IJCRR - 9(9), May, 2017
Pages: 09-13
Date of Publication: 23-May-2017
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Elucidation of the role of the minC gene in filament formation by Listeria monocytogenes under stress conditions
Author: Satyajit B. Kale, Swapnil P. Doijad, Krupali V. Poharkar, Sandeep Garg, Ajay D. Pathak, Abhay V. Raorane, Deepak B. Rawool, Nitin V. Kurkure, Sukhadeo B. Barbuddhe
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Aim: The study was conducted to understand structural changes in cell morphology of stress tolerant Listeria monocytogenes strains after exposure to the different food related stresses and to investigate the involvement of the minC gene in filament formation under stress as a putative mechanism. Methods: Morphological changes in L. monocytogenes were studied under the stresses of high salt concentration (12.5%), extreme pH (4.5 and 9.0) and low temperature (4\?C). The structural changes were recorded employing light and electron microscopy. The expression of the minC gene under stress was studied by qPCR. Results: Long filament formations were observed under salt stress, while, no structural changes could be observed for isolates grown in extreme pH and low temperature stresses. Scanning electron microscopic studies showed 3-10 times elongation of cells under stress which got reverted to normal size after removal of stress. Interestingly, it was noted that with the increase in stress, rod shaped cells became elongated. Six to 11 fold expression of the minC gene was observed under high salt stress. Conclusion: The results suggested that the filament formation could be one of the mechanisms by bacteria to tolerate high salt stress. It also supported the hypothesis that the minC gene over-expression could be the factor behind filamentous morphology
Keywords: Listeria mnocytogenes, Serogroups, Tolerance, Salt, minC, Morphology
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION Listeria monocytogenes is one of the 17 species of genus Listeria and is the cause of listeriosis in humans as well as in animals. It is an emerging foodborne pathogen with 20-30% case fatality rate, 50% neonatal death rate and 91% hospitalization rate (Sartor et al., 2015). Industrially processed and refrigerated foods revealed to be frequently linked to L. monocytogenes outbreaks than raw foods (Gianfranceschi et al., 2002). The pathogen has unique capabilities such as tolerance to high salt concentrations (> 10%) (Farber et al., 1992; Liu et al., 2005; Shabala et al., 2008), low temperature (down to 0°C) and diverse pH (pH 4.5 to 9.5) (Buchanan et al., 2004; Gandhi and Chikindas, 2007). Formation of filament (elongation of bacterial cell) is one of the stress responses under sublethal stresses (Giotis et al., 2007; Jones et al., 2013). This filament formation ability have been observed in L. monocytogenes under different stresses including high osmotic stress, low temperature, acidic and alkaline stresses (Bereksi et al., 2002; Giotis et al., 2007; Vail et al.,2012; Isom et al., 1995). The mechanism behind the filament formation under stresses has been studied in Gram negative bacteria, however, studies are largely lacking in Gram positive bacteria (Jones et al., 2013). It has been opined that when filamentous cells are exposed to more favorable growth conditions, there is rapid division of filaments into a number of individual cells (Giotis et al., 2007) which may pose major implications for the food industry.
The potential numbers of viable bacteria maybe underestimated and may exceed tolerated levels in foods when filamentous cells that are subjected to sub lethal stress conditions (Jones et al., 2013). The formation of FtsZ septal ring, positioning of the ring, maturation of the ring and then cell division are key stages in bacterial cell division (Scheffers, 2008). This septal ring positioning which is controlled by two different systems namely Min system and nucleoid occlusion need to be on right place and on right time (Scheffers, 2008). The Min system prevents cell division at cell poles in which MinC and MinD proteins form an inhibitor which is topologically regulated by DivIVA (Rothfield et al., 2005). The MinC inhibits FtsZ ring formation at poles result of this is septation permitted at middle position of cell and other possible sites of cell division are blocked (Rothfield et al., 2005). Studies in Bacillus subtilis have shown that effect of MinC on FtsZ to be pH dependant (Scheffers. 2008). Therefore, it is hypothesized that under stressed environmental conditions the minC gene is over-expressed and inhibits the FtsZ ring formation at all possible sites which ultimately inhibits the septa formation in L. monocytogenes (Scheffers. 2008). Indian Listeria Culture Collection (ILCC) has a large collection of strains of Listeria isolated from various sources and diverse geographical areas of India.
The collection has been screened previously for various stress responses and diversity. The objective of this study was to investigate the nature and dynamics of sublethal changes induced by stresses in high stress tolerant strains using scanning electron microscopy and to elucidate the role of the minC gene in L. monocytogenes under stressed conditions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS Listeria monocytogenes strains Listeria monocytogenes strains (n=13) were selected from the Indian Listeria Culture Collection (ILCC) based on their tolerance to high salt, low temperature, low pH and high pH. The strains were characterized previously biochemically and for their serogroups (Doumith et al., 2004). All the strains were maintained at -80°C in brain heart infusion (BHI) broth (Himedia, India) with 15% sterile glycerol (v/v) (Himedia, India). Determination of morphological changes under stress The strains with the highest stress tolerance (high salt, low temperature, low pH and high pH) were selected to detemine the morphological changes under particular stressed environmental conditions. In brief, to determine the morphological changes by high salt stress, 16-18 h grown culture in BHI broth (2 ml) in 12.5% NaCl were centrifuged, washed twice with PBS to remove media particles, resuspended in 2 ml of PBS and a loopful of culture was taken on glass slide.
The culture was stained by Gram staining and observed under compound microscope. Morphological changes were determined for strains in similar way after growth at different stresses of pH (4.5 and 9.0) and low temperature (4o C). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) Strains exhibiting high tolerance for each of stresses (high salt concentration 12.5%, low temperature (4o C) and extreme pH of 4.5 and pH 9.5) were analysed for morphological changes using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Bacterial strains were incubated in BHI broth (2 ml) under respective stress conditions. After 16-18 h, cell growth was harvested, washed twice with PBS, re-suspended in 2 ml of PBS and a loopful of culture was taken on cover slip and allowed to air dry. After air drying, the smear was fixed with 2.5% of glutaraldehyde for overnight and then dehydrated via successive passages of 10 minutes through 30%, 50%, 75%, 85%, 90%, 95% and 100% of ethanol.
This preparation was then allowed to air dry and then sputter-coated with gold. The gold coated smears were examined by scanning electron microscope (EVO 18, Carl Zeiss, Germany). Determination of genetic basis of filament formation The minC gene in L. monocytogenes was detected by PCR in all the stress tolerant strains (n=13). The primers for amplification of the minC gene were designed using Primer 3 (ver. 4.0) software. Fifty microlitre reaction mixture consisting of 55 ng of bacterial genomic DNA, 15 pmol of each primer (F: 5’-AGA ACT AAC TCA ATT GCT TGC AG 3’ and R: 5’CAA ATC TGT TTC AGT GAC CTC TTT-3’), 25 µl of 2X PCR master-mix (Sigma, USA). The reaction was performed in an thermal cycler (Eppendorf, Germany) with initial denaturation at 95o C, 5.0 min; denaturation 95o C, 45 s; annealing 51o C, 30 s; and extension 72o C, 1 min. (35 cycles); final extension at 72o C, 10 min. PCR products were analyzed by electrophoresis in 1% agarose gels and visualized under G:Box gel documentation system (Syngene).
Relative gene expression of the minC gene under high salt concentration The actual effect of salt stress on the minC gene expression was determined by qRT-PCR. The strains that formed filaments under salt stress were selected for the study. After growing the strains at mid-exponential phase under salt stress, RNA was isolated by using TRIzol reagent (Ambion, USA) following the manufacturers instruction. RNA yield was determined using the NanoDrop ND-1000 instrument (Thermo Scientific, USA) and RNA quality were checked by resolving it on 1.5% agarose gel. The cDNA synthesis was performed using SuperScript III First-Strand Synthesis SuperMix for qRT-PCR (Invitrogen, USA). Two hundred ng of total RNA were converted into cDNA in 20 µL according to manufacturer’s protocol. The contamination of residual of DNA was checked in each RNA sample by a control reaction which includes a cDNA synthesis without reverse transcriptase enzyme (no RT control).
The primers used in this reaction (Table 1) were designed by using Primer 3 software and optimized to achieve specific target gene amplification (product with a single melting peak). Quantitative-Real Time PCR mixture was prepared by using 10µL of 2x SYBR green master mix (Sigma, USA), 0.5 µL (10 nMol) of each forward and reverse primers 1µL of template cDNA and 8 µL of nuclease free water making volume to 20µL. As negative controls, water (no template) and the no RT control were applied. The reaction was performed in Light Cycler 96 (Roche, Switzerland). The reaction conditions were pre-incubation at 95o C for 10 min, then 40 cycles (95o C for 10s; 56o C for 20s and 72o C for 20s) followed by melting curve (65-97o C at 2.2o C/s and a continuous fluorescent measurement) and cooling.
The expression of minC gene was normalized against expression of reference 23s rRNA gene (Romanova et al., 2006). The transcript levels of the minC gene were determined in strain exposed to high salt stress as well as optimal (no salt stress control) conditions. The fold induction of the minC transcript in response of high salt stress was calculated relative to optimal conditions transcript level.
RESULTS Determination of morphological changes under stress Long filament formations were observed under salt stress (Fig. 1a and 1b), while, no structural changes could be observed for isolates grown under pH and temperature stresses. Therefore, effect on morphology under salt stress was further studied for longer time (till 72 h). With the increase in time, there was an increase in the length of filament (Fig. 1c). Compared to control, cells were present singularly (Fig. 1a) and few elongated cells were observed.
Therefore, it appeared that under stress conditions there could be inhibition of cell division. To verify this phenomenon, the bacteria grown under salt stress (BHI with 12.5% of NaCl) were transferred to normal BHI broth and incubated for 2 h and observed for cell morphology. Interestingly, all the cells were observed to occur singularly (Fig.1d) as observed in control. Scanning electron microscopy Scanning electron microscopic studies showed 3-10 times elongation of cells under stress which got reverted to normal size after removal of stress. The length of the cell found to be increased (8.45 µm) (Fig. 2a) as compared to control (1.53µm) (Fig. 2b) under high salt stress. Under pH and low temperature stresses, there were no significant changes observed in morphology. The length of filament under high salt stress was observed to be increased (13.84 µm, 14.16 µm, 16.03 µm) (Fig. 2c and 2d) with the longer time of incubation up to 48 h to 72 h indicating a positive correlation (R²=0.9145) with filament formation with stress duration.
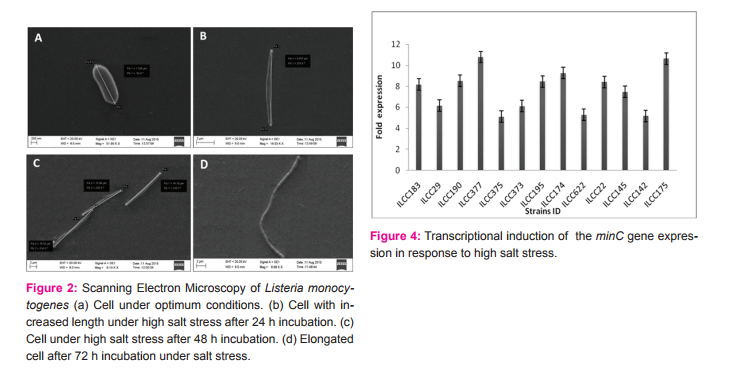
Determination of genetic basis of filament formation under high salt stress The minC gene in L. monocytogenes was detected by PCR. All the 13 salt stress tolerant strains studied showed the presence of 475 bp band of the minC gene (Fig 3). The induction of the minC gene transcription level under high salt stress was examined by qPCR. All tested 13 strains showed the 6 to 11 fold expression of the minC gene under high salt stress (Fig. 4), suggesting the possible involvement of the minC gene in altered morphology with filamentous structure in L. monocytogenes under high salt stress.
DISCUSSION The filament formation ability have been observed previously in L. monocytogenes under different stresses by different researchers including high osmotic stress, low temperature stress, acidic stress and alkaline stress (Bereksi et al., 2002; Giotis et al., 2007; Vail et al., 2012). It had been observed that as stress increased filamentation also increased (Giotis et al. 2007). These morphological changes under stress might infer that filament formation under stressed environmental conditions could be the one of the mechanisms of stress tolerance in L. monocytogenes. Changes in morphology of L. monocytogenes were observed after osmotic shifts. There was increase in length of the filament as with longer incubation (72 h). The bacteria regained normal size after removal of stress. This type of phenomenon was also observed earlier (Pratt et al., 2012). When it comes to the food processing and/or food preservation by using high salt bacteria which forms the filaments under stress could be the problem.
Since after exposure to the less stressed conditions filamentous cells immediately divides in individual cells, ultimately there is an increase in the number of bacteria in the food (Bereksi et al., 2002; Jones et al., 2002). The formation of filamentous cells leads to forming a single colony on solid media. This may results in a false estimation of bacteria in particular food product by cultural methods and false readings in predictive models for growth kinetics of bacteria based on CFU methods (Giotis et al., 2007) significantly increasing the risk to consumers. Though filament formation under stress has been observed in L. monocytogenes, however, studies are largely lacking (Jones et al., 2013). L. monocytogenes is normally exposed to various stresses during food processing and disinfection procedures which could influence its response and ability to persist in these environments, and thus contribute to defining conditions for better control in food processing plants (Magalhaes et al., 2016).
There was over-expression of the minC gene observed in strain with the filamentous morphology under high salt stress. It supported the hypothesis that the minC gene overexpression could be the factor behind filamentous morphology of L. monocytogenes under high salt stress and forming a filament could be the one of the mechanisms by bacteria to tolerate high salt stress. As it was preliminary study performed by taking single test strain, it would be more evident after testing more number of strains with filament forming ability for same hypothesis.
CONCLUSION It is concluded that the filament formation under stressed environmental conditions could be the one of the mechanisms of stress tolerance in L. monocytogenes as evidenced by morphological analysis of strains under stress. This study is a significant step towards dissecting the stress response of L. monocytogenes to the molecular events. Further investigations are required at molecular level to understand mechanism of filament formation, this will help towards better understanding of growth and survival properties of these filament and improvements in safety and risk assessment of food products.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. The research work is supported by grants from the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India (BT/01/CEIB/11/VI/13) to SBB and NVK. Source of Funding The Department of Biotechnology, Government of India to SBB and NVK. Conflict of interests None to declare.

References:
1. Bereksi N, Gavini F, Bénézech T, Faille C.. Growth, morphology and surface properties of Listeria monocytogenes Scott A and LO28 under saline and acid environments. J Appl Microbiol 2002; 92: 556–565.
2. Buchanan R, Lindqvist R, Ross T, Smith M, Todd E, Whiting R.. Risk assessment of Listeria monocytogenes in ready-to-eat foods. Microbiological Risk Assessment Series, 4. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 2004.
3. Doumith M, Buchrieser C, Glaser P, Jacquet C, Martin P. Differentiation of the major Listeria monocytogenes serovars by multiplex PCR. J Clin Microbiol 2004; 42: 3819-3822.
4. Farber JM, Coates F, Daley E. Minimum water activity requirements of the growth of Listeria monocytogenes. Lett Appl Microbiol 1992;15:103-105.
5. Gandhi M & Chikindas M L.. Listeria: a foodborne pathogen that knows how to survive. Int J Food Microbiol 2007;113:1–15.
6. Gianfranceschi M, Gattuso A, Tartaro S, Aureli P. Incidence of Listeria monocytogenes in food and environmental samples in Italy between 1990 and 1999: Serotype distribution in food, environmental and clinical samples. Eur J Epidemiol 2002;18: 1001–1006.
7. Giotis E S, Blair IS, McDowell DA. Morphological changes in Listeria monocytogenes subjected to sublethal alkaline stress. Int J food Microbol 2007;120:250–258.
8. Isom L L, Khambatta ZS, Molus J L, Akers DF, Martin S E. Filament formation in Listeria monocytogenes, J Food Prot 1995; 58:1031–1033.
9. Jones T, Gill C O, McMullen L, The behavior of log phase Escherichia coli at temperatures below the minimum for sustained growth. Food Microbiology 2002; 19:83–90.
10. Jones TH, Vail KM, McMullen LM. Filament formation by foodborne bacteria under sublethal stress. Inter J Food Microbiol 2013;165: 97–110.
11. Liu D, Lawrence ML, Ainsworth A J, Austin FW. Comparative assessment of acid, alkali and salt tolerance in Listeria monocytogenes virulent and avirulent strains. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2005;243: 373-378.
12. Magalhaes R, Ferreira V, Brandão T R, Palencia RC, Almeida G, Teixeira P. Persistent and non-persistent strains of Listeria monocytogenes: A focus on growth kinetics under different temperature, salt, and pH conditions and their sensitivity to sanitizers, Food Microbiol 2016;57:103-108.
13. Pratt AL, Chen B, Czuprynski CJ, Wong ACL, Kaspar CW. Characterization of osmotically induced filaments of Salmonella enterica. App Enviro Microbiol 2012;78:6704–6713.
14. Rothfield L, Taghbalout A and Shih, Y.L., Spatial control of bacterial division-site placement. Nature Rev Microbiol 2005; 3:959–968.
15. Sartor C, Grégoire E, Albanèse J, Fournier PE. Invasive Listeria monocytogenes infection after liver transplantation: a lifethreatening condition, Lancet. 2015;6736: 61831-61836.
16. Scheffers D -J. The effect of MinC on FtsZ polymerization is pH dependent and can be counteracted by ZapA. FEBS Letters 2008;582: 2601–2608.
17. Shabala L, Lee SH, Cannesson P, Ross T.. Acid and NaCl limits to growth of Listeria monocytogenes and influence of sequence of inimical acid and NaCl levels on inactivation kinetics, J Food Prot 2008;71:1169-1177.
18. Vail KM, McMullen LM, Jones TH. Growth and filamentation of cold-adapted, log phase Listeria monocytogenes exposed to salt, acid, or alkali stress at 3°C. J Food Prot 2012; 75:2142– 2150.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License