IJCRR - 5(11), June, 2013
Pages: 64-70
Date of Publication: 18-Jun-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
MOTOR PROFICIENCY IN HEARING IMPAIRED AND HEALTHY CHILDREN: A COMPARISON
Author: Atiya A. Shaikh, Aparna Sadhale
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objective: To score and compare gross motor and fine motor skills in hearing impaired and healthy children and to find co-relation between age and motor proficiency scores in both groups. Material and Method: 180 healthy children and 180 hearing impaired children were scored and compared with each other using short form battery test of Bruininks Osterestky Test of motor Proficiency. Results: There was a significant difference in scores of both groups in running speed, agility, balance, bilateral co-ordination activities, upper limb speed and dexterity and a positive correlation of scores with age in both groups. Conclusion: Hearing impaired children lack significantly in running speed, agility, balance, bilateral co-ordination activities, upper limb speed and dexterity as compared to healthy children, but both groups follow same trend of maturation
Keywords: Motor proficiency, children, healthy, hearing impaired
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
There are about 360 million people suffering from ‘Disabling Hearing Impairment’ all over the world. Another 32 million affected by hearing loss are children under age of 15. Hearing loss is the 7th most common cause of ‘Years lived with disability’ (YLD) globally. It contributes to a loss of over 36 million years of healthy & productive years of life, imposing a heavy social and economic burden on individuals, families, communities and countries. In India there are 63 million people who suffer from profound hearing loss. Of this, large percentage is of children between 0-14 years. There are 3 million hearing impaired children in India with almost 25,000 hearing impaired babies born every year 1 . Children with hearing impairment often experience delayed development of speech language and cognitive skills. This may result in slow learning and difficulty in progressing in school, thus difficulty to obtain, perform and keep employment. Both children and adult may suffer from social stigmatization and isolation as a result of hearing impairment. This also makes it more difficult for the individual to escape poverty by slowing progress in school and workplace. The cost of special education and lost employment due to hearing impairment can also impose a substantial economic burden on countries. Few investigators like Mykelbust2 , Wiegersma P H 3 , Crowe T K4 and Gonclave V M5 etc have tried to unmask such problems in other countries; none of such efforts have been documented in India. India being a developing country with limited resources it becomes all the more important for us to know the exact impairments in hearing impaired children so that correct management in those areas can be done. For above purpose a suitable proficiency assessment scale was required. When literature was searched, Bruininks Osterestky Test of Motor Proficiency was found to be the most suitable test according to the objectives. It has reliability of 0.84-0.87 and validity of 0.4-0.9 .It has been widely used in assessment of motor proficiency in children by previous researchers and has proved its sensitivity in various conditions7,8. Thus an attempt was made to compare motor proficiency in hearing impaired and healthy children with the help of short form battery of Bruininks Osterestky Test of Motor Proficiency. Keeping in mind the vast number of hearing impaired children in our society, above information will help to tackle the need of the hour of working towards their optimal performance in academics, sports, occupational skills and thus social participation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS RESEARCH DESIGN:
Cross sectional Inclusion Criteria: Healthy children and hearing impaired children of both genders between age group of 4. 6 yrs to 14.6yrs Exclusion Criteria Children with Mental retardation, known behavioral, cognitive, sensory, musculoskeletal or neuromuscular disorders Setting of the study Special schools, public schools in Pune Sample Size: 180 children with hearing deficit, 180 healthy children Sample Selection: Convenience Materials Used Balance beam, Ball, Blocks, Boxes, Measuring tape, Score sheet, Chairs, Clipboard, Stopwatch, Table, Target, Bruininks Ostrestky Test of motor Proficiency.
PROCEDURE
Ethical committee clearance from college authorities and consents from the school authorities and parents were obtained. Children were divided in 2 groups as hearing impaired and healthy. They were assessed for their motor proficiency using subtests from Bruinink’s Osterestky Test of Motor Proficiency. Scores for each test were noted.
OBSERVATION AND RESULTS
The hearing impaired group consisted of 95 male and 85 female subjects with mean age being 9.4 years .The healthy children group had 94 male and 86 females with mean age being 9.5 years (Table-1). When gross motor function scores of both groups were compared,using unpaired t test,there was a significant difference in scores for jumping up and clapping hands,walking forward heel to toe on balance beam,standing on preferred leg on balance beam,running speed and agility(p< 0.0001).The scores of catching a tossed ball with both hands and throwing ball at target with preferred hand in both groups did not have a significant difference (Table -2). On comparison of fine motor skill scores of both groups with unpaired t test, it was onserved that,there was a significant difference in scores of making dots in circle,sorting shape cards(p,0.0001).The scores of drawing a line through straight path ,copying a circle ,copying overlapping pencils did not show significant difference in both groups(Table-3) Analysis of trend of maturation was done by corelating age of children with total motor proficiency scores using spearman’s co-relation values .It showed a positive co-relation with r values being 0.904 and 0.906 for hearing impaired children group and healthy children group (graph-1).
DISCUSSION
A significant difference was found in scores of both groups for the test of running speed and agility. The test examined dynamic balance, balance in linear and angular acceleration. Affected predictive function of semicircular duct, faulty push pull mechanism and VOR can be the cause of affected dynamic balance9 and hence reduction of scores in hearing impaired children. For the test-standing on preferred leg on balance beam, hearing impaired children scored significantly low than healthy children. This can be attributed to the fact that the hearing impaired children receive abnormal input from a structurally abnormal vestibular system10,11,12,13 . The vestibular system serves to maintain a static position of the head in relation to the gravity for the purpose of maintaining balance and gaze stabilization14,15. Abnormal input from the vestibular system and lack of auditory perception leading to degeneration of infragranular layer of auditory cortex16 resulting in impaired motor output .The central auditory pathways can influence the cerebellum through the connections from the inferior colliculus and also can influence the motor neurons in spinal cord through the tectospinal tract17thus controlling postural control. Due to all these reasons, the balance in standing on preferred leg is affected in hearing impaired children. Walking heel to toe on balance beam is a relatively complex task which puts more demands on vestibular system which is already compromised in hearing impaired children9 ,so with reference to the mechanisms explained before13,14,15,16,17, scores are significantly reduced for this item in them. Normally the output relays from the inferior colliculus influence motor neurons of the spinal cord. Also the outputs from the inferior colliculus influence tectonuclear fibers which are responsible for controlling eye and head movements. The superior colliculus also sends signals to cerebellum17. Integration of all these leads to a co-ordinated reciprocal movement. Since the inputs to central auditory pathway are absent in hearing impaired children, there is degeneration of neurons in cochlear nuclei, superior and inferior colliculi,reduction in number of synapses along with degenerative changes in motor auditory cortex10,11,12,13. Hence leading to inappropriate processing so, when the child had to do a co-ordinated reciprocal movement like tapping feet alternately while making circle with fingers and jump up and clap hands, hearing impaired children scored significantly low as compared to healthy children. All these findings support the hypothesis that, hearing impaired children lack significantly in gross motor skill2, 3, 5,6,18 . Further two tests were used to assess upper limb coordination where the child had to catch a tossed ball with both the hands and throw a ball at a target with preferred hand. According to the literatures, the task was difficult to perform for hearing impaired children as the activities involve special and temporal co-ordination19, which is affected in hearing impaired children9 . Throwing a ball was done using preferred hand and the accuracy of throwing was judged which was equally good in hearing impaired children. Hearing impaired children used their visual and somatosensory system to judge the shift of centre of mass and maintain balance19. This is the most commonly played game in schools, hearing impaired children are trained to catch and throw the ball. It has been studied that when a function is lost, compensation and plasticity of the CNS may play some role in improvement motor performance. In cases of congenital sensoryneural hearing impairment, the other systems like visual system may try to compensate for the function of auditory and vestibular system. .With advancing age, there is increased experience which may be responsible for improved performance 20, 21 , hence hearing impaired children could perform equal with healthy children due to learning of compensatory mechanisms while practicing the game .Similar findings supported by few of other previous studies3, 4, 18 . Children were asked to draw a line through a straight path, copy a circle and copy overlapping pencils with preferred hand to assess visuomotor coordination. The children performed same in quality but took more time to finish the task. As the test does not consider the time required to finish the task, both the groups scored same on the point scale. Increase in duration to perform the task can be explained by Fitt’s law. According to it, movement time increases linearly with difficulty index due to visual constraints. More time is needed to upgrade the strategy22 . To test upper limb speed and dexterity children were asked to do sorting shape cards and making dots in circle with preferred hand. Both were time limited tests. Hearing impaired children showed significantly low scores in both tests as compared to healthy children. Visuomotor area 6A and parieto-occipital area 5 make the part of distributed network of retinal eye and hand related signals. These signals are all combined to form eye hand co-ordination. All these signals and information are processed in parieto occipital cortex. They also send signals to cerebellum leading to a controlled movement. Due to lack of signals from central auditory pathways, the neurons in parieto-occipital area are degenerated10, 11, 12 thus leading to compromised processing, hence the skills are slow in hearing impaired children. Previous studies have shown that hearing impaired children lack in gross motor skills9,10this study supports this fact and proves that ,all three systems (somatosensory, visual and vestibular) are needed to maintain good postural control15 The myelination of vestibulospinal, reticulospinal pathways, corticospinal, corticoreticulospinal pathways, ascending reticular activating system is complete by 8-10years in children23, 24. Synaptogenesis and requirement of appropriate motor unit results in a coordinated performance with advancing age22.Similar trend has been observed by other investigators15 . All this information can be used in screening of hearing impaired children for flaws in motor proficiency. They can be trained to use other compensatory strategies using the same information. Post training performance can again be judged using same scale. Job prescriptions and training can be started in schools depending on their capabilities. This would help them to gain maximum confidence and to come in main stream. The study was done in same geographic area and local schools with convenience sampling method, but the children of same age were selected to minimize error. Since Bruinninks Osterestky test of motor proficiency was used as outcome measure, we selected children of 4.6 years to 14.6 years. For minimizing further error, children were selected according to 3 groups as 4.6 yrs to 7.11 yrs, 8yrs to 10.11 yrs and 11 yrs to 14.6 yrs and 30 children in each group were selected. In future, detailed study can be done using a larger sample size for specific age groups from different schools. Children with different degrees and causes of hearing impairment, multiple impairments or trained vs. untrained children can also be studied for their motor proficiency in detail using this scale.
CONCLUSION
From the above study we conclude that, hearing impaired children lack significantly in running speed, agility, balance, bilateral co-ordination activities, upper limb speed and dexterity as compared to healthy children, but they follow same trend of maturation as that of healthy children.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We would like to thank students, parents and principals of all schools visited. Dr. Shilpa Parab (PT), Principal, Chaitanya Medical Foundation’s College of Physiotherapy, Pune for their support and encouragement. We acknowledge the great help received from scholars whose articles cited and included in references of this manuscript. We are grateful to authors, editors and publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature of this article has been reviewed and discussed. We are also grateful to IJCRR editorial board members and IJCRR team of reviewers who have helped to bring quality to this manuscript.
Permissions to reproduce published material:
Project published in book format by Lambert Academic Publishing. According to company policy author has a right to publish the material in article format.
References:
1. World Health Organization, health statistics and health information ,data and statistics:2013
2. Mykelbust H: Auditory disorders in children: A manual for differential diagnosis. Deafness and motor functioning. Grune and Stratto .New York, 1954. Pg 180-201.
3. Wiegresma O H, Vander Velde A: Motor development of deaf children. Journal of child psychology psychiatry 1983. Jan (24) ;( 1):103-11.
4. Crowe T k, Horak F B: Motor proficiency associated with vestibular deficits in children with hearing impairments. Physical therapy 1988 0ct; 68(10) 1493-9.
5. Goncalves V M, Piovesana A M, De Moura Riero M V: Evaluation of static equilibrium in a population of hearing impaired children. Arg. Neuropsychiatry 1993 Sept; 51(3):346- 51.
6. Gayle G W, Pohlman R L: Comparative study of dynamic, static and rotary balance of deaf and hearing children.perceptual motors skills 1990 june; 70(3) 883-8.
7. Bruininks R H (1978),Bruininks osterestky test of motor proficiency,Examiners manual(Revised edition)
8. BOTMP Technical information:AGS Publishing 2004
9. Gyton A C, Hall J E, Textbook of medical physiology.Function of cerebral cortex in hearing, 10th edition. Noida. Harcourt,Asia PTE Limited, 2001 pg 608-11
10. Moore D R: postnatal development of mammalian central auditory system and the neural consequences of auditory deprivation –Acta Otolaryngology suppl 1985: 421:19- 30.
11. Perier O, Alegria J, Buyse M, D’ Alimonte G, Gilson D: Consequences of auditory deprivation in animals and humans. –Acta Otolaryngology suppl 1984; 411:60-70.
12. Red E E, Cahill H B, Pongstaporn T, Ryugo D K: The effect of congenital deafness on auditory nerve synapses: Type I and Type II, miltipolar cells in anteroventral cochlear nucleus of cats –Journal of Assoc. Reaserch otolaryngology 2002 Dec; 3(4):403-17.
13. Deafness induced changes in auditory pathways Audi –Neurology:2001;6:305-318.
14. Shummway Cook A, Horak F, Black FO: Critical examination of vestibular function in motor impaired learning disabled children international journal of pediatric otorhinolaryngology, 1987 Nov 14(1):21-30.
15. Kaga K:Vestibular ‘compensation in infant and children with congenital and acquired vestibular loss in both ears’, International journal of pediatric otorhinology 2007 vol49(3):215-224
16. Rine R M,Cornwell G, Gank, Locascico C, O’ Hare T: Evidence of progressive delay of motor development in children with sensorineural hearing loss and concurrent vestibular dysfunction –Perceptual motor skills, 2000 June;90(3-2)1101-12.
17. Singh I B, Text book of human neuroanatomy, Cranial nerve nuclei and Brainstem: Internal structures . 7th edition.New delhi.Jaypee Brothers Publishers;2006 pg:105-122 and pg:124-143
18. Cynthia and Potter, Lyn Newman Silverman: Characteristics of vestibular function and static balance skills in deaf children – physical therapy. Vol 64 No.7, July 1984.
19. Gayle G W, Pohlman R L: Comparative study of dynamic, static and rotary balance of deaf and hearing children.perceptual motors skills 1990 june; 70(3) 883-8.
20. Siegel J C, Marchetti M, Tecklin J S: age related balance changes in hearing impaired children –Physical therapy 1991 March;71(3):183-81.
21. Surez H,Angeli S,surez A,Rosels B:Balance,sensory organization in children with profound hearing loss and cochlear implants,International journal of pediatric otorhinology 2007 Apr71(4):629-31
22. Shumway –Cook A, Wollacot MH : Motor control:Theory and practical application.Motor control Posture and balance, Development of postural control , Reach Grasp and manipulation .Motor Control,4th edition,city, Lippoincort, Williams & Wilkins , pg:119-139,143- 65,462
23. Lance J W, Mcleoid J G: A physiological approach to clinical neurology. supraspinal control of motor neurons .3rd edition.Great Britain.William Clowes(Beccles);1981 pg:108-111
24. Umphred D A , Byl N,Lazearo R T,Roller M. Neurological rehabilation, normal sequential, behavioural & physiological change through developmental arc pg.4th edition.china,Mosby Inc2001 page no:58-73
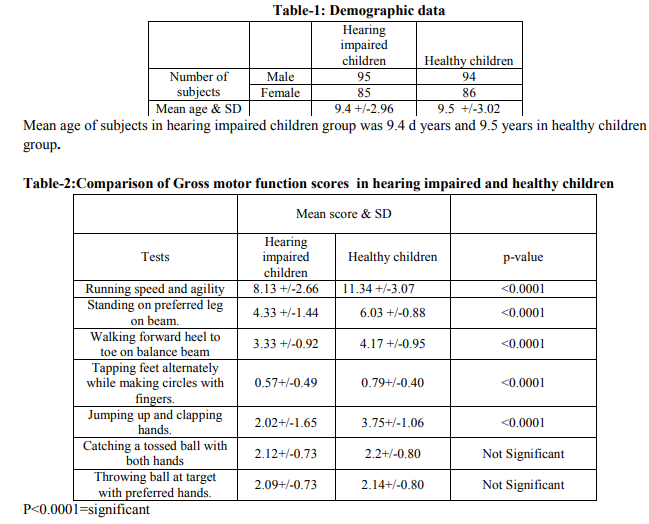
Hearing Impaired children lack significantly in skills like jumping up and clapping hands,walking forward heel to toe on balance beam,standing on preferred leg on balance beam,running speed and agility as compared to healthy children.


|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License