IJCRR - 9(9), May, 2017
Pages: 20-25
Date of Publication: 15-May-2017
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Formation and Reversion of VBNC Cells of Salmonella Typhimurium Preincubated in Different Substrates
Author: Nadezhda Skorlupkina, L. Blinkova, Yu. Pakhomov, A. Piyadina, D. Chistaykova
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objectives: Salmonella is one of the main dangerous opportunistic microorganisms, and it can persist in viable but nonculturable (VBNC) state in different foodstuffs, water, human or animal organisms etc. Thus it is important to know more about this form of bacterial existence.
Methodology: In this study Salmonella Typhimurium 79 strain was used, in which RP4 plasmid was introduced. Prior to entering nonculturability inducing conditions cells of the strain were preincubated in one of the substrates that are typical sources of Salmonella contamination. Several additives and conditions were evaluated in order to revert nonculturable Salmonella into vegetative state.
Results: Influence of preincubation in different substrates on speed and totality of entry into nonculturable state was determined. It was shown that preincubation in soil had the greatest impact on the Salmonella population. Control population, preincubated in nutrient broth, was the slowest to enter nonculturable state. Tested reversion factors had effects at different concentrations. The most efficient, though the slowest, way to revert Salmonella was to incubate VBNC cells in 0.9% NaCl.
Conclusion: Obtained data reveal some reasons for strain differences in speed of formation of VBNC cells. Reversion was achieved using several supplements and conditions.
Keywords: Nonculturable, Factors, Opportunistic microorganisms
Full Text:
Introduction
The viable but nonculturable (VBNC) state is defined as a state in which microorganisms are metabolically active but lack the ability to reproduce on routine culture media after stress. (Oliver, 2005) If bacteria in VBNC state can revert to physiologic activity, they will be considered alive and will have metabolic activity. (Oliver, 2000; Pakhomov Yu, et al., 2016) Many bacteria, including human pathogens, can enter into the VBNC state in presence of unfavorable environmental conditions. (Roszak D. B. et al, 1984; Oliver J.D. 2010) Transition of pathogenic microorganisms into a resting state is one of the basic mechanisms permitting the preservation of an infectious causative agent in the environment during interepidemic seasons or maintaining endemic area. (Bukharin O.V. et al, 2005) Cells enter VBNC state as a response to some form of natural stress, such as starvation, incubation outside the temperature range of growth, elevated osmotic concentrations (seawater), reactive oxygen concentration, exposure to white or UV light (Oliver, 2005; Shenghua Zhang, 2015). Every factor shifts bacteria into VBNC state with different speed, intensity, and launches various genetic mechanisms. (Bukharin O.V. et al, 2005) It is important to learn how bacteria enter VBNC state in different nature objects.
Bacteria in VBNC state don’t reproduce on standard culture media (Oliver, 2010). It is the main problem in research – contamination of different objects, e.g. foodstuffs, drinking water, human clinical specimens, etc. with nonculturable bacteria.
Methodology
Strains and culture conditions
For experiments Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium 79 was used with a plasmid RP4 that has resistance genes for ampicillin, tetracycline and kanamycin. Microbe was precultured in 100 ml of nutrient broth with 100 µg/ml of ampicillin and 50 µg/ml of kanamycin for 24 hours twice and then a population was produced on the same medium for 20 hours. Samples of possible Salmonella sources were inoculated with this population in an amount of 1% of the medium. These samples were: wet soil (substrain S), tap water (W), fresh vegetable salad (cucumbers, tomatoes, black olives, bell pepper and sunflower oil; substrain V) and minced chicken (P). They were not sterilized in any way to keep them natural as much as possible. Fresh nutrient broth without antibiotics (C) was chosen as the control substrate. All the samples were incubated for 7 days. Incubation conditions were mimicked those of natural sources of Salmonella. Water and soil samples were stored at room temperature, foods – at 0°C in the refrigerator and control media – in thermostat at 37 °C. After incubation bacteria were isolated from samples on nutrient agar with the same amounts of antibiotics. Salmonella were transferred into 200 ml of commercial artificial sea water (ASW). This medium was purchased in a local aquarium store, prepared according to manufacturer’s instructions and sterilized for 15 minutes at 121°C. ASW’s flasks with Salmonella were incubated in stationary conditions at room temperature in the darkness. Samples were taken periodically and plated on nutrient agar without antibiotics and on nutrient agar diluted fivefold.
Reversion of nonculturable cells
For reversion Salmonella in VBNC state for 8 month (C) was used. Stimulating supplements were inulin (powder, "Ryazanskie Prostory", Russia), Helianthus tuberosus powder with 70% inulin content (powder, “Eco-Pro”, Russia), vitamin C (ascorbic acid) (injection 50mg/ml, “Escom”, Russia), vitamin PP (nicotinic acid) (injection 10mg/ml, “RENEWAL”, Russia) and blood-substitute Aminopeptid (liquid, “Samson-Med”, Russia). Every supplement was added to nutrient broth at different concentrations: for inulin or Helianthus tuberosus powder it was 0.1%, 1% or 10%; for vitamin C or vitamin PP it was 0.01%, 0.05% or 0.1%; for blood-substitute it was 5%, 10% or 20%. Control was inoculated in nutrient broth without any supplements. The samples with and without supplement were inoculated with 1% Salmonella culture from one. Then they were incubated for 48 hours in thermostat at 37 °C. Every 24 hours, tests were taken and bacterial VBNC state was analyzed. Also in order to revert cells of all substrains suspensions were serially diluted in 0.9% NaCl up to 10-8. Diluted populations were incubated for 96 hours. Samples were taken periodically for CFU/ml assessment.
Viability and culture ability assays
For every sample (the first or the second part) viability and culturability were monitored. Total cell counts (TCC) were performed in Goryaev-Thoma counting chamber. Portions of viable cells were assessed under a luminescence microscope (OPTON, 8×40-time magnification) after staining with Live\Dead® double staining kit (Baclight™). Bacteria were plated on nutrient agar, plates were incubated in thermostat at 37 °C for 24 hours and CFU/ml values were defined. The number of VBNC cells was calculated as difference between amounts of viable cells and CFU/ml.
Statistical Methods
The data was analyzed by parametric statistical methods.
Results
Initial cell concentrations for all populations were about 4×107 cells/ml. During first week CFU/ml value lowered by one order of magnitude for all samples except C. At this point the lowest index was observed for the sample W (Table 1). After 3 weeks of incubation the lowest CFU/ml value was noted for the sample P – 3 orders of magnitude lower than initial value. In other populations it dropped by 2 orders of magnitude. Sample showed C the highest CFU/ml value for the first 3 months of incubation After 9 weeks population S exhibited only singular colonies which means that it is almost totally nonculturable. After 3 months this substrain started exiting nonculturable state.
Viability was tested using a luminescence microscope. It was shown that cells retained their viability for at least 8 months. Total cell counts remained relatively constant throughout the entire observation period (Table 2). However it was noted that in all populations cells became smaller and fluorescence grew dimmer. (Fig. 1)
Since it was shown that some microorganisms are able to resuscitate from nonculturable state when stressful factor is withdrawn (Su C–P. et al. 2013) we tried to use normal saline (isotonic protein-free poor medium) to resuscitate our bacteria.
The following dynamics were noted for resuscitation of Salmonella in our experiment: after 6 hours there was no noticeable difference when compared to cells in artificial seawater. After 24 hours for samples C and S 2 orders of magnitude increase in culturability was noted (from 3.62±0.32x105 to 5.13±0.49x107 and from 3.72±0.34x103 to 3.12±0.29x105 respectively. For samples V and P difference was 1 order of magnitude from 1.6±0.15x106 to 1.7±0.15x107 and from 1.3±0.12x105 to 5.9±0.52x106 respectively. There was no noticeable increase for the sample W at this point (Table 3). After 48 hours CFU/ml value increased by 2 more orders of magnitude for C and V and by 3 more orders of magnitude for S, P and W. After 96 hours resuscitation process was completed. Increased CFU/ml values after resuscitation may be explained by some amount of cellular growth and division of resuscitated cells even in poor environment of normal saline. After incubation for 96 hours in normal saline cells regained bright fluorescence that was noted in the beginning of the experiment which means that their metabolism probably returned to normal state and DNA decondenced. It was also noted that cells of S variant did not divide as actively as the rest of studied variants. It should be noted that we incubated Salmonella as serial decimal dilutions up to 10-8 and noted active growth after 24 – 96 hours in samples from tubes that showed singular or no colonies when plated immediately after dilution. Therefore such increase in numbers of CFU/ml cannot be attributed to division of remaining culturable cells.
For reversion Salmonella of population C was used which had been in VBNC state for 8 months. The amount of live bacteria was initially 99%, the amount of bacteria in VBNC state was 97±2%.
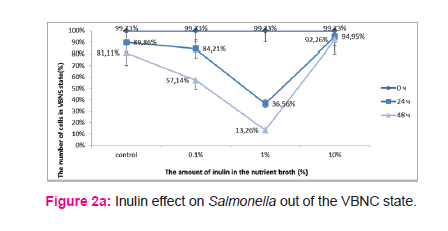
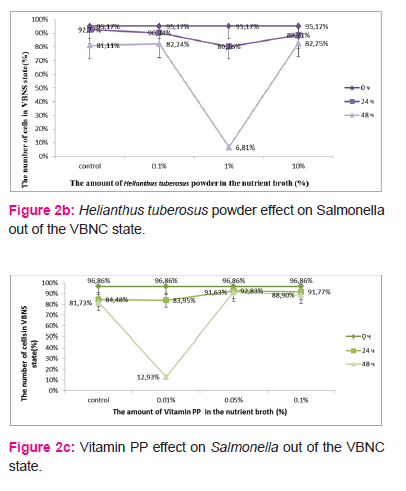
The content of inulin at 1% in nutrient broth Salmonella reversion appeared on the first day – 37% (CFU/ml - (1,7±0,21)x108, TCC/ml - (2,68±0,19)x108) cells in VBNC state, control – 90% (CFU/ml – (1,5±0,16)x107, TCC/ml - (1,48±0,11)x108 ). (Fig. 2, a) At 48 hours the number of bacteria in VBNC state was decreased to 13% (CFU/ml – (1,7±0,26)x109, TCC -(1,96±0,13)x109), control – 80% (CFU/ml – (1,6±0,68)x108, TCC/ml - (8,6±0,57)x108). At other concentrations significant differences were not observed. The content of 1% Helianthus tuberosus powder in nutrient broth Salmonella reversion was registered only on the second day (48 hours) – 7% (CFU/ml - (4,1±0,87)x109, TCC/ml - (4,4±0,31)x109) cells in VBNC state, control – 81% (CFU/ml - (3,4±0,43)x108, TCC/ml - (1,8±0,13)x109 ). (Fig. 2, b) At other concentrations significant differences were not observed. The content of 0.01% vitamin PP in nutrient broth Salmonella reversion was happened on the second day (48 hours) – 13% (CFU/ml - (1,01±0,15)x109, TCC/ml - (1,16±0,1)x109) cells in VBNC state, control – 82% (CFU/ml - (2,01±0,29)x108, TCC/ml - (1,1±0,1)x109). (Fig. 2, c) At other concentrations significant differences were not observed. At all concentrations vitamin C or blood-substitute Aminopeptid positive effect was not found for Salmonella reversion of the VBNC state in the vegetative cells. (Fig. 2, d)
Discussion
Obtained data suggest that preincubation of S. enterica Typhimurium 79 in different substrates before entry into stressful environment influences its speed of entry into nonculturable state. Preincubation in soil had the biggest influence on the microorganism. However, with time bacteria adapted to the stressful environment of the artificial seawater and numbers of CFU/ml stabilized. Sample S exhibited the least CFU/ml value in the second half of the incubation period. At the same time sample C incubated in rich optimal environment of nutrient broth had the highest culturability for the first three months. These differences caused by environmental conditioning in our opinion shed some light on question why there is a strain difference in speed and sometimes even possibility of entry into nonculturable state (Chaveerach P., 2003, Masuda Y., 2004).
We believe that after three months of incubation in artificial seawater there was some adaptation to the osmotic stress and numbers of CFU/ml somewhat stabilized and never dropped below 4.5?104 except for the sample S. Incubation in stressful conditions without aeration did not result in notable cell death. This is an expected result since oxidative stress is one of the major factors that promote entry into nonculturable state (Kong I.–S. et al., 2004).
Dwarfing of bacterial cells is one of the properties of nonculturable cells (Oliver J.D. 2010) and dimming of fluorescence may be due to slowed metabolism and condensing of cell DNA which makes it less available for DNA binding dyes.
In our experiments we observed some spontaneous resuscitation of bacterial cells. This phenomenon is most clearly visible for the sample S. This is probably due to presence of some stimulating agents from a minute portion of lyzed cells or cell adaptation to stressful environment.
After removing osmotic stress, we observed complete resuscitation in all sample populations. Increased CFU/ml values after resuscitation (compared to total viable counts in flasks with artificial seawater) may be explained by some amount of cellular growth and division of resuscitated cells even in poor environment of normal saline. After incubation for 96 hours in normal saline cells regained fluorescence as bright as that was noted in the beginning of the experiment which means that their metabolism probably returned to normal state and DNA decondenced. It was also noted that cells of S variant did not divide as actively as the rest of studied variants and the control population was the most active. It should be mentioned that we incubated Salmonella in normal saline as serial decimal dilutions of artificial seawater up to 10-8 and noted high CFU counts after 24 – 96 hours in aliquots from tubes that showed singular or no colonies when plated immediately after dilution. Therefore, such increase in numbers of CFU/ml cannot be attributed to division of remaining culturable cells.
Helianthus tuberosus powder or inulin at 1%, and 0.01% nicotinic acid in nutrient broth significantly accelerated the reversion of Salmonella from VBNC into active state. Probably small concentrations are insufficient to produce a positive effect, but large doses may manifest the inhibitory effect. During incubation with different concentrations of blood-substitute Aminopeptid or ascorbic acid we did not observe positive effect of the reversion of VBNC into active state. Perhaps Salmonella in VBNC state is not sensitive to these agents, or the factors’ concentrations were not optimal. The next problem is to optimize the amount of inulin or nicotinic acid by which better and faster reversion is promoted. Helianthus tuberosus powder is unsuitable for experimental work.
Conclusion
Thus it was established that preincubation in different substrates influenced speed of formation of nonculturable cells which may be one of the reasons for strain differences in this process. Also reversion of nonculturable cells was achieved using different supplements and conditions.
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Source of Funding
None declared
Conflict of interest
None declared

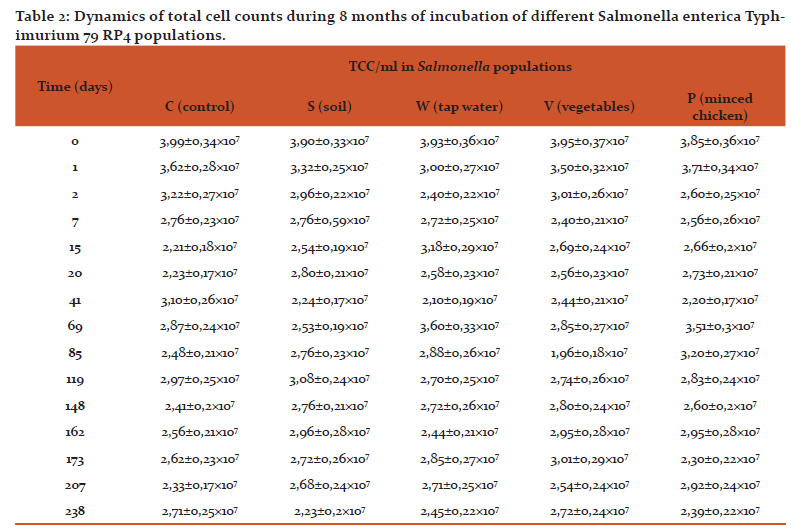
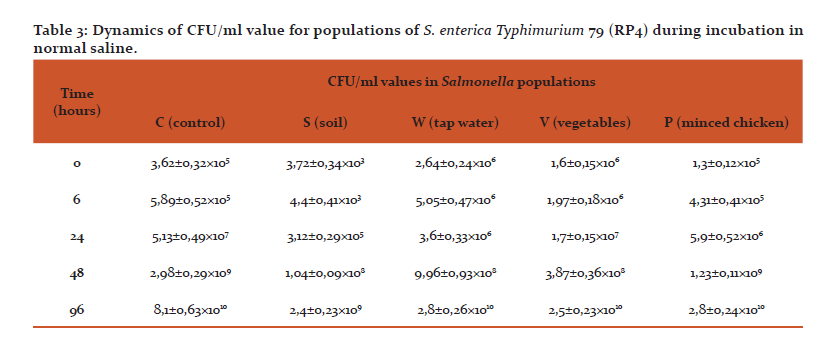
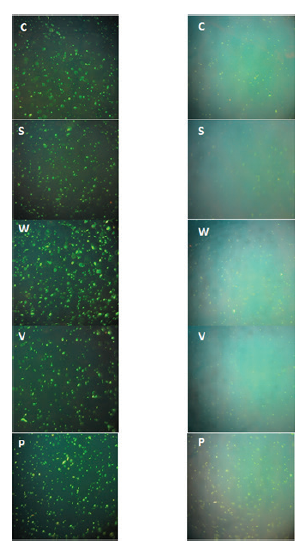
Fig. 1. Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium 79 cells. Left column – cells at the first day of incubation, Right column – cells after 8 months.

References:
- Bukharin O.V., Gintsburg A.L., Romanova Y.M., El-Registan G.L. Mechanisms of survival bacteria. Moscow: Medicina, 2005; 367p (in russian).
- Chaveerach P., A. A. H. M. ter Huurne, L. J. A. Lipman, and F. van Knapen Survival and resuscitation of ten strains of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli under acid Conditions Appl and Environ Microbiol, 2003; Vol 69, ? 1: 711–714
- Kong I.–S., A. Hülsmann, T.C. Bates, J.D. Oliver. The role of reactive oxygen species in the viable but nonculturable state in Vibrio vulnificus. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004; Vol. 50: 133–142.
- Masuda Y. Resuscitation of Tenacibaculum sp., the causative bacterium of spotting disease of sea urchin Strongylocentroutus intermedius from viable but non–culturable state. / Y. Masuda, K. Tajima, Y. Ezura Y. // Fisheries Science. 2004; Vol. 70(2): 277–284.
- Oliver, J.D. The public health significance of viable but nonculturable bacteria, In R.R. Colwell and D.J. Grimes (eds.), Nonculturable Microorganisms in the Environment. American Society for Microbiology Press, Washington, D.C.;2000: 277-299.
- Oliver, J. D. The viable but nonculturable state in bacteria. J. Microbiol.2005;43: 93–100
- Oliver J.D. Recent findings on the viable but nonculturable state in pathogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbial Rev. 2010. Vol. 34(4), P. 415–425.
- Pakhomov Yu.D., L.P. Blinkova, O.V. Dmitrieva, O.S. Berdyugina, N.N. Skorlupkina Resuscitating factors for nonculturable cells. Psysical chemistry for the chemical and biochemical sciences, April 2016; 335-342
- Roszak, D. B., Grimes, D. J., & Colwell, R. R. Viable but nonrecoverable stage of Salmonella enteritidis in aquatic systems. Canadian journal of microbiology, 1984; 30(3): 334-338.
- Shenghua Zhang, Chengsong Ye, Huirong Lin, Lu Lv, and Xin Yu*. UV Disinfection Induces a VBNC State in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015; 49(3): 1721-1728
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License