IJCRR - 4(24), December, 2012
Pages: 77-85
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
COMPARATIVE ANXIOLYTIC ACTIVITY OF VARIOUS DRUGS IN EXPERIMENTAL MODELS OF RATS
Author: Kedare Rahul Vittha, B.B. Ghongane, R.J. Wagh
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objective: The aim of present work was to evaluate the anxiolytic efficacy of traditional anxiolytics along with antihistaminic, antipsychotic and analgesic in rats. Materials and Methods: The elevated plus maze model (EPMM) , open field test(OFT) and novelty induced hypophagia model(NIHM) were used to assess the effect on anxiety. The activity of Buspirone, Hydroxyzine, Haloperidol, Fluoxetine and Pethidine was compared with Diazepam, a standard anxiolytic drug. Results: Diazepam produced maximum anxiolysis in all anxiety models. The high dose Buspirone (5 mg/kg) was more effective compared than the low and medium dose (1.25mg/kg, 2.5mg/kg).) which showed significant increase in the time spent and number of entries in open arm in EPMM. The same doses of Buspirone showed significant increased in number of ambulations and number of rearing in OFT. The high dose (5 mg/kg) of Buspirone showed significantly decreased latency in NIHM. Overall, the activity of high dose of Buspirone was significantly less when compared with Diazepam but significantly more when compared to Hydroxyzine, Haloperidol, Fluoxetine and Pethidine. Conclusion: The result of the present study showed that Diazepam produced maximum anxiolysis in all anxiety models. Buspirone (high dose), Fluoxetine, Hydroxyzine, Haloperidol and Pethidine have more significant anxiolytic activity as compared to control group in elevated plus maze and novelty induced hypophagia test. In open field test Buspirone(high dose), Hydroxyzine Fluoxetine, Haloperidol and Pethidine have more significant anxiolytic activity as compared to control group.
Keywords: Anxiolytics, Diazepam, Buspirone , EPM model, OFT , Novelty induced hypophagia
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Anxiety disorder is increasingly recognized as a highly prevalent and chronic disorder having onset during the teenage years, with an incidence of 18.1% and lifetime prevalence of 28.8%. The disorder is associated with significant disability (including educational and occupational) which has negative impact on the quality of life1 . Currently, the benzodiazepines are the most commonly employed medicinal treatments for the common clinical anxiety disorders. Long-term use of benzodiazepines is associated with side effects like psychomotor impairment, confusion, aggression, excitement, physical dependence and tolerance2 . The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are also effective in alleviating symptoms associated with these forms of anxiety but have g.i. related and dermatological reactions. Azapirones, is another class of agents with beneficial effects in disorders marked by anxiety or dysphoria of moderate intensity.3 The other mild anxiolytics like antihistaminics, antipsychotics and analgesics have adverse effects like sedation , ANS related and respiratory depression respectively. Therefore present study was planned to evaluate the anxiolytic efficacy of traditional anxiolytics along with antihistaminics, antipsychotics and analgesics in rats.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Male albino rats weighing between 150-250gm were used. The experimental protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee. The animals were maintained under standard conditions in an animal house approved by the Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision on Experiments on Animals (CPCSEA). The rats were divided into nine groups with six in each group.

Drugs used – The following drugs were used in the study: Diazepam Benzyl alcohol, Batch no: 902895 Exp.date Feb.2013 (Ranbaxy); Buspirone hydrochloride (Product code B7148); Hydroxyzine dihydrochloride (Product code H 8885 )Sigma Aldrich Co, ; Haloperidol Batch no: Halo/ 0703005 , Exp.date Feb.2012 (Stadmed Private Limited); Fluoxetine Hydrochloride Batch no: JK 10021 Exp.date April 2013 (Cadila pharm.ltd.); Pethidine Hydrochloride Exp.date Oct 2011 (Neon labs Ltd.). The other chemicals were of analytical grade.
Elevated Plus Maze Model (EPMM): The EPM apparatus consisted of two open arms (30 cm length x 10 cm width x 2.5 cm height) and two closed arms (30 cm length x 10 cm width x 15cm height) emanating from a common central platform (10 cm x 10 cm). The two pairs of identical arms were opposite to each other. The entire apparatus was elevated to a height of 50 cm above the floor level. The animals received the treatment as per the schedule, 30 min before the start of the session. At the beginning of the session, a rat was placed at the centre of the maze, its head facing the closed arm. It was allowed to explore the maze for 5 min. The time spent in the open/closed arms and number of entries in open/closed arms (An entry was defined as the presence of all four paws in the arm) and time/entry ratio ( = time spent/ number of entries ) were recorded with the help of stop watch 4 .
Open Field Test (OFT) : The Open Field Test apparatus consisted of a wooden box (50 cm height x 50 cm length x50 cm width ), with a dark gray floor, subdivided into 16 equal fields( each square of 12 cm x 12 cm). The experimental room was a sound attenuated, dark room. The Open Field Test, above 100 cm from the apparatus 40W bulb was focused. After 30 min of treatment, the rats were placed individually in a corner square of the OFT and the ambulation (The number of squares crossed), latency (Time taken by the animal to leave square in which it was placed ) and number of rearing (number of time the animal stands on the rear paws) were recorded for 5 min5 .
Novelty Induced Hypophagia Model (NIHM): Rats were singly housed in a standard polypropylene cage (Home cage) for ten days before training began. After completion of training for 3 consecutive days, rats were presented with diluted (milk: water; 1:3) sweetened condensed milk in a home cage with 10 ml pipette. They were allowed access for 30 min daily. Home cage testing was done on day 4 for which rats were briefly removed (for 20 min) from their cages. The cage was cleaned with spirit swab and testing done as soon as rats were returned to their cages. The latency to drink and total milk consumed in 30 min was recorded .It was done under dim lighting (approx. 50 lux).
Rat that never drank during the 30 min of home cage testing were eliminated from the experiment. Novel cage (Clear Plexiglas cage) testing was done on day 5, when rats were placed into new clean cages of the same dimensions, with pipette containing the milk positioned. Novel cage testing occurred under bright lighting (approx. 1200 lux), with white paper placed under cages to enhance aversiveness. Thus, each rat was trained to drink milk (days 1–3), tested in its home cage (day 4), and then tested in a novel cage (day 5). Finally drinking latencies and total milk consumed between home cage and novel cage were compared 6 .
Statistical analysis: The statistical analysis was done by software Primer of biostatistics and significance was assessed using a One way ANOVA followed by Dunnett test. The values are expressed as Mean + SEM and P < 0.05 was considered significant.
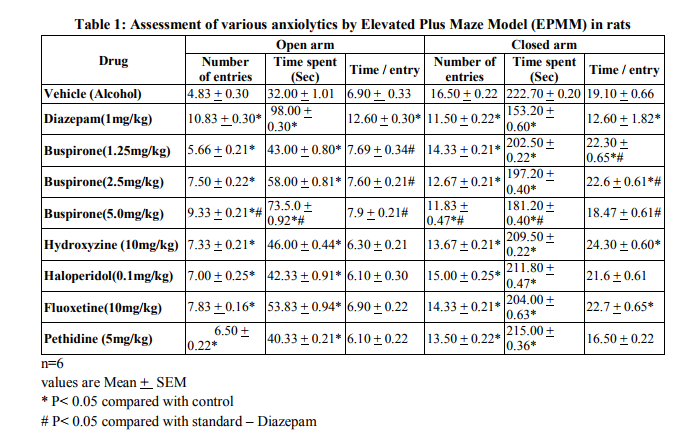
values are Mean + SEM * P< 0.05 compared with control # P< 0.05 compared with standard – Diazepam In the elevated plus maze model, vehicle group showed tendency to remain in the closed arm which suggest anxiogenic effect. The known anxiolytics viz. Diazepam and Hydroxyzine have produced significant increase in entries and time spent in the open arm as compared to vehicle group (anxiolytic effect). Similarly, in the Fluoxetine, Haloperidol and Pethidine group significant increase in entries and time spent in the open arm as compared to vehicle group (anxiolytic effect) was seen. The Buspirone in all the doses tested has produced significant increase in entries and time spent in the open arm as compared to vehicle group(anxiolytic effect).However , this increase with highest dose ie.5.0 mg/kg is significantly less compared to Diazepam; but significantly more than Hydroxyzine, Fluoxetine, Haloperidol and Pethidine.
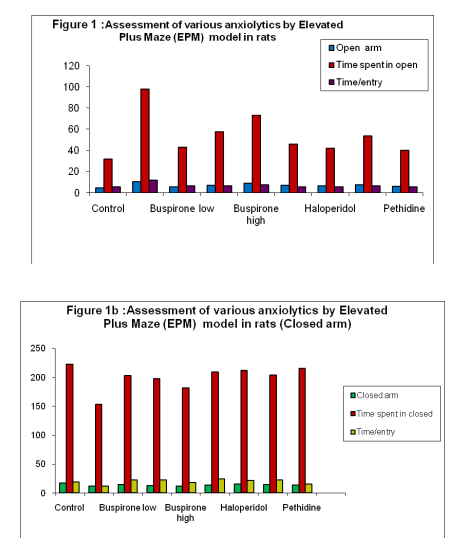
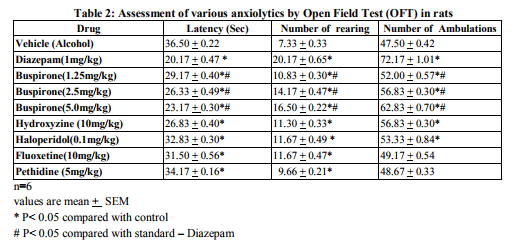
In the Open field model, The known anxiolytics viz. Diazepam and Hydroxyzine significant increase number of rearings and ambulation and decrease latency as compared to vehicle group (anxiolytic effect). Similarly, in the Fluoxetine, Haloperidol and Pethidine group have produced significant increase in number of rearings and decrease latency was observed as compared to vehicle group (anxiolytic effect).The Buspirone in all the doses tested has produced significant increase as compared to vehicle group(anxiolytic effect).However , this increase with highest dose ie.5.0 mg/kg is significantly less compared to Diazepam; but significantly more than Hydroxyzine, Fluoxetine, Haloperidol and Pethidine.
In the Novelty induced hypophagia model, The anxiolytics viz. Diazepam Hydroxyzine Fluoxetine, Haloperidol and Pethidine have produced significantly decrease latency as compared to vehicle group (anxiolytic effect). All doses of Buspirone produced significant decrease as compared to vehicle group (anxiolytic effect).However, this decrease with highest dose ie.5.0 mg/kg is significantly less compared to Diazepam .The consumption of milk significantly increased among known anxiolytics as compared to the vehicle group in a home cage. In Diazepam group consumption was more compared to vehicle group and other groups. All doses of Buspirone showed significantly increase consumption of milk as compared to vehicle group (anxiolytic effect).
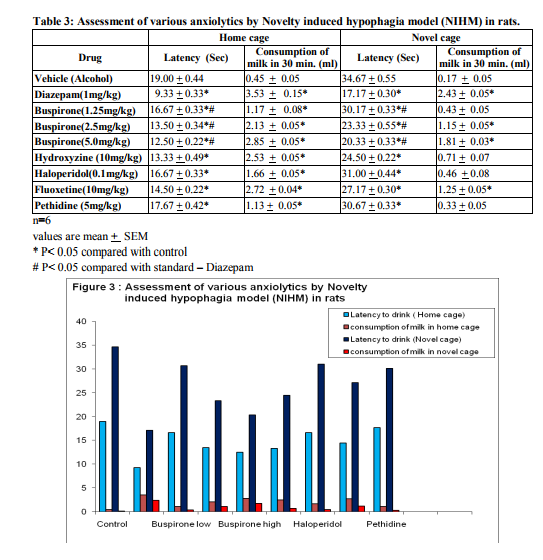
RESULTS
The high dose Buspirone (5 mg/kg) was more effective compared to the low and medium dose (1.25mg/kg,2.5mg/kg).) and significantly increased the time spent and number of entries in open arm in elevated plus maze test. The results of high dose of Buspirone were significantly less when compared with standard drug Diazepam and significantly more as compared to the Hydroxyzine, Fluoxetine, Haloperidol and Pethidine. In open field test the same dose of Buspirone showed significant increased in number of ambulation and number of rearing. The high dose (5 mg/kg) of Buspirone showed significant decreased latency and increase milk consumption in novelty induced hypophagia test.
DISCUSSION
This study investigated comparative anxiolytic activity of various drugs in animal models. The elevated plus maze test, open field test and novelty induced hypophagia were used. In these models Diazepam 1 mg/kg served as a standard drug. All these models have been used to assess neurobehavioral profile of animals under the influence of anxiolytics7 . The elevated plus maze model is a well established model for testing anxiolytics and was used to evaluate psychomotor performance and emotional aspects of rodents. This model is based upon the natural aversion of rodents to heights and open spaces has been validated for both rats and mice , bidirectionally sensitive to pharmacological manipulations.8 Benzodiazepines are the most widely prescribed class of psychoactive drugs in current therapeutic use. Results obtained on the elevated plus maze after the treatment of Diazepam revealed anxiolytic activity. It increases entries and time spent in the open arm, when compared with control and other anxiolytic drugs. These parameters are the most representative indices of anxiolytic activity 9 . They enhance the response to GABA, by facilitating the opening of GABA-activated chloride channels.10 All doses of Buspirone (1.25, 2.5 and 5.0 mg/kg ) showed significant increase entries and time spent in the open arm .The results of high dose of Buspirone were comparable to Diazepam and more significant to when compared with other anxiolytics. The doses of Buspirone may have selective partial agonistic effect at cell body 5 -HT1A which may lead to an anxiolytic like effect. 11 Hydroxyzine showed significant increase entries and time spent in the open arm, when compared with control group but less significant on comparison with diazepam and high dose of buspirone group. It is a H1-receptor antagonist that penetrates the Blood brain barrier and produced mild anxiolytic actions without muscle relaxation 12 . Haloperidol showed significant increase entries and time spent in the open arm, when compared with control group, the results of previous studies shown that treatment with haloperidol induced a significant enhancement in the general activity of rats observed in an open field test .Which suggest that haloperidol has mild anxiolytic activity13 . Fluoxetine significantly increase the number of open arm entries and time spent in open arm and also decreased the latency to enter in open arm as compared to control. A single intraperitoneal dose of Fluoxetine effectively altered behavior .The mechanism underlying these acute behavioral changes are unlikely to be the same as those mediating the behavioral effects that emerge chronically. The acute behavioral effects may result from a sharp peak in blood levels of Fluoxetine and its active metabolite norfluoxetine14 . Pethidine showed significant increase in entries and time spent in open arm when compared with control group. Opioids decrease release of excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system15 . The open field test was used to evaluate the animal emotional state and anxiety related behavior. It characterized by the normal aversion of the animal to an open, brightly light area. Thus, animals removed from their acclimatized cage and placed in environment express anxiety and fear, by showing alteration in all or some parameters. Diazepam showed significant increase in the number of square crossed, rearing and ambulation compared to control and other anxiolytics 8 . The high dose of Buspirone showed significant increased in number of square crossed, rearing and ambulation compared to the control group and less significant when compared with the diazepam. 10,13 Hydroxyzine , Fluoxetine , Haloperidol, and Pethidine significantly increased number of square crossed ,rearing and ambulation compared to the control group12,14,15 . The enhancement of neurotransmitters results in behavior associated anxiety, while antagonism in the system appears to produce an anxiolytics effect16 . The exposure to the novel environment resulted in a significant suppression of latency and food intake. Diazepam group showed significant decreased in latency and increased consumption of milk , when compared with control and others groups in home cage as well as novel cage testing. 8 All doses of Buspirone showed lesser latency to begin eating in the home and novel cage ,when compared with control group. There was significant increased food intake, when compared with control group. These results were less significant when compared with diazepam. 10 Hydroxyzine , Fluoxetine Haloperidol, and Pethidine significantly reduced latency and increased food consumption ( Home cage) , when compared with control group12,13,14,15 . All of the groups showed a greater latency to begin eating in the novel environment relative to the home cage, the complex interaction was examined by conducting an ANOVA on difference score calculated between home and novel cage17 .
CONCLUSION
The result of the present study showed that Diazepam produced maximum anxiolysis in all anxiety models. Buspirone (high dose), Fluoxetine, Hydroxyzine, Haloperidol and Pethidine have more significant anxiolytic activity as compared to control group in elevated plus maze and novelty induced hypophagia test. In open field test Buspirone (high dose), Hydroxyzine Fluoxetine, Haloperidol and Pethidine have more significant anxiolytic activity as compared to control group
References:
1. Thippeswamy BS, Mishra B. Anxiolytic activity of nymphaea alba linn. In mice as experimental models of anxiety. Indian journal of pharmacology 2011; 43 (1).p50- 55.
2. Thandaga S, Mohmood R, Krishna V , Thippeswamy B.S., Veerapur V.P. Evaluation of anxiolytic effect of Erythrina mysorensis Gamb.in mice. Indian journal of pharmacology .2012;44:p 489-492.
3. Baldessarini Ross J. Drug therapy of depression and anxiety disorders; Bruton LL, Lazo Js, Parker KL, editors. Goodman and Gilman’s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 11 th ed. New York Mc GrawHill, Medical Publishing Division 2006 p277- 279.
4. Weinstock M , Poltyrev T,Youdim C B. Effect of TV3326 ,a novel monoamine oxidase cholinesterase inhibitor,in rat models of anxiety And depression. Psychopharmacology. 2002;160:p318-324
5. Okali C.O, Ezike A.C, Agwagah O.C., Akah P.A .Anticonvulsant and anxiolytics evaluation of leaf extracts of Ocimum gratissimum, a culinary herb. Pharmacology Research.2010; 2:(1) p 36-40.
6. Bodnoff S R. , Suranyi-Cadotte B, Quirionl R, Meaney M J. A comparison of the effects of Diazepam versus several typical and atypical anti-depressant drugs in an animal model of anxiety. Psychopharmacology .1989; 97: p277-279
7. Tabassum I , Siddiqui Z N, Rizvi S J. Effect of Ocimum sanctum and Camellia sinesis on stress induced anxiety and depression in male albino Rattus Norvegicus. Indian journal of pharmacology. 2010 ; 42 (5) p. 283-288
8. Rodgers R.J., Lee C., Shepherd J.K. Effects of diazepam on behavioural and antinociceptive responses to the elevated in male mice depend upon treatment regimen and prior maze experience. Psychopharmacology.1992; 106 p102-110.
9. Shafaghi B. Anxiolytic effect of Echium amoenum L.in mice. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical research .2002;1:p37-41
10. Barua C C , Anxiolytic effect of hydroehthanolic extract of Drymaria cordata L Wild. Indian journal of Exp. Biology 2009; 47: p 969-973.
11. 11).Moser P.C. An evaluation of the elevated plus maze test using the novel anxiolytics effect. Psychopharmacology .1989;99:p 48-53
12. Logothetis, Mylonas I. A., Baloyannis S., Pashlidou M. , Orologas, Zafeiropoulosi A., Kosta V, Theoharides T. C. A pilot, open label, clinicaltrial using HydroxyzineIn multiple sclerosis. International Journal Of Immunopathology and pharmacology.2005;18:( 4) p 771-778
13. Bernardi M. M.,. De Souza H, Palermo J. Effects of Single and Long-Term Haloperidol Administration on Open Field Behavior of Rats. Psychopharmacology.1981; 73:p171 - 175
14. Kerri A H, Daniel C L, Rene´ H, Dulawa S C .Behavioral Effects of Chronic Fluoxetine in BALB/cJ Mice Do Not Require Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis or the Serotonin 1A Receptor. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008; 33: P 406–417
15. Patti C. L. Effects of morphine on the plusmaze discriminative avoidance task: role of state-dependent learning. Psychopharmacology.2006; 184: p1–12
16. Rauniar GP, Deo S, Bhattacharya SK .Evaluation of anxiolytics activity of tensarin in Mice. Kathmandu University Medical Journal. 2007; 5: (2)18,p 188-194
17. Bechtholt A J , Tiffany E ,Irwin L. Anxiolytic effect of serotonin depletion in the novelty induced hypophagia test. Psychopharmacology.2007;190:p531-40
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License