IJCRR - 6(23), December, 2014
Pages: 31-35
Date of Publication: 10-Dec-2014
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A STUDY ON CRIPPLING IN SKELETAL FLUOROSIS
Author: G. Ramkumar, P. Shanmugasundaram
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Ingestion of excess fluoride more than 1 ppm (parts per million) continuously in an endemic area causes fluorosis, a chronic disease due to fluoride intoxication. Fluorosis affects teeth, bone and non skeletal soft tissues in the body. Ingestion of 4 ppm of fluoride in a rural endemic area causes skeletal fluorosis and the clinical findings are analyzed and submitted Materials And Methods: Sengotur an endemic village for fluoride in Salem district of Tamil Nadu, India has been chosen for examination of patients with skeletal fluorosis. Estimation of fluoride in two wells from which the patients drink water was analyzed by iron selective electrode and it was found that the fluoride level of water in one well is 7.5 ppm and another well 5.2ppm. Patients were examined clinically for their appearance, movements of head, rigidity of neck; alterations in the chest, like scoliosis, movements of extremities, walking were examined clinically for a total number of 60 persons with 38 males and 22 females. Results: Rigidity of Neck and Restricted Movements of Skull, Kyphosis of thoracic vertebrae, Scoliosis in the chest, bending downwards to see the floor without seeing the sky, criss cross walking, Joint pains in the upper and lower extremities, Genuvarum with bowing of leg, Crippling state of patient without movement, Paraesthesia and Paraplegia are the findings recorded Conclusion: The study has revealed characteristic of skeletal changes which could be used as clinical diagnostic markers of skeletal fluorosis differentiating from all other osteodystrophies
Keywords: Drinking fluoride water 7 ppm, Rigidity of neck, skeletal deformity, Scoliosis, Kyphosis, Genuvarum, Bamboo spine, Scissors gait
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Environmental pollution of toxic substances causes human health hazards if they are exposed to excessive level of toxic substances.2 Fluoride is one of the toxic substances. The optimum level of fluoride is 1 ppm for the metabolic activities. Some authors suggest that they play a role in calcification process. More than 1ppm of fluoride in drinking water and food appears to be toxic. Fluoride exist in endemic places particularly in rural areas of rocky soils, well water,1 vegetables grown in fluoride soil, tea and fish and in air due to industrial pollution of fluoride. Excess fluoride causes the disease Fluorosis. Fluorosis is a chronic progressive disease of human beings who are exposed to different levels of excess fluoride from drinking water and food. This disease manifests as dental fluorosis affecting the teeth with mottled enamel, skeletal fluorosis affecting the bone and joint with osteosclerosis, exostosis formation2 and non skeletal fluorosis affecting soft tissues of different organs. The present paper deals with characteristic clinical findings of skeletal fluorosis from the examination of 60 persons (38 males and 22 females).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sengotur is a known endemic area for fluorosis in Salem district of Tamil Nadu in India and we went and examined patients with skeletal fluorosis. Rural population in this village drink fluoride water from two wells and they drink the water continuously for a long time, more than 30 years. The level of fluoride was estimated by ion selective electrode and the fluoride level was found to be 7.5 ppm in one well and 5.2 ppm in another well. Suspected people with skeletal fluorosis exposed to 7.5 ppm of drinking water were examined clinically with inspection and palpation of Skeletal system, physical appearance, movement of head and neck, movement of chest and lumbar area, joint movements of upper and lower extremities, bone changes and deformities, walking movements, and the positive findings were recorded. Pain and restricted movements of joints were elicited. Palpation was carried out in muscular and tenderness areas. In addition to this examination, patients were asked for their food habits, digestion, urine and bowel frequency etc were recorded.
RESULTS AND CLINICAL FINDINGS
In Sengotur village our study has not revealed any changes of skeletal fluorosis in children though they drink the same fluoride water. People after 22 years have developed mild body ache on exertion. This vague pain and tiredness affects their routine functions but they are not totally obstructed from their house hold and other job oriented works. Our study has showed skeletal fluorosis after 30 years with different signs and symptoms.
Changes in Head and Neck
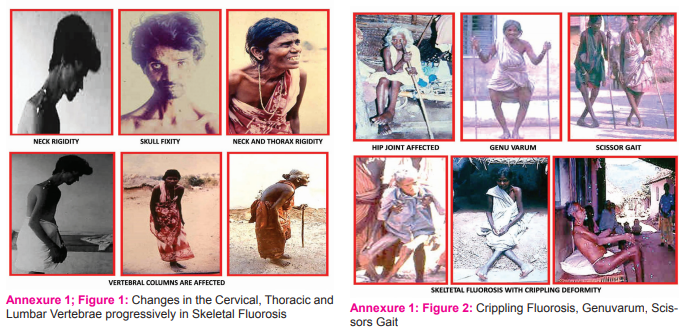
The skeletal changes were progressive and classical changes were seen as first in head and neck. Normal patients move head upward, downward, forward, right side, left side and total rotatory movement. The movement of head is brought out by the movements of cervical vertebrae. Cervical vertebrae are arranged one over the other and united with soft intervertebral disc. In skeletal fluorosis the patient develops progressive neck rigidity and stiffness resulting in the restricted movements of head. The patient cannot move his head downwards and cannot raise his head upwards. If the patient wants to see the sky, he cannot raise the head upwards, but he can raise his eyeballs above to see the sky. The patient cannot turn towards right side or left side and the rotatory movement of head is stopped. His head is fixed in one position along with neck. In case if he wants to see anything on one side he has to turn the whole body towards that side. The neck rigidity and the head fixidity is due to the fusion of vertebral bones in the cervical areas. The cause for the fusion is the progressive deposition of fluoride in the vertebral bone and also in the intervertebral disc. The intervertebral disc gets calcified and the vertebrae fuse together giving an appearance of Bamboo. The entire process of neck rigidity and fixidity of skull is progressive, depending upon the amount of fluoride deposited in the bone and disc.
Changes in the Thoracic region
When the thoracic vertebrae are affected, the patient develops in addition to neck rigidity, stiffness and pain in the back in the area of thoracic vertebrae. Though for some time the patient can stand straight and walks with the involvement of cervical and thoracic vertebrae, in the course of time the chest will bend forward and downward with rigidity of neck and thorax. When the patient walks, one can see the forward and downward bend of chest. They develop Kyphosis – abnormally increased convexity in the curvature of thoracic vertebrae as viewed from side. They also develop scoliosis – lateral curvature of vertebral column, they can’t turn their chest right or left side and these patients have pain in the back in the area of vertebral column. In skeletal fluorosis once they have developed forward bend, they cannot straighten the chest to normal straight position and the forward bend is permanent and irreversible. The rigidity of thoracic vertebral column is due to the fusion of vertebrae as fluoride deposit and causes calcification in the vertebral bone with the intervertebral disc.
Changes in the lumbar region
Every patient can bend downward and raise his chest upward. If anybody wants to take something in the floor they bend downward and after taking raise their body straight to the normal position. People with skeletal fluorosis develop bend of the lumbar area towards downwards. Once they have a bend they cannot raise their chest to the normal position because totally the thoracic and lumbar vertebrae fuse together and become rigid with inability to move upward for straight position. The patients cannot move the head, chest, lumbar area and bend downwards to see the floor. They walk with this bend if their joints and extremities are not affected. These patients can see only the soil in the floor and not the sky. They have pain in the vertebral column and this pain increases by taking any hard substances. However though their chest is bending downwards the patient is able to take food in sitting position
Changes in the sacral and coccygeal area
Changes in sacral and coccygeal region will occur progressively to the affected patients and the characteristic clinical finding is more bend towards floor. They will have pain in and around the vertebral column and walk with this bend if the hip joints are not affected.
Changes in the Joints
In our observation small joints are little painful but no stiffness and fixidity were found with normal movements of fingers.
Joints in Upper Extremities
Elbow joints and shoulder joints are very much affected in the form of progressive pain and stiffness. Normal individuals can raise and stretch both arms and bring both hands to touch the occipital area of the skull by joining the fingers, but patients with skeletal fluorosis cannot raise their hands and bring both hands to touch the occipital region. They also cannot bend the hands back to touch the middle of the back. While they walk theywill move the hands slowly and not freely. Pain in the elbow and shoulder joints are common and they cannot lift heavy things in their hands. Hip Joint Hip joints play an important role for normal individual to bend his chest and abdomen downwards and rise upwards to the normal position, but when the hip joints are affected the joints are stiff and painful restricting the movement of hip initially and causes difficulty to walk. While walking, the patient will move the right leg towards left and left leg towards right with the characteristic SCISSORS GAIT. Patients walk by holding sticks in both hands as an aid. The cross leg in walk may be due to neural affection in the hip joint. When the hip joint is more affected the patients will be crippling patients. Knee Joint Whenever knee joint is affected, the joint will have pain and restricted movement with flexon deformity. The joint space between two knee joints is widened as characteristic GENU VARUM. In few severe cases the patient had immovable knee joint either a single or both. Crippling of patient The patient is a crippled patient in skeletal fluorosis if his joints are very much affected and not able to move and lie down in the bed. In our observations we have seen 2 patients, 1 male and 1 female; they simply sit down in the village cot and can’t stand up and lie down in the bed. They hold a stick in hand; they pass urine and faeces in the sitting position to the commodes kept underneath the village cot. 2 patients both ladies lying down in the floor and can’t get up with right leg towards left and left leg towards right in Scissors Gait. 3 patients had a very slow walk with sticks and bend his thorax, abdomen downwards due to the involvement of vertebrae and hip joint. Patients with skeletal fluorosis looks like a living monuments giving problems to the family members Changes in the Neural System The vertebral column is more susceptible for fluoride toxicity. Apart from deposition of fluoride in the cancellous bone, Exostosis- a peripheral outgrowth of bone and osteophyte develop. They compress the spinal cord causing Paraesthesia of extremities, hemiplegia or quadriplegia7 . In our observation we have seen more than 20 patients with mild paraesthesia and only 1 patient with quadriplegia. We have not any patient with deafness, as it has been reported in the literature that osteosclerosis causes compression of auditory nerve. Though bone formation pressures the Optic nerve causing visual impairment and Auditory nerve to cause deafness as in Paget’s disease, we have not seen such visual and auditory impairments in skeletal fluorosis.
DISCUSSION
Skeletal fluorosis develops only after a prolonged and continuous exposure to toxic levels of fluoride in drinking water or food in rural population who are residing permanently without moving to other places.2 Our observation shows the skeletal fluorosis develops progressively after 25 years. This may be due to the slow bone remodelling in adult patients. We have not seen children with skeletal fluorosis, particularly by neck rigidity and skull fixidity but Tiotio M and Tiotio SPS9 have recorded skeletal fluorosis in six children aged 11 – 13 years. The less incidence of skeletal fluorosis in children is that during childhood, the metabolic activity of bone for remodelling to maintain the physiological equilibrium of bone is more active. This helps to prevent the retention of fluoride in the bone. The early changes occurs in skeletal fluorosis in cervical vertebrae as the cervical vertebrae being a cancellous bone with vertebral disc a soft tissue are very much susceptible for fluoride deposition and calcification for fusion of vertebrae. The vertebral column cannot be straightened from the bend position because of the fusion of vertebrae by calcification with fluoride.2 Our observation in the endemic area revealed that the severity and intensity of fluorosis varies from group of individuals in rural area though they are taking same level of fluoride content water. People who are economically poor with deficient dietary habits have developed skeletal fluorosis faster and the severity is more, but the people who are socio economically sound and take rich nutrition develop fluorosis slowly and not much severely. This shows that the development of skeletal fluorosis depends upon the nutritional status of the patient. Calcium, Vitamin C and Antioxidants plays an important role in the genesis of fluorosis and this has to be studied in depth. In our observation, we find few patients particularly ladies suffering from skeletal fluorosis do not have dental fluorosis but the remaining patients, both males and females have shown both dental fluorosis and skeletal fluorosis. Dental fluorosis develops affecting the enamel, during the development of tooth. The fluoride incorporated with calcium in enamel remains as it is after the enamel is fully calcified. Hence the dental fluorosis cannot be corrected and remain as a marker. The reason why few ladies have no dental fluorosis is that these ladies have taken drinking water free from fluoride during their childhood, preserving their tooth without fluorosis, but when they migrated to other places after marriages, they have taken fluoride rich water developing skeletal fluorosis. Though we have not recorded any deafness in skeletal fluorosis due to pressure of exostosis in auditory canal, perceptive type of deafness was noted in case of skeletal fluorosis, due to the result of pressure caused by exostosis on eighth nerve in the internal auditory meatus reported by ABN Rao and Siddique in 19623 A patient with skeletal fluorosis had developed paraplegia and it was suspected by spinal cord tumour but after the death of the patient autopsy was done and found no spinal cord tumour but a bony projection exostosis was found from the margin of the foramen magnum and piercing the spinal cord. The paraplegia suspected in that patient is due to the spinal projection of bony projection due to fluorosis in the margin of foramen magnum reported by Janarthanan et al 1957 4. Spinal compression due to skeletal fluorosis causing neurologic condition was reported by GV Satyanarayana et al7 . Compression of spinal cord and nerve roots from osteophytosis and sclerosed vertebral column and ossified ligaments were reported by Raja Reddy et al 15 In skeletal fluorosis not only the cervical and thoracic vertebrae fuses with one another by calcification of bone and intervertebral disc but also the vertebrae fuses with ribs and pelvic bone by the autopsy findings of Lyth 1946 6 In the present study it was found that one male patient who was suffering from severe skeletal fluorosis and not able to stand has shown abdominal breathing. On thorough examination by physician the lung condition was normal. The patient had rigidity of thoracic vertebrae and it was concluded that the abdominal breathing was due to the restricted movement of thoracic wall due to stiffness in chest caused by fluoride deposition. This type of abdominal breathing due to fixation of thoracic wall in skeletal fluorosis was reported by Short et al 12 The present clinical study has revealed that muscles and tendons in the area of bony attachment are abnormally prominent, tender and painful. Weather this prominence of muscle and tendon is due to fluoride deposition or pressure of bony projection is to be elicited. But the prominence of muscles and tendons with pain was due to the pressure of multiple exostosis and irregular bone laid down as seen in the skeleton of the patient with skeletal fluorosis as autopsy findings by Singh et al 19625 but muscles, tendons and capsules also gets calcified reported by S.P.S Tiotio et al 13 In certain osteodystrophies of bone the growth of long bones are affected causing stunted growth as in rickets, achondroplasia etc, but in our observation no such stunted growth were recorded but bend of bones were seen in few cases. The fluoride though causes bend but not involve in the calcification of enchondral ossification Overall our observation we found the skeletal fluorosis is progressing and lead to skeletal changes with deformity and crippling but not involving any vital functions of the organ
CONCLUSION
Careful clinical evaluation of patients with skeletal fluorosis reveals that the patient initially have tiredness, and fatigue. Later on they develop neck rigidity, skull fixidity with restricted movements. In the course of time the patients slowly develop forward and downward bending of chest, the characteristic scoliosis and Kyphosis. Involvement of lumbar vertebrae produces total bend of chest towards the floor and failure to see the sky. Progressive pain and restricted movements of upper extremities results in inability to raise the hands. Knee joints are affected with genuvarum and bowing of legs. Neural involvement causes Paraesthesia in early and later possibility in developing quadriplegia and paraplegia. Neural involvement in the hip cause’s scissors gait of legs, abdominal breathing was recorded in chest rigidity of skeletal fluorosis. It is not a killing disease but a crippling disease and skeletal fluorosis can be diagnosed by characteristic clinical findings.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors/ publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. Source of funding: Self funding Conflict of interest: Nil
References:
1. A Teartise on Fluorosis; Prof. (Dr) A.K. Susheela; Fluorosis Research and Rural Development Foundation; New Delhi
2. Amajit Singh: Endemic fluorosis. JAIDA Volume 37 No 1 Page 3-10 January 1965
3. A.B.N. Rao and A.H. Siddiqui; Some observations on eighth nerve functions in Fluorosis; Reprinted from The Journal of Laryngology and Otology, Vol LXXVI. No. 2. February 1962
4. Janarthanan T and Venkataswamy TJ; Endemic fluorosis with paraplegia. Madras Medical Journal 1:1 1957
5. Singh et al; Skeletal changes in endemic fluorosis. J Bone and Joint surgery. Volume 4413. No 4. 1962
6. Lyth.O; Endemic fluorosis in Kweichow, China. Lancet. 1946 Feb 16;1(6390):233-5
7. GV Satyanarayanamoorthy and D Narayana Rao; Studies in endemic fluorosis spinal compression due to skeletal fluorosis. Journal of Indian Medical Association. Vol XXII No 10 July 1953, Pages 396-399
8. Band CA BOIVING and Demeuusse C; Drug induced skeletal fluorosis. Fluoride 15 (3) 54-56; 1982
9. Sing A. Jolly SS. Bansar BC; Skeletal fluorosis and its neurological complications Lancet 1. 197. 1961
10. M Teotia, SPS Teotia and KB Kunwar; Archives of disease in childhood. 1971, 46, 686
11. Reddy DR. Neurology of endemic skeletal fluorosis. Neurol India 2009 57;7-12
12. Shortt, H.E; Mc Robert, G.R; Barnard, TW and Nayar, A.S.M. Endemic fluorosis in the Madras Presidency. Indi, J. Med. Res. 25:553-568, 1937
13. Teotia SPS, Endemic fluorosis in India. A challenging national health problem; J. Assoc . Phys India; 1984;32:347-52
14. SPS Teotia, M Teotia; Highlights of forty years of research on endemic skeletal fluorosis in India; 4th International workshop on fluorosis Prevention and Defluoridation of water, March 2004
15. Raja Reddy; Compression of spinal cord and nerve roots from osteophytosis, sclerosed vertebral column and ossified ligaments; Neurology of endemic skeletal fluorosis; Neurology India 2009, Vol 57, Issue 1.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License