IJCRR - 6(19), October, 2014
Pages: 01-04
Date of Publication: 10-Oct-2014
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
CELL PHONES OF HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS AS FOMITES HARBOURING POTENTIAL PATHOGENIC MICROORGANISMS
Author: V. Arulmozhi, Anand B. Janagond, S. Savitha, J. Kalyani, G. Sumathi
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Cell phones (CP) being used by healthcare providers are emerging as fomites capable of transmitting infections. Studies have shown presence of potentially pathogenic bacterial and fungal contamination of cell phones.
Aim: This study was conducted to detect microbial carriage of cellphones of healthcare providers Methodology: CPs of 50 healthcare providers (HCP), comprising doctors of various specialities, nurses and technicians working at various departments/areas of hospital were screened for possible bacterial and fungal contamination. Results: The overall rate of contamination of CPs of HCPs was 94%. Contamination with potential pathogens was found in 76% of CPs. S. aureus was the commonest (18/41) potential pathogen isolated and two CPs were contaminated with Methicillin Resistant
S. aureus (MRSA). Candida spp was isolated from 4% of CPs. Rates of contamination with potential pathogens in CPs used by doctors was 85%, nurses 71% and technicians 69%. Rate of contamination with potential pathogens was highest in the CPs used by HCPs having access to wards (89%) followed by OPDs (88%) and OT/ICU (85%).
Conclusion: CP contamination with potential human pathogens was common in HCPs working at various areas of the hospital including sensitive areas like OTs and ICUs and also irrespective of professional cadre. Rates of contamination with multi-drug resistant organisms were low in CPs. These findings stress the need for awareness of CPs as fomites, need for strict monitoring of hand hygiene and guidelines for routine decontamination of CPs in hospitals.
Keywords: Cell phones, Hand hygiene, Fomite, Staphylococcus aureus
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Cell phones (CPs) have become an indispensable accessory of today’s society and they are being used extensively in a hospital setting to optimize patient care and client communications. However, CPs are commonly handled (irrespective of the cleanliness of hands), rarely disinfected and could harbour pathogenic bacteria (1) Studies of healthcare workers’ CPs conducted elsewhere have reported the overall contamination rate to be 40- 98% (2,3,4,5). CPs are potential sources of HAIs along with medical staff, the patients’ own flora. (1) Information regarding role of CPs in spread of HAIs is limited in tropical countries like India (6). Contamination rates of CPs can vary in different hospital settings. The present study was done to assess the burden and type of contamination of CPs of health-care providers (HCPs) in a tertiary care hospital in Chennai so that magnitude of the problem can be estimated and appropriate control and preventive methods can be suggested.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study was conducted in a tertiary care hospital attached to a medical college in Chennai after ethical committee approval. 50 HCPs including doctors, nurses, technicians working in outpatient departments, wards, operating rooms, ICUs etc were randomly selected for the study. No prior information about the study was given to the participants to avoid bias. After participants’ informed consent their CPs were swabbed with sterile cotton swab soaked with sterile brain heart infusion broth covering both the surfaces completely. The swabs were immediately brought to the microbiology laboratory and inoculated on to nutrient agar, blood agar, McConkey agar and Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA) medium. All bacterial culture media were aerobically incubated at 37° C for 48 hours and SDA which was used for growing fungi was incubated at 25° C for 1 week. Colonies obtained were identified by standard microbiological procedures and antibiogram was done for potential human pathogens.
RESULTS
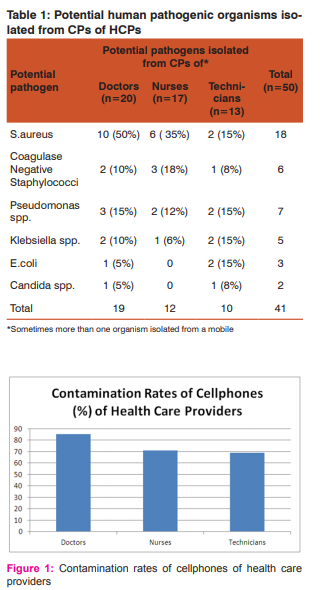
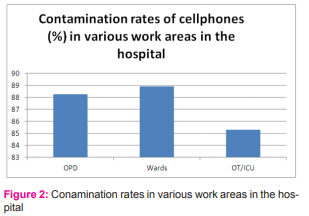
Cellphones of 50 HCPs working in a private tertiary care teaching hospital in Chennai were screened for bacterial and fungal contamination. Subjects comprised of 20 doctors, 17 nurses and 13 operating theater (OT) technicians. HCPs were belonging to various specialties (Medicine, paediatrics, dermatology, general surgery, orthopaedics, ENT, etc) and many were working in more than one area of the hospital; 34 were working in OTs/ Intensive care units (ICU), 27 in wards and 17 in outpatient departments (OPD). The overall rate of contamination of CPs of HCPs was 94% (47/50). Contamination with potential pathogens was found in 76% (38/50) of CPs. Swabs from three CPs did not yield any organisms. A total of 74 organisms were isolated out of which 41 isolates were potential human pathogens and 33 were non-pathogenic organisms. Swabs from 21 CPs yielded single organism, 25 CPs two organisms and one CP three organisms. Potential pathogens isolated (Table 1) included Staphylococcus aureus (18/41), Pseudomonas spp (7/41), Coagulase negative Staphylococci (6/41), Klebsiella spp (5/41), Escherichia coli (3/41) and Candida spp (2/41). Saprophytes isolated from the CPs included aerobic spore bearers (25/32) and Micrococci (7/32). S. aureus was the commonest (18/41) potential pathogen isolated and two CPs were contaminated with Methicillin Resistant S. aureus (MRSA) from a doctor and a technician both having access to OT. Contamination rates with potential pathogens of CPs used by doctors were 85% (17/20), nurses 71% (12/17) and technicians 69% (9/13) (Figure 1). Rate of contamination with potential pathogens was highest in the CPs used by HCPs having access to wards (89%, 24/27) followed by OPDs (88%, 15/17) and OT/ICU (85%, 29/34) (Figure 2).
DISCUSSION
Fomites play an important role in spread of hospital-acquired infections. A variety of surfaces, equipments and devices have been found to harbour pathogenic microorganisms, including drug resistant ones like MRSA and

VRE, in hospital settings. (2,7,8) Microbes can be transferred from person-to-person or from inanimate objects commonly used in hospitals (stethoscopes, pens, charts, fixed and mobile phones) to hands and vice versa. (3) Clean hands can become colonized after contact with contaminated surface or fomite while caring for patients and organisms can cause infection if they come in contact with susceptible hosts (3,8,9). Hand-to-mouth transfer of microbes after handling contaminated fomites during casual activities has also been documented (2). Clinically significant microorganisms like S. aureus, gram negative bacilli, Candida spp have been shown to persist on inanimate objects for weeks to months (8). High inoculums of the microbe, low temperature with relatively high humid environmrntal conditions provide best chances for long persistence of organisms (9). The longer a nosocomial pathogen persists on a surface, the longer it may be a source of transmission and thus endanger a susceptible patient or HCP (9). CPs are widely used and in close contact with the body. They are used for communication by HCPs in almost every location in a hospital including OTs and ICUs. (2,5). CPs allow for easy accessibility of the clinician so can help in providing timely patient care. The mobile phone technology not only allows for rapid communication but also enables storage of formulary data, clinical and diagnostic protocols that can be made available to a busy clinician at his finger tips (7,6). People frequently handle CPs and that too irrespective of the cleanliness of their hands (1). The use of CPs by HCPs in the ICU, burns wards and OTs may have more serious hygiene consequences, especially since they are used close to patients (3). The rates and composition of contamination of CPs in hospitals could be risky to general public in community if carried outside (2). More studies are required to estimate the burden of contamination of CPs of HCPs, spectrum of organisms so that appropriate preventive and control measures can be followed. In this study overall rate of contamination of CPs used by HCPs was 94% and that by potential human pathogens was 76%. The contamination rates were found high in our study and are comparable to findings of Bhat S et al and Padma K et al with overall contamination rates of 98% and 94% respectively (6, 5). S. aureus was the commonest pathogen found contaminating CPs (36%) and 4% CPs harboured MRSA. Majority of isolated S. aureus strains were sensitive to antibacterials tested (Fig). Though the MRSA were fonud in relatively less number of CPs both were found in CPs of HCPs having access to sensitive areas like OTs and ICU. Many previous studies also have found S. aureus as the commonest organism on HCPs’ CPs (12-56%) and MRSA was found in 1.9-18% CPs. Previous studies also have shown lesser rates of contamination with gram negative bacilli than gram positive cocci (2, 3, 6, 4, 5). Very few studies have looked for fungal contamination of CPs, in our study only 4% CPs were found to harbour fungi, both Candida spp. CPs of doctors harboured more pathogens (85%) compared to nurses (71%) and technicians (69%). Higher contamination of CPs of doctors than nurses was observed in other studies also (1,6). The reasons for the differences were not specifically studied. Contamination of CPs of HCPs was found to be high irrespective of the area of work in the hospital – wards (89%), OPDs (88%) or OTs/ICU (85%). A study comparing CPs of hospital and non-hospital settings showed spectrum of organisms isolated to be similar in both the groups but resistant organisms like MRSA were found only in the hospital setting (6). Today CPs, due to their various benefits, have become indispensable devices for HCPs and hence their complete restriction inside the hospitals is not practical. As the present study and the previous similar studies suggest, the problem of CPs as fomites carrying harmful microbes needs to be addressed. There is limited information available on CP disinfection methods that are both effective and do not damage the CPs.(1) Use of 70% isopropyl alcohol wipes, which is simple and can be routinely used, has been suggested to disinfect CPs by a few studies. (1,10) Sensitizing and training of HCPs about strict infection control procedures, hand hygiene, environmental disinfection methods are essential. (2,6) Engineering modifications such as use of hands-free mobile devices, use of surfaces that are easy to clean and disinfect, use of antimicrobial additive materials in CPs have been proposed as solutions (2,3). The Center for Disease Control (CDC) and Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee (HICPAC) have recommendations for routine decontamination of all hospital equipments (8). Similar guidelines extending to CPs are the need of the hour. A study done by Obasi C et al showed a selfcleaning unit to decontaminate small reusable objects, including electronic equipments like wall-phones, keyboards, in a hospital to be effective in a single cycle (8). Applicability of similar techniques to decontaminate CPs needs to be studied.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, this study highlights the high rates of contamination of CPs used by HCPs in a hospital setting. CP contamination with potential human pathogens was common in HCPs working at various areas of the hospital including sensitive areas like OTs and ICUs and also irrespective of professional cadre. Carriage rates of resistant organisms (MRSA) were low. These findings stress the need for awareness of CPs as fomites, need for strict monitoring of hand hygiene and guidelines for routine decontamination of CPs in hospitals.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Julian T, Singh A, Roussean J, Weese JS. Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcal contamination of cellular phones of personnel in a veterinary hospital. BMC Research Notes 2012;5:193-7.
2. Ulger F, Esen S, Dilek A, Gunaydin M, Leblebicioglu H. Are we aware how contaminated our mobile phones with nosocomial pathogens? Annals of Clin Micro Antimicrobiol 2009; 8:7-10.
3. Amira H, Al-Abdalall A. Isolation and identification of microbes associated with mobile phones in Dammam in eastern Saudi Arabia. J Family Community Med 2010;17:11-4
4. Data P, Rani H, Chander J. Bacterial contamination of mobile phones of health care workers. Indian J Med Microbiol 2009;3:279-81.
5. Panchal CA, Kamothi MN, Mehta SJ. Bacteriological profile of cell phones of healthcare workers at tertiary care hospital. J Evolution Med Dental Sciences 2012;1:198-202.
6. Padma S, Ezhilarasan R, Suchitra S, Anandhi L, Umamageswari S, Sangappan M, Kalyani J. Mobile phones: emerging threat for infection control. J Infection Prevention 2010;2:87-90.
7. Jeske HC, Tiefenthaler W, Hohlrieder M, Hinterberger H, Benzer A. Bacterial contamination of anaesthetists’ hands by personal mobile phones and fixed phone us in the operating theater. Anaesthesia 2007;62:904-6.
8. Obasi C, Agwu A, Akinpelu W, Hammons R, Clark C, Etienne-cummings R, et al. Contamination of equipment in emergency settings: An exploratory study with a targeted automated intervention. Annals Surgical Intervention Research 2009;3:8-16.
9. Kramer A, Schwebke I, Kampf G. How long do nososcomial pathogens persist on inanimate surfaces? BMC Infectious Diseases 2006;6:130-7.
10. Arora V, Devi P, Chadha A, Malhotra S. Cellphones a modern stayhouse for bacterial pathogens. JK Science 2009;11:127-9.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License