IJCRR - 5(24), December, 2013
Pages: 34-40
Date of Publication: 31-Dec-2013
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFECT OF HAND WASHING AMONG NURSING STAFFS IN TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL : A STUDY
Author: Suvarna Sande, Silpi Basak, Vidya Tawade
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background and objective: Health care Associated Infection (HAI) is a major problem worldwide. Contaminated hands of health care workers (HCWs) play an important role in the transmission of pathogens. Hand washing is considered to be the most effective method for preventing the transmission of micro-organisms between HCWs and patients. Hence the present study was undertaken to detect the microorganisms present on the hands of Nursing staffs before and after hand washing, in a tertiary care hospital. Method: Swabs were collected from 150 nursing staffs working in various wards and Intensive Care Units (ICUs), from hands before and after hand washing with antimicrobial soap. Swabs were inoculated on blood agar and Mac-Conkey's agar. Microorganisms were identified by standard methods. Detection of HAI pathogens were done according to Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute (CLSI) guidelines. Result: Out of total 150 samples collected before hand washing, growth was observed in107 (71.3%) samples and no growth in 43(28.7%) samples. Apart from skin commensals, Staphylococcus aureus (20.1%), Enterococcus faecalis (4.6%), Klebsiella pneumoniae (6%), E.coli (4%) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (1.3%) were detected. 05 Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains were also isolated from hand swabs collected before hand washing. No growth was obtained in 128 (85.3%) samples and growth were observed in 22 (14.7%) samples after hand washing , Conclusion: It is important to perform proper procedure of hand washing technique using an adequate quantity of antimicrobial soap to cover all skin surfaces for the recommended length of time.
Keywords: Health care Associated Infection (HAI), Hand hygiene
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Health care associated infection (HAI) is a major problem for patient’s safety and its surveillance. Prevention of HAI must be a first priority for every health care set up and institutions committed to making health care safer. The impact of HAI implies prolonged hospital stay, long-term disability, increased resistance of microorganisms to antimicrobials, massive additional financial burden for patients and their families and increased mortality. 1,2
In the mid-1800s, studies by Ignaz Semmelweis in Vienna, Austria, and Oliver Wendell Holmes in Boston, USA, established that organisms causing puerperal sepsis were transmitted via the hands of Physicians and Medical students who performed autopsy and directly entered the labour room. Semmelweis is considered not only the Father of Hand Hygiene, but his intervention is also a model of epidemiologically driven strategies to prevent infection. Many other investigations conducted over the past 40 years have confirmed that contaminated hands of Health Care Worker (HCW) play an important role in the transmission of health care-associated pathogens e.g Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Vancomycin resistant Enterococci (VRE) and Extended Spectrum β-lactamases(ESBL) , Amp C β-lactamases or Carbapenemases producing Gram negative bacilli.3,4,5,6
Bacteria present on the hands could be divided into two categories, namely resident or transient.
- Resident flora : Organisms like Coagulase Negative Staphylococci i.e. CONS (Staphylococcus epidermidis ,Staphylococcus hominis ,Oxacillin Resistant CONS ), Diphtheroids,Propionibacteria, Micrococci and Candida sp.,Pityrosporum (Malassezia) may survive and multiply in superficial layers of skin.
- Transient flora: These organisms colonize superficial layers of skin and can be easily removed by routine hand hygiene. They can be pathogens like Gram negative bacteria or Staphylococcus aureus and are acquired by HCWs from colonized or infected patients or from inanimate objects in the patient’s immediate environment and are the organisms most frequently to cause HAIs. 7,8
The transmissibility of transient flora depends on the microorganism present, the number of microorganisms on the surface, and the skin moisture. 9,10 Various studies have reported that total bacterial counts on the hands of HCWs have ranged from 3.9 x 104 to 4.6 x 106 colony forming unit / cm2 (CFU) and fingertip contamination ranged from 0 to 300 CFU. 3,4,5,6
Hence the present project was undertaken to study the bacterial flora present on the hands of Nursing staffs before and after hand washing with antimicrobial soap and water.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
This cross sectional study was conducted in Department of Microbiology. The project was approved by Institutional Ethics committee. 150 Nursing staffs working in various wards and ICUs of a tertiary care hospital in a rural set up were included in this study. Total number of 150 swabs (sterile swabs moistened with sterile saline) were collected from various sites of the hands (palm, web spaces, fingertip and beneath nail) before hand washing.
The Nursing staffs were told to wash their hands with antimicrobial soap performing all steps within specified time (15-20seconds).They were instructed not to touch the tap after washing hands and air dry their hands. After completely drying their hands, another swab from above mentioned sites were taken. All swabs were inoculated on blood agar and Mac-Conkey’s agar and incubated at 37 0C overnight and examined for microbial growth. The microorganisms were identified by standard methods.11 Detection of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) using Cefoxitin disc 30 µg and ESBL producing organisms by combined disc method (Ceftazidime 30 µg and Cefdazidime + Clavulanic acid disc 30/10 µg) were carried out. 12For detection of Carbapenemase producing Enterobacteriaceae, Modified Hodge test was done. For detection of HLAR (High level aminoglycoside resistant) Enterococci, High Level Gentamicin disc 120 µg and for Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci (VRE) , VRE agar having Vancomycin 6 µg/ml was used as per Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute ( CLSI) guidelines.12 Statistical analysis was done by standard statistical methods .13
RESULTS
Total 150 Nursing staffs working in various wards, ICUs and OT complexes were included in the study. Maximum staffs 36 ( 24%) were from Medicine ward followed by Surgery 27 (18%) and Pediatrics 27(18% ).(table1) Amongst 36 Nursing staffs from medicine ward , 28 Nursing staffs (77.7% ) had growth before hand washing. Though the number of Nursing Staffs from each specialties included in other wards were less, 18(85.7%) Nursing Staffs had growth before hand washing.
Out of total 150 samples collected before hand washing, growth of microorganisms was observed in 107(71.3%) samples and no growth in 43
(28.7%) samples. Growth of microorganisms were >103 colony forming unit (CFU) in all the samples. Out of 107 samples showing growth, 55 (51.4%) samples showed single type of bacteria, 41 (38.3%) showed two types of bacteria while 4 (3.7%) samples showed three types of bacteria.
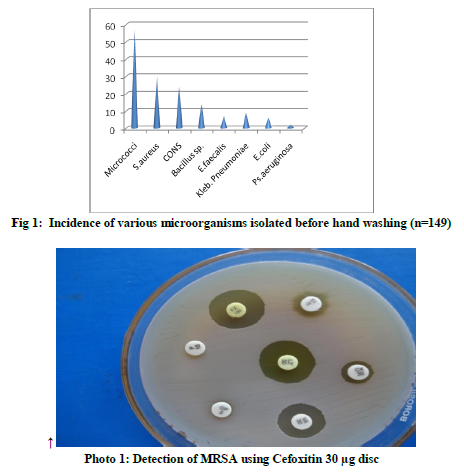
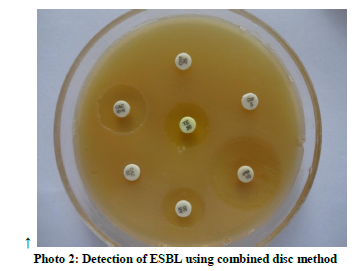
Out of 30 Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from hands of Nursing Staff before hand washing 5(16.6%) were MRSA. (table2) (photo 1) Out of 17 Gram negative bacilli isolated, 6 (35.2%) were ESBL producers(Klebsiella pnumoniae 4,E.coli 2) (photo 2) but no Carbapenam resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) or Carbapenamase producing Gram negative bacilli were isolated. 07 (4.6%) Enterococcus faecalis were isolated and all of them were High Level Aminoglycoside resistant. No vancomycin Resistant Enterococci (VRE) was detected in the present study. Two Enterococcus faecalis strains showed vancomycin sensitivity in the intermediate range (15-16 mm) and were repeated thrice. These two strains did not grow on VRE agar and hence were considered as Vancomycin sensitive.
After hand washing with antimicrobial soap and water, no growth was obtained in 128 (85.3%) samples and single type of growth in 22 (14.7%) samples. Growth of microorganisms was in between 50- 100 CFU. Apart from skin commensals, MSSA were detected in 22.7% samples.(table 3)
After hand washing, improvement was observed as there was no isolation of MRSA, Enterococcus species and Gram negative bacilli and hence no ESBL producers.
If the number of samples positive before and after hand washing is considered, statistical analysis reveals standard error of difference is 4.7, whereas the observed difference is 56.6. Since the observed difference between two groups is much more than twice the Standard Error of difference (2× 4.7= 9.4), we hereby conclude that efficacy of hand washing is significantly higher than without i.e. before hand washing. 13
DISCUSSION
Cross-transmission of organisms occurs through contaminated hands. HAI pathogens especially Multidrug resistant organisms (MDROs) e.g .Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Vancomycin resistant Enterococci (VRE) and Extended Spectrum β-lactamases (ESBL), Amp C β-lactamases or Carbapenemases producing Gram negative bacilli are transmitted by contaminated hands of HCWs. Hands also play important role in transmission of blood borne, faecal and respiratory tract viruses.14-21 Transmission of pathogens from one patient to another via HCWs’ hands requires five sequential steps.14
- Organisms present on the patient’s skin, or shed onto inanimate objects in immediate vicinity of the patient;
- Organisms transferred to the hands of HCWs;
- Survival of organisms on HCWs’ hands;
- Inadequate or entirely omitted hand washing or hand antisepsis or inappropriate agent used by the HCW
- The contaminated hands of HCWs must transmit the microorganisms to another patient directly or via inanimate object.
Factors influencing the transfer of microorganisms from surface to surface and cross- contamination rates are organisms involved, source and destination surfaces, moisture level and size of inoculum.
In the present study, before hand washing ,apart from skin commensals (micrococci, coagulase negative Staphylococci i.e.CONS etc.), transient flora i.e. Staphylococcus aureus (20.1% ),Gram negative rods (11.4%) and Enterococcus faecalis (4.6 % ) were obtained.(fig 1) In our study, out of 30 Staphylococcus aureus isolated, 5 (16.6%) were MRSA and out of 17 Gram negative bacilli isolated, 6 (35.2%) were ESBL producers and is a matter of concern. These organisms are potential threat of health care associated infection and also outbreak in health care set up. Several other studies have documented that HCWs can contaminate their hands or gloves with Gram-negative bacilli, Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococci or Clostridium difficile even by performing “clean procedures” or touching intact areas of skin of hospitalized patients or after touching inanimate objects.15-21
Ayliffe and colleagues 22 found that 15% of nurses working in an isolation unit carried a median of 1x 104CFU of Staphylococcus aureus on their hands; 29% of nurses working in a general hospital had Staphylococcus aureus on their hands (median count 3.8 x 103 CFU), while 78% of those working in a hospital for dermatology patients had the organism on their hands (median count, 14.3 x 106 CFU). The same survey revealed that 17–30% of nurses carried Gram-negative bacilli on their hands (median counts ranged from 3.4 x 103 CFU to 38 x 103 CFU).
Daschner 23found that Staphylococcus aureus could be recovered from the hands of 21% of ICU caregivers and that 21% of doctors and 5% of nurse carriers had >103 CFU of the organism on their hands. A study conducted by Waters V et al in two neonatal ICUs revealed that Gram-negative bacilli were recovered from the hands of 38% of nurses.24
In the present study, after hand washing with antimicrobial soap, Micrococci (50%), Staphylcoccus aureus (MSSA 22.7%), Bacillus species (18.1%) and CONS(9.09%) were detected. In these cases, it might be possible that nurses fail to perform appropriate technique of hand washing for recommended length of time. To avoid prolonged hand contamination, it is not only important to perform hand hygiene when indicated, but also to use the appropriate technique and an adequate quantity of the product to cover all skin surfaces for the recommended length of time. 14,25
Hand hygiene practice and it’s compliance has been the core issue worldwide especially in developing countries. Poor hand hygiene practices in hospital has led to number of outbreaks and adverse outcomes.26 The role of health care workers’ hands in cross transmission of organisms is best illustrated by the striking example of the study conducted by Pittet et al , where a hospital wide hygiene campaign with emphasis on alcoholic hand rub led to a sustained increase in hand hygiene compliance and reduction in HAI by more than 40% and transmission of MRSA was reduced by more than 50%. 27 Promotion of hand hygiene has become an important initiative with most of the countries and efforts are to be strengthened worldwide to provide safe patient care.
CONCLUSION
When health care workers do not follow the steps of hand hygiene between patient contact or during patient care, the microorganisms can be transmitted from patient to health care workers to other patients. It is important to perform proper procedure of hand washing technique using an adequate quantity of antimicrobial soap to cover all skin surfaces for the recommended length of time. We hereby conclude that efficacy of hand washing with antimicrobial soap is statistically significant in controlling the microorganisms on nurses hands than without hand washing.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors are thankful to DMIMS (DU) for the help while conducting the study.


References:
- All egranzi B Nejad SB, et al Burden of endemic healthcare associated infection in developing countries: systematic review and meta - analysis, Lancet, 2011; Vol 377: pg 228 - 241.
- World Health Organization (2011). Report on the burden of endemic health care associated infections worldwide. WHO Document Production services ISBN 9789241501507, Geneva
- Larson E. Effects of handwashing agent, handwashing frequency, and clinical area on - hand flora. American Journal of Infection Control, 1984, 11:76-82.
- Larson EL et al. Changes in bacterial flora associated with skin damage on hands of health care personnel. American Journal of Infection Control, 1998, 26:513–521.
- Maki D. Control of colonization and transmission of pathogenic bacteria in the hospital. Annals of Internal Medicine, 1978, 89:777-780.
- Pittet D et al. Bacterial contamination of the hands of hospital staff during routine patient care. Archives of Internal Medicine, 1999, 159:821-826.
- Price PB. The bacteriology of normal skin: a new quantitative test applied to a study of the bacterial flora and the disinfectant action of mechanical cleansing. Journal ofInfectious Diseases, 1938, 63:301–318.
- Evans CA et al. Bacterial flora of the normal human skin. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 1950, 15:305-324.
- Marples RR, Towers AG. A laboratory model for the investigation of contact transfer of micro-organisms. Journal of Hygiene (London), 1979, 82:237-248.
- Patrick DR, Findon G, Miller TE. Residual moisture determines the level of touch- contact-associated bacterial transfer following hand washing. Epidemiology and
Infection, 1997, 119:319–325.
- Collee JG, Miles RS, Watt B. Tests for the identification of bacteria. In: Collee JG, Marmion BP, Fraser AG, Simmons A, editors. Mackie and Mc Cartney Practical Medical Microbiology. 14th ed. Edinburg: Churchill Livingstone; 1996 . p. 131-50.
- Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests. Approved standarad M2-A7, 11th ed. Wayne PA: USA; 2007.
- Park K. Park’s Text book of Preventive and Social Medicine. 22nd edition. Jabalpur: Banarasidas Bhanot; 2013. Chapter 19, Health information and basic medical statistic : p 782-796.
- WHO guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health care. Geneva : World Health Organization : 2009.
- Sanderson PJ, Weissler S. Recovery of coliforms from the hands of nurses and patients: activities leading to contamination. Journal of Hospital Infection, 1992, 21:85–93.
- Boyce JM et al. Environmental contamination due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: possible infection control implications. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, 1997, 18:622–627.
- McBryde ES et al. An investigation of contact transmission of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Journal of Hospital Infection, 2004, 58:104–108.
- Duckro AN et al. Transfer of vancomycin-resistant Enterococci via health care worker hands. Archives of Internal Medicine, 2005, 165:302–307.
- Ray AJ et al. Nosocomial transmission of vancomycinresistant Enterococci from surfaces. JAMA, 2002, 287:1400–1401.
- Riggs MM et al. Asymptomatic carriers are a potential source for transmission of epidemic and nonepidemic Clostridium difficile strains among long-term care facility
residents. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 2007, 45:992–998.
- Bhalla A et al. Acquisition of nosocomial pathogens on hands after contact with environmental surfaces near hospitalized patients. Infection Control and Hospital
Epidemiology, 2004, 25:164–167.
- Ayliffe et al. Hand disinfection: a comparison of various agents in laboratory and ward studies. Journal of Hospital Infection, 1988, 11:226–243.
- Daschner FD. How cost-effective is the present use of antiseptics? Journal of Hospital Infection, 1988, 11(Suppl.A):227–235.
- Waters V et al. Molecular epidemiology of gram-negative bacilli from infected neonates and health care workers’hands in neonatal intensive care units. Clinical Infectious
Diseases, 2004, 38:1682–1687
- Lucet JC et al. Hand contamination before and after different hand hygiene techniques: a randomized clinical trial. Journal of Hospital Infection, 2002, 50:276–280.
- Hugonnet S, Harbarth S, Saz H, Duncan RA and Pitet D, Nursing resourus: a major determinant of nosocomial infection? current opin. Infect Dis. 2004: Vol 17 (4), PG 329-333.
- Pittet D, Hugonnet S, Harbarth S et al , effectiveness of a hospital wide programme to improve compliance with hand hygiene Lancet 2000; 356:1307-1312.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License