IJCRR - 6(8), April, 2014
Pages: 42-51
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
STUDY OF NOSOCOMIAL URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO CANDIDURIA AT BLDEU's SHRI B.M.PATIL MEDICAL COLLEGE AND HOSPITAL, BIJAPUR, KARNATAKA
Author: Raj Mohammed D. Malled, Prashant K. Parandekar, Annapurna G. Sajjan
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background of the study: Nosocomial urinary tract infections are the most common of hospital acquired infections comprising about 40%. Majority are related to catheterization or other predisposing factors. Candiduria is rarely encountered in otherwise healthy people with structurally normal urinary tract. It is however of common occurrence in hospitalized patients. Candida spp. account for almost 10-15% of nosocomial urinary tract infections. Objectives: Present study was undertaken to identify various pathogens causing nosocomial UTI, and further study including identification of yeasts and to analyze the various risk factors associated with candiduria in hospitalized patients. Methodology: 195 urinary isolates of patients admitted in hospital ?3 days were screened. The bacterial and yeast isolates were identified by conventional methods. Results: Of the 195 samples from the cases of suspected nosocomial UTI screened, 131(67.17%) yielded growth, amongst which 17 (12.9%) were Candida species. Amongst the bacterial isolates, E.coli (38.16%) was the most common followed by Citrobacter spp. (16.0%), Klebsiella pneumoniae (12.2%) and others. Whereas, among the Candida isolates C. tropicalis (41.1%) was found to be predominant followed by C. guillermondi (23.5%), C. albicans (17.6%), C. krusei (11.7%) and C.glabrata (5.8%). Majority of the patients were having various predisposing factors. Conclusion: Non albicans species were predominant amongst the Candida isolates, majority of patients were having predisposing factors emphasizing the need of proper surveillance of nosocomial UTI for appropriate treatment.
Keywords: Nosocomial UTI, Candiduria, non-albicans Candida
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are the most common nosocomial infections which account for about 40% of all hospital – acquired infections and constitute a major source for nosocomial septicemia and related mortality in acute care hospitals.1 The vast majority of UTIs occur in patients with temporary indwelling catheters. 1,2,3,4 The microorganisms usually responsible for catheter – associated UTIs are derived from the fecal flora native to the patient or originate in the hospital environment.1 They include Escherichia coli, Enterococcus species, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis and Candida species.2,4 An increasingly important subgroup of nosocomial urinary tract infections are those due to fungi, and almost all fungal urinary tract infections are caused by Candida spp.5 The predisposing factors frequently associated with candiduria are urinary tract instrumentation, prior surgical procedures, recent use of antibiotics, prolonged hospital stay, extremes of age, diabetes mellitus, female sex and use of immunosuppressive therapy.6,7 Candiduria or presence of Candida spp. in the urine is a relatively rare finding in otherwise healthy people.8 The presence of Candiduria may reflect only colonization of the bladder, perineum, or indwelling urinary catheter.9 It is rarely encountered as a community acquired infection in a structurally normal urinary tract as they usually present as complicated nosocomial infections. Candida spp. accounts for almost 10-15% of nosocomial urinary tract infections.10 The recovery of Candida species from urine samples presents the clinician with a diagnostic dilemma as to whether the presence of candiduria in a patient represents contamination, colonization or true infection.8 Though contamination of urine sample is very common, it can be ruled out by obtaining a second sterile urine sample. But till date, there are no reliable methods of differentiating colonization of urinary tract from true UTI with Candida spp.8,10 The specific identification of Candida spp. is important as it provides information in the choice of treatment, because C.glabrata and C.krusie are naturally resistant to fluconazole.11 Though Candida albicans is the most frequently isolated species, few observers have emphasized the changing microbial trends towards non-albicans Candida species.10,12 Hence, the present study was undertaken with the objective of identifying various pathogens incriminated in nosocomial UTI, to speciate the yeasts isolated in these infections and to analyze the various risk factors associated with candiduria.
METHODOLOGY
The study was undertaken after clearance from institutional ethical committee at BLDEU’s Shri B.M.Patil Medical College and Hospital, Bijapur, Karnataka from March 2012 to January 2013. After taking informed consent from the patients, a total of 195 urine samples of patients admitted in hospital for ?3days were screened.
Inclusion criteria
Patients admitted in the hospital for more than 3 days. Pure growth from urine sample with significant colony count of 104 colony forming units (cfu)/ml for Candida and 105 cfu/ml in case of bacteria were included.8 The specimen yielding Candida isolates were further subjected to repeat urine cultures. The Candida species reisolated after repeat culture were included in the present study.
Exclusion criteria
Absence of pyuria / mixed growth in the culture. Duration of admission in hospital is less than 3 days. Candida species failed to be isolated on repeat culture. In the Patients with candiduria, demographic details such as age, sex, duration of hospital stay, duration of catheterization and other clinical details were noted. Presence of other associated risk factors like diabetes mellitus, history of antibiotic use, any urinary tract instrumentation, any surgical procedures carried out on the patient or use of immunosuppressive drugs were also recorded.
Urine sample processing
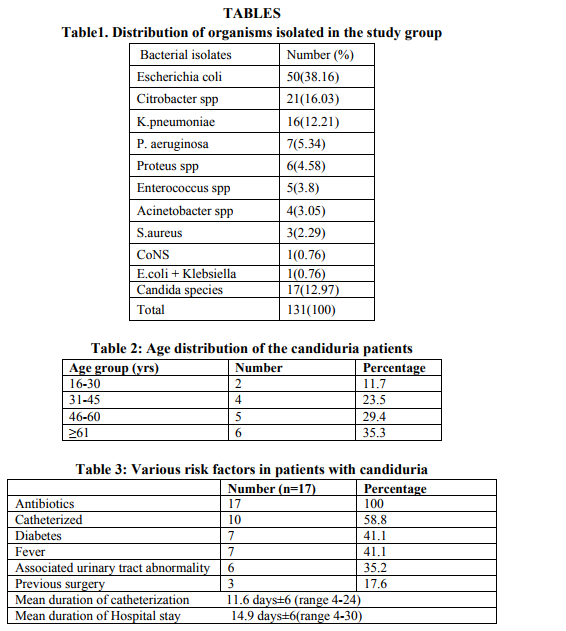
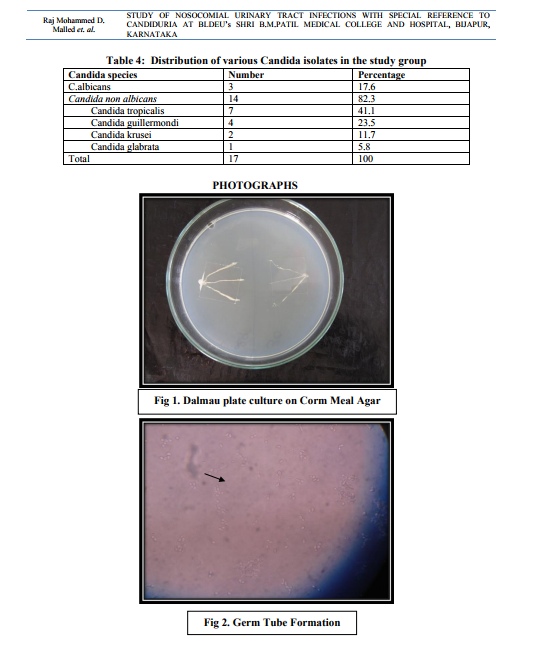
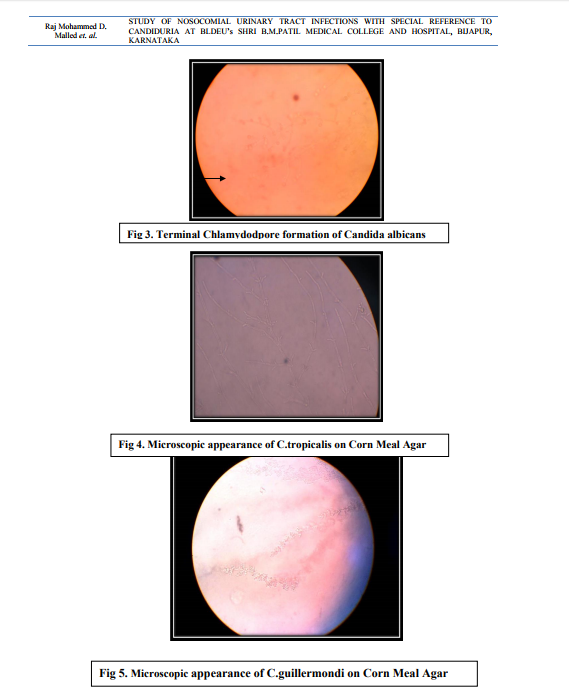
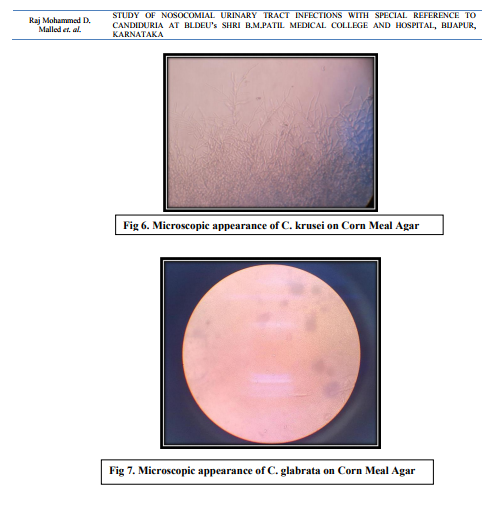
In case of non-catheterized patients a clean catch midstream urine samples were collected, whereas in catheterized patients sterile urine specimens were obtained via syringes after cleaning the catheters with an antiseptic solution.14 After direct microscopic examination in the form of wet mount and Gram stained smears, the urine samples were inoculated on Cysteine Lactose Electrolyte Deficient (CLED) and MacConkey’s agar using standard loop as per the semi quantitative culture technique. Moreover, the specimens showing budding yeast like cells on direct examination were inoculated on Sabourauds Dextrose Agar (SDA). The further incubation of these media was done at 370C temperature for 16-24 hours followed by identification by using conventional methods. The specimens yielding no growth after 16-24 hours were further incubated upto 48 hours and regarded as sterile if there is no growth.15 The Yeast cells identified on Microscopy are processed further for identification as follows a. Germ tube test – the Candida cultures were treated with human serum and incubated at 370C for 2-4 hours. A drop of the suspension is examined on the slide under the microscope. The germ tubes are seen as long tube like projections extending from the yeast cells.16 b. Chlamydospore formation - the Candida isolates were grown on the corn meal agar (CMA) plate and incubated at 250C for 2-3 days and later examined for microscopic morphology of the chlamydospores for identification of various Candida species.16
Statistical analysis
The results wherever applicable were analyzed by Fischer’s exact test for statistical significance by using Graphpad In Stat 3. The P value was calculated for determining whether the results obtained were statistically significant. P value of ?0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
RESULTS
The present study includes 195 samples from the cases of suspected nosocomial UTI of which 131(67.17%) yielded growth amongst which 17 (12.9%) were Candida species. The most commonly isolated organism was Escherichia coli-50 (38.16%), followed by Citrobacter spp.-21 (16.03%), Klebsiella pneumoniae -16 (12.21%) and others (Table 1.)
Demographic profile with regards to
candiduria: Majority of the patients with candiduria belonged to age group ? 61 years (35.3%) followed by age group 46-60 years (29.4%). (Table 2.) Amongst 94 culture positive males 11 (11.7%) showed candiduria whereas out of 37 culture positive females 6(16.2%) cases revealed candiduria (fisher’s exact test, P value = 0.565). Other associated risk factors of the study group are shown in Table 3. The average length of hospitalization during which candiduria developed was 14.9±6 days. The risk of developing candiduria was high in patients after 11.6±6 days of catheterization. Antibiotic usage was seen with all the patients for the duration of 5 to 8 days. Whereas one patient of candiduria was on fluconazole for 10 days in which Candida krusei was isolated. Moreover one case was on corticosteroids. 7 of the 17 patients (41.1%) were diabetic, and 6 (35.2%) were having associated urinary tract abnormality such as benign hypertrophy of prostate, renal and ureteric calculi. In the present study, amongst the cases of candiduria, non-albicans Candida spp. were the predominant species recovered responsible for 82.3% of nosocomial UTI. Candida albicans accounted for only 17.6% of nosocomial UTI. Amongst Non albicans Candida species, Candida tropicalis accounted for majority of the cases (41.1%). Distribution of various Candida spp. is given in table 4.
DISCUSSION
In the recent past, medical and surgical advances in the areas of medical technologies, have markedly altered the hospitalized patient populations leading to survival of greater number of hospitalized patients who are severely ill. These patients are at increased risk of nosocomial infections. Nosocomial infections constitute a serious public health problem, as they are a major cause of morbidity and mortality, and cause an increased time of hospitalization with associated enhanced healthcare costs.12 Therefore we studied a spectrum of organisms causing nosocomial urinary tract infections with special emphasis on nososcomial candiduria. In the present study we observed that Escherichia coli was the most common organism isolated (38.16%) followed by Citrobacter spp (16.03%), Klebsiella pneumoniae (12.21%) and Candida spp.(12.97%). Whereas, Kamat U et al.17 showed E.coli (49.1%), as the most common pathogen followed by P.aeruginosa (12.72%), Klebsiella spp. (12.7%) and Candida albicans (10.9%) in a similar study. Another study by Savas et al.18 demonstrated E.coli (31.4%) as the most common pathogen followed by Candida spp. (21.3%), Klebsiella spp.(10.6%) and Enterococci (6.9%). Our study revealed 12.97% of the isolates to be Candida spp. Similar observation was noted by Kamat U et al.17 who reports 10.9%. Whereas, Savas et al.18 reported 21.3% of the UTIs caused by Candida spp. This may be perhaps because of difference in the sampling techniques and antibiotic prescribing trends in the hospital. Of the Candida isolates in our study, 17.6% were Candida albicans, whereas 82.4% were Candida non-albicans. Amongst overall isolation of Candida species, C.tropicalis was found to be the predominant Candida spp. accounting for 41.1%, followed by C.guillermondi 23.5%, C.albicans 17.6%, C.krusie 11.7% and C.glabrata 5.8%. Many previous studies reported Candida albicans as the predominant species such as a study conducted by Febre N et al.11 who showed that C.albicans was isolated in 46.1%. Similarly Sobel JD et al.19 reported C.albicans in 50% of the cases followed by non-albicans Candida spp. Whereas a study conducted by Paul N et al.20 which showed C.albicans in 19% and C.tropicalis in 43% of the cases and a study by Jain M et al.10 revealed C.albicans in 28.6%, C.tropicalis in 52.9% and C.glabrata in 1.4% of the cases which are in accordance with our study. These findings suggests that there is a changing trend towards Candida non-albicans which might be due to the selection of less susceptible species by antifungal agents such as fluconazole.7 Analogous observation was seen in one case in our study group on fluconazole therapy in which Candida krusei was isolated. We found that candiduria was apparently more common in females (16.2%). This finding is well in accordance with other researchers also.6,8,19 But this statistical analysis revealed that there is no significant association of candiduria in females by fisher’s exact test (P value = 0.565). There have been few other observers who did not find significant difference in terms of female sex having more chances of candiduria.14 This may be perhaps be explained by associated various risk factors such as age, immunocompromised status, antibiotic therapy, instrumentation etc. We observed that nosocomial UTI due to Candida spp. was more common in the age groups >61 yrs, which is well in accordance with other researchers.10 Diabetes mellitus was seen in 41.1% of the patients with candiduria in present study. This is in agreement with the study conducted by Kauffman CA et al.5 who noted diabetes mellitus in 39% of candiduria in their study. Patients with diabetes are at increased risk for UTIs due to candida spp. Diabetes may predispose patients to fungal candiduria by predisposing them to Candida colonization, by enhancing urinary fungal growth in the presence of glycosuria, by lowering host resistance to invasion by fungi as a consequence of impaired phagocytic activity, and by promoting stasis of urine in a neurogenic bladder.8 Previous history of antibiotic use was seen in all the patients with candiduria. In a study by Guler S et al.14 88.2% of the cases with candiduria were on the antibiotics, whereas Passos XS et al.7 noted antibiotic use in all the patients with candiduria. Our finding is well in accordance with latter. Antimicrobial treatment was reported to be a risk factor for candiduria in 70-100% in various studies. It has been reported that approximately 30% of the adults gastrointestinal tract is colonized by Candida species and the colonization rates approached to 100% in patients receiving antibiotics.8 Antibiotic use suppresses susceptible endogenous bacterial flora in the gastrointestinal and lower genital tract and favors the colonization of epithelial surface with fungal species, thus increasing the chance of introducing the organisms into the urinary tract specially in the presence of indwelling urinary devices.7 In the present study 58.8% of the patients with candiduria were catheterized and the mean duration of catheterization was 11.6±6 days. Similar results were obtained by Passos XS et al.7 who verified that 92.6% of the patients with candiduria had urinary catheter. Urinary catheters serve as a portal of entry and most catheters become colonized if left for longer duration. There is a direct relationship between the duration of catheterization, candidial colonization and of nosocomial candiduria.10 With short term catheterization (upto 7 days), 10-50% patients develop infections, whereas in long term catheterization (>28 days), usually all patients develop urinary tract infection. The risk of catheter associated infections increases by approximately 10% for each day.21 With this observation we recommend that catheterization should be conducted when it is dire essential and for short duration as early removal of the urinary catheters lessens the burden of UTIs. In the present study associated urinary tract abnormality was seen in 35.2% of the cases and previous surgery in 17.6% of the cases. According to literature,22 obstruction to urinary flow at all levels is a key factor in increasing host susceptibility to UTI. Obstruction inhibits the normal flow of urine and the resulting stasis compromises bladder and renal defense mechanisms. Stasis also contributes to the growth of bacteria in the urine and their ability to adhere urothelial cells. Perhaps the similar mechanisms may be playing role for the colonization and invasion of Candida species in the cases of candiduria in our study group. Although the number of Candida species studied were limited, the present study highlights the increasing importance of candiduria in hospitalized patients with various risk factors which should not be ignored. Careful vigilance and monitoring of such cases is of utmost importance. Appropriate diagnosis of causative agent is essential as it impacts the therapy of these patients. Moreover, changing trend of Candida species towards non-albicans Candida species is being increasingly reported. Thus appropriate speciation of Candida is crucial for further management of these cases. This is necessary as the non-albicans Candida species such as C.glabrata and C.krusie are resistant to fluconazole which is commonly prescribed drug for the treatment.
CONCLUSION
Escherichia coli is the most frequent uropathogen isolated from nosocomial UTIs. Candida spp. are more common in patients admitted in hospital for prolonged periods in presence of other risk factors such as urinary catheterization, diabetes, previous surgeries, associated urinary tract abnormality and older age groups. Our study emphasizes the fact that there is a change in trend with shift towards non-albicans Candida spp. as the predominant pathogen causing nosocomial UTI which are more difficult to treat. Thus speciation should be performed for appropriate management of such patients.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed./
References:
REFERENCES
1. Taher MT, Golestanpour A. Symptomatic nosocomial urinary tract infections in ICU patients: identification of antimicrobial resistance pattern. Iranian journal of Clin Infect Dis 2009;4(1):25-29.
2. Kyschi MF, Namias N. Nosocomial urinary tract infection. Surg Clin N Am 2009; 89: 475- 481.
3. Maldonado SIC, Luna JAC. Nosocomial Urinary Tract Infections In: Dr. Ahmad Nikibaksh, editors. Clinical management of complicated urinary tract infection, Croatia: InTech Europe; 2011:225-238.
4. Khan BA, Saeed S, Akram A, Khan FB, Nasim A. Nosocomial uropathogens and their antibiotic sensitivity patterns in a tertiary referral teaching hospital in Rawalpindi, Pakistan. J Ayub Med Coll Abottabad 2010;22 (1):11-12.
5. Kauffman CA, Vazquez JA, Sobel JD, Gallis HA, McKinsey DS, Karchmer AW et al. Prospective multicenter surveillance study of funguria in hospitalized patients. Clin Infect Dis 2000;30:14-8.
6. Bukhary ZA. Candiduria: A review of clinical significance and management. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplant 2008;19(3):350-360.
7. Passos XS, Sales WS, Maciel PJ, Costa CR, Miranda KC,Lemos JA, et al. Candida colonization in intensive care unit patients’ urine. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2005;100(8):925-8.
8. Lundstrom T, Sobel J. Nosocomial candiduria: A review. Clin Infect Dis 2001; 32:1602-7.
9. Kauffman CA. Candiduria. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 41:S371-6.
10. Jain M, Dogra V, Mishra B, Thakur A, Loomba PS, Bhargava A. Candiduria in catheterized intensive care unit patients: Emerging microbiological trends. Indian J of Pathol Microbiol 2011;54(3):552-5.
11. Febré N, Silva V, Medeiros EAS, Wey SB, Colombo AL, Fischman O. Microbiological characteristics of yeasts isolated from urinary tracts of intensive care unit patients undergoing urinary catheterization. J Clin Microbiol 1999;37(5):1584-86.
12. Silva S, Negri M, Henriques M, Oliveira R, Williams D, Azeredo J. Silicone colonization by non-Candida albicans Candida species in the presence of urine. J Med Microbiol 2010;59: 747- 754.
13. Garner JS, Jarvis WR, Emori TG, Horan TC, Hughes JM. CDC definitions for nosocomial infections. In: Olmsted RN, ed.: APIC Infection Control and Applied Epidemiology: Principles and Practice. St. Louis: Mosby; 1996: pp. A1-20.
14. Guler S, Ural O, Findik D, Arslan U. Risk factors for nosocomial candiduria. Saudi Med J 2006; 27(11):1706-10.
15. Forbes BA, Sahm DF, Weissfeld AS. Baily and Scott’s Diagnostic Mirobiology. 10th Ed. Mosby Elsevier, Missouri, US 1998:842-856.
16. Chander J. Textbook of Medical Mycology, 3 rd Ed. Mehta publishers, New Delhi, India 2011: p278.
17. Kamat US, Fereirra A, Amonkar D, Motghare DD, Kulkarni MS. Epidemiology of hospital acquired urinary tract infections in a medical college hospital in Goa. Indian J of Urology 2009; 25(1):76-80.
18. Savas L, Guvel S, Onlen Y, Savas N, Duran N. Nosocomial urinary tract infections: microorganisms, antibiotic sensitivities and risk factors. West Indian med J 2006; 55(3):188- 93.
19. Sobel JD, Kauffman CA, McKinsey D, Zervos M, Vazquez JA, Karchmer AW et al. Candiduria: A Randomized, Double-Blind Study of Treatment with Fluconazole and Placebo. Clin Infect Dis 2000;30:19-24.
20. Paul N, Mathai E, Abraham OC, Mathai D. Emerging microbiological trends in candiduria. Clin Infect Dis 2004;39:1743-4.
21. Bose S, Ghosh AK, Barapatre R. The incidence of Candiduria in an ICU – A study. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research 2011; 5(2): 227-230.
22. Schaeffer AJ, Schaeffer EM. Infections of the Urinary Tract. In: Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, Peters CA editors. Campbell – Walsh Urology. 10th Ed. Vol 1. Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia, USA 2012. P. 257-327.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License