IJCRR - 6(7), April, 2014
Pages: 17-25
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY (FNAC) - AS A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN SALIVARY GLAND LESIONS
Author: Abhishek Raval, Hansa Goswami, Urvi Parikh, Prabhat Sharma, Venu Ghodasara, Safal Patel
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) is well accepted as a safe, reliable, minimal invasive and cost effective method for preoperative diagnosis of salivary gland lesions. Aims and Objectives: The aim of this study is to evaluate diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity and specificity of FNAC in various salivary gland lesions in correlation with their histopathology, which helps in the appropriate therapeutic management. Materials and Methods: A total of 88 FNACs were done on salivary gland lesions from January 2013 to November 2013 in the Pathology Department of one of the largest government tertiary care teaching hospital, Ahmedabad (Gujarat, India). Formalin fixed (10%), surgically resected specimens were received, they were processed and slides were prepared for histopathological diagnosis. The stained cytological and histopathological slides were studied, analyzed and correlated. Results: Our study included 88 patients who underwent preoperative FNAC for salivary gland lesions with subsequent surgical excision. Out of 88, 52 (59.1%) were males and 36 (40.9%) were females. Male to female ratio was 1.4: 1. The median age was 42 years. Parotid gland was involved in 60 (68.2%) cases, submandibular in 26 (29.55%) cases and other minor salivary glands in 2 (2.27%) cases. Out of 88, 79 cases (89.8%) were cytologically diagnosed as benign lesions and 9 (10.2%) were malignant. The most common benign cytological diagnosis was pleomorphic adenoma; 41 out of 79 cases (51.9%). Cytological diagnoses were compared with histopathological ones and were true-negative in 77 (97.5%), true-positive in 8 (88.9%), false-negative in 2 (11.1%) and false-positive in 1 (2.5%) cases regarding detection of malignant tumors. The overall cytological diagnosis achieved a sensitivity of 80%; a specificity of 98.7%, Positive Predictive Value of 88.9%, Negative Predictive Value of 97.5% and diagnostic accuracy of 96.6%. Conclusion: This study indicated that FNAC of salivary gland is a reliable and highly accurate diagnostic method for diagnosis of salivary gland lesions. It not only provides preoperative diagnosis for therapeutic management but also can prevent unnecessary surgery.
Keywords: Diagnostic Accuracy, Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC), Salivary Gland Lesions, Sensitivity, Specificity
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) is a safe, simple, cost-effective, accurate and minimal invasive for evaluation salivary gland lesions [1-4] . It plays an important role in the evaluation of salivary gland lesions. It has been used to differentiate non neoplastic lesions from neoplasms, and benign from malignant neoplasms [1, 5, 6] . Although salivary gland tumors are rare, they account for 2-6.5% of all the head and neck tumors and 21% to 46% are malignant [7], their superficial location, easy accessibility and high diagnostic accuracy makes FNAC, a popular method for evaluating them [8-10]. Salivary gland tumors are uncommon, the world wide annual incidence of salivary gland tumors ranges from 0.4 to 13.5 cases per 1,00,000 population [11]. Among the primary epithelial tumors, 64-80% occurs in the parotid glands, 7-11% occurs in the submandibular, less than 1% occurs in the sublingual and 9-23% occurs in the minor salivary glands [12- 14] . FNAC is not only useful in planning definitive preoperative diagnosis but also can prevent unnecessary surgery procedures [13, 15, 16, 17] . However, the management of patients with salivary gland lesions should not be based on cytology alone. It’s superior to the combination of physical examination and radiological findings [18- 20] . FNAC of salivary gland lesions has been performed at various institutions. A review of the recent reported series found that the diagnostic sensitivity of FNAC varied from 81-100%, the specificity varied from 94-100% and the diagnostic accuracy varied from 61-80% [19, 21] . Hence, the appropriate therapeutic management could be planned earlier, whether it was local excision for benign neoplasms, conservative management for non-neoplastic lesions, radical surgery for malignant tumors and chemotherapy or radiotherapy for metastasis and lymphoproliferative disorders [10] . Hence, the present study was done to know the diagnostic accuracy, which helps in an early diagnosis and appropriate therapeutic management.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
The present study was undertaken from January 2013 to November 2013 at Pathology Department of one of the largest government tertiary are teaching hospital, Ahmedabad (Gujarat, India). It comprised of 88 cases of salivary gland tumours which were diagnosed by FNAC. After taking the informed consent, the aspiration was done following a thorough clinical examination. The cytological findings were correlated with the histopathological findings. The nodule of interest was palpated and fixed with the thumb and the index finger of one hand. Under aseptic precautions, a 10 cc syringe with a 22-25 gauge needle was introduced into the nodule. The material was aspirated and smeared onto clean glass slides. The air dried and ethanol fixed smears were stained with Haematoxylin & Eosin (H&E), MGG (May Grunwald’s Giemsa) and Pap (Papanicolau) respectively. In cases of fluid aspiration, slides were prepared from the centrifuged sediment. Formalin fixed (10%); surgically resected specimens were received in the Department of Pathology, processed and stained with haematoxylin and eosin for histopathological examination. The stained cytological and histopathological slides were studied, analyzed and correlated. The definitive histopathological report was the gold standard diagnosis against which FNAC was compared. The discrepant diagnoses were categorized as sampling or interpretive errors. Data analysis was based on Galen and Gambino method to calculate Sensitivity and Specificity which was described below. Sensitivity for the presence of malignancy (true positive/true positive + false negative), specificity for absence of malignancy (true negative/ true negative + false positive), positive predictive value (PPV) (true positive/true positive + false positive), negative predictive value (NPV) (true negative/true negative + false negative) and accuracy of FNAC (true positive + true negative/total) were calculated and compared with other studies.
RESULTS AND OBSERVATIONS
Among the 88 cases included in the present study, there were 52 (59.1%) males and 36 (40.9%) females, with male to female ratio of 1.4:1. The age range was 16-82 years with a median age of 42 years. Parotid gland was involved in 60 (68.2%) cases, submandibular gland in 26 (29.55%) cases and other minor salivary glands in 2 (2.27%) cases. Out of 88 cases, 78 (88.64%) were benign and 10 (11.36%) were malignant. Out of total 78 benign lesions, 28 lesions were benign non neoplastic and 50 were benign neoplasms. In present study, the most common Non Neoplastic lesion was Chronic Sialadenitis in 22 (25%) cases followed by benign Cystic lesion in 6 (6.82%) cases and most common benign Neoplastic salivary gland tumor is Pleomorphic Adenoma in 42 (47.73%) cases followed by Warthin’s Tumor in 7 (7.95%) cases. [Table 1] In Histologically diagnosed 78 benign salivary gland Lesions, 1 case was misdiagnosed as a malignant by Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology. Amongst the malignancies, Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma and Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma were more common malignant tumor than other tumors like Acinic Cell Carcinoma, Polymorphous low grade Adenocarcinoma and infiltrating salivary duct carcinoma. [Table 2] In Histologically diagnosed 10 malignant salivary gland Lesions, 2 cases were misdiagnosed as a benign by Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology. Among total 88 cases, Fine Needle Aspiration Cytological diagnosis showed benign lesions in 79 (89.8%) and malignancy in 9 (10.23%) cases. The final histopathological diagnosis showed 78 (88.68%) benign lesions and 10 (11.36%) malignant neoplasms. The Comparison results are shown in Table 3. For entire group, the overall diagnostic accuracy is 96.6%, Sensitivity is 80%, Specificity is 98.7%, Positive Predictive Value is 88.9% and Negative Predictive Value is 97.5%. These results are summarized in Table 4.
DISCUSSION
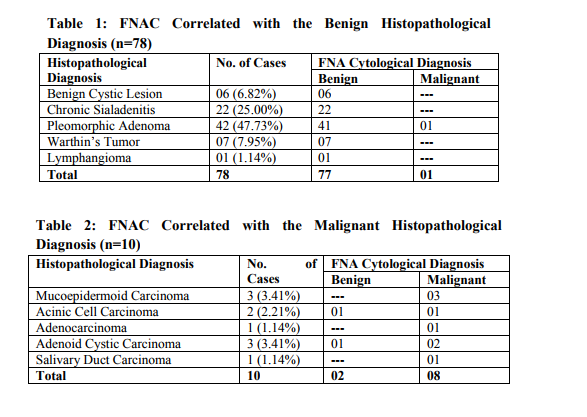
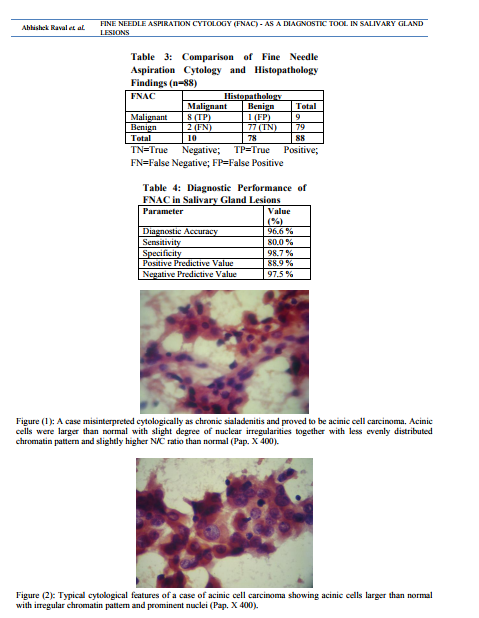
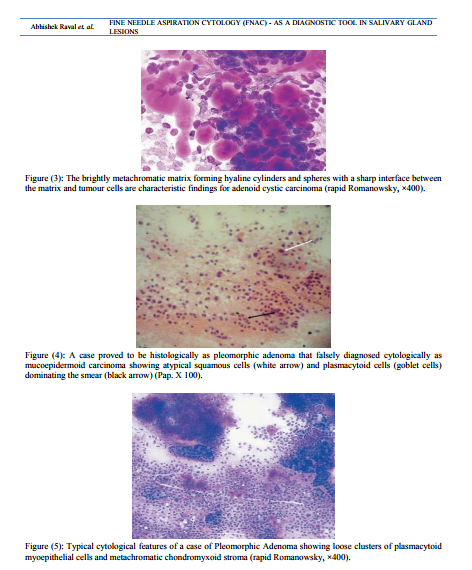
Tumors of the salivary glands comprise 2-6.5% of all head and neck tumors in adults [7]. FNAC is a safe, relatively non-traumatic and accepted diagnostic procedure that can quickly provides important preoperative information [22] . It is a very useful procedure in assisting clinicians in deciding whether a particular patient should be managed surgically [16, 23]. The main goal of FNAC is to determine if a mass is inflammatory and/or reactive, benign or malignant neoplasm and if possible, to render a specific diagnosis [24] . FNAC in salivary gland legions is one of the most difficult topics in cytopathology due to overlapping morphologic patterns in many benign and malignant neoplasms and the various differences in histological pattern that may be detected within the same tumor [25] . Cytomorphological features of most salivary gland lesions have been described; they are so characteristic and highly reproducible. If those criteria are present and strictly observed, the great majorities of the common variants of non neoplastic and both benign and malignant neoplasms can be diagnosed with high level of accuracy. However, there remain a proportion of problematic cases (perhaps 10-15%) for which cytological criteria have not yet been established [26, 27]. In such cases the diagnosis must be left opened with a few suggested differential diagnoses, rather than issuing a misleading report that will lead to inappropriate surgery [25] . In this study, benign and malignant tumor accounted for 88.64% and 11.36% of the salivary gland tumors, respectively, the majority of benign tumor was pleomorphic adenoma (47.73%). Among the malignant tumors mucoepidermoid carcinoma and adenoid cystic carcinoma were the most common. These frequencies were similar to those previously reported where salivary gland tumors are commonly benign and pleomorphic adenomas accounted for near half of benign tumors [28] . In this study, sensitivity and specificity of preoperative FNAC were 80.0% and 98.7%, respectively. Our results were within the range of that reported in the literature, where FNAC achieved a sensitivity of 62% to 98% and the specificity was usually higher ranging from 85 to 100% [29]. In a similar manner, the diagnostic accuracy achieved in our study was 96.6%, which compares well with other studies where the diagnostic accuracy ranged from 86% to 98% [30] . The accuracy is related to the experience of the cytologist, the type and quality of sample material. Heterogeneous structure of many salivary gland tumors and the overlap of some cytomorphological features, limit the accuracy of FNAC due to small size and selective sampling [31] . False positive and false negative diagnoses were pointer towards problems and pitfalls in cytological interpretation. The guiding principle of any cytologist should always be to reduce the rate of false diagnoses to the absolute minimum, so that the confidence of the referring specialist, in FNAC, is boosted and more important, no patient with malignancy is falsely assured or patient with benign lesion underwent an unnecessary surgical procedure [32] . In Histologically diagnosed 10 malignant salivary gland Lesions, 2 cases were misdiagnosed as a benign by Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology. The first case was diagnosed cytologically as chronic sialadenitis and proved to be acinic cell carcinoma. A review of the smear revealed that the acinic cells were larger than normal with slight degree of nuclear irregularities together with less evenly distributed chromatin pattern and slightly higher Nucleo / Cytoplasmic ratio than normal [Figure (1)]. Acinic cell carcinoma is a relatively rare malignant salivary gland neoplasm. Classically, the aspirates are highly cellular, composed of fragments and associated cells that are larger than benign ones, a characteristic feature is the presence of numerous dissociated naked tumor cell nuclei. When the classic features of acinic cell carcinoma are present, its diagnosis may not be difficult [Figure (2)]. However, problems arise when overlapping features are present [3]. The nuclear features of normal (non-neoplastic) acinar cells are quite similar to those observed in acinic cell carcinoma, the only subtle differences is the smaller size of the non-neoplastic acinar cell nuclei as compared with neoplastic acinar one and the basally oriented nuclei in normal cells, whereas in acinic cell carcinoma they are often centrally located. The most helpful diagnostic feature in the differential diagnosis is the low power arrangement of non-neoplastic salivary gland in a lobulated, rosette-like and acinar pattern, features which are readily can be observed in tissue sections rather than cytologic smears. Also, cells of acinic cell carcinoma, instead, are arranged in large, flat, monotonous, cellular sheets. In addition, a honeycomb appearance due to well defined cytoplasmic borders and syncytial fragments may be seen. At low power, one can also see the admixture of sheets of ductal epithelium and interstitial adipose tissue with lobulated nests of acinar cells in nonneoplastic salivary gland, while in acinic cell carcinoma, this pattern is characteristically absent [33] . The second case was a histologically proved adenoid cystic carcinoma diagnosed as pleomorphic adenoma on FNAC. The smear showed syncytial fragments composed of monotonous small tumor cells with high N/C ratio and hyperchromatic nuclei. Hyaline globules were absent, but focal areas of chondromyxoid background were seen. The distinction between pleomorphic adenoma and adenoid cystic carcinoma is clinically important. The stromal component does not always help. Hyaline stromal globule may be seen in pleomorphic adenoma and a fibrillar stroma can be seen in adenoid cystic carcinoma. Thus the differential diagnosis between these tumors can therefore not be based solely on the stromal component. Cytologic details must be closely studied. A well defined cytoplasm, no or few stripped nuclei, a bland finely granular nuclear chromatin and fragments of chondromyxoid matrix incorporating spindle cells favor pleomorphic adenoma while scanty cytoplasm, a high N/C ratio, naked nuclei, nuclear molding and nuclear hyperchromasia and coarseness favor adenoid cystic carcinoma [34] . [Figure (3)] In Histologically diagnosed 78 benign salivary gland Lesions, 1 case was misdiagnosed as a malignant by Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology. This case was histopathologically proved pleomorphic adenoma showed high cellular yield, stromal fragments resembled epithelial mucin, occasional mucin secreting cells and atypical squamous cells dominating the smear [Figure (4)]. The case was falsely diagnosed cytologically as mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Most pleomorphic adenomas are easily identified both histologically and cytologically because of their characteristic biphasic pattern, comprised of epithelialmyoepithelial cells and fibrochondromyxoid stroma in varying proportions [Figure (5)]. The cytological diagnosis of pleomorphic adenoma is obvious in typical cases, the focally striking variation in the histological pattern is rarely a problem in surgical pathology when the whole tumor can be examined, but can sometime cause difficulties in FNAC due to the limited sampling by needle biopsy, thus, one particular feature may dominate the smear to the extent that true nature of the tumor is not recognized [34]. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma and pleomorphic adenoma need to be differentiated as it is a recognized pitfall, chondromyxoid and fibrillary stroma is absent in mucoepidermoid carcinoma, squamous differentiation in pleomorphic adenoma may show keratinization, a feature much less evident in mucoepidermoid, goblet cells occur only infrequently in pleomorphic adenoma and plasmacytoid cells, since they have not been described in mucoepidermoid carcinoma are a good marker for pleomorphic adenoma [35] .
CONCLUSION
In summary, our study shows the high accuracy, sensitivity and specificity and confirms that Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) in salivary gland lesions is a valuable diagnostic tool in the workup of patients with salivary gland lesions. Many patients are saved the necessity of surgery. It is simple, accurate and cost effective method so it is suitable for developing countries with low financial resources. For these reasons, FNAC should be part of the initial evaluation of patients with major salivary gland lesions. However, we should realize that false positive and false negative results will always occur. We agree with the recommendation that use of FNAC in combine with clinical examination and radiological findings (the triple test) approach similar to that used in FNAC of breast lesion would protect false negative and false positive diagnoses and provide valuable and accurate diagnosis in the investigation of salivary gland lesions
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We would like to express our gratitude towards the Department of Pathology, B.J. Medical College, Ahmedabad. We also acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles cited and included in references of this manuscript. We are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. We are grateful to IJCRR editorial board members and IJCRR team of reviewers who have helped to bring quality to this manuscript.
References:
REFERENCES
1. Frable MAS, Frable WJ (1991). Fine needle aspiration biopsy of salivary glands. Laryngoscope, 101, 245-9.
2. Layfield LJ, Glasgow BJ (1991). Diagnosis of salivary gland tumors by fine-needle aspiration cytology: a review of clinical utility and pitfalls. Diagn Cytopathol, 7, 267-72.
3. Cajulis RS, Gokaslan ST, Yu GH, FriasHidvegi D (1997). Fine needle aspiration biopsy of the salivary glands: five-year experience with emphasis on diagnostic pitfalls. Acta Cytol, 41, 1412-20.
4. Buley ID, Roskell DE (2000). Fine-needle aspiration cytology in tumor diagnosis: uses and limitations. Clin Oncol, 12, 166-71
5. Cristallini EG, Ascani S, Farabi R, et al (1997). Fine needle aspiration biopsy of salivary gland, 1985-1995. Acta Cytol, 41, 1421-5.
6. Al-Khafaji BM, Nestok BR, Katz RL (1998). Fine-needle aspiration of 154 parotid masses with histologic correlation: ten-year experience at the university of Texas M.D. Anderson cancer center. Cancer, 84, 153-9.
7. Ellis G, Auclair P (1996). Tumors of the Salivary Glands, 3rd ed. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology. Washington, DC pp 17.
8. Mavec P, Eneroth CM, Franzen S, Moberger G, ZajicekJ. Aspiration biopsy of salivary gland tumours. Acta Otolaryngol 1964;58:471-484.
9. Persson PS, Zettergren L. Cytological diagnosis of salivary gland tumours by aspiration biopsy. Acta Cytol 1973;17:351- 354.
10. Cohen MB, Fisher PE, Holly EA, Ljung BM, Lowhagen T, Bottles K. Fine needle aspiration biopsy diagnosis of mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Statistical analysis. Acta Cytol 1990;34:43–49.
11. Auclair PL, Ellis GL, Gnepp DR, Wenig BM, Janney CG (1991). Salivary gland neoplasms: general considerations. In ‘Surgical pathology of the salivary glands. Major problems in pathology’, Eds Ellis GL, Auclair PL, Gnepp DR. WB Saunders, Philadelphia pp 135-64.
12. Fernandes GC, Pandit AA. Diagnosis of salivary gland tumours by FNAC. Bombay Hospital Journal 2000;42:108-111.
3. Qizilbash AH, Sianos J, Young JE, Archibald SD. Fine needle aspiration biopsy cytology of the major salivary glands. Acta Cytol 1985;29:503-512.
14. Spiro RH. Salivary neoplasms- An overview of 35 years of experience with 2807 patients. Head Neck Surg 1986;8:177-184.
15. Layfield LJ, Tan P, Glasgow BJ (1987). Fine needle aspiration of salivary gland lesions. Arch Pathol lab Med, 111, 346-353.
16. Stanley MW, Bardales RH, Farmer CE, et al (1995). Primary and metastatic high grade carcinomas of the salivary glands: a cytologichistoligic correlations study of twenty cases. Diagn Cytopathol, 13, 37-43.
17. Zhang S, Bao R, Bagby J, Abreo F (2009). Fine needle aspiration of salivary glands: 5- year experience from a single academic center. Acta Cytol, 53, 375-82.
18. Owen EERTC, Banerjee AK, Prichard AJN, Hudson EA, Kark AE (1989). Role of fineneedle aspiration cytology and computed tomography in the diagnosis of parotid swellings. Br J Surg, 76, 1273-4.
19. Stewart CJR, MacKenzie K, McGarry GW, Mowat A (2000). Fine needle aspiration cytology of salivary gland: a review of 341 cases. Diagn Cytopathol, 22, 139-46.
20. Kraft M, Lang F, Mihaescu A, Wolfensberger M (2008). Evaluation of clinician-operated sonography and fine-needle aspiration in the assessment of salivary gland tumors. Clin Otolaryngol, 33, 18-24.
21. Zbaren P, Nuyens M, Loosli H, Stauffer E. Diagnostic accuracy of fine-needle aspiration cytology and frozen sections in primary parotid carcinoma. Cancer 2004;100:1876- 1883.
22. Frable WJ. Thin needle aspiration biopsy. Philadelphia, WB Saunders. 1983, 119-151.
23. Qizilbash AH, Young J. Guides to clinical aspiration FNAC of Salivary Gland Lesions biopsy: Head & Neck. New York, IgakuShoin. 1988, 15-116.
24. Shiantani S, Matsura H, Hasegawa Y. Fine needle aspiration of salivary gland tumors. Int J Oral Maxillo Fac Surg. 1997, 26: 284-286.
25. Schindler S, Nayar R, Dutra J, Beddrossian CWM. Diagnostic challenges in aspiration cytology of the salivary glands. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2001, 18: 124-146.
26. Orell SR. Diagnostic difficulty in the interpretation of FNA of salivary lesions. Cytopathol. 1995, 6: 285-300.
27. Lowhagen T, Tani EM, Skoog L. Salivary glands and rare head and neck lesions: In Comprehensive Cytopathology, Edited by M Bibbo. Philadelphia, WB Saunders. 1991, 621- 648.
28. O’Dwyer P, Farrar WB, James AG, Mc Cabe DP. Needle aspiration biopsy of major salivary gland tumors. Its value. Cancer. 1986, 57: 554-557.
29. Koss LG, Melamed MR. Salivary glands. In: Diagnostic cytology & its histopathologic bases. 5th ed. Pheladilphia. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2006, 1230-60.
30. Rajwanshi A, Gupta K, Gupta N, Shukle R, Nijhwa R, Vasishta R. Fine needle aspiration cytology of salivary glands: Diagnostic pitfalls. Diagnostic Cytopathol. 2005, 34: 580- 584.
31. Mistry M, Sood S. Benign salivary gland tumors. J Otolaryngol Head & Neck Surg. 2004, 8: 49-52.
32. Abrari A, Ahmed S, Baksh V. Cytology in the otorinolaryngologist’s domain, a study of 150 cases, emphasizing diagnostic utility and pitfalls. Indian J Otolaryngol Head & Neck Surg. 2002, 54: 107-10.
33. Boccato P, Altavilla G, Blandamura S. Fine needle aspiration biopsy of salivary gland lesions. Acta Cytol. 1998, 42: 888-898.
34. Orell S, Sterrett G, Whitaker D. Fine needle aspiration cytology. Head & Neck. Livingstone Inc, New York. 2005, 41-82.
35. Elsheikh M. Salivary gland aspiration cytology. In: Atlas of difficult diagnoses in cytopathology. Atkinson B & Silverma J editors. 1st ed. New York. WB Saunders 1998, 451-80.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License