IJCRR - 6(13), July, 2014
Pages: 15-23
Date of Publication: 12-Jul-2014
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A STUDY OF SHORT TERM PULMONARY REHABILITATION ON EXERCISE CAPACITY, FORCED VITAL CAPACITY AND QUALITY OF LIFE IN CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE
Author: Christian Preeti S.
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive disease characterized by airflow limitation / obstruction that is either not reversible or only partially reversible. Pulmonary rehabilitation is an accepted non-pharmacological intervention for individuals with COPD. But there is 'no consensus' regarding the most favorable duration of pulmonary rehabilitation for patients with COPD. Objective: To determine the effects of a short term Pulmonary Rehabilitation programme on exercise capacity, forced vital capacity and Quality of life in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Methods: 30 mild-moderate COPD patients, who fulfill inclusion and exclusion criteria, were given conventional physical therapy and aerobic training for 5 days per week and continued for 4 weeks. 6 min walk distance; Forced vital capacity (FVC) and chronic respiratory questionnaire (CRQs) were taken at baseline before and after completion of rehabilitation program as outcome measures. Results: Results show statistically significant difference in 6 min walk distance (6 MWD), Dyspnea, Fatigue (p< 0.05). But no significant difference was found in FVC, Emotion and Mastery Conclusion: Through the study it has been observed that 6 MWD and CRQs shows more improvement whereas FVC shows no much improvement after 4 week of rehabilitation program. Hence it has been concluded that short term pulmonary rehabilitation is an effective and economical method for improving the exercise capacity and Quality of life but not similarly effective for FVC in patients with COPD.
Keywords: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Pulmonary Rehabilitation, Chronic Respiratory Disease Questionnaire, Forced Vital Capacity, 6 Minute Walk Test.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
According to World Health Organization Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a lung disease characterized by chronic obstruction of lung airflow that interferes with normal breathing and is not fully reversible. COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death worldwide.1-5 the problem is seen mostly among older adults, the true age-specific prevalence will be much higher, especially in countries where cigarette smoking is common. India can be projected as a classical example with reference to the rising burden of chronic respiratory diseases accounting for 7% of all death.6 Presumably the inflammation caused by cigarette smoking interacts with other host or environmental factors to produce excess decline in lung function that results in COPD. It is believed that inhaled noxious particles and gases results in lung inflammation, induce tissue destruction, and impair defense mechanisms that serve to limit or repair this damage. 5.
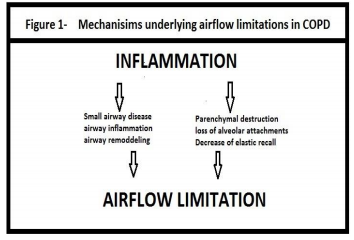
Since COPD includes irreversible obstruction and progressively decreased pulmonary function but Stopping exposure to these agents, even when significant airflow limitation is present, may result in some improvement in lung function and slow or even halt progression of the disease.5 None of the existing medication for COPD has been shown to modify the long-term decline in lung function. Therefore, pharmacotherapy for COPD is used only to decrease symptoms and complications. According to the Global initiative for chronic Obstructive Lung Disease recommendations, pulmonary rehabilitation is one of the main non?pharmacological treatment modalities. The rehabilitation program is provided by a multi-disciplinary team and typically consists of exercise, disease specific education, nutritional, psychological and social support.9, 10 There is strong evidence that pulmonary rehabilitation (PR) reduces symptoms, increases exercise tolerance and improves health-related quality of life in patients with COPD.11Updated clinical practice guidelines from the American College of Chest Physicians (2007) state that there is ‘no consensus’ regarding the most favorable duration of pulmonary rehabilitation for patients with COPD. However, the guidelines recommend programs of longer than 12 weeks in duration to better promote maintenance of benefits over time, but longer program must be weighed against the issues of hectic work schedule, adherence to the program and the potential for higher program costs.13It may encourage the irregularities in the treatment program, there have been a number of studies evaluating the effectiveness of short-term courses of pulmonary rehabilitation.7, 8, 9 With regard to cost and program duration, the study by Clini et al15 demonstrated that a short, intensive inpatient PR program, with up to 12 sessions held 5 days per week, led to comparable gains in exercise tolerance at a lower cost, compared to a longer outpatient program (exercise three times per week for ~8 weeks). Certainly, more research is required to determine the optimal duration of pulmonary rehabilitation for promotion of long-term exercise adherence and consequently, maintenance of outcomes. Hence there is a purpose and background for conducting the study.
MATERIALS AND METHODOLOGY
Study Design: Single group, pre test post test design Sample Design: Consecutive sampling Sample Size: 30 Patients Study Setting: Out Patient Department of Physiotherapy College Study Duration: 1 year (Dec 2011-Nov 2012)
Selection Criteria 12, 15, 17 Inclusion Criteria ? Mild to moderate COPD patients ? Those who can complete the 6 min walk test ? Age – 35 to 55 years ? Both male and female ? Patient who were willing to participate in the study Exclusion Criteria ? COPD with other cardiovascular disease ? COPD associated with other pulmonary disease ? COPD with musculoskeletal problems that would inhibit exercise ? COPD with neurological condition ? COPD patients with other systemic disorders. ? Current smokers ? Patients who had undergone any surgery in last one year ? Patients who had attended pulmonary rehabilitation within last 2 years
DATA COLLECTION PROCEDURE TOOLS
Cardiopulmonary assessment kit, Pen and Pencil, Evaluation form and CRQs sheet,Chairs with arm rests,Bathroom weighing scale,Stopwatch,10 meter Walkway,Treadmill,Disposable mouth piece for PFT and Nose clips,Schiller PC based spirometer
OUTCOME MEASURES
6 minute walk distance (6MWD) 12, 16 Forced vital capacity (FVC) 12, 14 Chronic Respiratory Disease Questionnaire (CRQ) 12, 14, 20
PROCEDURE
Consent to carry out the study was granted by the ethical committee and then baseline data including age, gender, BMI, admission diagnosis, PFT values, and chronic respiratory questionnaire were noted of those who fulfilled selection criteria.Informed consent was taken from patients before starting training. Standard care, as advised by the concerned physician, was strictly implemented throughout the intervention. Patients attended five days weekly with each session lasting for 45 minute / day for 4 weeks. Treatment was given in form of pursed lip breathing, thoracic mobility exercises for upper chest and side flexors of chest and treadmill walking for four weeks. Treadmill walking was started with warm up for 5 min and then after conditioning program was carried out for maximum 20 minutes. Treadmill walking speed was decided by calculating 80% of 6 minute walk test average speed. [6MWT average speed = (6MWT distance x 10) ÷ 1000 km / hr].21, 22, 24, 26, 27Conditioning program was followed by 5 minutes of cool down period. The session was terminated if patient complains about Fatigue, Headache, Confusion, Nausea, Severe dyspnea, Giddiness, Leg cramps or claudication.25, 26Out of 34 patients 4 have discontinued due to intolerance or some personal reasons. Results were compared and analyzed statistically for remaining 30 patients.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Mean and standard deviation were computed as measure of central tendency and measure of dispersion respectively. The intra group pre and post comparison of 6MWD and FVC were done by paired t- Test and intra group pre and post comparison of CRQs was done by Wilcoxon signed rank test. Differences were considered as significant at P< 0.05.
RESULTS AND INTERPRETATION
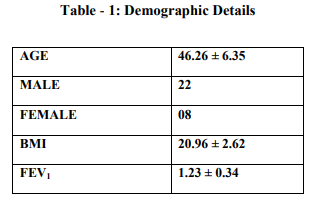
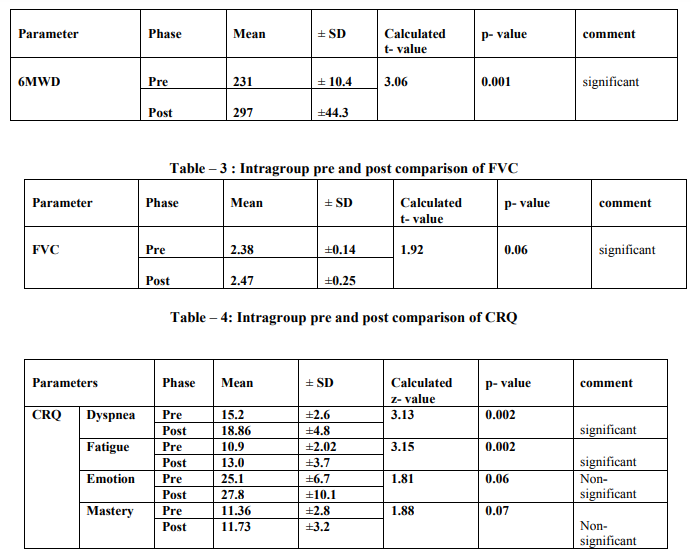
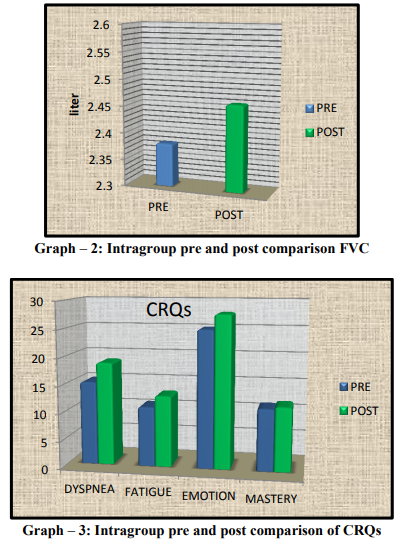
The rehabilitation group includes 30 patients. Patient’s characteristics are shown in Table 1. The mean and standard deviation before and after treatment was analyzed by using Paired t-test for values of 6MWD and FVC presented in Table 2 and Table 3 respectively.The mean and standard deviation of CRQs before and after treatment was analyzed by using Wilcoxon signed rank test presented in Table 4. Results show statistically significant difference in 6 min walk distance, Dyspnea, Fatigue (p<0.05). But no significant difference was found in FVC, Emotion and Mastery.All statistical analysis was done using Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS 16) for windows.
DISCUSSION
The present study was to determine the effect of a four week pulmonary rehabilitation program on exercise capacity, forced vital capacity and quality of life in mild to moderate COPD. Results showed improvement in exercise capacity, and reduced level of dyspnea and fatigue. Paired t-test was done for the values of 6 MWD before and after rehabilitation. For 6 MWD, p=0.001, which shows the statistically significant difference. The increase in FVC was improved but statistically insignificant in this study. According to Wilcoxon signed rank test for dyspnea and fatigue, p=0.002, which shows the significant difference. Results showed no improvement in emotion and mastery after rehabilitation. Patients with COPD often become homebound, isolated and depressed as they seek to avoid the dyspnea produced by everyday activities. It produces muscle weakness due to disuse and causes need for hyperventilation during exercise followed by dyspnea and fatigue.28, 29the present study shows that improvement in exercise capacity and reduced level of fatigue and dyspnea is due to lactic acidosis. When muscles move, even slightly, there is a greater accumulation of lactic acid in these types of patients. These lactic acids go to liver along with blood circulation and ultimately convert to glucose (Cori cycle), which provide energy for activities. Lactic acidosis, then, promotes healing and lowers the body's necessity for increased ventilation with exercise.30, 31 In COPD patients abnormal lung mechanics, impairment of gas exchange and destruction of the pulmonary vascular bed, directly impact the ability to sustain exercise. In many previous studies improvement in FEV1, FVC and SpO2 is controversial because in those studies only lower limb training was included which may not help to improve Spirometry values.23,31,32 But in this study the mean of functional vital capacity shows weak improvement before and after rehabilitation, it may be due to chest mobility exercise and pursed lip breathing. Chest mobility exercises affect the chest wall compliance and reduce chest wall stiffness. Donrawee Leelarungrayub had also suggested that thoracic mobility exercises are helpful for improving lung ventilation and gas exchange in COPD.18While pursed lip breathing reduces the respiratory rate and also produces positive back pressure of 5 cm H2O in mouth and hence prevent early collapse of the airway.15Hence it reduces dynamic hyper inflation which is another leading factor of exercise intolerance in the majority of COPD patients and also reduces the concurrent mechanical constrains on ventilation that contribute importantly to perceived respiratory discomfort and produce dyspnea. Zhonghuajie et. al. also suggested that pursed lip breathing can reduce respiratory rate and improve tidal volume in lung diseases.21 Assessment of quality of life showed improvement in dyspnea and fatigue but no improvement in emotion and mastery. It may be due to short duration of rehabilitation programme. Similar results were found in study of 3 week training programme done by Miyahara N et. al . 19 In summary, this study of 4 week pulmonary rehabilitation program shows improvement in 6MWD (an indicator of functional exercise capacity) and Quality of Life. These findings suggest that even if the program is of short term duration, it can still benefit patients with COPD. The increase in functional exercise capacity, even without an increase in maximal exercise capacity,will reduce dyspnea and improve endurance in patients with COPD. Limitations of the study are, the study was conducted on a smaller sample size, only mild to moderate COPD involved in the study, No follow up assessment was taken after 4 weeks and all the patients were not on same medication. Future research can be done in different subject groups with different age, different duration and on other respiratory disorders who require physical training.
CONCLUSION
Through the study it has been concluded that 6MWD and CRQs shows more improvement whereas FVC shows no much improvement after 4 week of rehabilitation program. Hence it has been declared that short term pulmonary rehabilitation is an effective and economical method for improving the exercise capacity and Quality of life but not similarly effective for FVC in patients with COPD.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
My most sincere thank to Dr E. Shanmugananth MPT cardio and respiratory diseases, Sr. lecturer, C. U. Shah Physiotherapy College, Surendranagar, for his keen interest shown in this research. I was also fortunate in having Dr. Gopal Nambi s, PT, PhD, Principal of C.U.Shah Physiotherapy college and Dr. R. Pravin Kumar MPT (Cardiorespiratory Conditions) Sr. lecturer, C. U. Shah Physiotherapy College, Surendranagar.I wish to express my gratitude to Mrs. Tintu Thomas, Lecturer cum Statistician and Dr.shashwatnagar, PSM (MD), C. U. Shah Medical College, Surendranagarfor their advice in statistical analysis and data presentation. I am very much grateful to my loving family members and friends for their interest in my academic excellence and also for their encouragement and support. I acknowledge the great help received from the scholars whose articles cited and included in references of this manuscript. I am also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. I am grateful to IJCRR editorial board members and IJCRR team of reviewers who have helped to bring quality to this manuscript.
References:
1. American Thoracic Society. Standards for the diagnosis and care of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J RespirCrit Care Med 1995; 152:77-121.
2. British Thoracic Society. Guidelines for the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax 1997; 52: 1-28.
3. Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis management and prevention of chronic obstructive lung disease. NIH Publication2001;2701:1-100.
4. Siafakas NM, Vermeire P, Pride NB. Optimal assessment and management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The European RespiratorForce. EurRespir J 1995; 8: 1398-1420.
5. Guidelines for Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) in India: A Guide for Physicians.Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci 2004; 46: 137-153.
6. K.J.R. Murthy, J.G. Sastry. Economic burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Burden of Disease in India 2012;234-275.
7. Votto J, Bowen J, Scalise P. Short stay comprehensive inpatient pulmonary rehabilitation for advanced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1996; 77:1115-1118.
8. Von Leupoldt A, Hahn E, Taube K, Schubert Heukeshoven S, Magnussen H, Dahme B.Effects of 3-week outpatients pulmonary rehabilitation on exercise capacity, dyspnea, and quality of life in COPD. Lung 2008; 186(6):387-91.
9. Skumlien S, Skogedal EA, Bjortuft O. Four weeks intensive rehabilitation generates significant health effects in COPD patients. Chronic Respiratory Disease 2007; 2:5-13.
10. Elpern EH, Stevens D, Kesten S. Variability in performance of timed walk tests in pulmonary rehabilitation programs. Chest 2000; 118: 98–105.
11. Carolyn L. Rochester, MD. Exercise training in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development 2003; 40(5):5980.
12. Nobuaki Miyahara,Ryosuke EDA,hiroyasutakeyama,Naomi kunichika,michihikomoriyama,keisukeaoe et al.Effect of short term pulmonary rehabilitation on exercise capacity and quality of life in participant with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Acta Med Okayama 2000;54(4):179-184
13. Pitta F, Troosters T, Probst VS. Are patients with COPD more active after pulmonary rehabilitation? Chest 2008; 134(2): 273-280
14. EinarHaave, Michael E Hyland, HaraldEngvik. Improvements in exercise capacity during a 4-weeks pulmonary rehabilitation program for COPD patients do not correspond with improvements in selfreported health status or quality of life. International Journal of COPD 2007;2(3): 355–359
15. Brenda O’Neill, Anne Marie,McKevitt, Sara Rafferty, Judy M Bradley,Doreen Johnston et al. A Comparison of Twice- Versus OnceWeekly Supervision during Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Chest 2002; 121:1085- 1091.
16. Hatem FS Al Ameri. Six minute walk test in respiratory diseases: A university hospital experience.Thoracic medicine 10.4103/1817- 1737.25865.
17. R H Green, S J Singh, J Williams, M D L Morgan. A randomised controlled trial of four weeks versus seven weeks of pulmonary rehabilitation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax 2001; 56:143– 145.
18. DonraweeLeelarungrayub. Chest Mobilization Techniques for Improving Ventilation and Gas Exchange in Chronic Lung Disease. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Current Concepts and Practice 2000; 13:410-411.
19. Fuchs-Climent D, Le Gallais D, Varray A, Desplan J, Cadopi M, Préfaut C.Quality of life and exercise tolerance in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: effects of a short and intensive inparticipant rehabilitation program. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1999; 78(4):330-5.
20. Gordon H Guyatt, Leslie B Berman, Marie Townsend. A measure of quality of life for clinical trials in chronic lung disease. Thorax 1987; 42:773-778.
21. Aeholland, knapman, DjBrazzale, Cj Hill, I Glaspole, N Goh, et al. Exercise prescription from 6-minute walk test achieves the suggested training intensity in interstitial lung disease. Austin Health, VIC 3084.
22. J.Alison. The validity of field walking tests in prescribing lower limb exercise intensity in clinical rehabilitation for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Australian New Zealand clinical trial registry 2012; 12609000439246.
23. Guyatt, G.H., L.B. Berman, M. Townsend. Long-term outcome after respiratory rehabilitation. CMAJ 1987; 137:1089-1095.
24. Zainuldin R,mackoy MG,Alison JA. Prescription of walking exercise intensity from the incremental shuttle walk test in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2012; 91:00- 00.
25. David C. Nieman. Fitness and Sports Medicine- A Health Related Approach. Mayfield Publishing Company 1995.
26. CorlnyKisner, Lynn Allen Colby. Therapeutics Exercise: Foundation and Techniques. 4th Ed. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers, Medical Publishers 2002; 150-165.
27. The Australian Lung Foundation and Australian Physiotherapy Association.August 2009.
28. Troosters T, Gosselink R, Decramer M. Short- and long-term effects of outpatient rehabilitations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomized trial. Am J Med 2000; 109:207-212.
29. Russell S. Richardson. Skeletal muscle dysfunction vs muscle disuse in patients with COPD.J App Physio 1999;86:1751-1752.
30. Christine Cadena. COPD: Rehab Therapy Improves Lactic Acid and Improves Exercise and Mobility. An Overview of the Impact of Therapy2007; 45-58.
31. Carter R, Nicotra B, Clark L. Exercise conditioning in the rehabilitation of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1988; 69: 118-122.
32. Ries AL,Kaplan RM, Limberg TM, Lela M. Prewitt. Effects of pulmonary rehabilitation on physiologic and psychosocial outcomes in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann Intern Med 1995; 122:823-832.
ABBREVIATIONS USED: COPD :
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease CRQ: Chronic Respiratory Disease Questionnaire FEV1:Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second FVC:Forced Vital Capacity PR:Pulmonary Rehabilitation 6MWD:6 Minute Walk Distance

|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License