification of the siRNA sense strand by adding a cholesterol moiety results in siRNA uptake and silencing of the targeted gene. (25, 26) As injection of dsRNA is not possible in field conditions, oral delivery and uptake of dsRNA in the gut becomes critical. Oral delivery of siRNA knocking down the expression of target genes in whiteflies have been reported earlier. Several known barriers such as feeding physiology and behavioural factors determine the efficacy when given though the oral route (27). The stability might also differ as several digestive enzymes degrade part of siRNA and reduce its availability for gene silencing. An siRNA delivery vehicle that seems to overcome these limitations is a targeted cyclodextrin polymer system (28, 29). The three delivery components condense the siRNA within nanocomplexes and target them to receptors on target cells. One approach for the delivery of viral or nonviral DNA-based expression is plasmids encoding shRNAs which are processed to siRNAs (Figure 1). These plasmids have been developed with the aim of condensing DNA for protection against degradation and for good cellular uptake. In principle, the delivery of shRNA expression vectors can also be employed therapeutically in vivo. For analytical purposes, these plasmids can also be transfected by liposomal gene delivery agents, creating stable knockdown cell lines. Recently, in order to elevate the transfection efficiency of non-viral vector system, microbubble and the sonoporation inducted by ultrasound could be used to increase the uptake of plasmid DNA (30, 31). However,liposomal delivery agents have shown some successes in delivery to the liver but may carry with them unfavorable toxicity profiles. The cyclodextrin containing polycations (CDP) self-assemble to form colloidal particles, and their terminal imidazole groups assist in the intracellular trafficking and release of the nucleic acid. CDP protects the DNA/RNA from degradation so that chemical modification of the nucleic acid is unnecessary. The colloidal particles are stabilized by surface decoration with polyethylene glycol (PEG). (Figure 3) Some of the PEG chains contain targeting ligands for specific interactions with cell-surface receptors. To develop more novel, safe and more efficient systemic delivery systems, ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction (UTMD), as a means of stimulating cell membrane permeabilisation for a purpose of transferring plasmid DNA or drug into cells, has been highlighted to offer advantage over viral technologies. When UTMD was combined with cationic polymers or liposome, the gene transfection efficiency had been markedly improved (32). RNAi meterials There are basically two strategies to induce RNAi. In the first, pre-synthesized siRNAs are introduced into target cells. The blunt end may activate signaling proteins and induce unwanted production of interferon by stress response pathways in this case, however, being more powerful, the 27nt siRNAs can be used in smaller doses, avoiding this effect. Various chemical modifications of siRNA also tend to limit this type of unwanted toxicity. Subsequently, plasmids expressing short hairpin RNA (shRNA) have been developed (Figure 1). Although siRNA and shRNA elicit comparable results in RNAi experiments, the use of shRNA expression vectors is more appealing with several advantages over chemically synthesized siRNA. For example, the use of plasmid to express shRNA is relatively inexpensive and has been shown to achieve long-term target gene suppression in cells. The efficient delivery and stable integration of these shRNA expression cassettes into the host genome can be efficiently achieved by using various systems. In addition, inducible or cellspecific gene silencing can be easily obtained in vivo by using a DNA-based shRNA vector (33, 34). Most constructs have used Pol III promoters, including U6, H1, which is small and simple, and easily inserted into viral vectors. The advantages of these promoters are that they direct high levels of shRNA expression, which in turn mediates highly efficacious silencing, however, exceedingly high levels of shRNA expression increases the probability of off-target silencing and elicit non-specific effects such as interferon response and cellular toxicity. Regarding the construction of shRNA vector, the most common strategy requires the synthesis, annealing, and ligation of two complementary oligonucleotides encoding a desired shRNA target sequence into an expression vector. Another strategy in constructing siRNA vector is PCR approach (35). But, the unreliability of this method is in part due to the errors in the synthesis of long oligonucleotides ( more than 50-mer). In mammalian cells, interferon-mediated antiviral response to long dsRNA (more than 30 bp) causes the shutdown of protein synthesis. Due to their short length, siRNAs are originally believed not to induce interferon-related responses. However, activation of immune responses via toll-like receptors and retinoic acid inducible gene-I by siRNAs has been reported (36). Some of these responses are sequence or structure dependent and can therefore be avoided. Chemical modification of siRNAs is routinely used to prevent induction of immune responses. 2′-O-methyl and 2′-fluoro substitutions effectively negate immune stimulation. Minimal alterations to the siRNA backbone are preferable to maintain silencing efficiency of the siRNA.
CONCLUSION AND PERSPECTIVE
RNAi has transitioned from a biological mechanism to a powerful technology and much progress has been made in developing RNAi based therapeutics. In general, the use of RNAi as a therapeutic tool is attractive and promising strategy for various diseases in many species. Although the effectiveness of RNAi is undoubted, there are limitations to exploiting the technology properly due to inefficient delivery. The therapeutic applicability and success of RNAi will largely depend on their efficient and safe in vivo delivery avoiding unwanted sideeffects. Still, the best strategy is to develop potent delivery formulation such that only a small dose is needed to silence the target gene for activity to be therapeutic. Toxicity would not be an issue at low doses. In addition, it will decrease the cost of application because both the materials and the formulation of delivery can be very expensive. To sufficiently address the issues, further studies in appropriate animal models are warranted. The RNAi might be useful to treat epidemics of viral disease, however, this seems to be unrealistic at present, as it would be impossibly expensive to make and deliver such a reagent to a large population of field species. Instead, making transgenic organism which express an anti-viral shRNA might be a feasible way to be resistant the virus, if possible. As promising novel technique for gene therapy, the future clinical application requires vigorous investigations of efficacy and discoveries in RNAi biology will continue to guide development of RNAi based therapies
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by grants-in-aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology in Japan and Nara Women's University Intramural Grant for Project Research. A part of the work had been implemented by having a grant provided by Yamada Bee Farm Grant for Honeybee Research.
Competing interests statement
The authors declared that no conflict of interest exists.

References:
REFERENCES 1. Rossbach M. Small non-coding RNAs as novel therapeutics. Curr Mol Med 2010; 10: 361-8.
2. Rassouli FB, Matin MM. Gene silencing in human embryonic stem cells by RNA interference. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009; 390: 1106-10.
3. Jaskiewicz L, Filipowicz W. Role of Dicer in posttranscriptional RNA silencing. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2008; 320: 77-97.
4. Seyhan AA. RNAi: a potential new class of therapeutic for human genetic disease. Hum Genet 2011. [Epub ahead of print]
5. Okamoto K, Murawaki Y. The Therapeutic Potential of RNA Interference: Novel Approaches for Cancer Treatment. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 2011. [Epub ahead of print]
6. Shekhar MS, Lu Y. Application of nucleicacid-based therapeutics for viral infections in shrimp aquaculture. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 2009;11: 1-9.
7. Zhu F, Zhang X. Protection of Shrimp against White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) with β-1,3-D: -glucan-encapsulated vp28-siRNA Particles. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 2011. [Epub ahead of print]
8. Dunn SR, Phillips WS, Green DR, Weis VM. Knockdown of actin and caspase gene expression by RNA interference in the symbiotic anemone Aiptasia pallida. Biol Bull 2007; 212: 250-8.
9. Grimm D, Pandey K, Kay MA. Adenoassociated virus vectors for short hairpin RNA expression. Methods Enzymol 2005; 392: 381-405.
10. ter Brake O, 't Hooft K, Liu YP, Centlivre M, von Eije KJ, Berkhout B. Lentiviral vector design for multiple shRNA expression and durable HIV-1 inhibition. Mol Ther 2008; 16: 557-64.
11. Weiwei M, Zhenhua X, Feng L, Hang N, Yuyang J. A significant increase of RNAi efficiency in human cells by the CMV enhancer with a tRNAlys promoter. J Biomed Biotechnol 2009; 2009: 514287.
12. Schultz N, Marenstein DR, De Angelis DA, Wang WQ, Nelander S, Jacobsen A, et al. Off-target effects dominate a large-scale RNAi screen for modulators of the TGF-β pathway and reveal microRNA regulation of TGFBR2. Silence 2011; 2: 3.
13. Winkler J, Stessl M, Amartey J, Noe CR. Off-target effects related to the phosphorothioate modification of nucleic acids. ChemMedChem 2010; 5: 1344-52.
14. Chen YZ, Yao XL, Tabata Y, Nakagawa S, Gao JQ. Gene carriers and transfection systems used in the recombination of dendritic cells for effective cancer immunotherapy. Clin Dev Immunol 2010; 2010: 565643.
15. Khan AA, Betel D, Miller ML, Sander C, Leslie CS, Marks DS. Transfection of small RNAs globally perturbs gene regulation by endogenous microRNAs. Nat Biotechnol 2009; 27: 549-55.
16. Bitko V, Musiyenko A, Shulyayeva O, Barik S. Inhibition of respiratory viruses by nasally administered siRNA. Nat Med 2005; 11: 50-5.
17. Verdurmen WP, Brock R. Biological responses towards cationic peptides and drug carriers. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2011; 32: 116-24.
18. Kongkaneramit L, Sarisuta N, Azad N, Lu Y, Iyer AK, Wang L, Rojanasakul Y. Dependence of reactive oxygen species and FLICE inhibitory protein on lipofectamineinduced apoptosis in human lung epithelial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2008; 325: 969- 77.
19. Bennasser Y, Yeung ML, Jeang KT. RNAi therapy for HIV infection: principles and practicalities. BioDrugs 2007; 21: 17-22.
20. Ladewig K, Niebert M, Xu ZP, Gray PP, Lu GQ. Efficient siRNA delivery to mammalian cells using layered double hydroxide nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2010; 31: 1821- 9.
21. Wilson DS, Dalmasso G, Wang L, Sitaraman SV, Merlin D, Murthy N. Orally delivered thioketal nanoparticles loaded with TNF-α- siRNA target inflammation and inhibit gene expression in the intestines. Nat Mater 2010; 9: 923-8.
22. Tripp RA, Tompkins SM. Therapeutic applications of RNAi for silencing virus replication. Methods Mol Biol 2009; 555: 43-61.
23. Bonifazi P, D'Angelo C, Zagarella S, Zelante T, Bozza S, De Luca A, et al. Intranasally delivered siRNA targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR inflammatory pathways protects from aspergillosis. Mucosal Immunol 2010; 3: 193-205.
24. Fulton A, Peters ST, Perkins GA, Jarosinski KW, Damiani A, Brosnahan M, Buckles EL, Osterrieder N, Van de Walle GR. Effective treatment of respiratory alphaherpesvirus infection using RNA interference. PLoS One 2009; 4: e4118.
25. Zimmermann TS, Lee AC, Akinc A, Bramlage B, Bumcrot D, Fedoruk MN, et al. RNAi-mediated gene silencing in nonhuman primates. Nature 2006; 441: 111-4.
26. Soutschek J, Akinc A, Bramlage B, Charisse K, Constien R, Donoghue M, et al. Therapeutic silencing of an endogenous gene by systemic administration of modified siRNAs. Nature 2004; 432: 173-8.
27. Baum JA, Bogaert T, Clinton W, Heck GR, Feldmann P, Ilagan O, et al. Control of coleopteran insect pests through RNA interference. Nat Biotechnol 2007; 25: 1322- 6.
28. Bøe SL, Longva AS, Hovig E. Cyclodextrincontaining polymer delivery system for light-directed siRNA gene silencing. Oligonucleotides 2010; 20: 175-82.
29. Davis ME. The first targeted delivery of siRNA in humans via a self-assembling, cyclodextrin polymer-based nanoparticle: from concept to clinic. Mol Pharm 2009; 6: 659-68.
30. Escoffre JM, Kaddur K, Rols MP, Bouakaz A. In vitro gene transfer by electrosonoporation. Ultrasound Med Biol 2010; 36: 1746-55.
31. Sakai T, Kawaguchi M, Kosuge Y. siRNAmediated gene silencing in the salivary gland using in vivo microbubble-enhanced sonoporation. Oral Dis 2009; 15: 505-11.
32. Daigeler A, Chromik AM, Haendschke K, Emmelmann S, Siepmann M, Hensel K, et al. Synergistic effects of sonoporation and taurolidin/TRAIL on apoptosis in human fibrosarcoma. Ultrasound Med Biol 2010; 36: 1893-906.
33. Gust TC, Neubrandt L, Merz C, Asadullah K, Zügel U, von Bonin A. RNA interference-mediated gene silencing in murine T cells: in vitro and in vivo validation of proinflammatory target genes. Cell Commun Signal 2008; 6: 3.
34. Chen SW, Chen YX, Zhang XR, Qian H, Chen WZ, Xie WF. Targeted inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta subunit in hepatic stellate cells ameliorates hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gene Ther 2008; 15: 142435.
35. Yoshida H, Okumura N, Kitagishi Y, Nagata Y, Nishimura Y, Shirafuji Y, Matsuda S. APRICOT-1-2-3, A VERSATILE APRICOT-1-2-3, a versatile approach to cost-efficient genes RNA interference using artificial dual promoter cassette system. International Journal of Current Research 2010; 5: 30-33.
36. Robbins M, Judge A, MacLachlan I. siRNA and innate immunity. Oligonucleotides 2009; 19: 89-102.
37. Yu M, Zu SZ, Chen Y, Liu YP, Han BH, Liu Y. Spatially controllable DNA condensation by a water-soluble supramolecular hybrid of single-walled carbon nanotubes and betacyclodextrin-tethered ruthenium complexes. Chemistry 2010; 16: 1168-74.
38. Li Z, Huang P, Lin J, He R, Liu B, Zhang X, et al. Arginine-glycine-aspartic acidconjugated dendrimer-modified quantum dots for targeting and imaging melanoma. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 2010; 10: 4859-67.
39. Mu P, Nagahara S, Makita N, Tarumi Y, Kadomatsu K, Takei Y. Systemic delivery of siRNA specific to tumor mediated by atelocollagen: combined therapy using siRNA targeting Bcl-xL and cisplatin against prostate cancer. Int J Cancer 2009; 125: 2978-90.
40. Rosazza C, Phez E, Escoffre JM, Cézanne L, Zumbusch A, Rols MP. Cholesterol implications in plasmid DNA electrotransfer: Evidence for the involvement of endocytotic pathways. Int J Pharm 2011. [Epub ahead of print]
41. Bartlett DW, Davis ME. Physicochemical and biological characterization of targeted, nucleic acid-containing nanoparticles. Bioconjug Chem 2007; 18: 456-68.
42. Kim BK, Doh KO, Bae YU, Seu YB. Synthesis and optimization of cholesterolbased diquaternary ammonium Gemini Surfactant (Chol-GS) as a new gene delivery vector. J Microbiol Biotechnol 2011; 21: 93- 9.
43. Fortune JA, Novobrantseva TI, Klibanov AM. Highly effective gene transfection in vivo by alkylated polyethylenimine. J Drug Deliv 2011; 2011: 204058.
44. Chen XA, Zhang LJ, He ZJ, Wang WW, Xu B, Zhong Q, et al. Plasmid-encapsulated polyethylene glycol-grafted polyethylenimine nanoparticles for gene delivery into rat mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Nanomedicine 2011; 6: 843-53.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License