IJCRR - 6(20), October, 2014
Pages: 01-10
Date of Publication: 20-Oct-2014
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
FREE AND FORCED VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF EXTRADOSED BRIDGE
Author: M. V. Sardesai, A. K. Desai
Category: Technology
Abstract:Cable supported structures have distinctive dynamic behaviour. Extradosed bridge, which is intermediate to Girder Bridge and cable stayed bridge, owing to its shallow cables, the structure behaviour of Extradosed Bridge differs from that of cable stayed bridge. The shallower cables add to the prestress in the deck. While there are many articles available on the design of specific extradosed bridges, very little has been published on their dynamic behaviour from a general perspective. The paper highlights the free vibration and forced vibration behaviour of the extradosed Bridge.
Keywords: Extradosed bridge, Girder bridge
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The recent research has shown that a Extradosed bridge, which is intermediate to Girder Bridge and a cable stayed bridge, adds substantial prestress to the deck because of the shallow pylon, are found to be economical for spans upto 250m. Dynamic response prediction has been the matter of research for many authors, in particular as the structural design of many structures is governed by the earthquake load cases or combinations thereof. The intrados is defined as the interior curve of an arch, or in the case of cantilever-constructed girder bridge, the soffit of the girder. Similarly, the extrados is defined as the uppermost surface of the arch. The term ‘extradosed’ was coined by Jacques Mathivat (1988) to appropriately describe an innovative cabling concept he developed for the Arrêt-Darré Viaduct , in which external tendons were placed above the deck instead of within the cross-section as would be the case in a girder bridge. To differentiate these shallow external tendons, which define the uppermost surface of the bridge, from the stay cables found in a cable-stayed bridge, Mathivat called them ‘extradosed’ prestressing.
Some features of extradosed bridge as given below;
• External appearance resembles cable-stayed bridge – but structural characteristics are comparable to those of conventional girder bridge
• The Girder Depth are lesser than that of conventional girder bridges
• The stay cables (prestressing tendons outside the girder) need no tension adjustment necessary for cable-stayed bridges, and can be treated as usual tendons as in girder bridges
• The height of pylon is half as that of cable-stayed bridge and hence easier to construct
• With small stress fluctuation under live load the anchorage method for stay cables can be same as that of tendons inside girder and thereby achieve economy
The reduced cable inclination in an extradosed bridge leads to an increase in the axial load in the deck and a decrease in vertical component of force at the cable anchorages. Thus, the function of the extradosed cables is also to prestress the deck, not only to provide vertical support as in a cable-stayed bridge. Extradosed bridges are characterised by a low live load stress range in the stay cables. With the rapid increase in span length, combined trend and also trend of using high strength materials have resulted in slender structures and a concern is being raised over dynamic behavior of such structures, in case of cable supported structures it is more pronounced as this further includes vibrations of cable elements also. An accurate analysis of natural frequencies is fundamental to the solution of its dynamic responses due to seismic and wind and traffic loads.
Highlights on Static Behaviour
The basic difference between cable stayed bridge and Extradosed Bridge is its tower height. For Cable stayed bridge the span to tower height ratio is generally kept at 5, whereas for Extradosed Bridge it is 10, which means Extradosed bridges have half the tower height than cable stayed bridge. The stiffer, lower towers enable the use of the full range of effective depth of cross-section. Since the short towers act as cantilevers, effectively prestressed by the dead load of the girder acting through the cables, they require relatively little reinforcement to resist bending due to live load. Neither a flexurally stiff girder nor backstays are required in order to provide adequate system stiffness to control deformations due to live load. With short towers, larger stay cables are required, but the towers are more economical than the tall towers normally found in cable-stayed bridges. The methods of providing stiffness in cable supported structures are shown in figure 2.
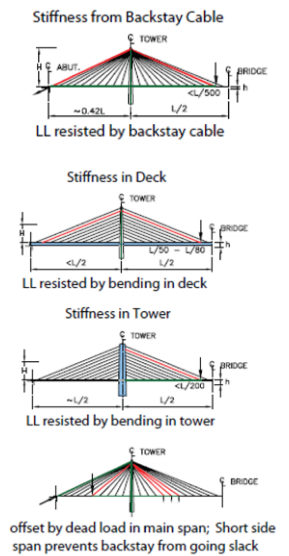

SETRA (2001) published recommended allowable stress limits that cover the full range of external cables. In that document, external prestressing tendons are defined as being subjected to a stress range of up to 15 MPa under live load while stays for cable-stayed bridges are subjected to a stress range of around 100 MPa and above. Extradosed cables are characterised as being subjected to a live load stress range between 30 MPa and 100 MPa and are not sensitive to wind vibrations. These specifications resulted from a need for design recommendations for bridges that do not fall into distinct categories, and they propose design limits and approximations based on rational principles. This explains use of 0.6fu allowable stress in the Extradosed cables, which leads to material economy
Governing Equations
A) Vibration of structure When finite element is used, each stay cable is modeled as either a single truss element with an equivalent modulus or number of cable elements with the original modulus. The deck and tower are modeled as BernoulliEuler beam elements with axial forces due to prestress imparted by horizontal component of cable force due to its shallow cables. Consider a typical Extradosed bridge as shown in figure 1; let us take a small section as shown in the figure 3 below. The boundary conditions for this element can be considered as that of beam on elastic the provided by cable. Further this beam will be subjected to prestressing force due to horizontal component of cable forces, as shown in figure 3 foundation to relate effect of elastic support below;
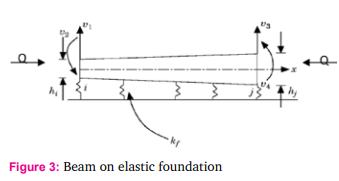
Now, consider an element i-j of length L of a beam on an elastic foundation as shown in Figure.3 having a uniform width b and a linearly varying thickness h(x). It will be a simple matter to consider an element having a linearly varying width if the need arises. Neglecting axial deformations this beam on an elastic foundation element has two degrees of freedom per node a lateral translation and a rotation about an axis normal to the plane of the paper and thus possesses a total of four degrees of freedom. The (4x4) stiffness matrix k of the element is obtained by adding the (4x4) stiffness matrices kB, kF and kQ pertaining to the usual beam bending stiffness and foundation stiffness and stiffness due to prestressing force (Q) respectively Since, there are four end displacements or degrees of freedom a cubic variation in displacement is assumed in the form v Aa = Eq. (1) Where, A= (1 x x2 x3 ) and aT= (a1 a2 a3 a4 ) (Displacement variation within element) The four degrees of freedom corresponding to the displacements v1 , v3 and the rotations v2 v4 at the longitudi nal nodes are given by q=Ca (Nodal displacements) Eq. (2) Where qT= (v0 v1 v2 v3 ) and C is the connectivity matrix for an element ij between x=0 and x=L as given in Figure 2 From equations (Eq.1) and (Eq.2) V=AC-1q Eq. (3) If E is the Young|s modulus and I=bh(x)3 /12 is the second moment of area of the beam Cross-section about an axis normal to the plane of the paper the bending moment M in the element is given by

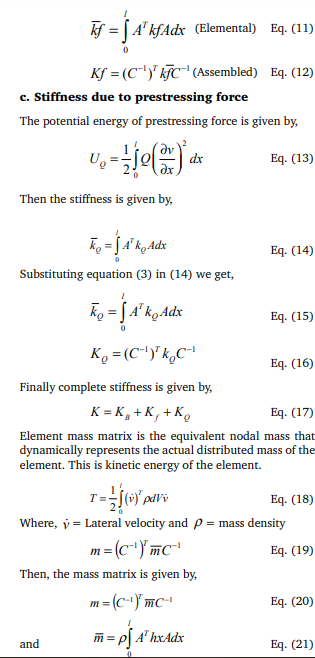
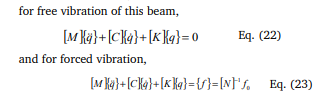
B) Vibration of Cables
i) With equivalent modulus
In global analysis of cable stayed / Extradosed bridges, one common practice is to model each cable as a single truss element with an equivalent modulus to allow for sag. The element stiffness matrix in local coordinates for such a cable element can be written as,
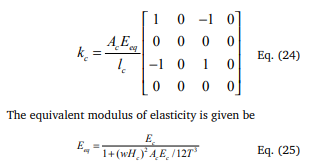
Where, Hc is chord length, Hc is the horizontal projection length, Ac is the cross-sectional area, w is the effective material modulus of elasticity, w is the weight per unit length and T is the updated cable tension of the cable. A certain cable profile has been assumed to account for the effect of cable sag. However, once the equivalent modulus has been obtained, the profile will not have a role to play in the final analysis, and hence the method cannot model transverse vibrations of the cable.
ii) With original modulus
Another approach for accounting for the transverse vibrations of cables is to model each cable by number of cables elements with the original modulus. Following the sign conventions adopted by Broughton and Ndumbara (1994), the element incremental stiffness matrix in local coordinates can be written as Where the updated element basic tension T and the element extension e along the deformed element longitudinal axis are given, respectively, by
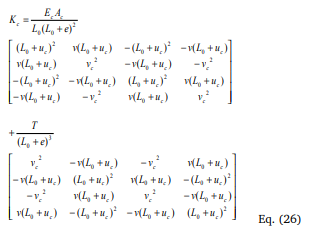
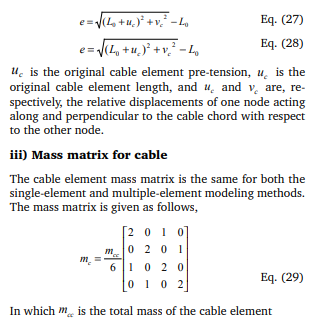
C) Vibration of stay cables To demonstrate the abilities of various methods in predicting local cable vibrations, each stay cable was analyzed as an inclined stay cable fixed/pinned at both ends to evaluate the natural frequencies of local vibrations. It is noted however that the real situation is slightly different, as the end anchorages themselves are movable. The first symmetric and anti-symmetric in-plane transverse vibration frequencies ω in radians per second can be computed, respectively, as Where l denotes the chord length, Tθ is static cable tension, m is the cable mass per unit length.
FREE AND FORCED VIBRATION ANALYSIS
Research methodology:
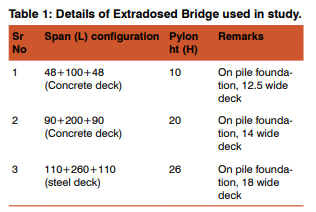
To study dynamic behavior of Extradosed Bridge, 3 numbers of models with variable parameters are prepared. Basic span configuration as applicable for Extradosed span is selected to be 120, 200 and 260m main span, the side span is about 0.45 of main span. The pylon height is varied from 8 to 12 to account for the effect of varying cable inclinations. The cable inclination varies from 17 to 30 degrees. The requirement of cable area and prestressing is as per preliminary design. Box beam superstructure is adopted with solid rectangular pylon designed by working stress method. For details of model refer table-1
The dynamic response of structure for free vibrations as well as forced vibration has been studied. Software SAP2000 V14 has been verified and used in the study. Deck is modelled as Euler Bernoulli Beam and the stay cables have been modelled as single truss elements in static/ dynamic analysis.
Free Vibrations of Extradosed Bridge
With the rapid increase in span length, combined trend and also trend of using high strength materials have resulted in slender structures and a concern is being raised over dynamic behaviour of such structures, in case of cable supported structures it is more pronounced as this further includes vibrations of cable elements also. An accurate analysis of natural frequencies is fundamental to the solution of its dynamic responses due to seismic and wind and traffic loads. The modal shapes and frequencies for above listed models are presented below;
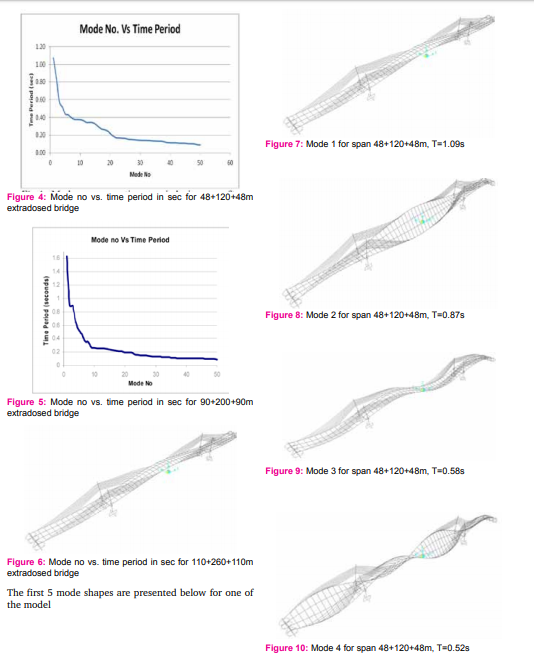
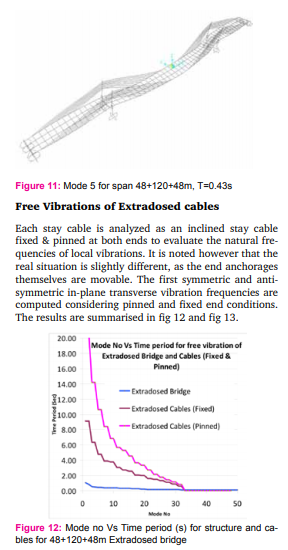
Free Vibrations of Extradosed cables
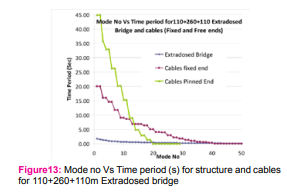
Each stay cable is analyzed as an inclined stay cable fixed & pinned at both ends to evaluate the natural frequencies of local vibrations. It is noted however that the real situation is slightly different, as the end anchorages themselves are movable. The first symmetric and antisymmetric in-plane transverse vibration frequencies are computed considering pinned and fixed end conditions. The results are summarised in fig 12 and fig 13.
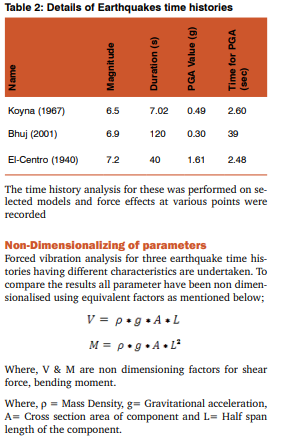
By looking at the mode shapes of the stay cables, it is possible to relate these natural frequencies of the “”fixed/free end’’ cables to those obtained by analyzing the whole bridge using the finite element method. The results are shown in fig 12 & 13. Apart from those natural frequencies that are obviously outside the range under consideration, all local cable vibrations can be reflected by finite element analysis with multiple-element modelling of stay cables. In addition to those pure local vibrations of stay cables, some new frequencies are also discovered indicating strongly the existence of coupled vibration modes. Obviously, these coupled vibration modes cannot be predicted by Equations. For investigating the possibility of coupled mode of vibration the time periods for various modes of vibration are superimposed for structure and cables. Forced Vibrations of Extradosed Bridge Forced vibration is studied for selected earthquakes; the earthquakes selected were having different characteristics as given in table 1
The time history analysis for these was performed on selected models and force effects at various points were recorded
Non-Dimensionalizing of parameters
Forced vibration analysis for three earthquake time histories having different characteristics are undertaken. To compare the results all parameter have been non dimensionalised using equivalent factors as mentioned below;
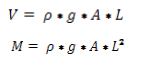
Where, V & M are non dimensioning factors for shear force, bending moment. Where, r = Mass Density, g= Gravitational acceleration, A= Cross section area of component and L= Half span length of the component.
Span and pylon height are non-dimensionlalized by using parametric length. The results obtained from the time history analysis in terms of bending moment and shear forced in the structure are non-dimensionalised and superimposed and presented in Fig 14 to 18
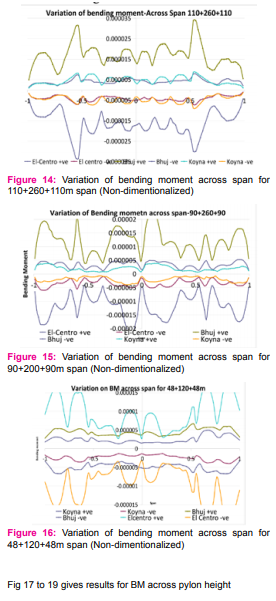
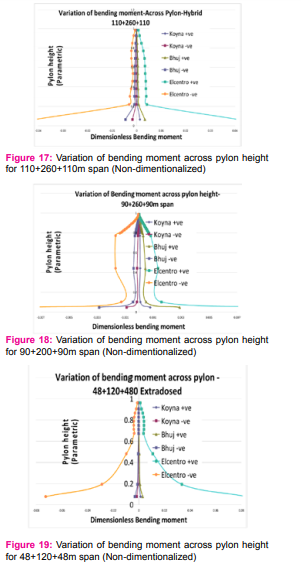
due to vibration of the deck. Due to the infinite number of damping values and angles of inclination that a cable may take, several values can be selected to represent typical cables. It is evident that zones of large-amplitude cable vibrations do tend to change with varying angles of inclination, when the geometric nonlinearity of the cable lessens, as the angle of inclination moves towards 90. Also, the onset of these regions of large-amplitude cable vibrations required higher amplitudes of cable end excitation as the damping of the cable increases. It was considered important that the stochastic excitation or parametric excitations, which may be occur due to various reason, but the main reason being the vehicles plying on the bridge, which was to be imposed on the cables, be representative of a prototype stochastic timehistory that might be imposed on a stay by a full-scale cable structure such as an extradosed bridge. Even though an approximation, cable structures, such as telecommunications masts and cable-stayed bridges, are subject to random wind forces, which have time-histories that are very similar to random normal distribution, for the lowfrequency bandwidth under examination. An extradosed bridge or other similar structure will act as a signal filter, by filtering wind signals (or white noise signals) through its own structural characteristics. The resulting dynamic response input will be the actual response of the structure to the wind load. This filtered signal or structural response can then be used as a stochastic time-history (stochastic support excitation) for the examination of a cable’s response to that time-history. As the wind will have varying characteristics, such as wind speed and wind direction, the force acting on the structure will also have varying characteristics. These will excite the structure at different frequencies with varying amplitudes of force. DISCUSSIONS Free Vibrations: - An accurate analysis of natural frequencies and mode shapes of cable supported structures such as Extradosed Bridge is fundamental to the solution of its dynamic responses due to seismic, wind and traffic loads. Now days, from economic considerations, the stay cables are often closely spaced, with the cable lengths and tensions gradually varying from position to position. The natural frequencies of their self-vibrations are therefore rather closely spaced. This may cause boundaryinduced vibrations of the stay cables. This complicates the overall dynamic behavior of cable stayed structures. In addition to pure local vibrations of stay cables, some new frequencies are also present indicating strongly the existence of coupled vibration modes, these coupled vibration modes cannot be predicted by equations. The frequencies of cables with actual boundary conditions are expected to lie in-between those of with fixed and pinned ends. For investigating the possibility of coupled mode of vibration the time periods for various modes of vibration are superimposed for structure and cables. The intersection zone (intersection of stay cable vibrations and bridge vibrations) suggests the possibility of coupled vibrations. Forced Vibrations: - Forced vibration studies of deck and pylon of three types of bridges reaffirms following facts for extradosed bridge, 1. Magnitude of bending moment / shear force is directly proportional to the magnitude of forcing function / PGA. 2. With increase in the distance between cables sup- With increase in the distance between cables supports the shear force in deck also increases. 3. Pylon stiffness does not have any effect on the deck moments/shear. 4. With increase in the pylon height/slenderness the shear force changes its sign in the upper part of pylon. 5. It is observed that only for cable stayed bridge with harp shape cable arrangement the shear force reduces at the junction of deck It is observed that there is some relationship between Peak Ground Accelerations and the response of structure, relationship between these needs to be established by further study
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
Katsuhiko Takami and Sumio Hamada (2005); Behavior of extradosed bridge with composite Girder; ASCE / Journal of Bridge Engineering.
H. Otsuka, T. Wakasa, J. Ogata, W. Yabuki and D. Takemura (2003); Comparison of structural characteristics for different types of cable-supported prestressed concrete bridges; Structural Concrete Mar-2002.
F T K Au, Y S Cheng, Y K Cheung, D Y Zheng (2000); On determination of natural frequency and mode shapes of cable stayed bridges; Applied methametical modeling.
A K Desai, J A Desai, H S Patil (2005); Co-relationship of Seismic (EDR) & (PGA) for Cable Stayed Bridge; NMB media
Anil K Chopra. (2003), “Dynamics of Structures”. Pearson Education, Inc. Second edition 1 – 844, Singapore.
Ito M. (1991), “Cable Stayed Bridges” – Recent Developments and their Future”, Elsevier Science Publishers B.V. 1 – 356, Amsterdam.
Gimisng N. J. (1983), “Cable Supported Bridges: Concept & Design”, John Wiley & Sons, 1 – 257, New York.
Y. Hikami, N. Shiraishi, Rain-wind induced vibrations of cables in cable stayed bridges, Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics 29 (1988) 409–418.
P. Broughton, P Ndumbaro, The analysis of cable and catanary structures, Thomas Telford, London, 1994.
Konstantinos Kris Mermigas, Behaviour and Design of Extradosed Bridges, MAsc thesis.
M V Sardesai, A K Desai, Investigation into Cable-Structure Interaction For Extradosed Bridge, International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications 2013.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License