IJCRR - 9(3), February, 2017
Pages: 48-52
Date of Publication: 10-Feb-2017
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Predictors of psychological distress and depression among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Author: Siva Ilango T.1, Maithreyi P.2, Siddharth S.3, Anand N. N.4, Nambi S.5
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim: Diabetes mellitus, being a chronic disorder has been found to be associated with psychological distress in the form of anxiety and depression. The present study aimed to ascertain the clinical predictors of psychological distress and depression among patients with diabetes mellitus.
Methodology: The present cross-sectional questionnaire-based study recruited 100 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus from a tertiary care hospital in India. Presence of distress was assessed using cut-off scores on General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-12). Binary logistic regression analysis was used to find the independent predictors of having psychological distress as per GHQ-12. Depressive symptoms were assessed using Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D) among patients who were found to be distressed as per GHQ-12.
Result: Psychological distress as per GHQ-12 cut-off was present in 51% of the sample. The patients with psychological distress were less likely to be married and belong to nuclear family, have a longer duration of diabetes mellitus, have higher fasting and post-prandial blood sugars, and were more likely to have dyslipidaemia, being prescribed insulin, have complications of diabetes mellitus and have a past history of depression. Logistic regression analysis revealed increased fasting glucose and use of insulin to be independent predictors of having psychological distress. Among those with significant distress, 18 (35.3%), 25 (49.0%) and 8 (15.7%) had mild, moderate and severe depressive symptoms according to HAM-D.
Discussion: The present study suggests that several diabetes-related clinical parameters predispose to the occurrence of psychological distress among patients with diabetes.
Conclusion: Clinicians need to be sensitive to the presence of psychological distress and depression in patients with diabetes who have such predisposing factors.
Keywords: Diabetes Mellitus, NIDDM, GHQ, Psychological distress, Depression
Full Text:
Introduction:
Diabetes mellitus is a multi-system disorder characterised by impaired glycaemic control and is associated with arange of medical complications. Adverse events may occur due to medication dosing and complications of the disorder may slowly progress. All these facets make the individuals with diabetes predisposed to have psychological distress in the form of depression and anxiety. [1, 2]
Several factors are likely to influence the occurrence of psychological distress among patients with diabetes mellitus.The relationship of glycaemic control with diabetes related distress has been conflicting with some studies supporting such an association, and others not being able to demonstrate such association. Insulin use, which is an invasive and painful treatment regimen, has been found to be associated with greater psychological distress. [3]
Addressing the psychological distress among patients with diabetes is associated with improved treatment outcomes. The better outcomes with interventions are not only in terms of relieving the distressing symptoms, but also improving the quality of life and general functioning. [4]
India probably houses the largest population of patients with diabetes mellitus. The health-care delivery and cultural characteristics in India are quite different in India, and differ in various regions of India.[5] Given such a high prevalence there is a need understand the prevalence and determinants of psychological distress among patients with diabetes in India. Hence this study aimed to assess the occurrence and predisposing clinical factors among patients with diabetes in Indian tertiary care setting.
Methods:
Setting and sample
The present cross-sectional questionnaire based study was conducted at a tertiary care hospital in south India. The present study was conducted in the outpatient of the department of medicine of the hospital. The present study was conducted among ambulant outpatients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The inclusion criteria were having type 2 diabetes mellitus for a period of at least 1 year and willingness to participate in the study. The exclusion criteria were those with severe complications precluding an interview and those not willing to provide informed consent.
Procedure
After obtaining informed consent, the participants were recruited into the study. Information was gathered from the patients, their care-givers and medical records using a semi structured proforma. Clinical characteristics recorded included duration of the diabetes in years, recent-most fasting and post prandial blood sugars, recent HbA1c, presence of dyslipidaemia, smoking or alcohol use, medication treatment, h/o depression and complications. Presence of psychological distress was ascertained using General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-12)[7]. The 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D) [8] was used to assess for depressive symptoms in patients scoring above the cut-off for GHQ-12.
Analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out using SPSS version 20. The sample was segregated into two groups: one with psychological distress as per GHQ-12 and one without psychological distress. The two groups were compared between each other using student t test for continuous variables and χ2 test for nominal variables. Multivariable analysis was conducted using binomial logistic regression analysis to find the independent predictors of having psychological distress. The clinical variables including age which showed at least a trend level association (p <0.2) in bivariate comparisons were entered into the regression equation. Forward Wald method was used to generate the regression equation and Nagelkerke’s R2estimate was used to find the variance explained by the model. A p value of less than 0.05 was considered significant and missing value imputation was not required for the present study.
Results:
The study included 100 participants. The characteristics of the participants are described in table 1. The sample comprised of 48males and 52 females. The mean age of the sample was 54.7 (±9.6) years with median of 55 years and a range of 36 to 85 years. The majority of the sample was currently married, educated up to 10th and above, was not currently employed, belonged to Hindu religion, nuclear family, from an urban residence with a family income of Rs 11,000 and above. The mean GHQ score was 4.7 (3.2) with a median of 4 and a range of 1 to 11.
Table 1: Demographic characteristics of patients with and without psychological distress (n = 100)
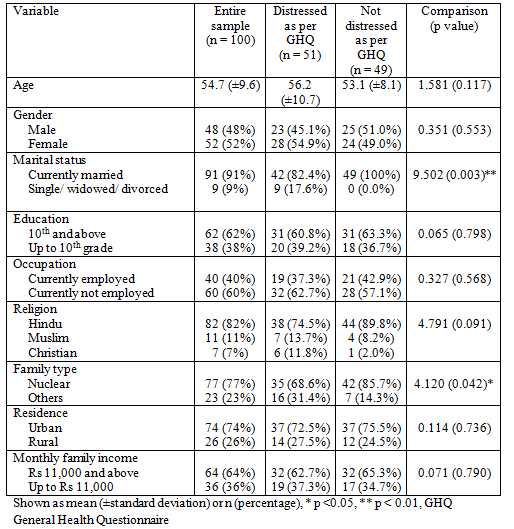
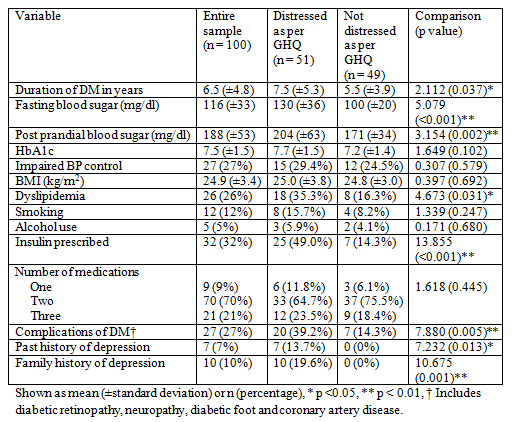
The clinical parameters of the sample are shown in table 2. The duration of diabetes mellitus ranged from 1 to 23 years (median 6 years) with a mean of 6.5 (±4.8) years. The patients who were distressed as per cut-off scores of GHQ were more likely to have a longer duration of diabetes mellitus, a higher fasting and post prandial blood sugar, and greater likelihood of having dyslipidaemia, insulin being prescribed, having complications of diabetes mellitus, and having a past and family history of depression. There was positive correlation of the fasting and post prandial blood sugars between themselves (r = 0.761, p <0.001) and with HbA1c (r = 0.445, p <0.001 and r = 0.508, p <0.001 respectively).
Table 2: Clinical characteristics of patients with and without psychological distress (n = 100)
As shown in table 3, logistic regression analysis was carried out to find the independent predictors of being distressed. Age and clinical variables were entered into logistic regression analysis, which was conducted using the forward Wald method.Higher fasting blood sugar and insulin use predicted increased likelihood of having psychological distress. Increase of fasting blood sugar by each mg/dl increased the propensity of being distressed by roughly 3.6%. Also, use of insulin increased the chances of being distressed as per GHQ by almost 3 times.
Table 3: Predictors of psychological distress as per logistic regression
|
Variable
|
B
|
Wald
|
Significance
|
Exp (B)
|
Confidence intervals
|
|
Fasting blood sugar
|
0.035
|
11.292
|
0.001
|
1.036
|
1.015 to1.057
|
|
Insulin use
|
1.272
|
5.482
|
0.019
|
3.571
|
1.230 to 10.309
|
|
Constant
|
-3.004
|
11.292
|
0.016
|
0.050
|
NA
|
DM Diabetes Mellitus, Variables entered into equation: Age and other clinical variables with p <0.2; Nagerkerke R2 value of 0.344, correct classification rate 78%.
HAM-D was assessed for patients showing significant distress on GHQ-12 (n = 51). The mean HAM-D score for the sample was 19.0 (±5.4) with a median of 19 and range of 9 to 29. Based on the HAM-D scores, 18 (35.3%), 25 (49.0%) and 8 (15.7%) individuals out of 51 patients who were distressed were classified as having mild, moderate and severe depressive symptoms. The HAM-D scores had a significant positive correlation with duration of diabetes mellitus (r = 0.432, p = 0.002), and fasting and post-prandial glucose levels (r = 0.449, p = 0.001 and r = 0.408, p = 0.003 respectively). HAM-D scores were found to be higher among those having dyslipidemia (mean HAM-D score 22.1 versus 17.3, student t = 3.251, p = 0.002), complications of diabetes mellitus (mean score 22.7 versus 16.6, student t = 4.667, p < 0.001), insulin use (mean score 22.7 versus 15.5, student t = 6.385, p < 0.001), past history of depression (mean score 24.1 versus 18.2, student t = 2.901, p = 0.006) and family history of depression (mean score 24.8 versus 17.6, student t = 4.428, p < 0.001).
Discussion:
Though there are lot of research relating to depression and diabetes done in western countries, only a few studies have been done in India. The present study suggests that about half of the diabetic patients had clinically significant psychological distress.This suggests that a substantial proportion of patients of type 2 diabetes mellitus might be suffering from symptoms of anxiety and depression which might go undetected. On further assessment using depression rating scale it was evident that one third of the total sample had symptoms of moderate to severe depression. Distress among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with poorer control of the disorder,[7] higher health-care costs,[8] and higher mortality.[9,10]
This study also finds that impaired fasting blood glucose and use of insulin were the clinical parameters associated with increased distress.Though there are conflicting findings regarding glycaemic control and depression from the research done previously, the observations from this study concur with the findings of recent meta-analysis. [2, 11] The exact mechanism linking depression and poor glycaemic control has not been understood but some studies suggest it could be related to poor self-care. Use of Insulin therapy as a risk factor for diabetes mellitus has been found in couple of studies [12, 13] and it is a significant finding noted in our study. Insulin is usually used in type 2 diabetes mellitus for people who had poor glycaemic control and after failure of control with oral hypoglycaemic agents. This is indicative of chronicity and severity of diabetes mellitus which can cause significant psychological distress. Moreover the stringent monitoring and frequent medical follow up could further increase the psychological distress.
Earlier studies of prevalence of depression among patients suffering from type 2 diabetes mellitus range from 30 to 80 percent. Meta-analysis by Anderson et al., showed a prevalence of 8 to 61 % of depression in diabetes [11]. In our study, one third of the sample had scores suggestive of moderate to severe depression using HAM-D and the findings are consistent with earlier studies both in India and overseas. Some of the factors that positively correlated with the presence of depression include duration of diabetes, increased fasting and postprandial blood sugars, diabetic complications, dyslipidaemia, insulin use, past and family history of depression.
The limitations of this study are the small sample size given the higher prevalence of diabetes mellitus in this part of the country and not including a control group to compare the variables causing depression in diabetes mellitus. It is a cross sectional study and hence causal relationships between depression and diabetes related variables could not be understood.
Conclusion:
The findings of our study suggests that around half of the people suffering from type 2 diabetes mellitus has significant psychological distress and one of the population suffer from moderate to severe depressive symptoms. People having less social support suffer more psychological distress. The clinical predictors that increase the level of psychological distress and depression are longer duration of diabetes mellitus, high fasting and post prandial blood sugar, presence of diabetic complications, use of insulin, past and family history of depression. This study confirms association of diabetes and depression, risk factors for the clinicians in ensuring better management of both depression and diabetes.
Acknowledgement: Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in the references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Source of Funding: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None.
References:
- Ali S, Stone MA, Peters JL, Davies MJ, Khunti K. The prevalence of co-morbid depression in adults with Type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabet Med J Br Diabet Assoc 2006;23(11):1165–73.
- Grigsby AB, Anderson RJ, Freedland KE, Clouse RE, Lustman PJ. Prevalence of anxiety in adults with diabetes: a systematic review. J Psychosom Res 2002;53(6):1053–60.
- De Sonnaville JJ, Snoek FJ, Colly LP, Devillé W, Wijkel D, Heine RJ. Well-being and symptoms in relation to insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 1998;21(6):919–24.
- Naseer Ali, Viveka P Jyotsna, Nand Kumar et al., Prevalence of Depression Among Type 2 Diabetes compared to Healthy Non Diabetic Controls. Journal of the association of physicians of India, September 2013, Vol. 61
- Amit Raval, Ethiraj Dhanaraj, Anil Bhansali, et al., Prevalence and determinants of depression in type 2 diabetes patients in a tertiary care centre. Indian J Med Res 132, August 2010, pp 195-200.
- James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, Cushman WC, Dennison-Himmelfarb C, Handler J, et al. 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA 2014; 311(5):507–20.
- Kuruvilla A, Pothen M, Philip K, Braganza D, Joseph A, Jacob KS. The validation of the Tamil version of the 12 item general health questionnaire. Indian J Psychiatry 1999;41(3):217–21.
- Hamilton M. A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1960; 23:56–62.
- Ciechanowski PS, Katon WJ, Russo JE. Depression and diabetes: impact of depressive symptoms on adherence, function, and costs. Arch Intern Med 2000;160(21):3278–85.
- Egede LE, Zheng D, Simpson K. Comorbid depression is associated with increased health care use and expenditures in individuals with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002;25(3):464–70.
- Katon WJ, Rutter C, Simon G, Lin EHB, Ludman E, Ciechanowski P, et al. The association of comorbid depression with mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2005;28(11):2668–72.
- Van Dooren FEP, Nefs G, Schram MT, Verhey FRJ, Denollet J, Pouwer F. Depression and risk of mortality in people with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PloS One 2013;8(3):e57058.
- Anderson, R.J., Freeland, K. E., Clouse, R.E., and Lustman, P.J. (2001) The prevalence of co-morbid depression in adults with diabetes. A meta-analysis. Diabetes Care, 6, 1069-1078
- Peyrot, M. and Rubin, R.R (1997) Levels and risks of depression and anxiety symptomatology among diabetic adults. Diabetes Care, 20, 585-590
- Hermanns, N., Kulzer, B., Krichbaum, M. et al. (2005) Affective and Anxiety disorders in a German sample of diabetic patients: Prevalence, comorbidity and risk factors. Diabet. Med., 22, 293-300






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License