IJCRR - 6(7), April, 2014
Pages: 01-10
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
OPTIMUM DIETARY INCLUSION LEVEL OF BACILLUS COAGULANS FOR GROWTH AND DIGESTIBILITY IMPROVEMENT FOR CATLA CATLA (HAMILTON)
Author: Anita Bhatnagar, Shashi Raparia
Category: General Sciences
Abstract:Purpose: The present studies were conducted to evaluate the optimum inclusion levels of probiotic Bacillus coagulans, isolated from the intestine of Catla catla for improved growth performance and nutrient retention. Methods: Catla fingerlings (avg. wt. 0.2\?0.02 g) were fed on isocaloric and isonitrogenous diets supplemented with 2×104 (D1), 2×105(D2) and 2×106(D3) Bacillus coagulans cells 100g-1 of feed for 90 days @ 4 % body weight per day in two equal installments in three replicates. The control treatment (DC) was not supplemented with Bacillus coagulans. Growth and digestibility parameters and intestinal enzyme activities were monitored. Results: The growth of fish in terms of live weight gain (g), growth per day in percentage body weight and specific growth rate were significantly (P< 0.05) high in feed D2 in comparison to other dietary treatments. Also, significantly (P< 0.05) high values of Apparent protein digestibility (APD), Gross conversion efficiency (GCE) and Protein efficiency ratio (PER) lower FCR (1.64\?0.02) was observed in the dietary treatment D2. Significantly (P?0.05) high values of digestive enzyme activities (protease, amylase and cellulose), carcass protein, and low excretion of metabolites (ammonia and phosphates) were also observed in feed D2. Conclusion: Results indicated that that supplementation of 2×105 cells 100g-1of probiotics, B. coagulans could be used to enhance growth performance and nutrient retention of C. catla.
Keywords: Bacillus coagulans, Catla catla, Dietary probiotic, Growth performance, Intestinal enzymes
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Development of commercial scale intensive aqua farming with high stocking densities, high food inputs and high organic load accompanies problems of aquatic pollution and disease outbreaks, affecting fish growth, survival and production(1). To combat these problems large amount of chemotherapeutics / antibiotics are often used; the abuse of these drugs has led to the development of multiple drug resistant bacteria (2, 3). Increased concern about these resistant microorganisms has led to several alternatives including the use of beneficial non-pathogenic micro-organisms as probiotics (4). The use of commercial probiotics in fish is relatively ineffective as most commercial preparations are based on strains isolated from non fish sources that are unable to survive or remain viable at high cell density in the intestinal environment of fish during the active growth phase of fish (5). Hence, there is elegant logic in isolating the putative probiotics from the host in which the probiotics is intended to use. The criteria for selection therefore, demands that the bacteria should be of same species origin,produces antimicrobial metabolites and should adhere to intestinal mucosa (6). Bacillus have been widely used as potential probiotics (7), since they secrete a variety of antimicrobial compounds and exoenzymes (5, 8). Ringpipat et al. (9) reported that use of Bacillus spp. (strain S11) provides pathogenical protection by activating both cellular and immune defenses. Zhou et al. (10) studied the effect of Bacillus sublitis, Bacillus coagulans and Rhodopseudomonas sp. on growth performance of Tilapia, but they used these probiotic bacterial cultures as water additives. Studies were undertaken in our laboratory to isolate gut adherent potential probiotic bacterium to improve fish growth and digestibility in Catla catla (11), however, the inclusion level of probiotic in feed of specific fish species need to be searched. Therefore, this study is attempted to investigate the effect of dietary supplementation of different inclusion level of probiotic bacterium Bacilllus coagulans, on growth performance, digestibility and nutrition retention in C. catla.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
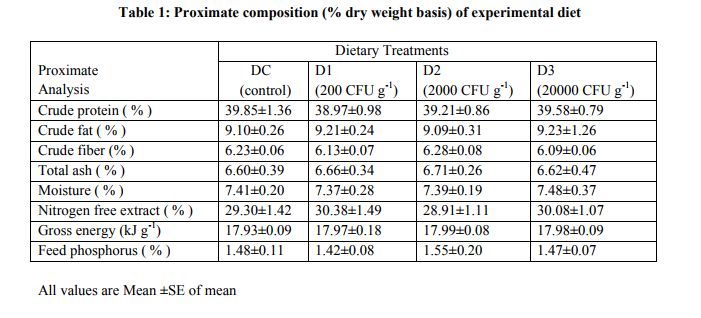
The present study was conducted at Aquaculture Research Unit, Department of Zoology, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra (29°58’N latitude and 76°51’E longitude), Haryana, India. Fingerlings of C. catla of average weight 0.2±0.02 g were obtained from local fish farm. Fingerlings were released into aquariums (50L capacity) after acclimatizing for 10 days to prevailing laboratory condition of water temperature (25±1°C), pH (7.2- 7.8) and oxygen range between 5-6 mg/L. Studies were conducted at room temperature for 90 days. Each aquarium was filled with de-chlorinated tap water and then stocked with 20 fish (fingerlings with average BW 0.2±0.02 grams and length 1.7±0.09 cm respectively).Aquarium water was renewed daily with water adjusted to laboratory temperature ( 25° C). The probiotic bacterium isolated from the intestine of Catla catla was identified from IMMTECH Chandigarh, India as Bacillus coagulans and mass cultured for 48 hours, at 30oC in shaken bottles with nutrient Agar media (Hi-Media, India). The cultures were centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 15 minutes at 40C, washed thrice with sterile 1 % NaCl solution and the pellets were re-suspended in sterile saline water. The processed soybean (40 %) based experimental diets were prepared by absorbing suspension of probiotic bacterium and a mechanical pelletizer to produce 0.5 mm pellets. To eliminate / inactivate antinutrient factors (ANFs), soybeans were hydrothermically treated at 15 psi and 121?C for 15 min; 1% chromic oxide (Cr2O3) was added as an external indigestible marker for digestibility estimations. Four dietary treatments (DC, D1, D2 and D3) were performed with three replicates of each treatment. In treatment 1 (DC), fishes were fed on artificial diet without probiotic bacteria (i.e. control diet). In treatment 2, 3 and 4, fishes were fed on artificial diet containing mass cultured Bacillus coagulansCC1 in proportions 2x104 , 2x105 and 2x106 cells 100g-1 of feed (Table 1). All these diets were isocaloric and isoproteic with approximately 40% proteins. After spraying the feed was air dried at room temperature. The bacterial concentration was calculated as 1.69 x 104 , 1.89 x 105 and 1.73 x 106 CFU 100 g-1 of feed D1, D2 and D3 respectively ( see table- 1 for proximate composition). Finally, the feeds were stored in vacuumed plastic container at 40C. All groups of fish were fed daily at 4% BW in 2 installments at 8:00 and 16:30 hours for 90 days. Average weight of all fish in each tank was measured, and the amount of feed was adjusted accordingly every 15 days. Each group of fish was exposed to their respective diet for four hours; thereafter, the uneaten feed was siphoned out, stored, and dried separately for calculating feed consumption per day. The fecal matter voided by the fish was collected every morning by siphoning. Fecal samples were dried in a hot air oven at 60?C and subsequently analyzed for digestibility estimations. At the end of the feeding trials, water samples from each aquarium were collected at two-hour intervals over a period of 24 h for the estimation of excretory levels of total ammonia (N-NH4+ ) and reactive orthophosphate following the American Public Health Association (12),and calculated following Sumagaysay-Chavoso (13). At the termination of experiment, the fish from all the treatments were individually weighed to the nearest gram and measured to the nearest millimeter and processed for subsequent analyses. From each treatment, eight fish were randomly sampled and kept on ice to remove the intestines which were processed for the determination of enzyme activity of protease (14), amylase (15), and cellulose (16). Proximate analysis (Dry matter, ash, crude protein, crude fat, NFE and phosphorus) of experimental diets and fish carcass (initial and final) was done following (17). Chromic oxide levels in the diets as well as in the fecal samples were estimated spectrophotometrically (18). Growth and nutrient retention parameters were calculated following Steffens (19). Apparent protein digestibility (APD) of the diets was calculated according to of Cho et al. (20).Live weight gain (g), percent weight gain, specific growth rate, feed consumption per day in percentage of body weight, feed conversion ratio (FCR), gross conversion efficiency (GCE), and protein efficiency ratio (GER) were calculated using standard method (19).Gross energy content of the diet and fish carcasses was calculated using the average caloric conversion factor of 0.3954, 0.1715, and 0.2364 Kj g−1 for lipid, carbohydrate, and protein, respectively (21), whereas metabolizable energy in diets and feeds was calculated using caloric conversion factors: 0.335, 0.138, and 0.188 Kj g−1 for lipid, carbohydrate, and protein, respectively (22). Statistical Analysis ANOVA followed by Duncan’s multiple range test (23) was applied to find out significant differences among dietary treatments
RESULTS
Survival rate (%) was high in all dietary treatments and slight mortality occurred only during the initial days of experiment. The growth of fish in terms of live weight gain (g), growth/day in percentage body weight and specific growth rate (SGR) were significantly (P<0.05) high in treatment D2 where fishes were fed on diet containing probiotics (Bacillus coagulans) , in proportion of 2X105 cells/100g (i.e.2000 cells g-1 ) of feed in comparison to dietary treatments DC, D1 and D3.Also, significantly (P<0.05) high values of digestibility parameters viz. Apparent protein digestibility (APD), Gross conversion efficiency (GCE) and Protein efficiency ratio (PER) and significantly (P<0.05) lower FCR (Fig. 3) was observed in the dietary treatment D2. Specific activities of digestive enzymes were significantly (P<0.05) high in all the dietary treatments in comparison to controls. The values showed an increasing trend from treatment DC to D2 (containing probiotics B. coagulans in proportion of 0, 2X104 and 2X105 cells 100 g-1 of feed respectively) thereafter, with further increase in the inclusion level of probiotic bacteria in DietD3(containing containing probiotics B. coagulansin proportion of 2X106 cells 100 g-1 of feed ) the values decreased. The data on weight gain revealed that initially up to 15 days not much variations were observed in the weight gain of group of fishes fed on varying dietary treatments. However, growth rate increased significantly (P<0.05) in the fishes fed on diet D2 (containing probiotics B. coagulans in proportion of 2X105 cells 100 g-1 =2000 cells g-1 of feed) after 30 till 90 days (Fig-1). Initial and final carcass composition with respect to proximate nutrients of test fish on basis of feeding trial is shown in Table-3. Crude Protein (%), gross energy (kJg-1) were found to be significantly (P<0.05) higher in the carcass of fish fed on diet D2. Moisture (%), Crude fat (%) was found to be significantly (P<0.05) higher in dietary treatment DC (without probiotics). Nitrogen free extract (NFE) was found to be highest in diet D3 (containing probiotics Bacillus coagulans in proportion of 2X106 cells 100g -1 of feed). However, no significant (P<0.05) variations were observed in total ash (%) of carcass of fishes fed on different diets. The data on water quality characteristics pertaining to four dietary treatments is presented in table-4. In general, significantly (P<0.05) low values in total ammonia excretion and reactive phosphate production (mg Kg-1 BW d-1 ) were recorded in fish fed on diet D2. Peak values of ammonia excretion occurred approximately 6h after feed was given to fish and second peak at 12h after feeding while oPO4 production showed an initial high level at 2h post feeding and second peak at 8h post feeding (Fig-2A & 2B).
DISCUSSION
This experiment was conducted to evaluate the optimum dose of probiotic supplementation in the formulated feed for Catla catla. The optimum probiotic (B. coagulans) level which resulted in high growth in C. catla fingerlings in terms of live weight gain (g), growth percent gain, SGR and nutrient retention (PER, GCE and APD) was found to be around 2 x 105 cell/100g of feed that is 2000 CFU g-1 of feed. FCR values decreased with each increase in the dietary probiotic content up to 2x105 cell/100g of feed. Thereafter, further increase in dietary probiotic level resulted in increase in FCR and growth depression. Although, all the feeds were isonitrogenous but the concentration of probiotics in dietary treatment D2 might have been helpful for proper nutrient utilization. Whole body carcass composition and lesser nitrogen and phosphate excretion were also observed in dietary treatment D2 (B. coagulans supplemented at the rate of 2000 CFU g-1 of diet) which is attributed to proper probiotic concentration, whereas lesser carcass composition and greater nitrogen and phosphate excretion were observed in dietary treatment D3 (B. coagulans at 20000 CFU g-1 of diet) which could have also noticed to the overall low feed utilization level. The high APD values for the diet containing B. coagulans at 200 CFU g-1 of diet may be attributed to high dietary utilization and best growth. When the data for live weight gain and APD was subjected to Orthogonal polynomial curve analysis adding trend line to show the expected dose dependent response (Fig. 3& 4) it was clearly observed that optimum inclusion level was somewhere near dietary treatment D2 indicating that optimum dietary supplementation of Bacillus coagulans appears to be around 2000 CFU g-1 of diet. Orthogonal polynomial fit curves to the data on FCR in different dietary treatments depicts an inverted curve (Fig. 5), showing the better feed conversion in treatment D3. Bazaz and Keshavenath (24) also found similar results. The present study also reports such a finding where all the feeds were isocaloric & isonitrogenous but 2 x 105B. coagulans Cells/100g (=2000 CFU g-1 of diet) exhibited better growth as well as better digestibility and physiology. Ghosh et al. (25) with B. circulans as probiotics in feed for Labeo rohita fingerlings and Ringpipat et al. (9) with Bacillus sp. as probiotics in Paneus monodon also reported similar results. The specific enzyme activities were also found high in treatment D2 and lowest in control DC which may be due to better dietary protein utilization due to colonization of probiotics bacteria and its exogenous enzyme production. Most of the amino acids normally found in protein undergo transamination reaction and transaminases are localized in both cytosol and mitochondria (26) which is induced by high protein diet however, in the present studies the diets were isocaloric and even then growth rate and digestive physiology varied. The nutritional value of the diet depends upon the digestive capabilities of the fish which in turn is affected by the activity of the digestive enzymes present in the digestive tract (27). The activity of the digestive enzymes (Protease, amylase and cellulose) were high in a group fed in diet containing probiotic bacterium at rate of 2x105 cells / 100g of feed). Enzyme activity increase with increasing dietary probiotic level in comparison to control while it decreases at much higher probiotic concentration (2x106 cells/100g of feed). This shows that when probiotics supplementation exceeds the optimum level, no further improvement in growth performance and nutritive physiology of the fish was observed rather these parameters decreased. This shows that probiotics bacteria incorporated in the feed with high inclusion level might have competed amongst themselves, as a result their colonization was not proper, resulting in the decline in exogenous/ extracellular enzyme production, thus low digestibility, low growth and high feed conversion ratio. The excretion of metabolites N-NH4 and oPO4 in the holding water also increased with increase in the inclusion level of probiotic bacteria above the optimum dose. This may again be attributed to low feed utilization due to less amount of digestive enzymes. When dietary utilization is low deamination of unutilized feed protein occurs and excretion of metabolites in the holding water increases. Although it is said (28) that mode of action of probiotic is ecological also and it optimize the nitrification and denitrification rates in the water. However, when the value exceeds the optimum limit, there is effect on nutritive physiology decreasing growth performance and increasing excretion of metabolites in holding water. These results indicate that probiotic stimulate the digestion through the supply of digestive enzyme and certain essential nutrients to animals. Probiotics are known to improve enzymatic activity in the gut by producing several enzymes not produced by the host. Similar observations were also reported by (29) who observed that complex polysaccharides can be better utilized by the host in the presence of direct feed microbes. Unfortunately, the information regarding the mode of action of probiotics used in aquaculture is incomplete. However, the benefits have been reported which includes improvement in nutrition by detoxification of potentially harmful compounds in feeds denaturing of potentially digestible matter in the diet by hydrolytic enzyme including amylases and proteases and production of vitamins. Thus, the B. coagulans strain used in the present studies showed beneficial effect on the digestive processes of the fish specially, when the inclusion level is optimum. This observation draws attention to an essential inference that the probiotic concentration which was used in this feed might be helpful for optimum dietary utilization. It was also observed the P/E ratio was highest in D2 fed fishes although with highest dietary utilization. Mohanty et al. (30) reported that higher the dietary utilization, higher the P/E ratio.
CONCLUSION
The results obtained in the present study support the use of probiotic bacterium (B. coagulans FGB CC1) for better growth and proper nutrient utilization. The finding further suggest that the concentrations of probiotics applied in formulated diet D2 (2 x 105 cells/100g of feed i.e. 2000 cells g -1 ) was able to increase overall physiological performance like increase in intestinal enzymes along with growth parameters and decrease in excretion of metabolites in the holding water, thus, enhances the defense mechanisms in the fingerlings of Catla catla. However, further investigations should be applied by preparing the feeds with different concentrations of this probiotics bacterium B. coagulans formulating two best feeds according to the results achieved in this study. Findings should be confirmed before commercialization.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors are thankful to the chairperson Department of Zoology, Kurukshetra, University Kurukshetra, India for providing necessary facilities to carry out this work. Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed



References:
REFERENCES
1. Austin B, Austin DA. Bacterial Fish Pathogen: Disease of Farmed and Wild Fish. 3rd ed. (Revised). Goldalming: Springer-Praxix; 1999.
2. Alderman DJ, Hasting TS. Antibiotic use in aquaculture: development of antibiotic resistance potential for consumer health risk. Int J Food Sci Technol 1998; 33:139-55.
3. Bisht A, Singh UP, Pandey NN. Bacillus subtilis as potential probiotic for enhancing growth in fingerlings of common carp (Cyprinuscarpio L.). Indian J Fish 2012; 59(3):103-8.
4. Guarner F, Malagelada JR. Gut flora in health and disease. The Lacent 2003; 360:512-9.
5. Moriarty DJW. Microbial Biotechnology: a key ingredient for sustainable aquaculture, Infofish Int 1996; 4:29-33.
6. Vine NG, Leukes WD, Kaiser H, Daya S, Baxter J, Hecht T. Competition for attachment of aquaculture candidate probiotic and pathogenic bacteria on fish intestinal mucus. J Fish Dis 2004; 27(6):319-26.
7. Ziaei-Nejad S. The effect of Bacillus sp. bacteria as a probiotic on growth, survival and digestive enzyme activity of Indian white Shrimp, Fenneropenaeusindicus, larvae and post larvae [Msc thesis]. Tehran University; 2004.
8. Moriarty DJW. Control of luminous Vibrio species in penaeid aquaculture ponds. Aquaculture 1998; 164:351-8.
9. Ringpipat S, Phianphak W, Piyatiratitivorakul S. Effects of probiotic bacterium on black tiger shrimp Penaeusmonodon survival and growth. Aquaculture 1998; 167:301-13.
10. Zhou X, Tian Z, Wang Y, Li W. Effect of treatment with probiotics as water additives on tilapia (Oreochromisniloticus) growth performance and immune response. Fish Physiol Biochem. (doi 10.1007/s10695-009- 9320-z).
11. Bhatnagar A, Raparia S, Kumari S. Influence of isolated Bacillus coagulans on growth performance and digestive enzyme activities of Catla catla. JNNST 2012; 6(3):225-35.
12. APHA. Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water. 20th ed. American Public Health Association. New York; 1998.
13. Sumagaysay-Chavoso NS. Nitrogen and phosphorus digestibility and excretion of different size groups of milkfish (ChanoschanosForsskal) for formulated and natural food –based diets. Aquac Res 2003; 34(5):407–18.
14. Walter HE. Probionases : Methods with haemoglobin, casein and azocoll as substrates. In : Bergmeyer HU, editor. Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, Vol. V. Verlag Chemic: Weinheim; 1984. p. 270-7.
15. Sawhney SK, Singh R. Introductory Practical Biochemistry. Narosa Publishing House; 2000. p.452.
16. Sadasivam S, A Manickam. Biochemical methods. New Delhi, India: New Age International Publishers; 1996.
17. AOAC, (Association of Official Analytical Chemists). Official methods of analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists Incorporation, Arlington, USA; 1995. p.684.
18. Furukawa A, Tuskahara H. On the acid digestion method for determination Chromic oxide as an indicator substance in the study of digestibility in fish. Bull jap soc sci fish 1966; 32:502–6.
19. Steffens W. Principles of fish nutrition.Chichester, NY: Horwood; 1989.
20. Cho CY, Slinger S J, Bayley H S. Bioenergetics of salmonids fishes: energy intake, expenditure and productivity. Comp Biochem Physiol B 1982; 73: 25–41.
21. Henken AM, H Lucas, PAT, Tijseen MAM Michiels. A comparison between methods used to determine the energy content of feed, fish and faecal samples. Aquaculture 1986; 58:195–201.
22. Brett JR, Groves TTD. Physiological energetics. In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ, Brett JR editors. Fish Physiol vol. 8. New York: Academic Press; 1979. p.280–352.
23. Duncan DB. Multiple range and multiple Ftests. Biometrics 1955; 11: 1-42.
24. Bazaz MM, Keshavanath P. Effect of feeding levels of sardine oil on growth, muscle composition and digestive enzyme activities of Masheer Tor khudree. Aquaculture 1993; 115: 111-9.
25. Ghosh K, Sen SK, Ray AK. Supplementation of an isolated fish gut bacterium, Bacillus circulans, in formulated diets for rohu, Labeo rohita fingerlings. Bamidgeh 2003; 55 (1): 13- 21.
26. Wada H, Marino Y. Comparative studies on glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminases from the mitochondrial and soluble fractions of mammalian tissues. In: Harris RS, Wool IG, Loraine JA, editors. Vitamins and Hormones. New York: Academic Press; 1964. p.411-44.
27. Phillips AM. Nutrition, digestion and energy utilization. In: W.S. Hoar W S, Randall D J, editors. Fish Physiology. vol 1. New York: Academic Pres; 1969. p.391-432.
28. Dong H, Fredrickson JK, Kennedy DW, Zachara JM, Kukkadapu RK, Onstott TC. Mineral Transformation associated with the microbial reduction of magnetite. Chem Geol 2000; 169: 299-318.
29. Swain SK, Rangacharyulu PV, Sarakar S, Das KM. Effect of a probiotic supplement on growth, nutrient utilization and carcass composition in Mrigal fry. J Aquac 1996; 4: 29-35.
30. Mohanty SN, Swain SK, Tripathi SD. Rearing of (Catla catla Ham) spawn on formulated diets. J Aquac Trop 1996; 11:253-258.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License