IJCRR - 6(1), January, 2014
Pages: 63-68
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
STUDY OF KNOWLEDGE, ATTITUDE AND PRACTICE OF GENERAL POPULATION OF WAGHODIA TOWARDS DIABETES MELLITUS
Author: Gunvanti B. Rathod, Sangita Rathod, Pragnesh Parmar, Ashish Parikh
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objectives: The prevalence of diabetes in India has grown over the past decade. There are virtually less number of epidemiological studies assessing the level of awareness of diabetes mellitus among the general population. This study aims to assess the baseline levels of knowledge, attitude and practices of general population of Waghodia. The baseline results were used to develop a counselling program and to assess whether this intervention could produce any improvement in diabetes awareness and practices. Material and methods: A suitably designed and validated KAP questionnaire was administered and responses were coded and analysed. Results: Altogether, 56.14 % of respondents scored 100% in the questions related with knowledge. However 17.58% scored 100% in the attitude questions and15.78% scored 100% in practice questions. Conclusion: We can conclude that the responders had good knowledge but poor attitude and practice towards diabetes. Repeated reinforcement and motivation along with health education will definitely bring about a positive change in practices.
Keywords: Diabetes, KAP, General population
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Demographic transition combined with urbanisation and industrialisation has resulted in drastic changes in lifestyles globally. Consequently, lifestyle related diseases like diabetes mellitus, have emerged as a major public health problem. Diabetes mellitus, a common metabolic disorder, which accounts for a high incidence of morbidity leads to various events including micro and macro vascular complications. [1] Diabetes is characterised by a state of chronic hyperglycemia resulting from a diversity of aetiologies, environmental and genetic, acting jointly. [2] Diabetes affects 10-16 % of urban population and 5.33-6.36 % of rural population and this is projected to double by 2030. [3] It is now a global epidemic with devastating humanitarian, social and economical consequences. It is an epidemic of 21st century. [4] Total number of people with diabetes is projected to double between 2000 and 2030. [5] In India, the older members of the population who have had diabetes for a relatively long time are protected from risk of diabetic complications because of their physical activity patterns and dietary habits (making healthier food choices), while the current younger generation face high risk of diabetic complications due to a sedentary and stressful lifestyle. Over the past few years, the working patterns have changed, with fewer people involved in manual labour (e.g., as in the agriculture sector) and more and more people opting for physically less demanding office jobs. Another factor for the increase in risk for diabetes mellitus is the 'fast food culture' that has overwhelmed our cities and towns. The 'fast foods' that are rich in fats and calories are readily available in numerous food shops. As the majority of the young working population depend on these unhealthy 'junk foods,' this may partly explain the rise in diabetes incidence in the younger age-groups. The serious spread of disease can cripple the nation’s fiscal and human resources; therefore, it is the time to act now and do as much as possible to cover almost all aspects of the disease. The overwhelming burden of the disease threatens to stunt economic growth and undermine the benefits of improved standards of living and education. Proper education and awareness programmes developed according to the need of the society can improve the knowledge of general population and change their attitude. [6] Obtaining information about the level of awareness is the first step in formulating a preventive programme for the disease. There is need to investigate KAP among general population to aid in future development of programmes and techniques for effective health education. KAP surveys are effective in providing baseline for evaluating intervention programmes. [7] This study aims to assess the baseline levels of knowledge, attitude and practices of general population of Waghodia towards diabetes.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
A suitably designed and validated KAP questionnaire was administered at baseline. [8] The questionnaire was pretested and verified for errors. [9] The questionnaire covered three areas: knowledge, attitude and practice. There were a total of 25 questions, with 14 questions related to knowledge about diabetes, 5 questions to assess the attitude of the patient towards the disease, and 6 questions regarding practices. This questionnaire was filled in at a face-to-face interview with the investigator. In scoring method, twenty five was the maximum possible score in which each correct answer was carry one point and incorrect or unsure answer was carry no point. The interviewer did not in any way try to improve the knowledge of respondents. Gujarati or English version of questionnaire was provided as per requirement of individual.
RESULTS
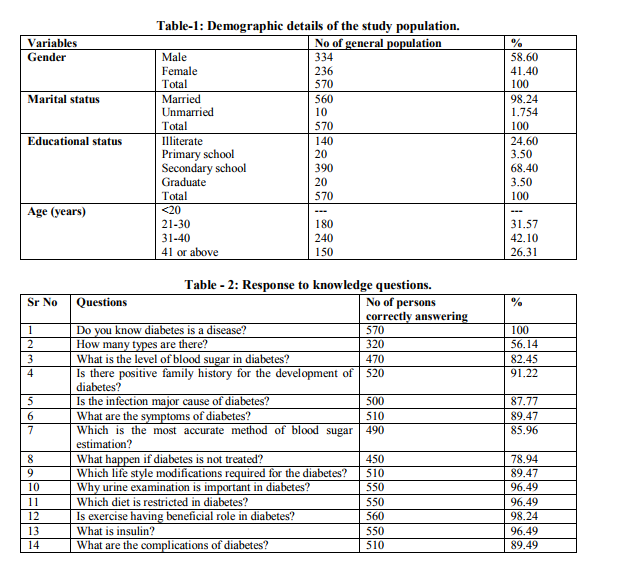
Most of the respondents (42.1 %) were aged 31- 40 years, followed by those aged 20-30 years. Most of them (71.9 %) were educated up to graduate level as per Table – 1. The major source of knowledge for the general population was television (32 %) and newspaper (30 %) followed by family physician (28 %). However 10 % received information from friends and relatives. Majority were aware about the causes, symptoms and complications of the disease as per Table – 2. We observed poor score in attitude part of the questionnaire and only 35 % had positive attitude towards exercise as per Table – 3. Only 43.85 % of responders had their blood sugar checked. Only 17 % of responders were able to answer 50 % of practice questions correctly as per Table – 4.
DISCUSSION
Diabetes mellitus is believed to be the commonest and most devastating chronic disease in human history. It has afflicted mankind for thousands of years and continues to do so at anexponential rate. [10] Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by hyperglycemia. It is associated with abnormalities in carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism, and results in chronic complications, including micro vascular, macro vascular and neuropathic disorders. [11] The prevalence of Diabetes mellitus has risen dramatically over the past two decades. It is estimated that the prevalence of diabetes in adults worldwide will rise to 5.5 % in 2025 (as compared to 4 % in year 1995), with India contributing the major part. [12] Many causes have been postulated for the rise in the number of cases, including urbanization, sedentary lifestyles, poor nutrition and obesity. People with Diabetes mellitus who wish to live normal lives need to know a lot about their illness. [13] Thus, awareness on Diabetes mellitus and its complication has become an integral and essential part of Diabetes mellitus care for the people in the society. Almost 90 % of responders answered 50 % of the knowledge questions correctly. Still a large proportion of population that is almost 40.3 % were not able to score above 10. This is comparable to the results of a study done in Malaysia by Ambigapathy R., et al. [14] who reported 87 % respondents able to answer 50 % knowledge questions correctly. The lack of proper knowledge of each responder should be given individual attention for good practice and fill the gap of this 10 % to 100 % as studies report that there is a positive correlation between knowledge and good attitude. [14] Regarding Attitude 17.5 % scored above 50 % in this study, however, reports from Malaysia revealed good attitude with 98 % scoring above 50 %. [14] Attitude towards Here we can observe that 35 % had habit of exercise. Many studies have confirmed the beneficial role of physical activity in improving glycemic control. Due to inadequate glycemic control there are high chances of developing complications. Great efforts would be needed by health teams to enhance education and improve the knowledge of the diabetics in our society. There is increasing amount of evidence that patient education is the most effective way to lessen the complications of diabetes. [15] Over all 49 % answered the 50 % of practice questions and only 15.74 % scored 100 % which was showing poor score for practice whereas Malaysian study revealed 99 % answering 50 % questions correctly. [14] Monitoring of blood glucose is a simple and practical procedure acceptable for those who can afford it and facilitates the attainment of good glycemic control but unfortunately in our local population the practice was not good as 56 % responded that their blood sugar level has not been checked in past as per Table – 4. Education and counselling about all the aspects of diabetes is needed. Knowledge regarding diabetes forms the basis for informed decisions about diet, exercise, weight control, blood glucose monitoring, and use of medications, foot and eye care, and control of macro vascular risk factors. [16] Group education as well as individualized education programmes should be planned which can lead to better preventive and management techniques in diabetes. The educational programmes for the health professionals and paramedical staff are also important because several studies have reported the positive impact of counselling by clinical pharmacists on glycemic control and quality of life outcomes in the diabetic population. [17] Thus there is need for arranging large scale awareness programs for the general population and also to identify and use media to spread the message which could change the attitude of our population in the future.
CONCLUSION
Though good number of the respondents had positive knowledge levels regarding diabetes, the same can’t be said about the levels of attitudes and practice. Diabetes and its complications can largely be prevented if appropriate and timely measures are taken. Health education plays a verycrucial role in prevention and control of diabetes and its complications. We found reasonable gap between knowledge, attitudes and practices, so to overcome that it is very important to formulate and implement certain strategies by which positive attitudes can be converted into beneficial practices. Attitude and practices of general population can be definitely improved by structured programmes. Knowledge of medical and para-medical personnel regarding diabetes can be improved by frequent continued medical education programs, seminar and short discussion on diabetes. All of the above can be achieved by increasing quality of health education and improving applicability of scope of health education at all level.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.

References:
REFERENCES
1. Srinivasan AR, Niranjan G, Kuzhandai Velu V, Parmar P, Anish A. Status of serum magnesium in type
2 diabetes mellitus with particular reference to serum triacylglycerol levels. Diabetes Metab Syndr., 2012; 6: 187- 189. 2. Epidemiology of chronic non-communicable diseases and conditions. In: Park’s Textbook of Preventive and Social Medicine, 20th edition, M/s Banarsidas Bhanot Publishers, Jabalpur, 2009, p. 314-358.
3. Pradeepa R, Mohan V, The changing scenario of the diabetes epidemic: Implications for India, Indian J Med Res, 2002; 116: 121-32.
4. Tabish SA, Is diabetes becoming biggest Epidemic of the twenty first century?, International Journal of health sciences, 2007; 1: 5-8.
5. Upadhyay DK, Palaian S, Shankar PR, Mishra P., Knowledge, attitude and practice about diabetes among diabetes patients in western Nepal, Rawal Med J., 2008; 33(1): 8- 11.
6. Shera AS, Jawad F, Basit A, Diabetes related knowledge, attitude and practices of family physicians in Pakistan, J Pak Med Assoc, Oct 2002; 52(10): 465-70.
7. Ruzita T, Osman A, Fatimah A. et al., The effectiveness of group dietary counselling among non- insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) patients in resettlement scheme areas in Malaysia, Asia Pacific J Clin. Nutr, 1997; 2: 84-87.
8. Rathod GB, Parmar P. Comparison regarding knowledge, attitude and practice of blood donation between health professionals and general population. Int J Cur Res Rev, Nov 2012, 04 (21): 114-120.
9. Parmar P, Rathod GB. Study of knowledge, attitude and perception regarding medicolegal autopsy in general population. Int J Med Pharm Sci, Feb 2013; 03 (06): 1-6.
10. Aldasouqi SA, Alzahrani AS, Terminology in diabetes; an example of resistance to change, Saudi Med J, Sep 2004; 25(9): 1289-91.
11. Stephan ND, Daryl KG, Insulin, oral hypoglycaemic agents, and the pharmacology of the endocrine pancreas. In: Hardman JG, Limbird LE editors. Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological basis of Therapeutics, 10th edition, New York: Mc Graw Hill; 2001, p. 1686-7.
12. King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH, Global burden of diabetes, 1995-2025: Prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections, Diabetes Care, 1998; 21: 1414.
13. Stam DM, Graham JP, Important aspects of self management education in patients with diabetes, Pharm Pract Manag Q, 1997; 17: 12-25.
14. Ambigapathy R, Ambigapathy S, Ling HM, A knowledge, attitude and practice (KAP) study of diabetes mellitus among patients attending Klinik Kesihatan Seri Manjung, NCD Malaysia, 2003; 2: 6-16.
15. Mazzuca SA, Moorman NH, Wheeler Ml, The diabetes education study: A controlled trial of the effects of diabetes education, Diabetes Care, 1986; 9: 1-10.
16. Murata GH, Shaha JH, Adam KD, Wendel CS, Bokhari SU, Solvas PA, et al., Factors affecting diabetes knowledge in Type 2 diabetic veterans, Diabetologia, 2003; 46: 1170-8.
17. Adepu R, Raheed A, Nagavi BG, Effect of patient counselling on quality of life in Type- 2 diabetes mellitus patients in two selected south Indian community pharmacies: A study, Indian J Pharm Sci, 2007; 69: 519-24.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License