IJCRR - 6(7), April, 2014
Pages: 46-51
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
THE EFFECT OF EXERTIONAL HEAT STRESS INDUCED HYPOHYDRATION ON COGNITIVE PERFORMANCE IN HUMAN
Author: Medha Kapoor, Laxmi Prabha Singh, Shuchi Bhagi, Shashi Bala Singh
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim: Investigations on the effect of hypohydration on cognitive function present with ambiguous and contradictory results. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of exertional heat stress induced hypohydration (Graded hypohydration: 2% and 4%) on cognitive function in Human. Methodology: Six healthy military personnel (age: 25\?4 years, height: 172\?4cm, weight : 66\?3 Kg) performed sub-maximal exercise at 45 ?C and 30% Relative Humidity (RH) in Human Climatic Chamber (HCC) till the desired levels of hypohydration were achieved (2% or 4%). Cognition was assessed using stroop color and word test and PGI battery. Result and Conclusion: Cognitive performance was found to be unaltered upon 2% or 4% hypohydration. The cognitive function was retained under hypohydration demonstrating cognitive resilience in response to moderate body fluid deficits (up to 4%).
Keywords: Exertional heat stress, hypohydration, stroop color and word test, PGI battery test, cognition
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Hypohydration, commonly known as dehydration refers to a fall in body water level below normal. Certain occupational workers such as soldiers and athletes are prone to hypohydration, as they have to undergo extensive physical activity at high temperatures [1]. More that 1% of body weight loss due to fluid loss is referred to as mild hypohydration. 4% of hypohydration is somewhat moderate and severe dehydration corresponds to fluids deficit of 5% percent or more. Investigations on the effect of hypohydration on cognitive function present with ambiguous and contradictory results. Significant alterations in cognition have been reported in response to hypohydration as low as 1-2 % [2, 3]. Hypohydration above 2% body mass has been shown to impair endurance exercise performance in hot environments [4, 5]. Moderate hypohydration has been found to be associated with cognitive performance decline at elevated temperature. However, there are many contradictory reports suggesting that hypohydration doesn't affect cognition. This ambiguity can be attributed to difference in methodology to induce hypohydration and cognitive function tests employed [2, 3]. We have attempted to evaluate the effect of exertional heat stress induced hypohydration on cognitive function in Human. Six healthy military personnel performed sub-maximal exercise at 45 ?C and 30% RH in the HCC till the desired levels of hypohydration were achieved (2% or 4%). It is acknowledged that the hypohydration in Military and sports settings can at certain occasion be much more severe than 4%, but due to the concerns of subject safety, hypohydration above 4% was not included in the experimental design. The cognitive function was assessed both before and after exercise in the HCC using stroop color and word test and PGI battery. Cognitive performance was found to be unaltered upon 2% or 4% hypohydration demonstrating cognitive resilience in response to moderate body fluid deficits (up to 4%).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Participants: Six healthy male [age 31.33 ± 2.5 years, height 170.4 ± 7.5 cm, body mass 76.85 ± 5.1 kg, body surface area 1.87± 0.1m2 ] participated in the study. Inclusion criteria consisted of a medical history free of musculoskeletal, cardiac, endocrine, and heatrelated illnesses. Prior to the study, the experimental procedure including the risks involved was explained to each participant. Written consent was then obtained. Institutional ethical committee for humans approved all protocols and procedures. Preliminary Procedures: One week of familiarization and preliminary testing were carried out one month before the experimental trials. During preliminary testing, volunteers performed cognitive function test of similar pattern to acquaint them to the nature of test which will be provided in experimental condition inside the Human Climatic Chamber (HCC) in order to reduce training and learning effects. Each familiarization session took place in a 25 C 30 % RH. Experimental design: To assess the effects of exertional heat stress induced hypohydration on human cognition, the participants were made to perform sub-maximal exercise [6] in Human Climatic Chamber (HCC) simulated at 45 ?C and 30% RH. The exercise was performed at two separate occasions to attain two different hydration states: 2% body weight reduction or 2% hypohydration and 4% body weight reduction or 4% hypohydration. The two exercise sets were separated by at least two weeks to ensure the reestablishment of normal physiological status by nullification of the effect of previous exposure. All the participants were instructed not to engage in any vigorous physical activity for at least 24 hours prior to each exercise session and consume normal balanced diet throughout and also, to refrain from alcohol and smoking. All the sessions were conducted approximately at the same time of the day for each participant. 4% hypohydration represents a state of significant body water loss and the value was chosen to facilitate a comprehensive assessment of potential implications of severe hypohydration on human body. We couldn’t evaluate the effect of a more severe hypohydration due to the volunteers’ safety considerations. To evaluate the effect of graded hypohydration on brain dysfunction, cognition, and psychopathology, the stroop color and word conflict test [7] was undertaken by volunteers at two time points: before and after the desired level oh hypohydration was attained. Stroop color and word conflict test is a mental stress test involving sensory rejection and has been used as a model of the defense reaction in humans. The test consists of three pages. The first is a word page with color names printed in black ink. The second is the color page with ‘Xs’ printed in different colors and the last page is the conflict page displaying words from the first page printed in colors from the second page yielding three scores based on the number of items completed on each of the sheets described above as the respondent reads words or names in the ink colors as quickly as possible within a time limit. The values obtained are a reflection of the cognitive flexibility, creativity, and reaction to cognitive pressures. The Stroop color and word conflict test is a quick, easy and highly reliable test for neuropsychological assessment applicable to individuals with age ranging from 15 to 90. It provides valuable diagnostic information on brain and assesses cognitive processing with accuracy. Along with this, PGI memory test was also administered. PGI memory scale [8, 9], which is standardized on Indian population, is used mostly in India. It is an Indian adaptation of the Wechsler Memory Scale. It includes 10 subtests including forward and backward digit spans, one minute delayed recall of a word list, immediate recall of sentences, retention of similar word pairs, retention of dissimilar pairs, visual retention, visual recognition, recent memory, remote memory and mental balance test. This test provides a reliable and easy means to assess memory dysfunction. Administration of the scale is simple and takes approximately 20–30 min. Standardized norms are available according to age and education. Separate norms are available for three education levels: 0–5 years of schooling, 6– 9 years of schooling and ≥10 years of schooling. Experimental procedure: The subjects were instructed to ingest 5 ml of water per kilogram body weight 2 h before reporting to the laboratory to attain a euhydrated state [10]. After reporting to the laboratory the subjects were made to rest for 60 minutes. troop color and word conflict test and battery test were carried out in Human Climatic Chamber (HCC) maintained at 25 C and 30% RH. After completion of the test which was taken as control, the oral temperature was recorded outside the chamber using YSI electrodes from which the core body temperature was deduced. Skin mean temperature was calculated using Ramanathan equation [11]. Initial nude body weight was measure using digital human weighing machine model PFPF 100K and make PERFECT. The participant then entered the HCC maintained at 45°C and 30% RH and performed sub-maximal exercise (standardized step test, 15 steps/min) [6] until targeted hypohydration level was attained. After the attainment of desired level of hypohydration, Stroop color and word conflict test and PGI battery test were carried out in chamber itself. The post exposure core body and skin mean temperature was obtained as soon as the participant came out of the chamber.
Statistical
analysis: All variables were analyzed using student t-test. At least a 95% confidence level (p<0.05) is used as a thresh hold for statistical significance.
RESULTS
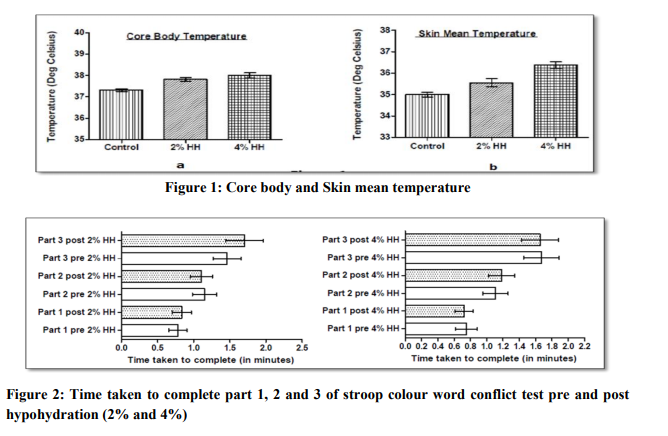
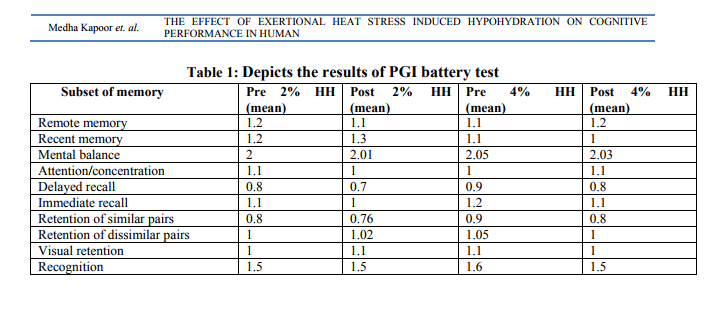
Body Weight: Pre exercise and post exercise (2% HH) weights were 76.79 ± 5.2 and 75.15 ± 5.2 kg respectively with a loss of 1.64 ± 0.11kg body weight and for 4 % hypohydration pre and post exposure body weights were found to be 77.26 ± 4.8 and 74.39 ± 5.0 kg respectively with a loss of 2.87 ± 0.4 kg of body weight. Body Temperature Responses: Core body temperature was measured using oral temperature with correction factor which was found to be 37.31 ± 0.14, 37.82 ± 0.25, p<0.01 (0.008) and 38.00 ± 0.33, p<0.01 (0.008) in euhydrated state, Post 2 % hypohydration and Post 4% hypohydration status respectively. Mean skin temperature was calculated using Ramanathan formula [11] using 4 point measurement i.e. 0.3* (Tchest + Tbiceps) + 0.2* (Tcalf + Tthigh) which is found to be 35 ± 0.2, 35.55 ± 0.5, p<0.05 (0.018) and 36.38 ± 0.4, p< 0.001 (0.0003) in euhydrated state, Post 2 % hypohydration and Post 4% hypohydration status respectively. Figure 1 represents the core body and skin mean temperatures under the three conditions i.e. Control, 2% hypohydration and 4% hypohydration. Stroop color and word conflict test: Time taken to complete the test was almost same pre and post 2% and 4% hypohydration. Also, No significant change was observed in the number of correct answers given by the volunteers. Figure 2 depicts time taken to complete part 1, 2 and 3 of stroop colour word conflict test pre and post hypohydration (2% and 4%). PGI battery test: No significant difference was detected pre and post 2% and 4% hypohydration. This indicates that no change in memory status was observed. Table 1 depicts the results of PGI battery test.
DISCUSSION
To the best of our knowledge, this is first study to examine the potential accumulative effects of heat stress and graded hypohydration (2% and 4%) on human cognition. Learning effects were minimized by training each volunteer using similar patterned test a month before the experiments to familiarize them with the cognitive function test. No significant difference was observed in cognition employing stroop color and word conflict test and PGI battery test pre and post hypohydration (both 2 and 4%). This indicates that hypohydration up to 4% is not severe enough to affect cognitive function in Human. We understand that under military and sports settings, the severity of hypohydration could be much more but we couldn't subject Human volunteers to a greater degree of hypohydration because of ethical and safety concerns. Though the cognition remained unaffected pre and post hypohydration, there was an evident increase in irritability in all the volunteers and they were comparatively uncooperative while undertaking PGI battery and stroop color and word test. The present study suffered from the limitation of the sample size being very small with only 6 participants but quite a few other studies have also accounted minimal or no effect of exposure on human cognitive performance due to hypohydration [12, 13, 14]. However, more extensive study involving a large number of volunteers and standardized methodology is required to get more reliable results.
CONCLUSION
The study results indicate that moderate hypohydration up to 4% induced in response to exertional heat stress doesn't affect cognition. However, experiments conducted with a larger sample size would add a higher degree of certainty to the conclusions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We would like to thank Dr. Thiruthara P Baburaj, Mr. Abhishek Bhardwaj, Dr. Rajender K Gupta, Mr. Amir Chand Bajaj, Mr. Gulab Singh and Mrs. Pooja Chaudhary for their help and support. We would also like to extend our sincere thanks to Defence Institute of Physiology and Allied Sciences for funding our research work. We acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. We are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
REFERENCES
1. Singh LP, Kapoor M, Singh SB. Heat: not black, not white. It's gray!!! J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2013;24(4):209-24.
2. Lieberman HR. Hydration and cognition: a critical review and recommendations for future research. J Am Coll Nutr. 2007 Oct;26(5 Suppl):555S-561S.
3. Ganio MS, Armstrong LE, Casa DJ, McDermott BP, Lee EC, Yamamoto LM, Marzano S, Lopez RM, Jimenez L, Le Bellego L, Chevillotte E, Lieberman HR. Mild dehydration impairs cognitive performance and mood of men. Br J Nutr. 2011 Nov;106(10):1535-43.
4. Cheuvront SN, Carter R 3rd, Sawka MN. Fluid balance and endurance exercise performance. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2003 Aug;2(4):202-8.
5. Sawka MN. Physiological consequences of hypohydration: exercise performance and thermoregulation. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1992 Jun;24(6):657-70.
6. Evaluation of physical performance on the basis of test. In: Åstrand PO, Rodahl K., editors. Textbook of Work Physiology: Physiological basis of exercise. 4 th ed. USA: McGraw-Hill; 2003. p. 280-290.
7. Golden, C. J. (1976), Identification of brain disorders by the stroop color and word test. J. Clin. Psychol.,32: 654– 658.doi: 10.1002/1097- 4679(197607)32:33.0.CO;2-Z
8. Pershad D, Verma SK. Handbook of PGI Battery of Brain Dysfunction (PGIBBD) Agra: National Psychological Corporation; 1990.
9. Pershad D, Wig NN. The Construction and Standardization of a Clinical Test of Memory in Simple Hindi. National Psychological Corporation, Agra, 1977.
10. Montain SJ, Coyle EF. Influence of graded dehydration on hyperthermia and cardiovascular drift during exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1992 Oct;73(4):1340-50.
11. Ramanathan NL. A new weighting system for mean surface temperature of the human body. J Appl Physiol. 1964 May;19:531-3.
12. Adam GE, Carter R 3rd, Cheuvront SN, Merullo DJ, Castellani JW, Lieberman HR et al. Hydration effects on cognitive performance during military tasks in temperate and cold environments. Physiol Behav. 2008 Mar 18;93(4-5):748-56.
13. Patel AV, Mihalik JP, Notebaert AJ, Guskiewicz KM, Prentice WE. Neuropsychological performance, postural stability, and symptoms after dehydration. J Athl Train. 2007 Jan-Mar;42(1):66-75.
14. Szinnai G, Schachinger H, Arnaud MJ, Linder L, Keller U. Effect of water deprivation on cognitive-motor performance in healthy men and women. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005 Jul;289(1):R275-80.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License