IJCRR - 4(19), October, 2012
Pages: 100-121
Date of Publication: 15-Oct-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFECT OF CONTAMINATION ON BOND STRENGTH OF ORTHODONTIC LIGHT CURE ADHESIVE SYSTEM- A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Author: K. Ambika, S. Aravind Kumar, K. K. Shanta Sundari
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim: The aim of the systemic review is to emphasize the effect of contamination on bond strength of orthodontic light cure adhesives. Methods: The search was carried out by electronic database- Advance PubMed. The studies were selected if they met the following criteria: It should be In-Vitro study. Specimen used should be human or bovine teeth. Media used for contamination are saliva, blood or water. Orthodontic brackets or buttons bonded to the enamel surface of the teeth with orthodontic light cure adhesives by direct bonding technique. Results: Thirty articles were selected based on the inclusion criteria. Bond strength of different orthodontic primers and adhesives were recorded as variables of interest. Conclusion: It was concluded that contaminations affect the bond strength of orthodontic light cure adhesives.
Keywords: Bond strength, moist contamination, orthodontics, light cure adhesives.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The conventional method for bonding the orthodontic brackets to enamel surface necessitates three different agents: an enamel etchant, a primer solution, and an adhesive resin. It is paramount to keep the tooth surface absolutely dry during bonding to provide proper bonding between the enamel and adhesives. This is estimated as bond strength of the material. Clinically accepted bond strength for orthodontic bracket is range from 6 to 8 MPa (Reynolds 1975)1 . Michael G Buonocore (1955)2 revolutionized dentistry with his depicting finding of etching and bonding of acrylic to enamel. He embarked on his bonding research in July 1954 by etching the enamel for 30 seconds with 85% phosphoric acid and then rinsing the surface with water. Retief et al3 also illustrated the surface conditioning is essential for increasing the bond strength of bonding material to enamel. In 1962, Bowen introduced bisphenol A-glycidyl dimethacrylate (bisGMA) resin. Bis-GMA proved to be stronger and more stable than the acrylic and epoxy resins which were in use at that time4 . In 1964, there was a revolution in the orthodontic society when Newmann5 successfully bonded orthodontic brackets to the teeth, by means of the acid-etch technique and an epoxy-derived resin. Bonding procedure includes: a) Thorough prophylaxis to provide a clean bonding surface. b) 37% phosphoric acid gel or aqueous solution applied for approximately 15 seconds to etch. c) Rinsing with copious amounts of water. d) Dry the surface with moisture and oil-free air to show the frosty, chalky white demarcated etched enamel surface. e) Apply the primer and bond the bracket with composite under a dry field and cure it with light cure unit. The presence of moisture contamination during bonding of orthodontic brackets is the most common reason for bond failure. Contamination causes plugging of the porosities produced by acid etching and a reduction in surface energy. Eventually resin penetration is impaired, and micromechanical retention is compromised6 . The contamination may be due to either water or saliva or blood or combination of these three. To overcome the effect of contamination, lots of newer adhesives have been introduced in the market with a minimal variation in composition. The purpose of the systematic review is to emphasize the effect of contamination on bond strength of orthodontic light cure adhesives. Structured Question Does the contamination affect the bond strength of orthodontics light cure adhesive system? Search Strategy Electronic databases: Advance Pubmed
SEARCH METHODOLOGY
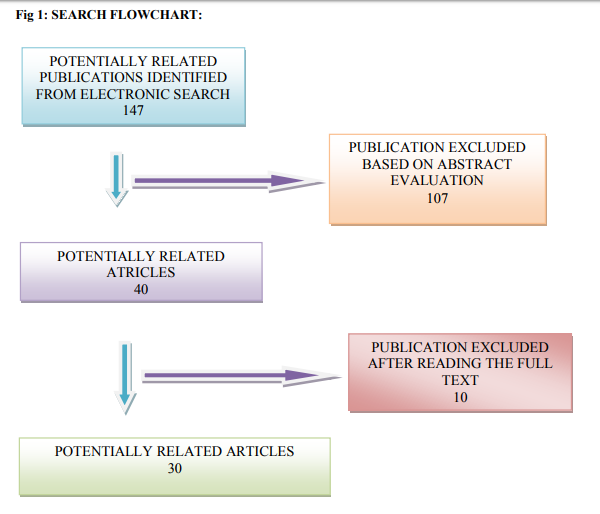
The search methodology applied in PUBMED was as follows: (adhesives or dental adhesives or light cure adhesives or light cure adhesive or composite or dental composite or light cure composite or light cure resin) and (saliva contamination or water contamination or blood contamination) and (bond strength or dental bond strength or shear bond strength or orthodontic debonding or bond failure or debracketing).(Fig 1)
Inclusion Criteria
Studies were selected if they met the following criteria:
1. In-vitro studies
2. Specimen may be human or bovine teeth
3. Media used for contamination are saliva, blood or water.
4. Orthodontic brackets and buttons bonded to the enamel surface of the teeth with orthodontic light cure adhesives.
5. Direct bonding technique.
Exclusion criteria
1. Ex-vivo or in-vivo studies are excluded.
2. Studies done using materials other than orthodontic adhesives.
3. Studies done using chemical cured and dual cured adhesives.
RESULT
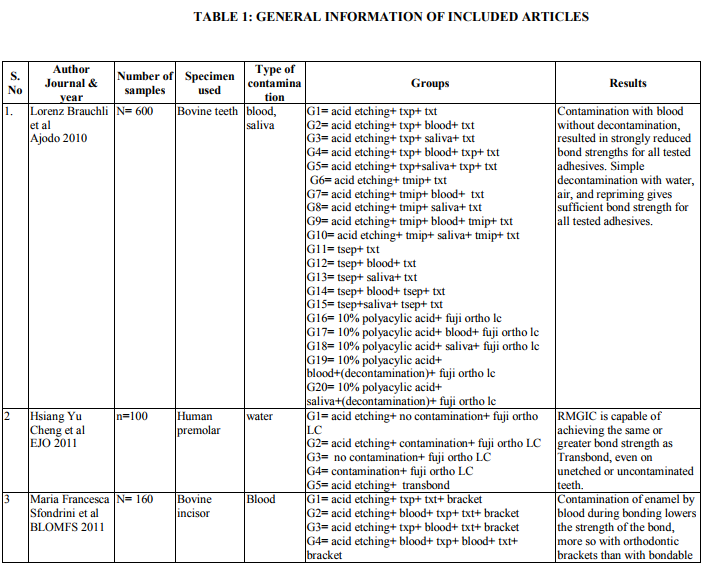
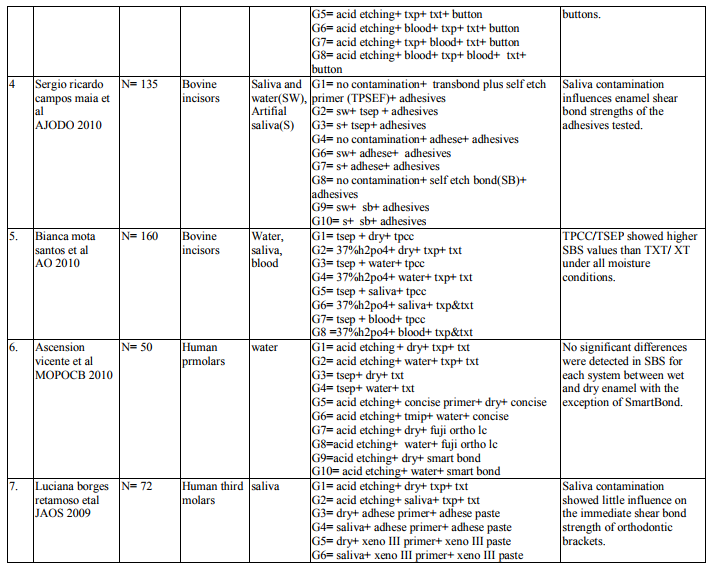
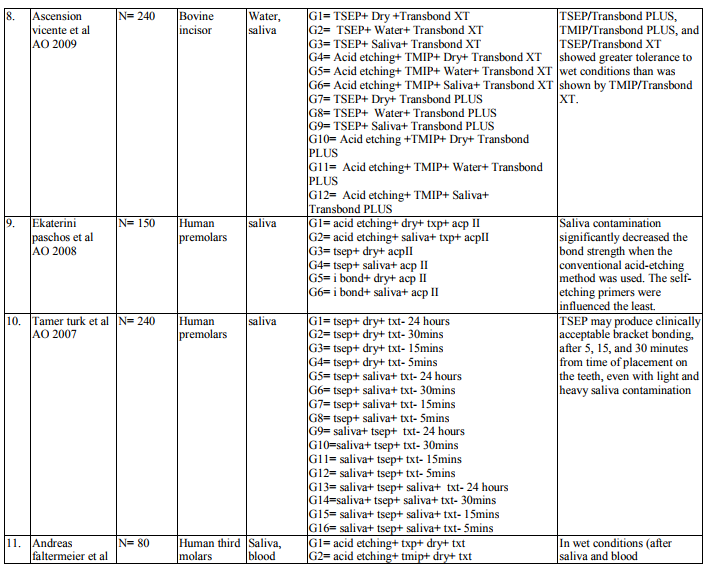
1.irty articles were selected based on the inclusion criteria.
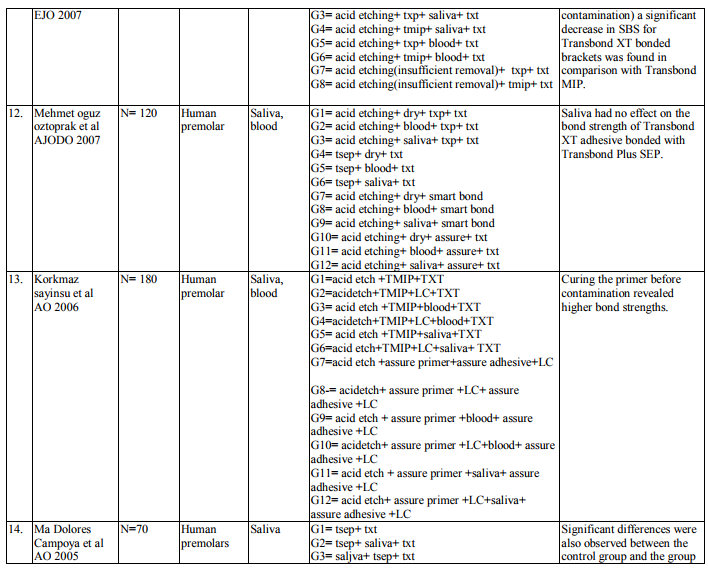
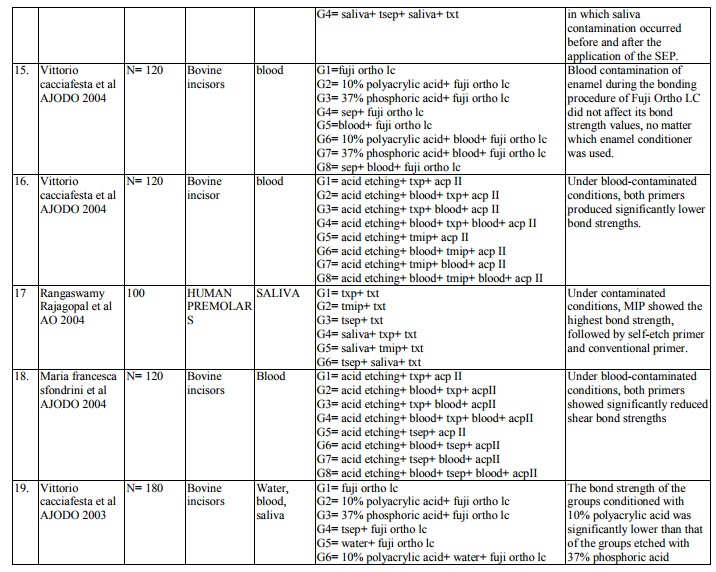
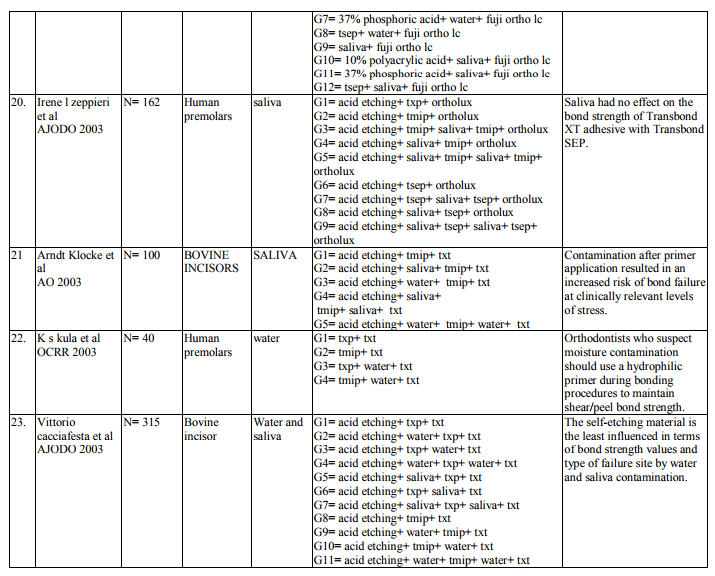
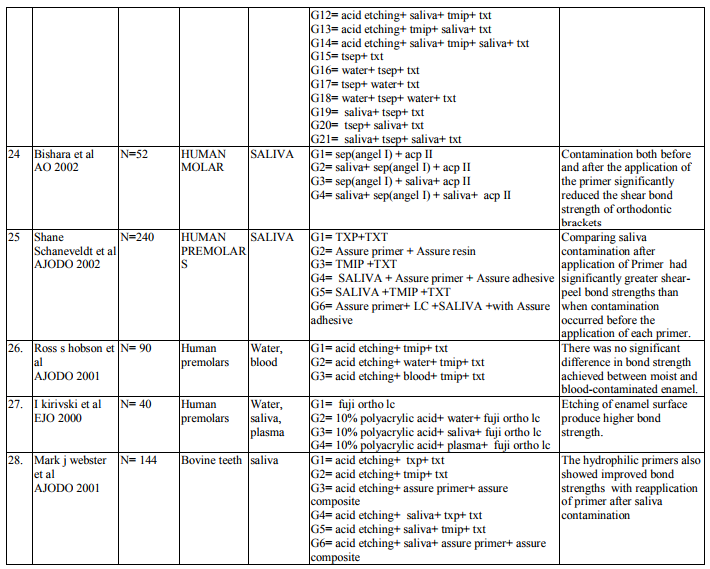
2. Bond strength of different orthodontic primers and adhesives were recorded as variables of interest. (Table 3)
DISCUSSION
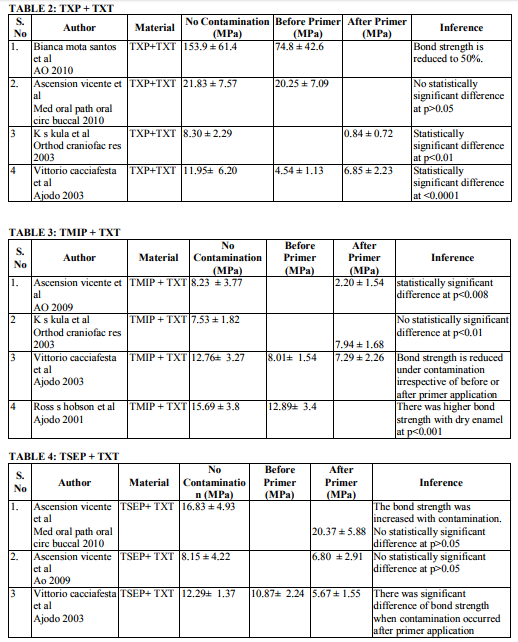
Water Contamination Bonding the bracket directly to enamel surface is technique sensitive. It needs absolute dry environment. Contamination of etched enamel surface leads to an inappropriate sealing of the microporosites by primer. Thereby reducing the bond strength of the adhesives. Common contaminations in clinical practice are water, saliva and blood. This systemic review is concentrating on the bond strength of orthodontic light cure adhesives influenced by contamination. Hobson et al8 found that the saliva contamination is more complex than water. Saliva consists of water, polysaccharides, protein, enzymes (Eiriksson et al9 ). Saliva forms an organic smear layer on the etched surface. Blood has greater mechanical barrier compare to saliva due to its organic and inorganic substances. As per the inclusion and exclusion criteria, there are 11 articles which showed the effect of water contamination under different primers and adhesives (table 2-6). The bond strength of Transbond XT primer (TXP) and Transbond XT adhesive (TXT) are found to be reduced under water contamination expect in the study by Vicente et al10. He found that the bond strength of TXP under water contamination is low compared to dry environment but there was no significant difference between the dry and wet condition.
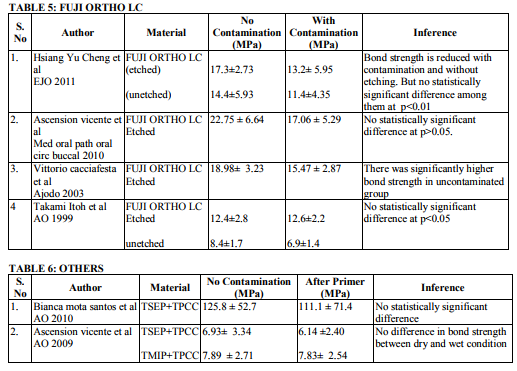
Transbond moisture insensitive primer (TMIP) is a hydrophilic primer which is found to overcome the hydrophobic nature of TXT by adding HEMA and ethanol solvent. Four articles enumerate the effect of water contamination on the bond strength of TMIP and TXT. There was reduction in the bond strength under water contamination. The controversy to it is evident with Kula et al 200311 findings. There was no statistically significant difference between the dry and wet condition. Transbond self etching primer (TSEP) has reduces two steps (etching and priming) into single step which in turn reduces the time consumption during bonding. Three articles enumerate about the effect of water after application of TSEP. There was no difference of bond strength in two articles expect Cacciafesta et al12 findings where there was significant difference in bond strength under contamination after primer application. There are four articles who evaluated the bond strength of Fuji Ortho LC, resin modified glass ionomer cement light cure adhesives. There was statistically significant difference in bond strength in both dry and wet condition as well as under etched and unetched surfaces.
Salivary Contamination
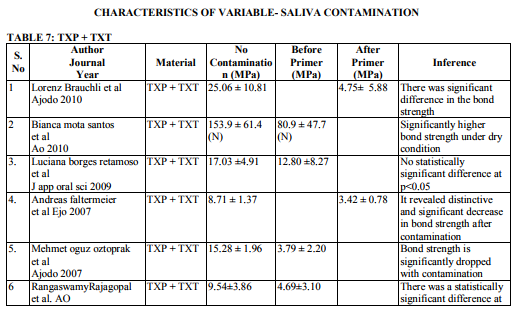
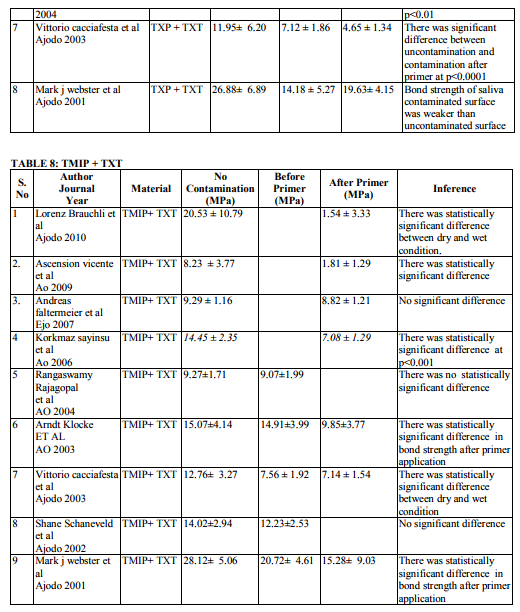
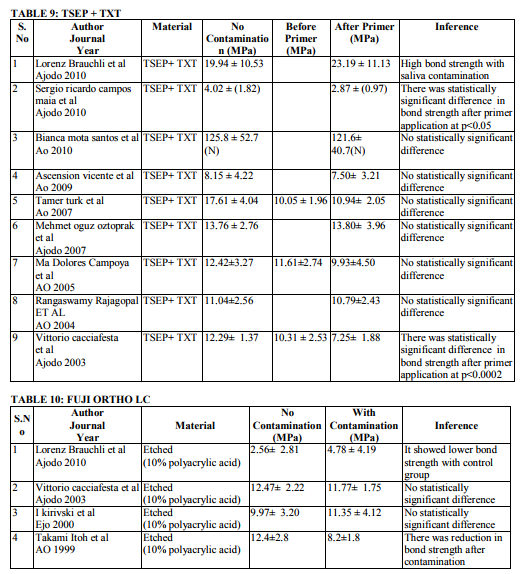
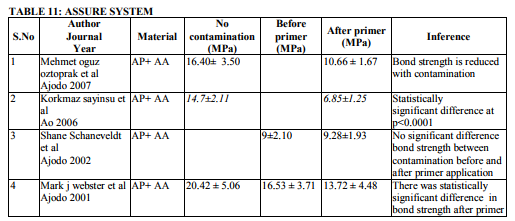
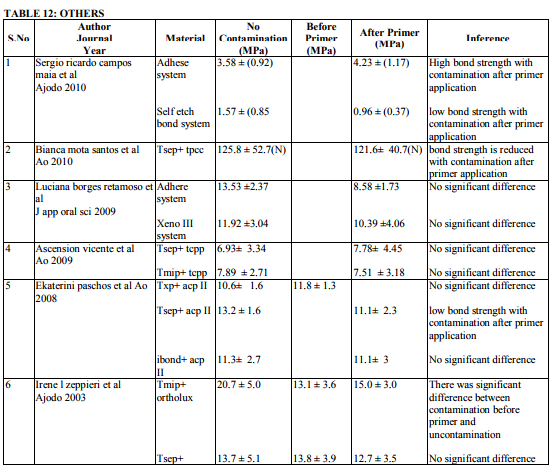
Saliva is the most common media for contaminating the etched surface. Precaution should be taken in bonding to prevent salivary contamination. Saliva will form an organic smear layer on the etched surface which prevents the penetration of primer into the microporosites thereby enhancing the bond failure rate. Twenty two articles are dealing with effect of salivary contamination on bond strength of different adhesive system (Table 7-12). The combination of Transbond XT Primer and Transbond XT adhesives are evident in eight articles. All the articles reveal that, salivary contamination affects the bond strength of the TXP irrespective of contamination either before or after primer application. Transbond Moisture Insensitive Primer can withstand the mild moist environment. TMIP and TXT show statistically significant difference in the bond strength with contamination of saliva after primer application. But contamination before primer application does not affect the bond strength. Nine studies proved it. Transbond Self Etch Primer is a single step technique where etching and priming occurs simultaneously, contamination after primer application did not affect the bond strength. There are nine articles. Vittorio Cacciafesta et al12 found that there was decrease in bond strength by contamination after primer application. Lorenz Brauchli et al13 found increase in the bond strength after primer application. It is due to denaturation and degradation of saliva protein by its etching component. Bond strength of Fuji Ortho LC under saliva contamination was evaluated in four studies. There was no statistically significant difference between dry and wet condition. Lorenz Brauchli et al13 showed increase in bond strength after contamination. This was contrary to other studies. Adhesive system other than above mentioned adhesives have reduced bond strength under saliva contamination compared to uncontaminated groups.
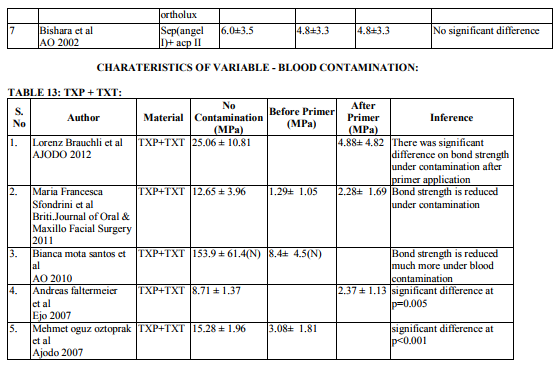
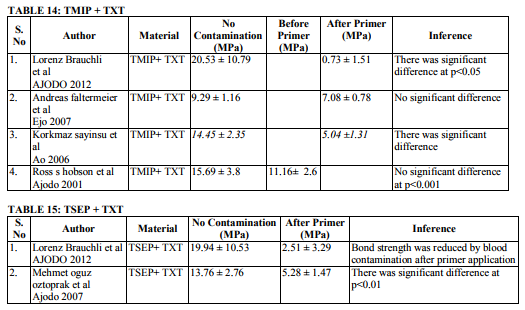
Blood Contamination
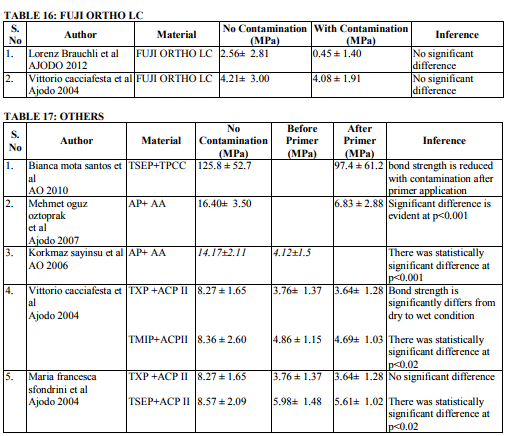
Contamination by blood extremely affects the bond strength of the orthodontic adhesives (Table 13-17). This was proved in various studies (Brauchli et al13, Sfondrini et al14, Santos et al15 , Oztoprak et al16, Sayinsu et al17). Blood contamination affects the bond strength irrespective of material used. There was decrease in the bond strength after the application of TSEP under blood contamination. Fuji Ortho LC also was affected by blood16 . Decontamination of the contaminated tooth surface by rinsing with water can increase the bond strength and it will be approximating to the bond strength achieved without contamination.
Repeat etching is not needed in the decontamination procedure. It is just cleaning a contaminated surface with water and air which was sufficient to obtain adequate bonding forces (Brauchli13). Webster18 compared a control group with a contamination group (without repriming) and a decontamination group (repriming only). They found significantly reduced bonding forces in both the situations. The decontamination in the investigation by Zeppieri19 also consisted of repriming without previous rinsing with water. Only TSEP achieved successful bonding forces in the decontamination groups. In the studies by Eiriksson20, 21 all self-etching primers achieved successful bonding forces after decontamination with water, air, and repriming. The data that was outliner in all the articles is Adhesive Remnant Index (ARI). It was used to assess the amount of adhesive left on the enamel surface. ARI scores were used as a complex method of defining bond failure rate among the enamel, the adhesive and the bracket base (Caccisafesta et al 200312).
INFERENCE
Contamination by water, saliva or blood affects the bond strength of all orthodontic adhesives either before or after the application of primer. Effect of these contaminations on TSEP after its application is found to be less. Fuji Ortho LC is unaffected by these contamination irrespective of its nature. Decontamination procedure after contamination increases the bond strength of TSEP.
CONCLUSION
Contamination affects the bond strength of the orthodontic light cure adhesives, but the extent of effect is different for different adhesive system.
SUMMARY
This systematic review is to emphasize the effect of contamination on the bond strength of orthodontic light cure adhesives. Search was done in Advance PubMed and after applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, thirty articles are related to the topic of interest. The bond strength of adhesives with or without contamination is listed out. The reading is evaluated for both before or after primer application of different adhesives. It was concluded that effect of contamination affect the bond strength of the orthodontic light cure adhesives and it affects less on TSEP.
References:
1. Reynolds IR. A review of direct orthodontic bonding. Br J Orthod 1975;2:171-8
2. Buonocore MG: A simple method of increasing the adhesion of acrylic filling material to enamel surfaces. J Dent Res 34:849-853, 1955
3. Retief DH, Dreyer CJ, Gavron G: The direct bonding of orthodontic attachments to teeth by means of an epoxy resin adhesive. Am J Orthod 58:21-40, 1970
4. William A. Brantley, Theodore Eliades: Orthodontic Materials : Chapter 10, Page 202
5. Newmann GV: Bonding plastic orthodontic attachments to tooth enamel: NJ State Dental Journal 1964: 36:346-59
6. Rajagopal R, Padmanabhan S, Gnanamani J. A comparison of shear bond strength and debonding characteristics of conventional, moisture-insensitive, and self-etching primers in vitro. Angle Orthod. 2004;74:264-8.
7. Miller RA. Laboratory and clinical evaluation of a self-etching primer. J Clin Orthod 2001;35:42-5.
8. Hobson RS, Ledvinka J, Meechan JG: The effect of moisture and blood contamination on bond strength of a new orthodontic bonding material. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2001 Jul;120(1):54-7.
9. Eiriksson SO, Pereira PN, Swift EJ Jr, Heymann HO, Sigurdsson A: Effects of saliva contamination on resin-resin bond strength. Dent Mater. 2004 Jan;20(1):37-44.
10. Vicente A, Toledano M, Bravo LA, Romeo A, de la Higuera B, Osorio R: Effect of water contamination on the shear bond strength of five orthodontic adhesives. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2010 Sep 1;15(5):e820-6
11. Kula KS, Nash TD, Purk JH: Shear-peel bond strength of orthodontic primers in wet conditions. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2003 May;6(2):96-100.
12. Cacciafesta V, Sfondrini MF, De Angelis M, Scribante A, Klersy C: Effect of water and saliva contamination on shear bond strength of brackets bonded with conventional, hydrophilic, and self-etching primers. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003 Jun;123(6):633-40.
13. Brauchli L, Eichenberger M, Steineck M, Wichelhaus A: Influence of decontamination procedures on shear forces after contamination with blood or saliva. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010 Oct;138(4):435-41.
14. Sfondrini MF, Gatti S, Scribante A: Effect of blood contamination on shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets and disinclusion buttons. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011 Jul;49(5):404-8. Epub 2010 Jul 23.
15. Santos BM, Pithon MM, Ruellas AC, Sant'Anna EF: Shear bond strength of brackets bonded with hydrophilic and hydrophobic bond systems under contamination. Angle Orthod. 2010 Sep;80(5):963-7.
16. Oztoprak MO, Isik F, Sayinsu K, Arun T, Aydemir B: Effect of blood and saliva contamination on shear bond strength of brackets bonded with 4 adhesives. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2007 Feb;131(2):238-42.
17. Sayinsu K, Isik F, Sezen S, Aydemir B: Light curing the primer-beneficial when working in problem areas? Angle Orthod. 2006 Mar;76(2):310-3.
18. Webster MJ, Nanda RS, Duncanson MG Jr, Khajotia SS, Sinha PK. The effect of saliva on shear bond strengths of hydrophilic bonding systems. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2001; 119:54-8.
19. Zeppieri IL, Chung CH, Mante FK. Effect of saliva on shear bond strength of an orthodontic adhesive used with moisture-insensitive and self-etching primers. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2003; 124:414-9.
20. Eiriksson SO, Pereira PN, Swift EJ, Heymann HO, Sigurdsson A. Effects of blood contamination on resin-resin bond strength. Dent Mater 2004;20:184-90.
21. Eiriksson SO, Pereira PN, Swift EJ Jr, Heymann HO, Sigurdsson A. Effects of saliva contamination on resin-resin bond strength. Dent Mater 2004;20:37-44.
22. Hsiang Yu Cheng, Chien Hsiu Chen, Chuan Li Li, Hung Huey Tsai, Ta Hsiung Chou and Wei Nan Wang. Bond strength of orthodontic lightcured resin-modified glass ionomer cement.European Journal of Orthodontics 33 (2011) 180–184
23. Sergio Ricardo Campos Maia, Vanessa Cavalli, Priscila Christiane Suzy Liporoni, and Marcos Augusto do Regob. Influence of saliva contamination on the shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets bonded with self-etching adhesive systems. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2010;138:79-83
24. Luciana Borges Retamoso, Fabrício Mezzomo Collares, Eduardo Silveira Ferreira, Susana Maria Werner Samuel. Shear bond strength of metallic brackets: influence of saliva contamination.J Appl Oral Sci. 2009;17(3):190-4
25. Ascensio´n Vicentea; Ana Menab; Antonio Jose´ Ortizc; Luis Alberto Bravoc. Water and Saliva Contamination Effect on Shear Bond Strength of Brackets Bonded with a MoistureTolerant Light Cure System.Angle Orthod. 2009; 79:127–132.)
26. Ekaterini Paschosa; Jean-Oliver Westphalb; Nicoleta Iliec; Karin Christine Huthd; Reinhard Hickele; Ingrid Rudzki-Janson F. Artificial saliva contamination effects on bond strength of self-etching primers. Angle Orthodondontist, 2008 78(4);716-21
27. Tamer Turka; Selma Elekdag-Turkb; Devrim Iscic; Fethiye Cakmakc; Nurhat Ozkalaycic. Saliva Contamination Effect on Shear Bond Strength of Self-etching Primer with Different Debond Times. Angle Orthodontist, Vol 77, No 5, 2007; 901-6
28. Andreas Faltermeier, Michael Behr, Martin Rosentritt, Claudia Reicheneder and Dieter Müßig. An in vitro comparative assessment of different enamel contaminants during bracket bonding, European Journal of Orthodontics 29 (2007) 559–563
29. Ma Dolores Campoya; Ascensio´n Vicenteb; Luis Alberto Bravoc. Effect of Saliva Contamination on the Shear Bond Strength of Orthodontic Brackets Bonded with a SelfEtching Primer. Angle Orthod 2005;75:865– 869.
30. Vittorio Cacciafesta, DDS, MSc, PhD, Maria Francesca Sfondrini, MD, DDS, PhD, Andrea Scribante, DDS, Marco De Angelis, DDS, and Catherine Klersy, MD, MSc. Effect of blood contamination on shear bond strength of brackets bonded with a self-etching primer combined with a resin-modified glass ionomer. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2004;126:703-8
31. Rangaswamy Rajagopal, MDS; Sridevi Padmanabhan, MDS; Janakirama Gnanamani, MDS. A Comparison of Shear Bond Strength and Debonding Characteristics of Conventional, Moisture-Insensitive, and Selfetching Primers In Vitro. Angle Orthod 2004;74:264–268.
32. Maria Francesca Sfondrini, MD, DDS, Vittorio Cacciafesta, DDS, MSc, PhD, Andrea Scribante, DDS, Marco De Angelis, DDS, and Catherine Klersy, MD, MSc. Effect of blood contamination on shear bond strength of brackets bonded with conventional and selfetching primers. (Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2004;125:357-60)
33. Vittorio Cacciafesta, DDS, MSc, PhD, Maria Francesca Sfondrini, MD, DDS, Lucia Baluga, DDS, Andrea Scribante, DDS, and Catherine Klersy, MD, MSc. Use of a self-etching primer in combination with a resin-modified glass ionomer: Effect of water and saliva contamination on shear bond strength. (Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2003;124:420-6)
34. Arndt Klocke, Dr med dent, MS; Jianmin Shi, MScb; Ba¨rbel Kahl-Nieke, Dr med dent, PhDc;Ulrich Bismayer, Dr rer nat, PhD. In Vitro Investigation of Indirect Bonding with a Hydrophilic Primer. (Angle Orthod 2003;73:445–450.)
35. Vittorio Cacciafesta, DDS, MSc,a Maria Francesca Sfondrini, MD, DDS,b Marco De Angelis, DDS,c,Andrea Scribante, DDS,c and Catherine Klersy, MD, MScd. Effect of water and saliva contamination on shear bond strength of brackets bonded with conventional, hydrophilic, and self-etching primers. (Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2003;123:633-40)
36. Samir E. Bishara, BDS, DDS, D Ortho, MSa; Charuphan Oonsombat, DDS, MSb; Raed Ajlouni, DDS, MSb; Gerald Denehy, DDS, MSc. The Effect of Saliva Contamination on Shear Bond Strength of Orthodontic Brackets When Using a Self-Etch Primer.(Angle Orthod 2002;72:554–557.)
37. Shane Schaneveldt, DDS, MCID, a and Timothy F. Foley, DDS, MCIDb. Bond strength comparison of moistureinsensitive primers. (Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2002;122:267-73)
38. Kirovski and S. Madzarova. Tensile bond strength of light cured glass ionomer cement when used for bracket bonding under different conditions: an In-Vitro study. European journal of Orthodontics; 2000; 22; 719-723.
39. Douglas Rix, BSc, DDS, MC1D,a Timothy F. Foley, DDS, MC1D,b and Antonios Mamandras, DDS, MC1D. Comparison of bond strength of three adhesives: Composite resin, hybrid GIC, and glass-filled GIC. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2001;119:36-42
40. Takami Itoh, Noriatsu Matsuo, Tadao Fukushima, Yusuke Inoue, Yasuhisa Oniki, Mitsunari Matsomoto, Angelo A.Caputo. Effect of Contamination and Etching On Enamel Bond Strength of New Light Cured Glass Ionomer Cements. Angle Orthod 1999;69(5):450-456.

|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License