IJCRR - 5(8), April, 2013
Pages: 84-90
Date of Publication: 25-Apr-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFICACY OF DEEP CERVICAL FLEXOR STRENGTH TRAINING VERSUS CONVENTIONAL TREATMENT IN CERVICOGENIC HEADACHE
Author: Rabiul Islam, Nishat Quddus, Mohammad Miraj, Shahnawaz Anwer
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness of Pressure-biofeedback as an add-on therapy with conventional exercise on deep cervical strength, pain, and headache disability index in patient with cervicogenic headache. Design: Pretest-posttest experimental group design. Methods: Thirty patients (17 men, 13 women) with cervicogenic headache participated in the study completed the trial. Subjects were randomly placed into two groups receiving the pressure biofeedback training (n=15) and a control group (n=15). The pressure biofeedback group received biofeedback stabilizer (PBU) guided DCF strength training along with conventional treatment program for 3 days a week for 3 week, whereas the control group received an exercise program only. Pain intensity was assessed with a visual analogue scale (VAS) and the headache score of the patients were measured by the Headache Disability Index (HDI) respectively. Results: On between group comparisons, pressure biofeedback group has shown significant improvement in pain intensity and headache disability score as compared to control group at the end of trial (p< 0.05). Conclusion: The results of the study suggests that the deep cervical flexor's training using pressure biofeedback along with conventional exercise was more effective to reduce pain intensity and Headache Disability and thus improving the endurance capacity of deep cervical flexor muscle over a period of 3 weeks for the management of CGH.
Keywords: Pressure-biofeedback stabilizer, Deep Cervical Flexors exercise, Cervicogenic Headache, Neck pain
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Headache is a common and often incapacitating condition affecting a large number of individuals. It has been estimated that a headache in some form will be experienced by at least 90% of the population at some stage of their lives.1 Headache’s arising from musculoskeletal disorders of the cervical spine termed cervicogenic headache (CGH).2 Neck pain and cervical muscle tenderness are common and prominent symptoms of primary headache disorders.3 Less commonly, head pain may actually arise from bony structures or soft tissues of the neck, a condition known as CGH.4 Headaches will strike 2/3 of the population at any one given time, 15-20% are vascular and remaining 80-85% are placed under a multitude of diagnostic categories, and may be related to depression, fatigue and structures in cervical spine.5 With a point prevalence of 16% in the general population, headache is one of the most common human ailments. The recent clinical investigations of many studies have shown that the cervical spine to be responsible for the majority of headaches in general population.5 Recently Bogduk has demonstrated experimentally that disorders of the cervical spine can cause headache.6 The computer aided evaluation of the functional roentgenograms of the cervical spine in ventral and dorsal flexion studied in 15 cervicogenic headache patients and 18 controls showed a statistically signifacant hypomobility (p<0.05) of craniocervical joints C0- C2 and an impaired overall motility of the superior cervical spine (C0-C5). Various studies have shown associated muscle tightness, impaired strength endurance ratio and impaired neuromotor contract in subject with cervicogenic headache (Bansevicius and Sjaasted, 1996).6, 7 Literature demonstrated that patients with CGH had significantly less strength and endurance of the deep neck flexors compared to age-matched control. Upper cervical flexor strengthening has been found to be effective in cervicogenic headache patients.7 Using pressure biofeedback unit has been established in a single clinical trial (Jull et al, 2002) and in two of the case reports (Beeton and Jull, 1994 and Shannon M. Petersen, 2003)8,9 target on re-training the DCF muscles which has been shown to decreased neck symptoms and headache. Various physical rehabilitation approaches can be used to treat cervicogenic headache like trigger point injection,8 muscle energy technique, thrust manipulation, post- isometric muscle relaxation,10 biofeedback, C2-C3 facet joint blockade11 and surgical procedures. Mobilization of upper cervical spine (C0, C1, C2 and C3), spinous process and facet joints and its effects on frequency, duration and intensity of cervical headaches were studied and found to be effective.12 So the present study was intended to evaluate the effectiveness of Pressure-biofeedback as an add-on therapy with standard exercise on deep cervical muscle strength and pain in patient with cervicogenic headache.
METHODS
Subjects:
A total number of thirty patients (17 men, 13 women) with cervicogenic headache completed the trial. The criteria for inclusion were: both males and females, age group 24 – 39, patients matching cervicogenic headache diagnostic criteria established by international headache society. Unilateral or side-dominant headache without side shift, headache with neck stiffness and or pain, headache frequency of at least once per week over a period of 3 months. Subject were excluded if they had headache not of cervical origin, headache with automatic involvement, any associated symptoms like dizziness or visual disturbance, any congenital condition of the cervical spine, and history of any surgery around cervical region, and also specified bilateral headache/suggestive of migraine.
Study design
Pre-post test experimental group design was selected for testing the hypothesis, where a baseline reading was taken prior to the intervention, rest measurements were taken, on 7th day, 14th day and 21st day. These reading were then compared to find out the effect on independent variables. The outcome measure or dependent variables, selected for this study were pain, and Headache Disability Score. These variables were measured using VAS scale, and Headache Disability Index.
Procedure
Subjects were screened according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Those found suitable for participation in the study were explained about the procedure and were requested to sign the consent forms. Subjects received verbal description of all the procedure, patients was randomized to experimental (group A) and control groups (group B), each consisting of 15 patients
Measurement of Headache Disability Index
The Head disability index was given to the patients and they were instructed to take the choice closest to the one which indicated the true subjective assessment of the subject disability for that particular item. The scores for each item were added and the final score was concluded. The measurements were taken at baseline (pre intervention), week 1, week 2 and at the end of treatment protocol i.e. week 3
Measurement of pain intensity
The subject was asked to mark along the line of VAS scale to denote his level of pain. The distance from mark 0 was calculated in cm and was recorded. The measurements were taken at baseline (pre intervention), week 1, week 2 and at the end of treatment protocol i.e. week 3.
Intervention
Experimental group (group A) received the Pressure-biofeedback guided strength training plus the conventional exercise program whereas Control group (group B) received the conventional exercise program alone. Both the group received moist heat by hydro-collator pack for 20 minute prior to exercise.
Moist heat therapy:
Patient was positioned in supine lying on a treatment couch. The patient was asked to expose the area to be treated. Hydrocollator pack was wrapped in a Makin tosh, and then placed under the cervical region for 20 minute. Intervention was given for 3 weeks (6 days/3 week).
Manual traction: Manual traction was given after positioning the patient in supine lying (the patient should be as relaxed as possible), head resting in therapist’s hands. The fingers of both hands were placed under the occiput and applied traction force. The therapist must also be careful not to squeeze the head too tight. Five to ten sets of manual traction were given; each set of manual traction was given for 10 seconds. Sessions were given on alternate days for three weeks.
Passive stretching (for neck muscle): The upper trapezius stretch was given by the contra lateral side bending, the patient is positioned in supine lying or sitting, the head-neck region was passively bent on right side (to stretch left side) to the restrictive barrier. Asked the patient not to move the shoulder, a sub maximal, isometric contraction of the left upper trapezius of 6-15 seconds duration, cycle is repeated for three times on alternative days for three weeks.
Deep neck flexor muscle training: 13 The deep neck flexor exercise described by Jull was performed with the patient supine with the cervical spine in the neutral position and a stabilizer pressure biofeedback unit (Chattanooga group, Hixson, TN) placed under the cervical lordosis. The pressure sensor was inflated to 20 mm Hg. The patient was instructed to slowly nod the head. As muscular activation of the deep cervical flexors occurs, the cervical lordosis slightly flattens and registers as an increased in pressure on the pressure sensor. The activation score is the pressure that can be achieved and held steadily for 10 seconds. The performance index of the muscles holding capacity is calculated by multiplying the target pressure by the number of successful repetitions. Ideal performance of the upper cervical flexor muscles would register on the pressure sensor as an increase in pressure of 10 mm Hg held for 10 seconds, 10 times on alternate days for three weeks.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Statistical analysis was done using SPSS 15.0 Software. An independent t-test was used to compare the changes in VAS score in both the groups at baseline, week 1, week 2 and after the end of treatment protocol i.e. at week 3. To compare the changes in HDI score in both groups at baseline, week 1, week 2 and after the end of treatment sessions i.e. at week 3, Mannwhitney U test was used. A statically significant difference was defined as p less than 0.05.
RESULTS
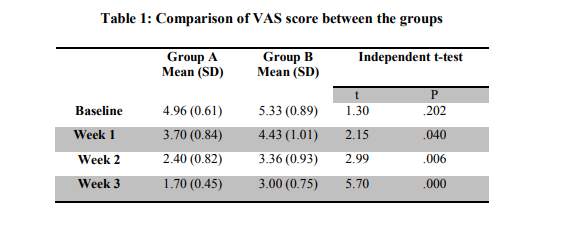
Pain intensity
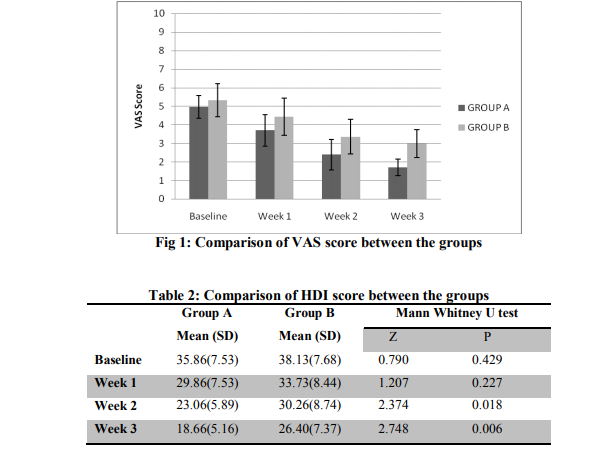
For both the groups the baseline value of VAS score was statistically insignificant (p=0.202). The reading at the end of week 1 was found to be statistically significant between groups (p=0.040).
The reading were remained significant at week 2 and week 3 (p<0.001) (Table 1).
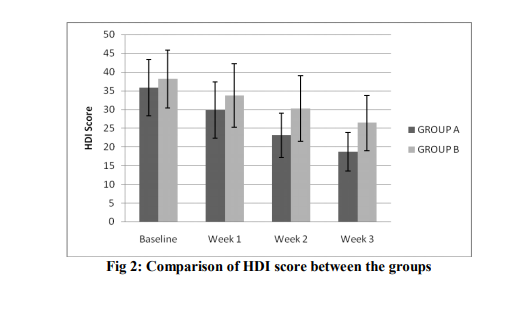
Headache Disability Score
In both the groups, the baseline value of HDI was statistically insignificant (p=0.429). The reading was statistically insignificant at week 1 between two groups (p=0.227). However, the readings at the end of week 2 and week 3 was found to be statistically significant between two groups (p=0.018, p=0.006 respectively) (Table 2).
DISCUSSION
This study was conducted in an attempt to identify the effect of Pressure biofeedback training on the deep cervical flexor (DCF) muscles strengthening in patients with cervicogenic headache. The findings suggest that Pressure biofeedback unit improves the strength of deep cervical flexor muscles while performing deep cervical flexors training. The results of the study demonstrated that a combination of Pressure-biofeedback along conventional exercises brought greater gains in both outcome measures, including pain intensity and headache disability. These effects were largely gained during the 3 weeks of treatment period.
Headache disability influencing Deep Cervical Flexor’s strength:
In the present study, there was decrease in the headache score from baseline to 3rd week of intervention of Pressure biofeedback unit along with the conventional neck exercises. This implies that both the treatment methods were effective in managing cervicogenic headache patients. Our findings are in accordance with those obtained by Jull et al 2002, 23 who reported reduction of headache intensity in their patients. Similarly Beeton and Jull 18 and Shannon M. Petersen,9 demonstrated effectiveness of deep cervical flexor’s training (using pressure biofeedback unit) in reducing the headache frequency. Further the findings of Jull G, Barrett C, and Magee R. concur with the above results. Their results showed that even though muscle tightness has not been shown to be strong feature in cervicogenic headache, limitations in cervical muscle strength and endurance has been associated with CGH.24,25 So deep cervical flexor’s training was effective for the management of cervicogenic headache. More recently, Jull et al 9 reported on the effectiveness of manipulative therapy and a lowload exercise program for individuals with CGH. They found that both manipulative therapy and specific exercise was effective in reducing headache frequency and intensity. So results of present study could be explained by means of strengthening of deep cervical muscles using PBF unit produced better outcomes after 3 weeks post intervention than conventional group which was devoid of these exercises.
Reduction in pain intensity
The pain intensity for the both groups from baseline to 3rd week reduced significantly. However; the finding has shown that improvement was statistically significant in group A at the end of 3rd week when compared with group B (p<0.001). Thus suggesting that Pressure biofeedback along with conventional exercise was more effective in reducing pain, for the management of cervicogenic headache. The findings are consistent with Jull et al12 who reported that exercise and manipulative therapy was more effective in reducing pain intensity when compared exercise/manipulative therapy alone. Further Shannon M. Petersen9 , in their study provided evidence that DCF training was effective for the treatment of cervicogenic headache and beneficial effect was found for reduction of pain intensity. So it may be hypothesized that improvement on muscle strength is one of the main cause of reducing pain. The factors that may have lead to reduction in pain could be due to pressure biofeedback unit and conventional treatment which included hydrocollator pack, isometric exercise and manual traction.
Moreover the subject of both groups received 20 minute of hydrocollator pack prior to exercise over a period of 3 weeks. Benson et al14 suggested that as a consequence of mild heating skin mechanoreceptor pathways are influenced which, in turn, may contribute to pain modulation. Lehman and Delateur15 suggested that heating the secondary afferent muscle spindle nerve ending and Golgi tendon organs could be a way in which an inhibitory influence is applied to the motor neuron pool to diminishuscle excitation and thereby reduce pain. It has been postulated that isometric exercise changes the metabolic level in the neck muscles peak tension to develop and for metabolic changes to begin to occur in the muscle with each contraction. Manual traction of cervical spine occasionally would give transient relief.16 The intradisc pressure is hardly increased during passive traction (Andersson, Schultz and Nachemson, 1983).17,18The rationale for traction is based on the mechanical and reflex mechanisms spinal elongation through an increase of intervertebral space and relaxation of spinal muscle is assumed to be the most important of the proposed mechanisms by which traction could be effective.16,17,18 The advantages of manual traction include localization, feedback, specificity, and patient comfort. The physiological effect of traction includes decompression of articular, neurologic, and vascular structures, soft tissue stretching and mechanoreceptor stimulation for the relief of pain and reduction of muscle tone. Thus the factors that could have lead to a reduction in pain are hydrocollator pack, manual traction and isometric exercise regardless of the cervicogenic headache patients.
CONCLUSION
The results of the study showed that deep cervical flexor’s training using pressure biofeedback along with conventional exercise was more effective than conventional exercise alone in decreasing pain intensity and Headache Disability and thus improving the endurance capacity of deep cervical flexor muscle over a period of 3 weeks for the management of CGH.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. We are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. K Niere, P Robinson. Determination of manipulative physiotherapy treatment outcome in headache patients. Manual therapy 1997; 2(4):199-205.
2. Sjaastad O, Fredriksen TA, Pfaffenrath V. Cervicogenic headache: Diagnostic criteria. Headache 1998;38:442-445.
3. Blau JN, MacGregor EA. Migraine and the neck. Headache 1994;34:88-90.
4. Sjaasted O, Saunte C, Hovdahl H, Breivik H, Gronback E. “Cervicogenic” headache. A hypothesis. Cephalalgia 1983;3:249-256.
5. Nilsson N. The Prevalence of Cervicogenic Headache in a Random Population Sample of 20-59 Year Olds: Spine 1995;20(17):1884- 1888
6. Gwendolen A. Jull. Grieve’s modern manual therapy. The vertebral column. 2nd edition. Cervical headache: A review 1994;333-347.
7. Darryl D Curl. Classification of headache: A new look. “Chiropractic approach to head pain” (Chap. 9) Williams and Wilkins, 1994: 182-189.
8. Beeton K. Jull G. Effectiveness of manipulative physiotherapy in the management of cervicogenic headache: a single case study. Physiotherapy 1994;80:417-423
. 9. Shannon M. Peterson. Articular and muscular impairments in cervicogenic headache: Acase report. Journal of orthopedic and sports physical therapy 2003;33:21-30.
10. Fernandez Cesar, Calos Juan. Performance of the craniocervical flexion test, forward head posture, and headache clinical parameters in patients with chronic tension-type headache: A pilot study. JOSPT 2007; 37(2):33-39.
11. Bovfim G., Berg Rakel, Dale L. Cervicogenic headache: anesthetic blockades of cervical nerve (C2-C5) and facet joints (C2/C3). Pain 1992;49:315-320.
12. Gwendolen Jull, Patricia Trott, Helen Potter et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial of exercise and Manipulative Therapy for Cervicogenic Headache: Spine 2002;27:1835- 1843.
13. Jull G, Barrett C, Magee R et al. Further clinical clarification of the muscle dysfunction in cervical headache. Cephalalgia 1999;19(3):179- 175.
14. Benson TB, Copp EB. The effects of therapeutic forms of heat and ice on the pain threshold of the normal shoulder. Rheumatol Rehabil 1978;13:100-104.
15. Lehman JF, DeLateur BJ. Therapeutic heat. In therapeutic heat and cold. Baltimore: Williums and Wilkins.p404-562; 1982.
16. H Duane Saunders. Use of spinal traction in the treatment of neck and back conditions. Clinical orthopaedics and related research 1983; 179:32-38.
17. Geert JMG van der Heijden, Anna JHM Beurskens et al. The efficacy of traction for back and neck pain: A systematic, blinded review of randomized clinical trial methds. Physical therapy 1995;75(2):93-104.
18. Mary J. Murphy. Effects of cervical traction on muscle activity. JOSPT 1991;13(5):220- 225.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License