IJCRR - 6(1), January, 2014
Pages: 79-88
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFICACY OF BARK OF ACACIA ARABICA IN MANAGEMENT OF BACTERIAL VAGINOSIS : A RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL
Author: Rumaiza Jahufer, Wajeeha Begum
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Back ground and Objective: Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a polymicrobial syndrome having alteration of vaginal flora involving a decrease in Lactobacilli and predominance of anaerobic bacteria. Objective was to evaluate the efficacy of the Bark of Acacia arabica (chal babool) as an alternate therapy in the management of Bacterial Vaginosis. Methodology: This was a prospective, single blind, standard controlled randomized clinical trial on 45 patients (30 patients in test group and 15 in control group) who attended in and outpatient Department of OBG, National Institute of Unani Medicine hospital, Bangalore, India with complaint of abnormal vaginal discharge or vulvovaginal pruritus. Married patients aged 18- 45 years with regular cycles and diagnosed as having BV were included in this study. Patients were excluded if there was a blood stained discharge, any organic pelvic pathology, systemic illness, malignancy, AIDS, syphilis, gonorrhoea, pregnant and lactating women. Decoction of Chal babool was given orally (30gms twice daily) for one month and standard drug Tab. Metronidazole (400mg twice daily) for 7 days was given in test and control group respectively. For diagnosis and cure rate of bacterial vaginosis, Amsel's criteria were used. Results: There was a significant improvement in the subjective and objective parameters; test drug was found to have similar effective as in control drug in the management of Bacterial Vaginosis (P =1.000) statistically. Conclusion: Patients in both groups have shown improvement by treatment. This study confirms the efficacy of chal Babool as potent astringent and antimicrobial. Phase -3 clinical study shall be recommended with large sample size and prolonged duration.
Keywords: Bacterial vaginosis, Chal babool, Clue cells, Whiff test, Randomized controlled trial
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a polymicrobial syndrome having alteration in vaginal flora involving a decrease in Lactobacilli and predominance of anaerobic bacteria including Gardnerella vaginalis, Mobiluncus species, Prevotella species, Mycoplasma hominis and Atopobium vaginae, is among the most common cause. Vaginal discharge is the most common complaint of women of childbearing age. At least 50% of patients have no symptoms [1,2,3]. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has recently included bacterial vaginosis on their list of emerging infectious diseases [2]. The BV diagnosis was based on Amsel’s criteria [3,4]. The pH of normal vaginal fluid is usually in the range of 3.8 to 4.5. Low pH inhibits bacterial growth and decreases bacterial attachment. In BV the pH is usually above 4.7[5]. Overall there is a significant increase in the vaginal secretion to 109 –1011/gm instead of 105 –106 /gm, with increase of 100 fold to 1,000 fold bacteria[6].BV is more common in women with sexual transmitted infections (STIs), who have recently changed their sex partner, multiple sexual partner, cigarette smoking, stress, low Socioeconomic Status (SES), use of intra uterine contraceptive device (IUCD), frequent vaginal douches, early age at first intercourse and black ethnicity[1,5,7,8,9].The prevalence was 63% in women with multiple sexual partners, 34% in monogamous sexual relationship and 24-51% in lesbian women [10,11]..Women taking vitamin or nutritional supplements were less likely to have bacterial vaginosis[12], and recurrence is common[5,10,13]. BV has been associated with complications like a six fold increased rate of postpartum endometritis, a threefold of pelvic inflammatory, a three to fourfold of vaginal cuff cellulites, amniotic fluid infection and chorioamnionitis [14] and increases the risk of HIV transmission 2-4 fold [14, 15]. In Unani system of medicine white discharge per vaginum (sailanur rehm) is treated with many single drugs since ancient period. Therefore Bark of Acacia Arabica (Chal babool) was selected as research drug as it possess astringent (habis), styptic (qabiz)[16,17,18,19,20], desiccant (mujaffif), tonic(muqawi)[18], antibacterial, antimicrobial, antiseptic properties [20,21,22,23,24].Keeping the above mentioned properties in view an attempt has been made to evaluate the effect of bark of Acacia Arabica in the management of BV.
METHODOLOGY
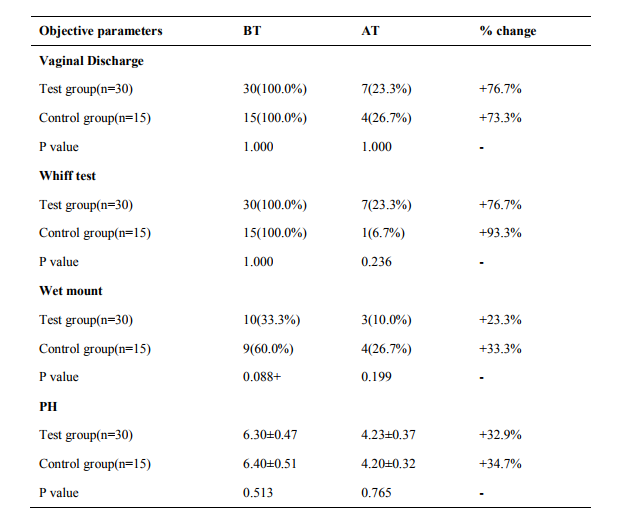
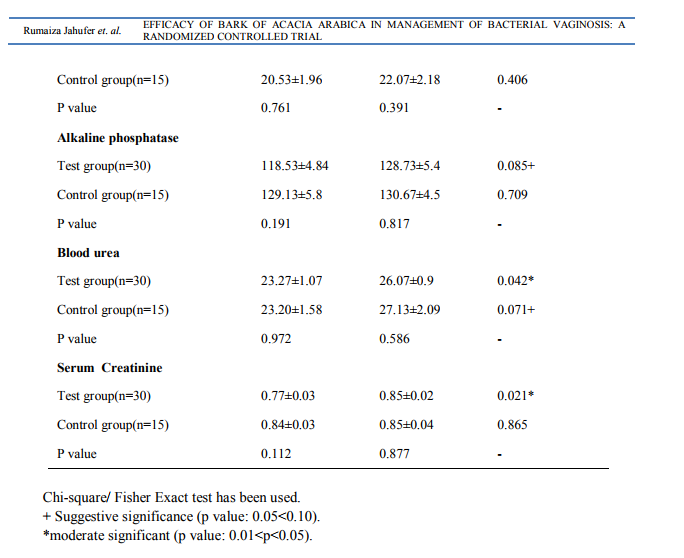
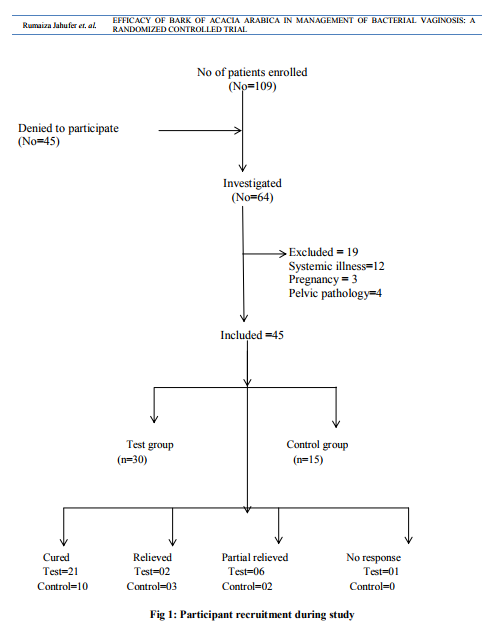
Study design: A prospective, single blind, standard controlled randomized, pre and post evaluation clinical trial was conducted on 45 patients (30 patients in test group and 15 in control group) who attended in and outpatient department of OBG at National Institute of Unani Medicine hospital, Bangalore, India with complaint of abnormal vaginal discharge or vulvovaginal pruritus during November 2011 to April 2013.The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by institutional Ethical Committee, NIUM, Bangalore. Married patients aged 18- 45 years with regular cycles and diagnosed as having BV were included in this study after receiving informed consent. In both symptomatic and asymptomatic groups, the diagnosis of BV was based on the presence of at least 3 of the 4 clinical criteria proposed by Amsel and co-workers: adherent watery vaginal discharge, vaginal pH > 4.5, positive amine test, and presence of clue cells [25].Women were excluded if there was a blood stained discharge, any organic pelvic pathology, systemic illness, malignancy, AIDS, syphilis, gonorrhoea, pregnant and lactating women. A detailed history including demographic profile of patients was noted. Following complete evaluation of history and clinical examination, patients were subjected to baseline investigations of complete blood picture, complete urine analysis, random blood sugar, ESR, HIV, VDRL, pelvic ultrasound and Pap smear to exclude systemic illness and pelvic pathology. Safety of drug was assessed by SGOT, SGPT, alkaline phosphatase, blood urea and serum creatinine before and after the treatment. Diagnosis by Amsel’s criteria ie.Vaginal pH was measured by Ranbaxy pH indicator with a range of 4 to7. The pH strip used was a colour-fixed indicator stick. The amine test was considered positive when secretions emitted a fishy amine odor with the addition of 10% KOH[26]. Vaginal secretions were combined with 2 drops of normal saline on a slide and covered with a cover slip for the wet mount. Examination under high-powered microscopy identified the percentage of clue cells
Interventions
The patients were randomly allocated in to test (n=30) and control (n=15) groups by lottery method. Decoction of chal babool was given orally (30gms twice daily) before meal for one month and standard drug Tab. Metronidazole (400mg twice daily) for 7 days in test and control group respectively. Patients were called after two weeks during trial. At each visit vaginal pH, wet mount and amine test were performed. After the completion of the 4 weeks, pre and post treatment values of symptoms and signs were analyzed to evaluate the response or effect of the treatment. Follow up was scheduled to look for recurrence in two visits at 2 weeks and 4 weeks following completion of therapy in those patients who respond with treatment or who were clinically cured.
Assessment
Cure rate was assessed by Amsel’s criteria. Complete cure was considered when there was absence of signs of Amsel’s criteria and associated symptoms. Relief of disease was considered when significant changes in Amsel’s criteria with absence of associated symptoms. Partially relieved was considered when significant changes in Amsel’s criteria with presence of associated symptoms. No response for treatment was labelled when no change in pre-treatment subjective and objective parameters either during or after the treatment.
Statistical Analysis
The Statistical software SPSS 15.0 was used for the analysis of the data. Descriptive and inferential statistical analysis has been carried out in the present study. Results on continuous measurements were presented on Mean ? SD (Min-Max) and results on categorical measurements were presented in number (%).Significance was assessed at 5 % level of significance. Student’s t test (two tailed, independent) ,Chi-square/ Fisher Exact test has been used to find the significance of study parameters on categorical scale between two or more groups.
RESULTS
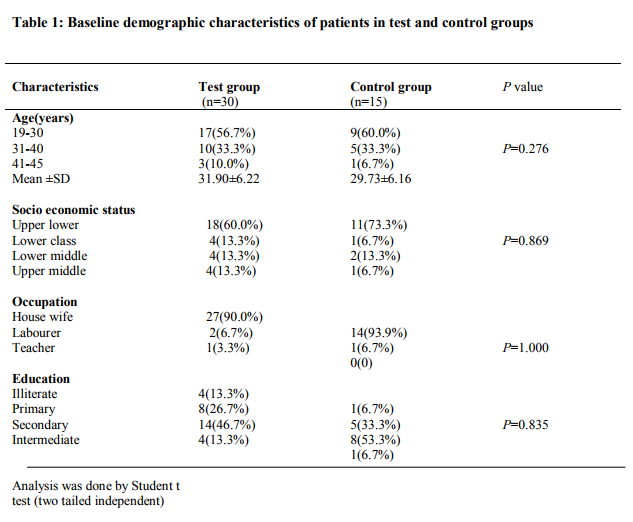
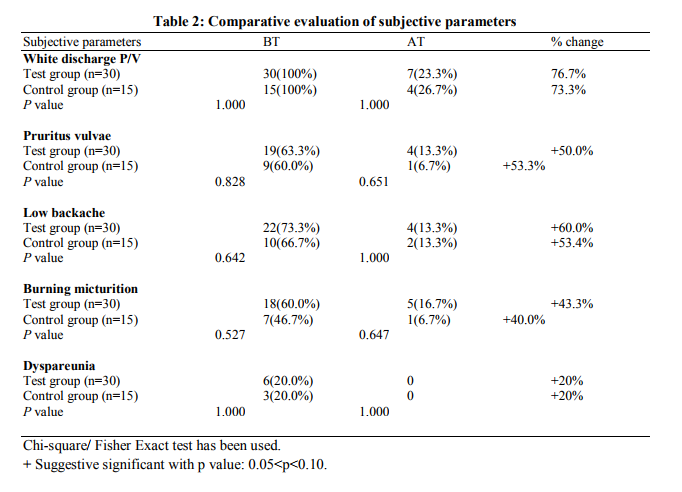
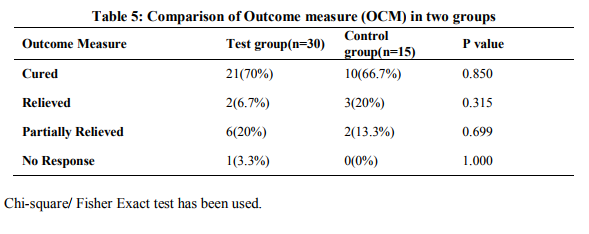
Patients’ recruitment is mentioned in Fig. 1. A significant improvement of white discharge was observed in test group 23(76.7%) compared to control group 11(73.3%) after intervention Table2. In present study associated symptoms like pruritus vulvae in 28(62.2%), low backache in 32(71.1%), burning micturition in 25(55.5%) and dyspareunia in 9(20%) were reported in test group. The symptoms were reduced with suggestive significance with P value 0.05< P< 0.10 after comparison of both groups after treatment. (Table2) DISCUSSION A detailed analysis revealed that the mean age of patients was 31.90±6.22 in the test group and 29.73±6.16 in the control group. According to SES majority of patients belongs to Upper Lower class (64.4%). Women educated in primary and secondary schools were the most commonly affected groups [13/45(28.9%) and 22/45(48.9%), respectively]. A majority of the patients were housewives (91.1%) as shown in Table 1. Present study showed that the test drug was significantly effective as metronidazole in BV. Table 1 shows majority of the patients were in the age group of 19 - 40 years. The mean ages of participants were 31.90±6.22 and 29.73±6.16 in test and control group respectively. This finding is correlated with the statement of Ayenalem S et al and Xueqiang et al. that disease is more commonly seen in childbearing age group [1, 27].In present study the incidence of bacterial vaginosis was observed more in low SES i.e 40 (88.8%) when compare to upper group, 5 (11.2%) (Table1). This finding is correlated with the statement of many studies conducted. [11, 28,29,30].Yang LR et al. reported that lower genital tract infections are found in low SES [31]. Table 1 shows the number of patients were maximum in the illiterate and secondary level education 40(88.9%) compared to intermediate and higher education 5(11.1%). This finding is in accordance with the statement of previous studies that the disease is more prevalent in illiterate people [28,29,32,33]. Our study showed that incidence of bacterial vaginosis is concerned with occupation of patients (Table 1) i.e., maximum in house wife group 41(91.1%) compare to working class 4(8.9%). Similar finding were reported by Holzman C et al [34]. A significant improvement of white discharge was observed in test group 23 (76.7%) compared to control group 11(73.3%) after intervention. This improvement may be due to antibacterial, antimicrobial, astringent properties of bark of Acacia arabica. [20,21,24]. In present study associated symptoms like low backache and dyspareunia were reported. The symptoms were reduced with suggestive significance. These findings are correlated with previous study conducted by Rajvaidhya et al states that the extract from bark of babool is highly astringent herb may block the body's pain triggers [35]. No adverse effect of test drug was observed during the trial and all the safety profile investigations were within normal limits, hence Acacia arabica was found as safe drug. The limitation of the study was small sample size causing statistical error. Therefore further trial can be carried out to confirm the efficacy and potency of drug on large number of patients.
CONCLUSION
It may be concluded that bark of Acacia Arabica was found to be beneficial in patients of bacterial vaginosis due to its antimicrobial, antibacterial, astringent, styptic, desiccant and tonic effects. It can serve as an alternate remedy for metronidazole, in which relapses are more. This study confirms the efficacy and safety of Acacia arabica as alternate therapy in the management of bacterial vaginosis. Phase three clinical trial can be carried out to confirm the efficacy and potency of research drug. Conflict of interest None
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors are grateful to the Department of Ayurveda, Yoga, Unani, Siddha and Homeopathy (AYUSH), Ministry of Health, India, Director IIM and commissioner, Colombo for providing all facilities to complete the research.

References:
REFERENCES
1. Ayenalem S, Yusuf L, Ashenafi M. Lactic Acid Bacterial Vaginosis among Outpatients in Addis Ababa. Ethiop J Health Dev. 2010; 24(3):198-204.
2. Misic M, Randelovic G, Kocic B, Antic S, Stojanovic M, Mladenovic V. Complications associated with Bacterial Vaginosis. A Review Article ACTA FAC MED NAISS 2005; 22 (4): 161-165.
3. Martinez RCR, Franceschini SA, Patta MC, Quintana SM, Gomes BC, Martinis ECPD et al. Improved cure of bacterial vaginosis with single dose of tinidazole (2g), Lactobacillusrhamnosus GR-1, and Lactobacillus reuteri RC- 14: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Can J Microbiology 2009; 55: 133-138.
4. Larsson PG, Pedersen BS, Ryttig KR, Larsen S. Human lactobacilli as supplementation of clindamycin to patients with bacterial vaginosis reduce the recurrence rate; a 6- month, double-blind, randomized, placebocontrolled study. BMC Women's Health 2008; 8(3):1-8.
5. Eschenbach DA. Screening, Diagnosis and Management of Bacterial Vaginosis. Issues in Management of STDs in Family Planning Settings: 71-75. [cited on 06/03/12] Available at www.popline.org. 6. Robinson DT, Boustouller YL. Damage to oviduct organ cultures by Gardnerella vaginalis.Int J Exp Path 2011; 92: 260–265.
7. Turovskiy Y, Noll KS, Chikindas ML. The aetiology of bacterial vaginosis. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2011 May; 110(5):1105-28.
8. Hay P. Bacterial Vaginosis. Journal of Paediatrics, Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2002 ;Sep/Oct; 36-40
. 9. Gillet E, Meys JF, Verstraelen H, Bosire C, Sutter PD, Temmerman M et al. Bacterial vaginosis is associated with uterine cervical human papillomavirus infection: a metaanalysis. BMC Infectious Diseases 2011; 11(10): 1-9.
10. Verstraelen H, Verhelst R, Vaneechoutte M, Temmerman M. The epidemiology of bacterial vaginosis in relation to sexual behavior. BMC Infectious Diseases 2010; 10(81):1-11.
11. Anonymous Bacterial Vaginosis.Inverness Medical International (IMIL), Priory Business Park 2009 July; 3-16 [cited on 23/04/12] Available at www.balanceactiv.com.
12. Holzman C, Leventhal JM, Jones NM, Wang J. Factors Linked to Bacterial Vaginosis in Non pregnant Women. American Journal of Public Health 2001 Oct; 91(10):1664-1670.
13. Berek JS, Adashi EY, Hillared PA. Novak’s Gynaecology. 12th ed. London: Williams and Wilkins; 1996;430-431.
14. Zahra A, Fateme G, Reza AM. Comparison of the effectiveness of vitamin C vaginal tabletwith metronidazole vaginal gel in the treatment of bacterial vaginosis African Journalof Pharmacy and Pharmacology 2010 July; 4(7): 484-489.
15. Pirotta M, Fethers KA, Bradshaw CS. Bacterial vaginosis. Australian Family Physician 2009 Jun; 38 (6): 394-397.
16. Ghani N. Khazainul Advia. New Delhi: Idarae Kitabul Shifa; YNM: 339-340.
17. Ibn Sina. Al-Qanoon Fit-Tib (Urdu trans. by Kantoori GH). New Dehli: Idarae Kitabus Shifa; 2007:341.
18. Kabeeruddin M. MakhzanulMufradat. New Delhi: Ejaz Publication House; YNM; 118- 119.
19. Hakeem MAH. Bustan ul Mufradat. New Delhi: Idarae Kitabul Shifa; 2002: 120.
20. Zahoor N, Usmanghani K, Akram M, Asif HM , Saleem QE, Sami A et al. Pharmacological activities of Acacia arabica. Crown Journal of Medicine 2011 Nov; 1(2): 09-11.
21. Shazia M, Saadia MA, Jasmine F, Arif JM, Huma M. Anti-Microbial screening of some medicinal plants extracts. International Journal of Research in Ayurveda and Pharmacy 2011; 2 (4):1258-1264.
22. Malviya S, Rawat S, Kharia A, Verma M. Medicinal attributes of Acacia nilotica LinnA comprehensive review on ethno pharmacological claims. Int J of Pharm and Life Sci 2011 June; 2(6): 830- 837.
23. Yasir M, Shrivastava R, Jain P, Das D. Hypoglycaemic and Antihyperglycemic Effects of Different Extracts and Combinations of Withania coagulans Dual and Acacia arabica Lamkin Normal and Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats. Pharmacognosy Communications 2012 AprJun; 2(2): 61-66.
24. Banso A. Phytochemical and antibacterial investigation of bark extracts of Acacia nilotica J Med Plant Res 2009 Feb; 3(2): 082- 085.
25. Amsel R, Totten PA, Spiegel CA, Chen KS, Eschenbach DA, Holmes KK. NSV Diagnosticcriteria and microbial and epidemiological association.Am J Med 1983; 74:14-22.
26. Egan ME, Lipsky MS. Diagnosis of vaginitis. Am Fam Physician. 2000; 62:1095-1104.
27. Xueqiang F, Yingzhi Z, Yanfang Y, Yutao D, Huiqing L. Prevalence and risk factors of Trichomoniasis, Bacterial vaginosis and candidiasis for married women of child bearing age in rural Shandong. Jpn J Infect Dis 2007; 60:257- 261.
28. Pawanarkar J and Chopra K. prevalence of lower reproductive tract infection in infertile women. Health and population 2004; 27(2):67-75.
29. Jones FR, Miller G, Gadea N, Meza R, Leon S, Perez J et al. Prevalence of bacterial vaginosis among young women in low-income populations of coastal Peru. International Journal of STD and AIDS 2007; 18: 188–192.
30. Valiani M, Zolfaghari M,Nazemi M, Pirhadi M, Ebrahimian S. The relationship between family planning methods, individual hygiene, and fertility with vaginal infections among the women referring to selected health centers in Isfahan city. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2011 winter; 16(1):83–92.
31. Yang LR, Zhao H, Wang HP, Li Y, Niu JP, Su KJ et al. Improving ability of married women to prevent reproductive tract infections in rural western China. Environmental health and preventive medicine 2006 Sep; 11: 233-240.
32. Ashraf-Ganjoei T. Risk factor for bacterial vaginosis in women attending a hospital in Kerman, Islamic Republic of Iran. East Mediterr Health J 2005 May; 11(3):410-5.
33. Bhalla P, Chawala R, Garg S, Singh MM, Raina U, Bhalla R et al. Prevalence of bacterial vaginosis among women in Delhi, India. Indian J Med Res 2007 Feb; 125: 167- 172.
34. Holzman C, Leventhal JM, Jones NM, Wang J. Factors Linked to Bacterial Vaginosis in Nonpregnant Women. American Journal of Public Health 2001 Oct; 91(10):1664-1670.
35. Rajvaidhya S, Nagori BP, Singh GK, Dubey BK, Desai Pand, Jain S. A Review on Acacia Arabica- An Indian medicinal plant. IJPSR, 2012; 3 (7):1995-2005.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License