IJCRR - 6(13), July, 2014
Pages: 70-77
Date of Publication: 12-Jul-2014
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A SIMPLIFIED METHOD OF FAST TRACKING FMECA USING SMART SOFTWARE TOOL: A CASE STUDY
Author: Ahmed Tijjani Dahiru
Category: Technology
Abstract:Many approaches were modelled to achieve quality and reliability of manufactured goods and delivered services. Reliability Centred Maintenance RCM, Ishikawa Diagrams, Event Tree Analysis ETA, Fault Tree Analysis FTA, Failure Mode Effects and Criticality Analysis FMECA were few examples of risk mitigation and reliability enhancements. In this study FMECA as an appropriate tool for reliability modelling is justified based on prescriptions of modified Mil-Std-1629A enhanced by the opportunities of the newer standards such as BS-5760-5, IEC-60812, and SAE AIR-4845-93. This analysis use the electrical distribution network of Mallam Aminu Kano International Airport Nigeria as a case study, where the system is sub-divided into three major subsystems as 33kv substation, main control and standby units. The FMECA is performed at indenture level 3 where basic components and parts such as circuit breakers, transformers, generators, armoured cables, switch gears etc are located and failure modes being identified and analysed. For faster and easier implementation, software called ELECTRACE was developed and used for implementation as a result of the high prices at which commercial FMECA software are obtained. The developed ELECTRACE was used to implement FMECA by drawing out clear worksheets and plotting criticality matrix where failure modes are easily spotted and identified based on criticality rankings derived from classes of severity and frequencies of occurrence. Large number of failure modes in the case study was found to have concentrated within acceptable positions of low criticality ranks, with few falling within unacceptable positions of high criticality ranks. However, mitigating the few high criticality ranking failure modes exposes the lower criticality ranking failures as disturbing partly because of their high concentration. The developed ELECTRACE was very useful and effective in this analysis and is flexible enough to be applied for FMECA implementation in any electrical, electronic or mechanical systems operating in other sections of the airport such as navigational aids, airspace management, airways handling, meteorology, service stations and beyond.
Keywords: Reliability, FMECA, Electricity Distribution, Software, worksheets, criticality matrix
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Failure Mode Effects and Criticality Analysis (FMECA) has been a traditional and very popular method of risk assessments been developed and deployed in operations of various industries such as defence, automotive, space missions, manufacturing, processes etc. for achieving reliability and operational costs reduction. The effectiveness of FMECA was probably the reason behind its adoption and implementation for decades. Part of its successes was the standards, Mil-Std-1629, BS-5460-5, SAE AIR-4845-93, IEC-60812 etc. prepared to guide through its implementations. Evolutions in technology that gives rise to a more complex systems was a serious challenge to FMECA implementation which necessitated the developments and use of different tools for tracking up with those periodic changes. Although other risk assessment and reduction techniques exist, Fish Bone (Ishikawa) Diagram, Fault Tree Analysis (FTA), Reliability Centred Maintenance (RCM) etc. FMECA remains relevant for its simplicity and comprehension. The long time it takes FMECA to be used as an effective tool for risk mitigation, however were met with series of challenges among which are the laborious and the bulk of paper work involved, which call for many hands and time to prepare. This trend may not be acceptable to rapid changes experienced within the technology world. Introduction of software in the wake of ICT revolutions to facilitate FMECAs was a welcomed development. It was seen widely to address issues of labour involved and provide means of quicker implementation. There was a number of software commercially available, XFMEA, FAULTREE, FAILMODE, QUICKMODE. In general terms, the software eases and speeds up the FMECA processes. This is justified mostly in large systems that are critical to the economy and safety of lives, such as the electrical power systems as an airport facility.
THE CASE STUDY
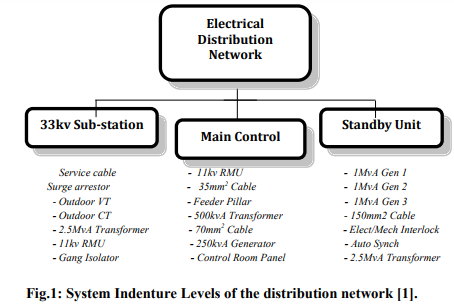
A FMECA was carried out on electrical distribution network of Mallam Aminu Kano International Airport (MAKIA), Nigeria’s Electrical Distribution Network [1]. The purpose was to highlight the frequency and severity implications of failures occurring in such a strategic section of the airport, looking at social, economic, security benefits derived. The large electrical distribution network’s data of the entire system when collected was classified into systems, sub-systems and modules to ensure the bottom-up approach of the systems’ analysis as illustrated in the hierarchical diagram shown in Fig. 1. The system’s hierarchical diagram is categorised vertically according to the functional sub-units and the components or parts, and horizontally according to the indenture levels 1, 2 and 3. With this every part or component can be easily reached, recorded and analysed. It is usual to find parts and components making up the distribution network to comprise of simple and complex, delicate and robust, cheap and expensive etc. such as single and multi-core cables, 5kVA and 1000kVA standby systems, fuses and circuit breakers, ring main units (RMUs) and cable lugs and contacts etc. Among the challenges one may experience during data collection is the large number of components and parts, the accessibility, as some equipments are live all the time and some are found hanging overheads and others buried underground.
The Cost Implications of Commercial Software
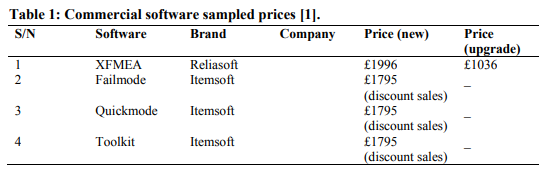
The traditional FMECA is known to be carried out involving a lot of paper work. The use of software facilitated FMECA in recent times reduced the need for the paper prints. Thus, the collected data, the Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) worksheets which always precede the FMECA [2] and the criticality matrix can be recorded, analysed, processed, presented and stored without need for prints. Shopping for the appropriate software for analysis of the mined data could somehow not be an easy task as the prices of the items were found to be high even at promotional rates, a summary shown in Table 1. The reviewed prices of the software could be attributed to the number of applications they contain, which for FMECA sake could be a waste and add to the complications of the software packages. Imagine a large team being expected to carry out a work in this case study in a more comprehensive manner, for example a 1000kVA standby to be taken as unit to be decomposed for FMECA. The cost of the software to be used will definitely be much higher. Since FMECA has been traditionally simple, the trend should be maintained using software or any other tools.
Development of ELECTRACE as Alternative
Objectives at this juncture should be directed at provision of simplified or smart software tool as an alternative to the high cost and complicated commercial software for purpose of carrying out FMECA with a speed and less stress at a reduced cost. The efforts here are to address costs and many other applications contributed complications of commercially available software. Two approaches were therefore explored for achieving this aim.
- Modifications of existing software to suit the present needs.
- Generate codes for developing the target software.
The first approach was proved to be most suitable for this purpose and Microsoft Office was used. The choice of Microsoft Office is influenced by its popularity, availability and low cost, which can be obtained as low as £79. Thus, Microsoft was adopted and deployed in the following manner.
- The FMEA worksheets were produced by modifications and manipulations of Microsoft Excel platform.
- The criticality matrix was produced by adding labels on XY scatter chart on Microsoft virtual basic
Since the software tool developed for this work is for tracing of failure modes in electrical systems, it is branded as ELECTRACE, having the unique features as follows;
- Easy access to the data stored.
- Easy trace of the information such as items’ description, failure modes, failure effect(s), frequency and severity values etc.
- Auto-sum or Auto-product of the data values.
- Direct reflection of changes on the criticality matrix when implemented on the FMEA worksheets.
- Comprehensive nature of the FMEA worksheets.
- Clear dashboard presentation of failure modes on criticality matrix based on failure modes’ criticality ranking
The Implementation of FMECA using ELECTRACE
The FMECA implementation can be simplified successfully using ELECTRACE. The worksheets and criticality matrix where predetermined for ELECTRACE to present results for analysis. The worksheets contain entries such as codes for identification of modules and analysis,
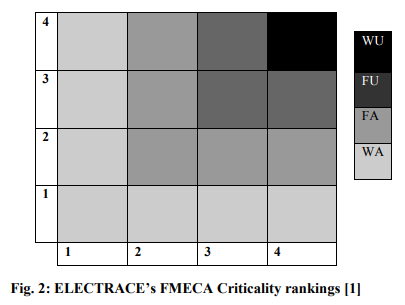
descriptions of the modules, function of the modules and their failure modes. The worksheets also contain local and system failure effects, the failure detection method and severity class of the failure modes. Loss frequency was derived from the products of base failure rates λb, environmental stress factors α, and duty stress factors were obtained from the US Army TM-5-698-5 [3] and Moss [2] respectively. The entries were based on modified Mil-Std-1629A standard [4]. The modifications of the Mil-Std-1629A were due to short comings of the Mil-Std-1629A for factors such as aging, which is addressed by newer standards such as BS-5760-5, IEC-60812, SAEAIR-4845-93 etc. [5] The criticality matrix is produced by ELECTRACE as a 4×4 matrix, upon which criticality ranking of all the failure modes are determined. With criticality matrix as a tool, failure modes are exposed based on criticality rankings, which may be used as a prompt for action towards mitigation. The criticality rankings in this regard are classified based on the frequency of occurrence from the data earlier obtained from case study and severity of occurrence according to the products of contributing factors’ indices. The classification of the criticality ranking thus goes as follows [1]; ? Widely Acceptable (WA): A band within which risks are tolerated and conveniently operated with. Risks within this band continue to exist because there cannot be 100% elimination of risks whatsoever. ? Fairly Acceptable (FA): The failure modes falling within this band are allowed without mitigation temporarily for period of time pending when opportunity comes up for the periodic and/or scheduled activities. It is important to note that ignoring failure modes within this criticality band for longer time may cause the failure modes to migrate to a band of higher criticality ranking. ? Fairly Unacceptable (FU): These ranks of failure modes cannot be accepted and calls for immediate action towards mitigation. This may however only affect part(s) involved, module or subsystem. Consequences could be losses due to downtime and minor injuries. ? Widely Unacceptable (WU): An emergency action need to be taken as failures within this band can cause loss to life, permanent injuries, colossal damages or loss of investments. This indicates zero tolerance to failure modes appearing on this band of ELECTRACE’s criticality matrix.
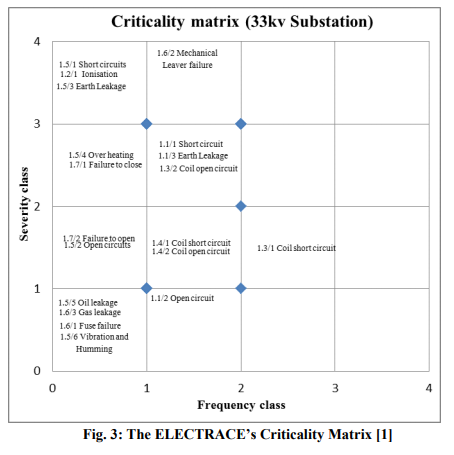
It is worthy of note that the software tool is easy to be used for implementation because its features are simple, clear and inexpensive. The four criticality bands also are easily interpreted and mastered. The implementation of FMECA for the case study using ELECTRACE was done with ease and speed as expected. It is usual to have the analysis in FMEA worksheets before the emergence of criticality matrix. The worksheets presented by ELECTRACE were comprehensive and changes can be implemented with high flexibility. The criticality matrix presents all the failure modes analysed by the worksheets, prioritising those with higher severities and frequencies of occurrence (fig. 3). The matrix at this stage can hence be used by design or maintenance engineers to take action towards mitigation against disturbing failure modes and continue to retain those with lower ranks. In events where higher ranked failure modes are mitigated, those with lower ranks are exposed more and remain the decision of the project team (design or maintenance).
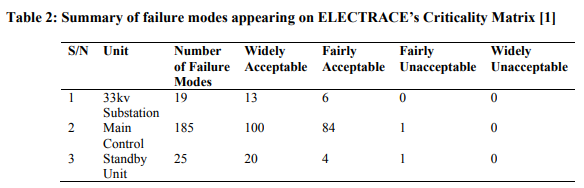
THE ELECTRACE’S FMECA RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
From the ELECTRACE’s criticality matrix, larger number of failure modes concentrates within WA bands of the three units (33kv substation, main control and standby units) of the distribution networks. The FA bands also contains fairly large number of failure modes, but the most interesting side of the analysis is only two failure modes appear at FU bands, with none appearing at WU band. Thus, mitigations at this instance are only two within unacceptable regions, although it may require scheduled action. This indicates largely a healthy situation at the distribution system, but an immediate actions need to be taken against 3.4/1 Short circuitand 2.7/1 Short circuit (not shown) appearing at FU band of the criticality matrix. Failure modes at FA band of the matrix such as 1.3/1 coil short circuit (shown in Fig. 3) could be given a softer mitigation handling, may be a planned preventive or opportunity maintenance. Other failure modes which are found at WA band could conveniently be tolerated. This could however be a factor of expertly managerial decision.
CONCLUSIONS
With ELECTRACE as a tool, a very complex system of electrical power distribution of an international airport can be analysed with greater speed and ease and at relatively lower cost. The application of ELECTRACE can be extended to other facilities within airport and beyond. The entire work carried out to in this study apart from data collection was done solo. Data collection was indeed tedious due to size of the distribution facilities. Being stranger to the network one may need engineers and technicians on ground for familiarisations towards the success of the data collection.. This indicates the effectiveness of the software used in this analysis. This implies that other facilities within or outside airports, simple or complex such as meteorology, navigational aids, service stations etc. can be analysed successfully with ELECTRACE, which was developed for this work. The large number of maintenance requirements in this analysis being exposed by ELECTRACE’s criticality matrix somehow appeared to be disturbing. Application of Reliability Centred Maintenance (RCM) could be a form of effective solution to the high maintenance demands in terms of cost due down time and logistics.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The author appreciates the contributions of Dr Chakib Kara-Zaitri and Mr Mukhtar I Bello of University of Bradford, United Kingdom for their guidance and support in the literature, data mining, software development etc. I as well acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The author is also grateful to authors to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Dahiru, A.T. (2013)“Development and Implementation of a Smart FMECA Software Tool for Electricity Distribution Networks” MSc thesis, School of Engineering Design and Technology, University of Bradford, Bradford,.
2. Andrews,J.D. and Moss, T.R. (2002). Reliability and Risk Assessment, 2nd ed. London: Professional Engineering Publishing Limited,.
3. Department of Army Headquarters, Washington DC. Technical Manual (2006, 22 Jul). Survey for Reliability and Availability Information for Power Distribution, Power Generation, And Heating and Ventilating and Air Conditioning (HVAC) Components for Commercial, Industrial And Utility Installation. [Online] Available: http://www.barringer1.com/mil_files/TM-5- 698-5.pdf [Accessed: 06 Jun 2012].
4. The United States Department of Defence, Military Standard: Procedure for Performing a Failure Mode Effect and Criticality Analysis. (1980, Nov 2). [Online]. Available: http://www.sre.org/Pubs/Mil-Std-1629A.pdf [Accessed: 31 Aug 2012].
5. Agarwala, A. S. (1990). Shortcomings of MilStd-1629A Guidelines for Criticality Analysis. Pp. 494-496, Available: IEEEXplore, DOI:0149 144X/90/0000-0494. [Accessed: 03 Sep 2012].
6. Kumamoto,H. and Henley, E.J. (1996).Probabilistic Risk Assessment and Management for Engineers and Scientists, 5th ed. New York: IEEE Press,
7. British Standard: Reliability of Systems, Equipment and Components – Part 5: Guide to Failure Modes Effects and Criticality Analysis (FMEA and FMECA), BS 5760-5 (1991).
8. Standard for Automotive Engineers, AIR4845. (1993).
9. International Standard: Analysis Techniques for System Reliability – Procedure for Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), IEC 60812. Second Edition (2006-1).
10. Microsoft Corporation. Article ID. 213750. (2013). How to use macro to add labels to data point in a xy scatter chart or in a bubble chart Excel.[Online]. Available: http://www.support.microsoft.com/kb/213750. [Accessed: 22 Jan 2013]
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License