IJCRR - 6(4), February, 2014
Pages: 07-14
Date of Publication: 20-Feb-2014
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
DETERMINING MALE ATTITUDE AND BEHAVIOR ON DECISION MAKING AND SPOUSAL COMMUNICATION IN FAMILY PLANNING: A STUDY CONDUCTED AMONGST LITERATE MALES OF PUNJAB, INDIA
Author: Aditya Sood, Parika Pahwa
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Men play a key role in bringing about gender equality, since in most societies men exercise dominance in nearly every sphere of life, so male involvement in family planning not only helps accepting a contraceptive, but also ensures its effective use and continuation. Objective: This study was undertaken to know the attitude and behavior of literate males on Family Planning, spousal communication and decision making power sharing equation in Punjab, India. Method: A Cross- sectional descriptive study was conducted with 225 males; both married and unmarried, 75 were selected each from 3 districts of Punjab by random sampling method. A semi structured self administered questionnaire was used as a tool for data collection. Result: It was found that 95% of our respondents were aware about condoms followed by Withdrawal (84%), Emergency contraceptive pills (81%), and Tubectomy (79%) respectively. Out of all the available modern FP methods; Female and Male Sterilization usage is just around 19% and 1% respectively. In merely 23% cases, wives initiated discussion on Reproductive Health matters and for majority of the couples, FP discussions starts after the birth of 1st child. The major reasons for non communication between couples on FP were \"shyness\" and \"male perception that this is an unnecessary talk\". Further it was found that only 65% men reported being comfortable if the female partner initiates discussion on the total number of children the couple should have. Conclusion: Spousal communication and power sharing on decision making plays an important role in promoting shared responsibilities and parenthood and our study reveals that it is lacking in the literate society of Punjab and in order to change this scenario; Community based organizations, Non Governmental organizations and Women self help groups should emphasize on spousal communication and sensitization of men on their female partners reproductive health needs.
Keywords: Family Planning, Contraceptives, Male, Attitude, Behavior
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
India being the second most populous country in the world, launched the National family welfare programme in year 1951 with the objective of reducing Total Fertility rate to the extent necessary to stabilize the population, consistent with the requirements of the national economy.2 One of the main objective of the program was to spread knowledge of family planning methods and develop a favorable attitude of contraceptive methods among the people.3 Although from the efforts of this programme, the contraceptive usage has been increased over a period of time but still there is poor acceptance of contraceptive methods either due to ignorance, fear of complications and lack of male support of their female partner.
Traditionally, most family planning programs had focused only on women. The basic assumption was “since women are the ones who bear children; it will be enough to concentrate on women only to bring down the fertility levels.” However, childbearing is the outcome of a participation of both partners in a conjugal union and men together with women play key roles in reproductive health decision-making including family planning. In fact, men not only take decisions for them but also often play the dominant roles in decisions crucial to the reproductive health of women. Reproductive health of women largely depends upon knowledge, attitude and behavior of men towards family planning4 . Involving men in matters related to reproductive health is an indispensable strategy to contain the incidence of unwanted pregnancies and spread of RTIs, STDs and HIV/ AIDs which are evidences of men's risky sexual behavior. Realization of the need to focus on men had resulted at the 1994 International Conference on Population and Development (ICPD) in Cairo as well as at the 1995 World Conference on Women in Beijing5 . It was understood that special efforts should be made to recognize men as equal partners with women in all matters pertaining to reproductive health and family planning. It is now clear that the target of reducing MMR to 100 by 2015 will not be met without the concerted efforts of all involved. Men, as partners, fathers, husbands, policy makers and community leaders have a critical role to play in safeguard the health of women during pregnancy and beyond6 . Male involvement in family planning and reproductive health may improve equality in gender relation, promoting better relationship between men and women through which they can take decision regarding family planning jointly and equal responsibility of sexual behaviour7 . There is limited literature available specifically of Punjab on male involvement that examines their role in reducing maternal mortality and ensuring safe motherhood. Keeping all these facts in view, a study was carried out with main objective to assess the knowledge, attitude and practices of contraceptive methods among literate males of Punjab.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A cross sectional descriptive study was carried out in three districts of Punjab namely Ludhiana, Ferozepur and Mohali in the month of April and May 2012. The relevance of choosing these 3 districts was that Ludhiana is the most populous city of Punjab with good literacy rate and economic development, Mohali is situated at the periphery of State Capital i.e. Chandigarh which has access to all the health facilities and Ferozepur is the border city located at international border with Pakistan. Literate married and unmarried men of age group 18-60 years and education qualification above 10th standard were included in the study. A total of 225 males, 75 from each district irrespective of caste, religion or socioeconomic status were selected by random sampling method. All the participants were clearly explained the purpose of the study and signed written consent form was taken from them. The pretested self administered semi structured questionnaire was used for collection of data. For collecting the data, private and government banks, corporate offices, private companies, government offices, schools, and BPO’s of these districts were targeted and selected randomly. Respondents were asked about their socioeconomicand demographic profile; knowledge attitude perception and practice of family planning, decision making power regarding various aspects of family planning etc. A maximum of three visits were made at places before the required sample size was obtained. Data analysis was done with the help of excel and SPSS 16. The data was tabulated in terms of frequency distribution of different variables. Chi-square test of significance was employed for testing associations. P_<0.05 was considered for statistical significance.
RESULTS AND FINDINGS SECTION
Section A: Socio demographic Profile
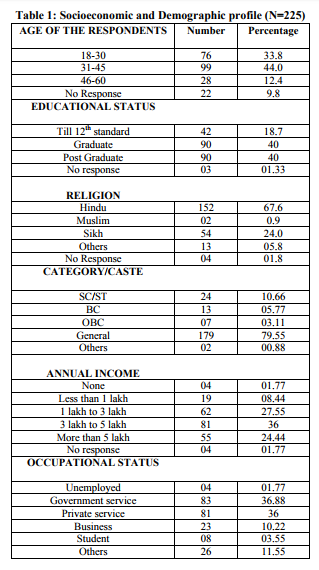
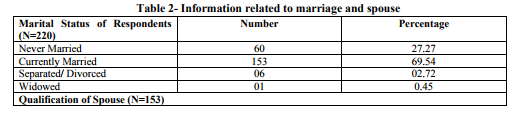
Most of the respondents (44%) were in the age group of 31-45 years, 80% of them were either graduates or post graduates. Majority of them (67.6%) practice Hindu religion.General category accounts for the major chunk of the population that we interviewed. The marital status of the respondent shows that 70% are currently married and 56% have been married for more than 10 years.
SECTION B: Family Planning
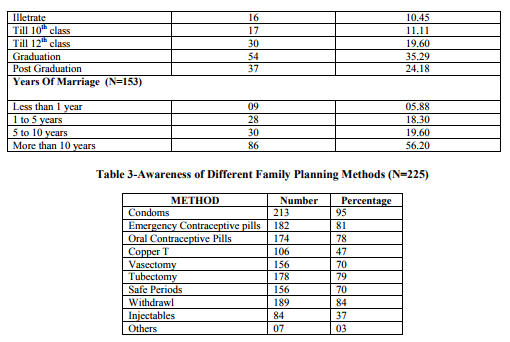
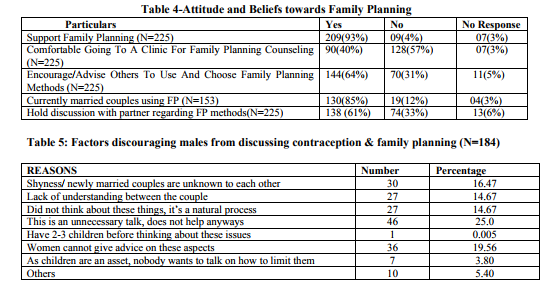
Data reveals that Condom was the most widely known method of contraception. 93% of respondents were in full support of FP but when it comes to encourage or advise others for it, only 64% agreed to it. 61% of the respondents revealed that they hold discussions with their partners regarding FP. On analyzing data about the factors discouraging couples from discussing about FP, it was found that 46% respondents feel FP talks are unnecessary and does not help anyways and 36% opined that women cannot give advice on such issues.
SECTION C: Attitude about reproductive decisions making processes
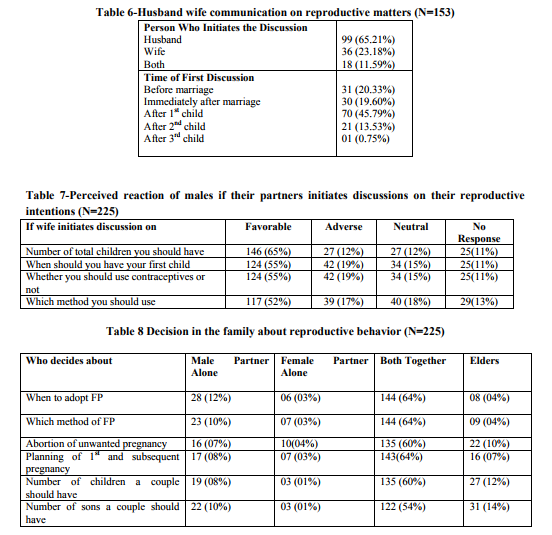
The study also looks into the attitude of the couple about reproductive decision making process and it was found that in 65 % cases males were the initiators of discussion. Most of the couples (46%) held their first FP discussion after having first child. In 65% cases, men reported being comfortable if the female partner initiates discussion on the topic “number of children they should have”. The comfort level dropped to 55% when female partners initiated discussions on “when to have the first child and whether or not to use contraception”. Comfort level was minimum at 52% on the issue of method of contraception. In 64% cases, decisions like, “when to adopt FP” and “which method to use for FP” was made by both the partners together. It’s also seen that elders of the family still play a prominent role in FP decision of couples, as evident from the data; they are mostly involved in influencing decisions related to number of children a couple should have (14%) especially number of sons (12%).
DISCUSSION
World Health Organization defines FP as a way of thinking and living that is adopted voluntarily, upon the basis of knowledge, attitudes and responsible decisions by individuals and couples, in order to promote the health and welfare of family groups and thus contribute effectively to the social development of a country. With this definition as a source of inspiration, this study was designed to look into the practices and attitude of literate males in State of Punjab towards contraception, Family planning decisions, spousal communication and power sharing equation with their female partners. Awareness about condom was highest (95%) which is still lesser than the national average of 97.6% (NFHS3).There awareness level of methods like OCPs, withdrawal, rhythm (safe period) method was found to be more than that of urban males nationally (NFHS3). Spousal communication is important in FP8 and in our study we found that 61% couples were holding discussions with their partners regarding FP. Absence of spousal discussion makes it difficult for women to negotiate contraceptive use, a common determinant discovered in many reproductive studies9 . When we compared our results with some studies done on males from rural areas of Punjab with no or minimum education, it was found that many reasons furnished by literate urban men of Punjab for not holding discussions and adopting FP were similar to the former, which led us to believe that education has not been able to change the mindset of men in the state yet. The husband’s support is a good predictor for future practice and continued use of FP methods10 . A study from Indonesia, which is also a patriarchal society just like Punjab suggests that couple centered approaches to FP are viable in patriarchal societies.11 Responsible parenthood includes family planning and avoiding unwanted pregnancies.12 Surveys around the world increasingly are interviewing men and reporting their role in the reproductive health of women13 and that is what we have tried to achieve from this. International studies from a variety of regions have shown that reproductive health programs are likely to be more effective for women when men are involved in healthcare system in some way but that does not mean that the women should not have a say or right to put forward their opinion and point of view when it comes to FP and contraceptive usage by their partners, as it seems to be happening in the state of Punjab. Though all of our respondents were literate and belonged to urban districts of Punjab still their power sharing equation with female partners was not good. Spousal communication is existent but seems to be a single channel affair as majority of important decisions regarding contraception, FP and reproductive behavior is being taken by men .Women are made part of the discussions but the final decision making power rests with the men, as evident from the result and finding of our study.
CONCLUSION
Literacy and good socioeconomic background alone cannot change men’s attitude and beliefs towards Family Planning and contraception. Specific educational programme on the issues of sexual and reproductive health would have to be included in secondary and higher education. Punjab still being a patriarchal society, needs special attention from the Government and development partner’s .Target audience needs to be identified through base line surveys and ground level studies in order to design Behavior Change Communication models. Counseling and quality services associated with strong information and sensitization campaigns on FP has been proven to be successful in other parts of the world already, and so shall be implemented here also. Though spousal communication and proper knowledge of modern methods of contraception has improved, public health facilities should also motivate and encourage men to avail the services on FP and reproductive health. A favorable social and cultural atmosphere needs to be created by the community and religious leaders so that discussing FP and contraception is no longer a taboo for men and women. A lot needs to be done to make men more sensitive towards the reproductive health needs of their partners. As spousal communication plays an effective role in promoting shared responsibilities and parenthood, it should be further promoted by Community based organizations and Non Governmental organizations. Efforts need to be put in from the provider’s side to train and equip their public health institutions to cater to the specific sexual and reproductive health needs of men.
References:
1. Varma G.R., Rohini A.: Attitude of spouse towards Family Planning: A study among married Men and Women of a rural Community in West Godavari District, Andhra Pradesh. Anthropologist, 2008, 10 (1): 71-75.
2. Abdul Nasir J., Tahir M.H., Zaidi A.A: Contraceptive attitude and behavior among University men: a study from Punjab, Pakistan. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad, 2010 Jan-Mar;22(1):125-8
3. Kamal M et al : Determinants of Male Involvement in Family Planning and Reproductive Health in Bangladesh. American J of Human Ecology, 2013; 2(2): 83-93.
4. Narang H., Singhal S.: Men as partners in maternal health : an analysis of male awareness and attitude. International J. of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology, 2013 Sep; 2(3):388-392.
5. Narang H., Singhal S.: Men as partners in maternal health : an analysis of male awareness and attitude. International J. of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology, 2013 Sep; 2(3):388-392.
6. Kamal M et al : Determinants of Male Involvement in Family Planning and Reproductive Health in Bangladesh. American J of Human Ecology, 2013; 2(2): 83-93.
7. Brachett, J.W. 1978. “Family planning in four Latin American countries-Knowledge, Use and unmet need- Some findings from World Fertility Survey.”International Family Planning Perspectives 14 (40): 116-23)
8. Greene EM, Mehta M, Julie P, Deirdre W, Bankole A, Singh S: Involving Men in reproductive health; contributions to development. 2009. www.unmillennium project.org/documents/Greene_et_al-final.pdf. (Cited on 11/04/2011)
9. Toure L: Male involvement in family planning a review of selected program initiatives in Africa. 1996. http://pdf.usaid.gov/pdf_docs/PNABY584.pdf (Cited on 28/05/2013)
10. Janine L, Barden OF, Ilene S, Speizer: Indonesian Couples’ pregnancy ambivalence and contraceptive use. Int Perspect Sex Reprod Health 2010,36(1):36–4
11. International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Narang H et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2013 Sep;2(3):388-392 www.ijrcog.org )
12. Salem R. Men's surveys: New Findings. Population Report. Series M No 18 Baltimore, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. The INFO Project Spring. 2004.)
13. Mbizvo MT, Bassett MT. Reproductive health and AIDS prevention in sub-Saharan Africa: the case for increased male participation. Health Policy Plan. 1996 Mar;11(1):84-92.)
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License