IJCRR - 4(23), December, 2012
Pages: 111-117
Date of Publication: 15-Dec-2012
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
PATTERNS OF MORTALITY AND MORBIDITY IN PERFORATED DUODENAL ULCERS IN SOUTH RAJASTHAN
Author: Vishwas Johri, Minaxi Sharma, Ramnath Takiar, Chandra Prakash Joshi
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:The Incidence of duodenal ulcer perforation is decreasing in many parts of the world [1]. However in tropical countries it still is a leading cause of abdominal sepsis. Since 1950, the number of patients with ulcer disease has decreased all over the world. The number of perforated ulcers, on the other hand, has changed very little, and the death rate from perforated duodenal ulcers in older patients has increased, particularly in those that were older than 65 years [2].The present study is an endeavour to document various trends viz. demography, mortality and associated factors, morbidity, average hospital stay and associated co-morbid diseases observed in a tertiary hospital in south Rajasthan.
Keywords: Duodenal ulcer perforation
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
World over perforation complicates duodenal ulcer about half as often as bleeding and most perforated ulcers are on the anterior surface of the duodenum. The patient population tends to be elderly (mean age 60–70), chronically ill patients often (40–50%) taking ulcerogenic medication. The incidence of perforated duCONCLUSIONodenal ulcer in the West is relatively stable, the age of presentation increasing, and the sex incidence becoming more even [3] . The continuing problem with perforated duodenal ulcer stands in contrast to the fall in admissions for uncomplicated duCONCLUSIONodenal ulcers noted since the 1970's and largely attributed to the introduction of H2 antagonists. In the developing world the clinical picture is different with a high male: female ratio (approximately 8: 1), younger age, and a strong link with cigarette smoking [3] . In addition in the developing world there is a high incidence of patients who present late and this may partly account for the high mortality (16- 20%) reported in some studies [3,6] . Helicobacter pylori is implicated in 70–92% of all perforated duodenal ulcers even if those secondary to Non-Steroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs are included [3, 12]. The second most common cause of perforated duodenal ulcer is the ingestion of Non-Steroidal Antiinflammatory drugs. The number of perforated duodenal ulcers related to Non-Steroidal Antiinflammatory drugs has increased greatly in developed countries such that 40–50% of perforated duodenal ulcers are caused by them. The least common cause is pathologic hypersecretory states, such as Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, although these should be considered in all cases of recurrent ulcer after adequate treatment [3] .
MATERIAL AND METHODS
This prospective study was conducted at the Department of Surgery, RNT medical college and MB government hospital, Udaipur.
The study included 161 consecutive patients (150 males; 11 females) with perforated prepyloric/duodenal ulcer spread over a period of 18 months who presented to us in emergency. The diagnosis was made by a combination of history, clinical examination, gas under the diaphragm on radiological scout film and emergency explorative laparotomy.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The data collected was entered into a database. Statistical processing and various calculations were performed with SPSS software (14th Version).Distribution of subjects according to their age, sex, personal history, co-morbid conditions, post operative complications, duration of stay were obtained. Relative risk was calculated by age and co-morbid illness.
RESULTS
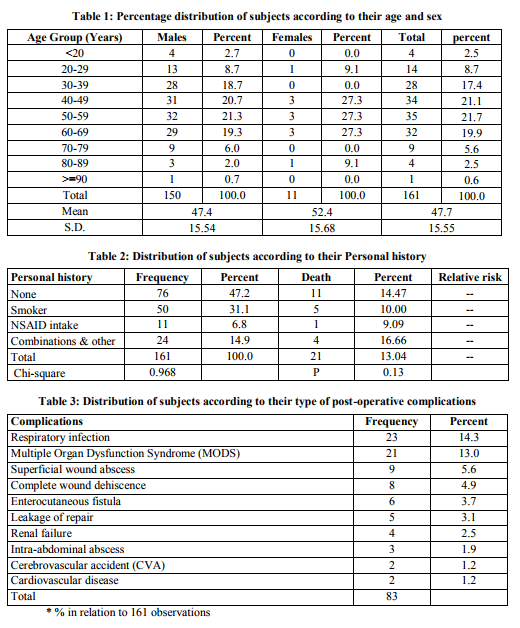
The statistically classified and tabulated data revealed some important characteristics about the patients, the disease and the prognosis. The percentage distribution of patients according to their age and sex is shown in table 1. 150 male and 11 female cases were registered during the study period. The minimum age was 15 years and maximum age was 93 years. Maximum numbers of patients were found to be between 30-69 years. Relationship between enlisted personal habits and their association with perforation and mortality is shown in table 2. It was found that almost half of the patients (47.2%) had no previous history of alcohol, smoking, corticosteroid, NSAID or antineoplastic drug intake. Significant numbers (31.1%) of patients were found to be smokers. NSAID intake was found in only 6.8% patients. None of these personal habits was found to significantly affect the prognosis of the patient in terms of mortality. About 88.6% of the patients had no co-morbid illness associated with the problem of perforation. Polytrauma (3.8%) emerged as the major co-morbid condition associated with the problem of perforation followed by cardiovascular disease (2.5%), COPD (1.3%) and others (2.4%).112 patients (69.6%) had no post-operative complications.
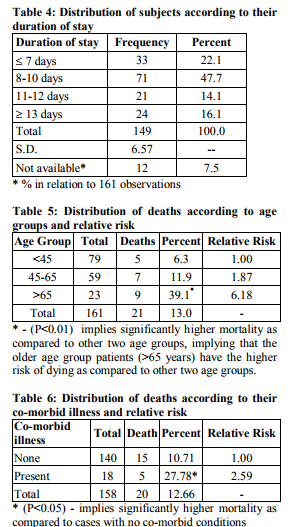
The remaining 49 patients had 83 post-operative complications (Table 3) with respiratory infections 23(14.3%) and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome 21(13%) being the most common. Among these 49 patients, 25(51%) had one post-operative complication, 14(28.6%) had two complications and 10(20.4%) had 3 complications. Table 4 shows that about 22.1% of the patients had their stay in hospital below 8 days while a great majority (47.75%) had stayed for 8-10 days. Rest of all the patients had stayed for more than 10 days. The mean duration of hospital stay was 10.7 days and range being 1-57 days. Among the patients, 133 patients (82.6%) recovered completely. Significantly 21 (13.0%) patients’ died. 7 patients (4.3%) left the hospital by other means such as against medical advice (3), on request (2) or even by absconding (2). Table 5 shows distribution of deaths according to age groups and relative risks. An increasing trend of mortality was found with increasing age. The patients with age above 65 years almost had 6.2 times higher risk of dying as compared to those who are below 45 years of age. In table 6 distributions of deaths according to their comorbid illness was sought. The patients with any co-morbid illness being present, showed almost 2.6 times higher risks of dying as compared to those patients who were not having any comorbid illness.
DISCUSSION
The oldest evidence for the type of perforated peptic ulcer reported till date was in a 60 year old Chinese man who died in 167 B.C. Autopsy revealed he died of a perforated prepyloric ulcer[4].Simple closure of the ulcer using an omental patch, as popularized by Graham in 1938, is the method most widely used today[5] . Overall, perforated peptic ulcer account for 10% of all hospital admissions related to ulcer disease and occurs in 7 to 10 patients per 100,000 population per year [5]. The post surgical mortality in a case of perforated duodenal ulcer varies from 4.2%4 to 16.0% [6].As against the conventional wisdom, no seasonal variation has been observed in the incidence of peptic ulcer [7] . In the present study, majority of patients (80.1%) were between 30-69 years. A significant percentage (28.0%) of patients was from the age group of above 60 years while in general population this percentage is around 10% .The overall mean age of the patients was 47.7±15.55 (SD) years, range being 15-93 years. The mean age of the male patients was 47.4±15.54 while that of female patients was 52.4±15.68 years. There were 150 male (93.1%) and 11 female (6.9%) patients registered during the period of study. Male to female ratio was 13.6:1. Mishra et al. (2003) [8] found that mean age of presentation was 38.9 years which is quite a young population. Interestingly, this study was also conducted in India. Most of other studies that were conducted abroad report patients in the higher age group. Boey J et al. (1987) [9] reports a mean age of 51.3±17.8 years with male to female ratio being 3.6:1.Englund R et al. (1990) [10] found that median age for presentation was 70 years. Male to female ratio was 1.2:1. Evans JP et al. (1997)[11] reports a mean age of 69.7 years and male to female ratio of 1:1.07. It shows that mean age of presentation is significantly higher in the studies that were conducted in developed countries. The lower age of affliction in our country can partially be attributed to high incidence of Helicobacter pylori infection in the developing countries [12].In the developed countries Helicobacter pylori infection has been taken care of and the most common predisposing factor in these countries seems to be increased use of NSAID drugs, intake of which is common in elderly population [2, 3] . It is therefore recommended that all patients of peptic perforation apart from surgical management should receive therapy aimed at eradicating the H. pylori infection.
In our study, about half (47.2%) of the patients had no history in terms of smoking, NSAID, corticosteroid and immunosuppressive drug intake. Highest association was seen with smoking which was found in 31.1% of patients. The NSAID intake was found in only 6.8% patients. History of corticosteroid intake was only found in one patient. The personal history of above mentioned variables showed no association with the mortality among the patients. Contrary to what we found, in an epidemiological study, Langman (1989) [13] found doubling or quadrupling of the risk of peptic ulcer complications or death in NSAID users. Dayton MT et al. (1987) [14] reported that in their series of 151 patients, 17% had an association with steroid use. They also reported 85% mortality in such patients when their age was higher than 50 years. Jordan PH et al. (1995) [2] reported that death rate from perforated duodenal ulcers in older patients has increased, particularly in women older than 65 years age. Circumstantial evidence suggests that this increase is the result of increased use of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. This seeming contradiction between the various studies can be explained on the basis of very low incidence of NSAID and corticosteroid intake by patients in our study group. In our study, a majority (88.6%) of patients were found not suffering from any co-morbid illness. This was because patient’s structure had a younger age bias. Due to the same reasons instead of other systemic illnesses, polytrauma (3.8%) emerged as the major category of comorbid illness. These patients were receiving NSAIDs and that may have resulted into duodenal ulcer perforations. The patients with any co-morbid illness, showed almost 2.6 times higher risk of dying as compared to those who had no co-morbid illness (P = 0.040). Similarly, Mishra et al. (2003) [8] found significant association between co-morbid illness and mortality (P = 0.0004). Boey J et al. (1982) [15] found significant association between comorbid illness and mortality (P < 0.001).Sillakivi T et al. (2000) [16] also found significant association between co-morbid illness and mortality (P < 0.001). In our study, 82.6% patients showed complete recovery after the treatment. Overall 21 patients (13.0%) died during the course of treatment, 7 patients were lost during the post-operative period. They left the hospital against medical advice (3), on request (2) and absconded (2). The mortality in our study would have been higher had these patients stayed, as all of them were terminally ill. Mortality in male patients was 12.5%. Mortality was higher (27.2%) amongst the female patients (P = 0.158; not significant). As compared to our study Mishra et al [8] reported less (10.7%) mortality. Boey J et al. (1982) [15] reported a very low (4.2%) post-operative mortality rate. Kay PH et al. (1978) [6] have reported a very high mortality of 16.0% in their series of perforated duodenal ulcers.Svanes C et al. (1989) [17] in their study reported a postsurgical lethality rate of 6.6%. They also reported a higher crude mortality rate for females which was due to the fact that the women studied were older than the men. Sillakivi T et al. (2000) [16] in their study reported 5.6% mortality in surgically treated perforated peptic ulcer. Male mortality was 3.2% and female mortality was higher at 13.7%. Female sex was not found to have an independent effect on mortality in multifactorial analysis. Higher mortality rate in them was again attributed to higher age at the time of presentation. In our study, 70% of patients reported no postoperative complications. Respiratory infection (14.3%) and MODS (13%) were the more common complications. MODS was found in 21 patients and was found to be almost uniformly fatal.
In our study, 47.75% patient had a hospital stay of 8-10 days, 22.1% patients had stayed for less than 8 days. The remaining patients had stayed for more than 10 days. The mean duration of hospital stay was 10.7±6.57 (SD) days. The range of hospital stay varied from 1-57 days. The mean duration of hospital stay in the study carried out by Mishra et al.[8] was 13.4 days (range 1-54).Boey J et al(1987)[9] found the median acute hospital stay of 4.9 days. Complications however prolonged hospitalization to a median of 14 days (range2-88).
CONCLUSION
Duodenal ulcer perforation in south Rajasthan is a disease of younger population [47.7±15.55 (SD) years] with overwhelming male preponderance [M:F::13.6:1]. The lower age of patient population is partly attributable to high incidence of H. pylori infection found in them as most of these patients hail from low socio-economic background. And therefore it is strongly recommended that anti H. pylori drug regimen form an essential part in post-operative management of such patients. Almost half of our patient population did not have history of smoking, NSAID, corticosteroid and immunosuppressive drug intake. Owing to younger age bias of study group majority (88.6%) of patients were found not suffering from any comorbid illness, but when present it increased the mortality up to 2.6 times. Overall mortality rate (13%) was on the higher side when compared to other study groups.30% patients had no postoperative complication and those who developed more than one post-operative complication had higher rate of mortality. The average duration of hospital stay was 10.7±6.57 (SD) days which was consistent with other study groups. Conflict of interest The authors report no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Sanchez-Bueno F, Marin P, Rios A, Aguayo JL, Rohles R, Pinero A et al. Has the incidence of perforated peptic ulcer decreased over the last decade? Diag Surg, 2001; 18:444-8.
2. Jordan PH, Thornby J. Perforated Pyloroduodenal ulcers: Long – terms results with omental patch closure and parietal Cell Vagotomy. Ann Surg, 1995; 221(5) 479-88.
3. Hill AG. Management of perforated duodenal ulcer. In: Holzheimer RG, Mannick JA, editors. Surgical Treatment: Evidence-Based and Problem-Oriented. Munich: Zuckschwerdt; 2001. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK692 6/
4. Cheng TO. Glimpses of the past from the recently unearthed ancient corpses in china. Ann Int Med, 1984; 101:714-15.
5. Jordan PH, Morrow C. Perforated peptic ulcer. Surgical clinics of North America, 1988; 62(2): 315-29.
6. Kay PH, Moore KTH, Clark RG. The treatment of perforated duodenal ulcer. Br J Surg, 1978; 65:801-3.
7. Negre J. Seasonal periodicity of peptic ulcer: A myth LANCET, 1985; 1: 1504-5.
8. Mishra A, Sharma D, Raina VK. A simplified scoring system for peptic ulcer perforation in developing countries. Indian J Gastroeterol, 2003; 22:49-53.
9. Boey J, Choi SKY, Alagaratnam TT, Poon A. Risk stratification in perforated duodenal ulcers. Ann Surg, 1987; 2005:22-6.
10. Englund R, Fischer R. Survival following perforation of peptic ulcer. Aust NZ J Surg, 1990; 60:795-800.
11. Evans JP, Smith R. Predicting poor outcome in perforated peptic ulcer disease. Aust NZ J Surg, 1997; 67:792-5.
12. Sebastian M, Prem Chandran VP, Elashaal YIM, Sim AJW. Helicobacter pylori infection in perforated peptic ulcer disease. Br J Surg, 1995; 82:360-62.
13. Langman MJS. Epidemiologic evidence on the association between peptic ulceration and antiinflammatory drug use. Gastroenterology, 1989; 96: 640-46
14. Dayton MT, Kleckner SC, Brown DK. Peptic ulcer perforation associated with steroid use. Arch Surg, 1987; 122: 376-80.
15. Boey J, Wong J, Ong GB. A prospective study of operative risk factors in perforated duodenal ulcers. Ann Surg, 1982; 195:265-9.
16. Sillakivi T, Lang A, Tein A, Peetsalu A. Evaluation of risk factors for mortality in surgically treated perforated peptic ulcer. Hepatogastroenterology, 2000; 47:1765-8.
17. Svanes C, Salvesen H, Espehaug B, SΦreide O, Svanes K. A multifactorial analysis of factors related to lethality after treatment of perforated Gastroduodenal ulcer. Ann Surg, 1989; 209 (4): 418-23.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License