IJCRR - 4(6), March, 2012
Pages: 111-118
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
DRUG USE IN MEDICINE OUT-PATIENT DEPARTMENT: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY IN A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING HOSPITAL
Author: Arvind Kumar Yadav, Neha Sharma
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objective: To study the prescribing pattern of drugs in patients attending medicine outpatient department and to evaluate the drug used for rationality with the help of W.H.O core drug prescribing indicators. Methods: This prospective study was carried out in medicine outpatient department of a tertiary care teaching hospital for two months. The data was collected
from patients of all age and from either sex after taking written informed consent, in a proforma which included the patient's demographic details and the drugs prescribed. Data were analyzed for drug use pattern. Results: Total 450 prescriptions (2143 drugs) were analyzed. The analysis of pattern of drug use revealed that NSAIDS, vitamins, and antibiotics were the most frequently prescribed drug groups. Amongst antibiotics penicillin group was most commonly prescribed group. Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid combination was found be the most commonly prescribed antibiotic. FDCs in the form of multivitamin preparations were found to be highest in number. FDCs accounted for 36.73% of medicine formulations prescribed in our study. WHO core drug prescribing indicators show polypharmacy, and less drug prescribing by generic names. Only 35.09% of drugs were prescribed from the WHO Essential drug list. Antibiotics and injections were prescribed in 41.55% and 8.2% of encounters respectively. Conclusion: There is a need to educate the prescriber on rational drug therapy for benefits and safety of the patients. There is also need to conduct similar studies at frequent intervals of time, which would reflect the changing pattern of drugs in medicine out-patients.
Keywords: Prescribing pattern, fixed dose combinations, polypharmacy, essential drugs
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Irrational prescription of drugs is a common occurrence in clinical practice so, it is necessary to define the prescribing pattern and to target the irrational prescribing habits for giving feedbacks to clinicians for the benefit of the patients. [1] Irrational drug use can lead to reduction in quality of drug therapy, increased risk of side effects and drug resistance. [2] In the recent years studies on drug utilization have become potential tool to be used in the evaluation of health care system. Drug utilization research was defined by W.H.O (World Health Organization) in 1977 as ?the marketing, distribution, prescription and use of drug in the society, with special emphasis on the resulting medical, social and economic consequences?. [3] The assessment of drug utilization is important for clinical, educational and economic purposes. [4]
The ultimate goal of drug utilization research must be to assess whether drug therapy is rational or not. Rational use of drug implies the prescription of a well documented drug in an optimal dose on a right indication, with the correct information and at an affordable price. [3] Without knowledge on how drugs are being prescribed and used, it is difficult to determine rational drug use and to suggest measures to change the habits for the benefit of patients. Various factors influence the prescribing behavior of clinicians and to change the behavior it is necessary to understand the reasons behind it. [5] The important criteria for rational use are accurate diagnosis, proper prescribing, correct dispensing, suitable packing and patient adherence. [2] To assess the scope for improvement in rational drug use in OPD, the World Health Organization (WHO) has formulated a set of ?core drug use indicators‘. The WHO indicators are to be used to focus on the local health problems. The core prescribing indicators measure the performance of the prescriber, the patient care indicators measure what patients experience at health facilities, and facility indicators measure whether the health personnel can function effectively. [3] There has been constant development of many therapeutic agents and new therapeutic strategies, so drug utilization pattern needs to be evaluated from time to time so as to increase the therapeutic efficacy and decrease adverse effects. [6] Previously only few studies have been conducted to study the pattern of prescription in Rajasthan. No such study is carried out at our institute so the present study was undertaken to investigate the prescribing pattern of drug use in patients attending the medicine outpatient department of a tertiary care teaching hospital and to evaluate the drug used for rationality with the help of W.H.O core drug prescribing indicators and other drug prescribing parameters.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study was carried out in medicine outpatient department (OPD) of a tertiary care teaching hospital. This hospital satisfies the health care needs of thousands of patients of city and patients coming from nearby areas. This prospective study was carried out in medicine OPD on Monday to Saturday between 10 am to 12 noon during the period of May 2011 to June 2011. The data was collected from patients of all age and from either sex, who visit the medicine out-patient department of the hospital. All cases with drug prescription were included during the study period and the patients not willing to give information were excluded from the study. A total of 450 patients were included during the study period of two months. Approval from the institutional ethics committee was taken before starting the study. Written consent was taken from the patients or their relatives in an ?Informed Consent Form‘, after explaining them about the study in brief, in their local language. The data was collected in a case record form from the patient‘s case paper. This includes patient‘s demographic details, O.P.D registration number, provisional diagnosis/or diagnosis, chief complaints and complete prescription (Drug name, dose, frequency, and duration of prescription). Many of the drugs were prescribed by their brand names. Some drugs were prescribed from the hospital pharmacy by generic names. The generic names of drugs and generic contents of each formulation were obtained from commercial publication like Indian Drug Review (IDR). All the data/ or the parameters were expressed in percentage and finally the analysis was done for WHO core drug prescribing indicators (Average number of drugs per prescription, percentage of drugs prescribed by generic names, percentage of encounters with an antibiotic prescribed, percentage of encounters with an injection prescribed and percentage of drugs prescribed from the essential drug list).[3] Other parameters like prescribing frequency of drug or drug group and also prescribing frequency of fixed dose combinations (FDCs) were also analyzed. All the data collected was analyzed by using appropriate statistical tests.
OBSERVATIONS & RESULTS
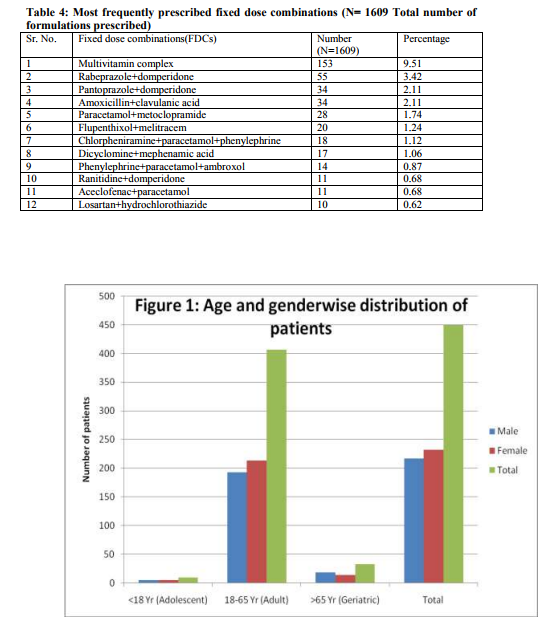
A total of 450 patients were included during the study period of two months. Of these 217 (48.22%) were males and 233 (51.78%) were females. The age of patients ranged from 12 years to 85 years. The adult age group (18-65 years) was found to be highest in number [407 (90.44%)] who visited medicine OPD. (Figure 1) Total 2143 drugs were prescribed in 450 patients in 1609 medicine formulations. The average number of drugs per patient was 4.76. Other WHO drug prescribing indicators are shown in Table 1. Various groups of drugs were prescribed in 450 patients. Most commonly prescribed drug group was NSAIDS (11.71%) followed by vitamins (10.31%), antibiotic (8.73%), and anti ulcer drugs (8.35%). (Table 2) The most commonly prescribed group of antibiotic was penicillin group (50.27%) followed by quinolones (29.95%), tetracyclines (10.70%), macrolides (3.74%). Most commonly prescribed antibiotic was found to be amoxicillin and clavulanic acid combination. (Table 3) Total number of fixed dose combinations was found to be 591 out of total 2143 drugs in 1609 medicine formulations. Most frequently prescribed FDC was multivitamin complex (9.51%), followed by rabeprazole and domperidone (3.42%). (Table 4).
DISCUSSION
Prescribing pattern of medicines reflects the physician‘s attitude towards the disease and the role of drugs in its treatment. Correct diagnosis of a disease and its management with medicines, constitute important aspects of patient care. The age distribution of the patients showed that the adult age group was found to be highest in number who visited medicine OPD. The large population of adult patients attending the OPD was also observed in a previous study. [7] A possible reason could be that this study was done in medicine OPD so patients below 12 (Pediatric patients) and older patients with multiple diagnosis which usually in-door patients were not included. Gender analysis revealed that female patients were slightly more in number (51.78%) compared to males (48.22%). Similar pattern was found in other study. [2] WHO core drug prescribing indicators measure the performance of health care providers in several key dimensions related to the appropriate use of drugs in outpatient settings. The average number of drugs per prescription was 4.76 which are higher than the recommended limit of 2.0. [8] In our study this could be because of higher percentage of involvement of FDCs in prescriptions. Similar findings have been reported in other studies from India. [9, 10, 11] Studies conducted in Nigeria (3.2) and Nepal (2.91) have also shown similar finding. [12, 2] This shows that polypharmacy and overprescribing are common in practice. Polypharmacy may lead to drug-drug interactions, adverse drug reactions, and cost of therapy. [13] Various reasons can account for this situation like lack of self confidence in doctors for diagnosing and treating common disease conditions; unrealistic expectations and demand for quick relief from the patients; availability of non-essential and irrational drug combinations; and aggressive medicine promotion and unethical marketing practices of pharmaceutical companies. [14] Most of the drugs in our study were prescribed by brand name; only 0.009% of drugs in our study were prescribed by generic name. This value is much less than other studies. [7, 9, 10, 12] The low percentage of drugs prescribed by generic names in our hospital is a matter of concern and the reasons for these should be investigated. This could be because our study was done in a private hospital where medical promotion of drugs by brand names is common and also involvement of more number of FDCs in prescription which are usually prescribed by brand name. Generic prescribing decreases the risk of wrong medicines being given to patients as many medicines with different generic names have similar brand names. Prescribing medicines by generic names avoids the confusion and makes the medicine therapy rational and cheaper. Moreover in the teaching institutions world over, in textbooks, in scientific journals and in the research publications, medicines are always mentioned by generic names. Despite this, most doctors prescribe the medicines by their brand names. The reasons for this could be tradition, aggressive medicine promotion, availability of multi-ingredient fixed dose drug combinations etc. [13] Antibiotics and injections were prescribed in 41.55% and 8.2% of encounters respectively which is lower than that reported by other studies. [10, 15] The lower number of encounters with an antibiotic or injection prescribed in our study is a welcome sign and has to be encouraged. Irrelevant use of the antibiotics can lead to the increased adverse events and increased chance of the bacterial resistance to the antimicrobial. [16] Use of the injection should be limited because it can cause local toxicity and also increase the risk of the toxicity and overall cost of the treatment for the patients. [17] Only 35.09% of drugs were prescribed from the WHO Essential drug list in our study. 39.6% and 66.9% of drugs were prescribed from the essential drug list in studies conducted in Nepal and India respectively. [7, 10] The low rate of prescribing of essential drugs is a matter of concern. Lack of awareness about essential drug concept and essential drug list among prescriber could be the cause of less prescribing from the Essential drug list. In our study it could be because of excessive use of multivitamin and combination preparations. It must be noted though that Essential drugs are primarily meant for primary healthcare systems while we studied drug utilization in a tertiary care teaching hospital. Increase in the use of essential medicines makes the medicine therapy more rational. [18] In our study most commonly prescribed drug group was NSAIDS followed by vitamins, antibiotics, and anti ulcer drugs. Other studies conducted in India have shown similar pattern. [9, 10] Amongst antibiotics, penicillin group was the most frequently prescribed drug group followed by quinolones, tetracycline, and macrolides.
Most commonly prescribed antibiotic was found to be amoxicillin and clavulanic acid combination which is a rational combination. These both drugs in this combination have similar pharmacokinetic properties which make this combination rational. Study done in Nepal has shown use of combination of ampicillin and cloxacillin which is an irrational combination which only adds cost and adverse effects of both drugs. [7] The antibiotics used in our hospital were well established one like penicillin group and this is to be welcomed. The use of antibiotics should be in accordance with the sensitivity patterns of microorganisms in the particular area. [19] If the organisms are sensitive to older antibiotics they should be used. The newer antibiotics are expensive and patients may not be able to afford a full course and they may opt for a truncated course increasing the likelihood of resistance. The newer antibiotics should be kept in reserve. Also, more data is available for older antibiotics which have been used in a larger number of patients and for a longer period of time. FDCs accounted for 36.73% of medicine formulations prescribed in our study. Multivitamin preparations were found to be most common FDC. In a previous study in Uttaranchal, India, FDCs accounted for 59% of drugs, [9] while study done in Nepal, FDCs accounted for 59% of drugs prescribed and multivitamin preparation was highest in number. [7] The use of combination products reduces the number of pills to be taken, cost of packing and dispensing fee. The patient adherence may be improved, as lesser number of drugs has to be ingested. There is an inverse relationship between patient adherence and the complexity of the regimen. [2] However, a problem noted was the use of irrational drug combinations in a few instances like multivitamin preparations are mostly considered as irrational, [20] which are prescribed in our study as well as in other studies. [7] It requires special attention to prevent excessive use of multivitamin preparations in prescriptions. Any drug utilization study based on the WHO core drug use indicators has limitations. Determining the quality of diagnosis and evaluating the adequacy of drug choices is beyond the scope of the prescribing indicators. In this study mean cost of drugs and mean duration of prescription were not calculated. Sample size is small in this study because data was collected for a period of two months only and data was collected for 2 hr only per day. Seasonal variation cannot be evaluated. So Further studies in this area using a larger sample size and for longer duration should be carried out, and a well designed training programme should be conducted on rational drug use. Prescriber education may be helpful in encouraging rational prescribing.
CONCLUSION
Drug use studies are a necessary tool for assessing prescribing patterns in hospitals, recognizing areas for improvement and improving drug prescribing practices in these facilities. For achieving the goal of rational use of medicines it is not sufficient to choose the right medicines only but also they must be employed in the most appropriate manner. This study revealed ample scope of improving the prescribing pattern by keeping the number of medicines as low as possible, prescribing medicines by generic names, prescribing more medicines from essential dug list, less use of antibiotic and injection. Some of the drug combinations being used were irrational. So rational fixed dose combinations should be encouraged and unnecessary use of multivitamin preparations should be avoided. There is need for some interventions to improve the standards of drug prescription. More studies are needed to be conducted to sensitize the practitioners about rational prescribing.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. We are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Das B. Prescribing trend of fixed-dose drug combinations in a tertiary hospital in Nepal. J Inst Med 2000; 22:145-49.
2. Alam K, Mishra P, Prabhu MM, Shankar PR, Subish P, Bhandari RB, et al. A study on rational drug prescribing and dispensing among outpatients in a tertiary care teaching hospital of Western Nepal. Kathmandu Uni Med J. 2006; 15:436-44.
3. World Health Organization. Introduction to drug utilization research. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2003.
4. Uppal R, Nayak P, Sharma PL. Prescribing trends in internal medicine. Int J Clin Pharm Ther Toxicol 1984; 22:373-76. 5. Soumerai SB. Factors influencing prescribing. Aust J Hosp Pharm 1988(Suppl); 18:9-16.
6. Krishnaswamy K, Dinesh KB. A drug survey-precepts and practices. Eur J clin Pharmacol 1985; 29:363-70.
7. Lamichhane DC, Giri BR, Pathak OK, Panta OB, Shankar PR. Morbidity profile and prescribing patterns among outpatients in a teaching hospital in Western Nepal. MJM 2006; 9:126-33.
8. World Health Organization. How to investigate drug use in health facilities: selected drug use indicators. EDM research series no.7. Geneva. World Health Organization; 1993; 1:1-87.
9. Rishi RK, Sangeeta S, Surendra K, Tailang M. Prescription audit: experience in Garhwal (Uttaranchal), India. Trop doct. 2003; 33:76-9.
10. Bhartiy SS, Shinde M, Nandeshwar S, Tiwari SC. Pattern of prescribing practices in the Madhya Pradesh, India. Kathmandu Uni Med J 2008; 6:55-9.
11. Zaveri HG, Mansuri SM, and Patel VJ. Use of potentially inappropriate medicines in elderly: a prospective study in medicine out-patient department of a tertiary care teaching hospital. Indian J Pharmacol. 2010; 42:95–8.
12. Enwere OO, Falade CO, Salako BL. Drug prescribing pattern at the medical outpatient clinic of a tertiary hospital in southwestern Nigeria. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2007; 16:1244-9.
13. Mirza NY, Desai S, Ganguly B. Prescribing pattern in a pediatric outpatient department in Gujarat. Bangladesh J Pharmacol 2009; 4:39- 42.
14. Ansari KU, Singh S, Pandey RC. Evaluation of prescribing pattern of doctors for rational drug therapy. Indian J Pharmacol. 1998; 30:43-6.
15. Chukwuani CM, Onifade M, Sumonu K. Survey of drug use practices and antibiotic prescribing pattern at a general hospital in Nigeria. Pharm World Sci 2002; 24:188-95.
16. Rees RE, Betts RF, Gumustop B. Handbook of antibiotics. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincottt Willium and Wilkins; 2000.
17. Brunton LL, Lazo JS, Parker KL, editors. Goodman & Gillman‘s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 11th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2006.
18. Desai S. Essential drugs and rational drug therapy. Bull Soc Rational Ther. 2001; 12:2-7.
19. World Health Organization. WHO global strategy for containment of antimicrobial resistance. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2001.
20. Poudel A, Palaian S, Shankar PR, Jayasekera J, Izham MIM. Irrational fixed dose combinations in Nepal: need for intervention. Kathmandu Uni Med J 2008; 6:399-405.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License