IJCRR - 6(24), December, 2014
Pages: 24-30
Date of Publication: 20-Dec-2014
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
NORMATIVE VALUES OF TANDEM AND UNIPEDAL STANCE IN SCHOOL CHILDREN
Author: Sneha D. Dhanani, Lata D. Parmar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: There were very few studies done on unipedal stance in school children and there was no study found on tandem stance in school children to the best of our knowledge Aim: To establish normative values of tandem and unipedal stance in school children. Study Design: Descriptive study Methodology: 250 subjects, meeting inclusion-exclusion criteria were included Each participant then completed timed unipedal balance test on right and left foot, and tandem stance test on right foot in front of left foot. The tests were performed barefoot on a floor surface. The timed measurements were completed using a stopwatch. Results: Mean age of participants was 11.76\?3.499. Mean range of unipedal stance (rt. and lt.) between 6-17 years (total participants) was 1.14\?0.352 to 2.55\?0.702 seconds. Mean range of tandem stance between 6-17 years was 1.47\?0.520 to 3.26\?0.953.The results showed that age had statistically significant correlation with the both static balance tests (p value 0.000 and r value >0.5), but gender did not show any significant correlation for balance performance in both these static balance tests. BMI also did not show any statistically significant correlation for both the static balance tests. (p value 0.000, r value < 0.5). There is statistically significant correlation found between rt. and lt. unipedal stance. (r value .817** and p value 0.000 ) Conclusion: Reference values for tandem and unipedal stance were established. Key Words: Balance skills, Dynamic balance, Static balance
Keywords: Balance skills, Dynamic balance, Static balance
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Balance is a complex process involving the reception and integration of sensory inputs and the planning and execution of movement to achieve a goal requiring upright posture. It is the ability to control the center of gravity (COG) over the base of support in a given sensory environment.1 Balance control is temporally organized from the head to feet, according to a descending organization. In motor development, the first period is characterized by the development of postural responses along a cephalocaudal gradient. Overall balance ability and postural stability increase and mature by 6 to 10 years of age2 there are many systems within the body that work in concert to keep the centre of mass (COM) within the base of support (BOS) when maintaining static postures and to move the COM in relation to the BOS in a controlled manner when engaged in dynamic tasks.3 Before birth, different brain regions develop at different rates, and sensory organs initially develop independently of the brain regions to which they will later be connected. The vestibular sense or proprioception begins to function before the fetus first shows a righting reflex at 25 weeks and probably plays a part in bringing the fetus into a head-down position before birth. 4, 5 Balance and posture evaluations address whether sensory information from the vestibular system coordinates and integrates with vision and somatosensory information from the muscles and joints. Such tests require the child to balance under various vision conditions (e.g., with eyes open and closed or with a moving visual field) and varied standing surfaces (e.g., on a firm, soft, or moving surface).6 Numerous techniques have been described to measure standing balance, with varying levels of challenge in different populations. The Timed unipedal stance test (also referred to as timed single limb stance, unipedal balance test, one leg stance test, and one-leg standing balance) is a simple test for measuring static aspects of balance that can be used in a variety of settings and requires minimal equipment or training.7 Standing balance is the necessary precursor to all upright loco motor skills.7 Static balance is the ability to maintain a posture in a resting position, while dynamic balance is the ability to maintain postural control during the performance of functional tasks.8, 9 The task of standing on one leg requires initially voluntary shift of the COM to the leg which will be stood on, followed by maintenance of postural orientation in space, by controlling weight, maintaining the vertical alignment of the rest of the body and equilibrium. One leg standing assesses postural steadiness in a static position by a quantitative method, measurement being the number of seconds that an individual can maintain a one leg stance. The underlying assumption being that the better one’s postural steadiness, the longer such a position can be held. Tandem stance is the ability to stand in a heel-to-toe position, reflects the degree of postural steadiness when the BOS in the medial/lateral direction is narrow, also known as the sharpened Romberg test. Tandem stance was developed on the basis of classic Romberg’s sign and originally utilized as a bedside indicator of abnormality of the proprioceptive system.8, 10, 11 There is an information deficiency of norms regarding balance skills, especially in our country and taking into consideration that such information will contribute to both the planning of developmentally adequate movement programs and the study of developmental specificities during such critical years as the school age, the aim of the present research was to establish normative value of tandem and unipedal stance. AIM To establish normative value of Tandem stance and Unipedal stance in school children, age group between 6 to 17 years.
OBJECTIVE
• To establish the minimum duration of Tandem stance.
• To establish the minimum duration of Unipedal Stance.
MATERIALS NAD METHODS
Ethical clearance was received from Sumandeep Vidyapeeth Institutional Ethical Committee (SVIEC). Study Design: Descriptive Study Study Population: school children
Inclusion criteria:
All School going children – age group between 6-17 years were eligible for inclusion.
Exclusion criteria:
Children with any neurological, musculoskeletal, and cardiovascular deficit that affect balance.
• Any history of balance impairment.
Outcome measures
• Duration in seconds in Tandem stance test.
• Duration in seconds in Unipedal stance test. Methodology: Following ethical permission from Sumandeep Vidyapeeth Ethical Committee (SVIEC), various schools were approached for official permission from the Head / Principal of the School. The Principal / teachers and students were explained about the project and requested for informed consent. Verbal assent was ensured from small children apart from written permission from Principal / teacher.
Methodology:
Following ethical permission from Sumandeep Vidyapeeth Ethical Committee (SVIEC), various schools were approached for official permission from the Head / Principal of the School. The Principal / teachers and students were explained about the project and requested for informed consent. Verbal assent was ensured from small children apart from written permission from Principal / teacher.
Each participant was enquired of baseline questions and checked for inclusion criteria. First of all, the anthropometric measurements of the subjects were taken. Prior to balance testing, participants were familiarized with the balance test and provided practice sessions on the testing procedures to decrease the chance of a learning effect occurring during testing. The tests were conducted at the same times of the day (between 10.00 am to 5.00 pm) when the body was in rest, and measures were taken to prevent distraction due to environmental factors (anyone talking, any noise). The procedure lasted 10-12 minutes for each child. The tests of whole group were completed within 15-20 days. Each participant then completed timed unipedal balance test i.e. standing on right and left foot alternatively, and tandem stance test on right foot in front of left foot. The tests were performed barefoot on a floor surface. For two balance tests, each subject completed 3 trials on each leg. A 15-second rest was given between trials set to avoid fatigue. For all trials, the participants placed their hands across the chest and time started upon elevation of the opposite foot from the floor. Participants focused on a target placed at eye level, in front of them. A stopwatch was used to time the test. This study was carried out in School’s class room.Tests were done in separate room where source of light was good and also in secured place so that risk of fall during tests was prevented. For unipedal stance, participants were asked to stand barefoot on the limb of their choice, with the other limb raised so that the raised foot is near but not touching the leg / ankle of their stance limb. Prior to raising the limb, the subject was instructed to cross his arms over the chest as shown in figure 1and2. The stopwatch was used to measure the amount of time the subject was able to stand on one limb. Time commenced when the subject raised the foot off the floor and time ended strictly when the subject either: (1) used his arms (i.e., uncrossed arms), (2) used the raised foot (moved it toward or away from the standing limb or touched the floor), (3) move the weight-bearing foot to maintain his balance (i.e., rotated foot on the ground). The procedure was repeated 3 times the mean of the 3 trials were recorded.7 For tandem stance, participants were made to stand with feet in a heel-to-toe position on straight line drawn with chalk stick on the floor, and arms across the chest, with eyes open as shown in the figure 3 and 4. Time commenced when the subject placed the rt. foot in front of left foot on the straight line and time ended strictly when the subject either: (1) use his arms (i.e., uncrossed arms), (2) displace any foot,(3) movement of the foot from original position/ stepping. The procedure was repeated 3 times and the mean of the 3 trials was taken.


RESULTS
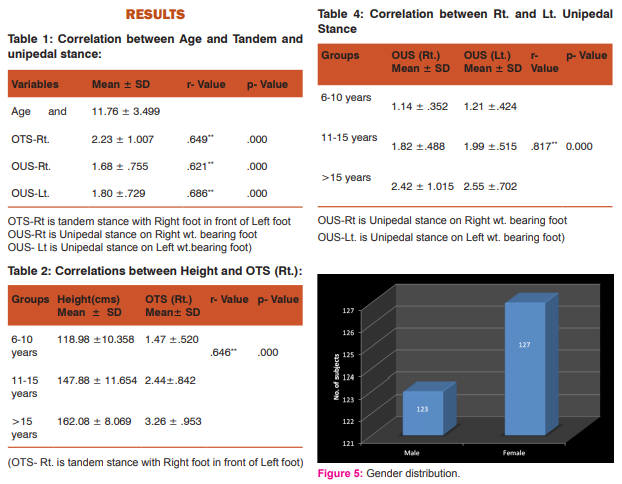
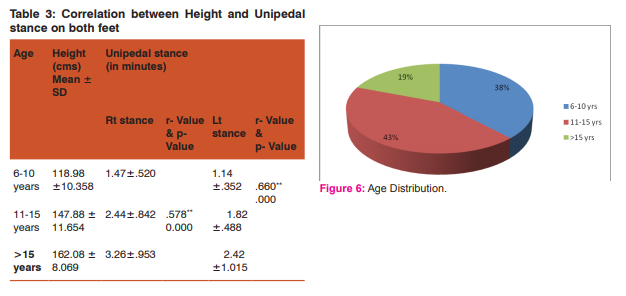
There were total of 250 school children included, of them 123 were males and 127 were females (fig.5). Figure 6 shows the percentage of distribution in the three groups age wise, 38% were in 6-10 years, 43% in age group 11- 15 years and 19% >15 years of age. Only 24 of 250 were with left hand dominance. Mean difference of Height, weight and BMI is shown in figure 7 Figure 8 shows Mean values of Tandem and Unipedal stance between males and females. Unipedal stance is studied of both the lower limbs. 1) Tandem Stance(Rt. foot in front of Lt. foot): • 6-10 yrs: 1.37 - 1.58 sec. • 11-15 yrs: 2.28 - 2.60 sec. • ≥15 yrs: 2.98 - 3.53 sec. 2) Unipedal Stance on maximum range Weight bearing (both) feet: • 6-10 yrs: Min. =1.21-1.30 sec. • 11-15 yrs: Min. = 1.92- 2.09 sec. • ≥15 yrs: Min. = 2.72 - 2.76 sec. Table 1 shows correlation between Age and Tandem and unipedal stance. Highly significant relationship is seen with r value > 0.5 and p- Value 0.000 Similarly Table 2 and 3 show significantly high correlations between height and the two balance tests. Table 4 shows that unipedal stance between right and eft lower limbs were highly correlated with r=.817**
DISCUSSION
The study aimed to establish normative values of tandem and unipedal stance in normal school children. There were very few studies done on unipedal stance in school children and there was no study found on tandem stance in school children to the best of our knowledge, these two tests of balance were therefore chosen for the study. In the present study, the total numbers of participants were 250, of which 123 were males and 127 were female. The tandem stance and unipedal stance was studied in school children of mean age 11.76±3.499. It was found that, age had statistically significant correlation with the static balance tests (p value 0.000 and r value >0.5) but gender did not show any significant correlation for balance performance in both these static balance tests. Similarly, other studies7, 8, 9, 13, have also suggested that age have greater significant correlation with balance than gender. However, significant differences between rural and urban school boys’ coordinative and balancing abilities have been reported by Raghupathi K etal.9 Barbara A. Springeret et al, 7 studied 549 participants, in which 258 were female, and 291 male (aged 18- 80+). They have also taken mean and best of 3 Unipedal Stance Test times (similar to the present study) for males and females of 6 age groups and found that there is no interaction between gender and test condition, and also no significant difference was found for gender. But there were significant main effects for age category and they have also concluded that difference in Unipedal Stance Test times is not gender specific but is related to age. 7 The authors7 have interpreted that elderly subjects had difficulty maintaining balance in the static phase due to difficulty adjusting postural control during the initial dynamic phase of one-leg stance. Another possibility for the decrease in stance times for elderly subjects is a decrease in lower extremity muscular strength and endurance. 7 Fotini Venetsanou et al,8 have taken balance subtest of the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency and found that age have great significant correlation with both the subtest than gender. They have also concluded that age seems to be a significant factor for preschoolers’ performance in terms of balance skills, while gender does not and interpreted that it can be by the rapid progress caused by the biological processes of development during the period between four and eight years of age but for gender differences, at the preschool age, the biological characteristics of boys and girls are similar rather than diverse and differences between genders can be found- may be, in “modern” societies, qualitative differences in encouragement, support, and opportunities regarding participation in play-game type of activities can be identified and may have greater influence on balance, and also balance is a multidimensional structure and as such cannot be affected by only a couple of factors. 8 V. Hatzitaki et al, 12concluded that balancing under static conditions was strongly associated with the ability to perceive and process visual information, which is important for feedback-based control of balance. Adults, 11- to 13-year-old children have the ability to select varying balance strategies (feedback, feed forward, or both), depending on the constraints of a particular task.12 Oya Erkut At?lgan et al, 14 studied 60 children, aged 9-11 years. They have used static balance tests: Bipedal static balance with Eyes open (EO) and eyes closed (EC) and Unipedal static balance with respectively on right and left foot, eyes open for 30 seconds. They found that boys had good bilateral and unilateral balances than the girls but there was no statistical significant differences found for Romberg test and unilateral (right leg) static balance of the subjects between genders and concluded that unilateral static balance (left leg) parameters of the boys were statistically significant while there wasn’t any significant difference of unilateral static balance (right leg) of the boys and the girls and interpretated that boys have a more active life than the girls in Turkey, 14 they play games on the streets more. The authors of this study therefore state that static balance (EO-EC- Left foot) of the boys was better than the girls because they did more physical activities. Soccer is also a very popular sport branch in their country and boys play soccer on the streets in early ages with their friends.14 In present study however, right and left were highly correlated on unipedal stance (r=.817) In present study height was found to be significantly correlating with the balance performance for both the tests. (p value 0.000 and r value >0.5). This has been interpreted as due to the rapid progress caused by the biological processes of development during the period between four and eight years of age as explained by Fotini Venetsanou etal.8 However, body mass index (BMI) did not show any statistically significant correlation with balance performance for both the static balance tests (r value <0.5). Eva D’Hondt et al, 15 studied 117 children between the age of 5 and 10 years (61 normal-weights, 22 overweight, 34 obese of which 60 were girls and 57 were boys). They used Movement Assessment Battery for Children and found, Scores for balance and ball skills were significantly better in normal-weight and overweight children as compared with their obese counterparts. They have also found similar trend for manual dexterity, and concluded that general motor skill level is lower in obese children than in normal-weight and overweight children. Accordingly they also stated that poor Socio Economic Status is likely to be associated with lower motor skill performance in children. Available data on this topic suggest that a low familial Socio Economic Status is an environmental risk factor for motor development, and especially for fine motor coordination.15
CONCLUSIONS
The reference values were established for the school going children. In agreement to the literature age and height were found to have greater impact on the static balance. Gender and Body Mass Index did not have significant impact, also there was no significant difference between the right and left unipedal stance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. Authors would like to extend thanks to the students and the Schools of Vadodara without whom this study would have been impossible. The authors are also grateful to Sumandeep University trust for all the support provided.
References:
1. Darcy A. Umphred, NEUROLOGICAL REHABILITATION, Fifth Edition, ch.23, pg no.740.
2. Chemin Joseph Aiguier et al, Development of Locomotor Balance Control in Healthy Children, Vol. 22, No. 4,1998,pp. 527–532.
3. Westcott SL et al, Evaluation of postural stability in children: current theories and assessment tools. Phys Ther. 1997; 77:629-645.
4. Parncutt, R. et al (2006), prenatal development, The child as musician Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, pp1-31.
5. Susan J. Herdman, Vestibular Rehabilitation, Third Edition, Ch.1, pg no.2, 3.
6. Gaye W. Cronin et al, Pediatric Vestibular Disorders Recognition, Evaluation and Treatment, Vestibular Disorders Association.
7. Barbara A. Springer et al, Normative Values for the Unipedal Stance Test with Eyes Open and Closed,Journal of Geriatric Physical Therapy Vol. 30;1:07.
8. Fotini Venetsanou et al , THE EFFECTS OF AGE AND GENDER ON BALANCE SKILLS IN PRESCHOOL CHILDREN, Physical Education and Sport Vol. 9, No 1, 2011, pp. 81 – 90.
9. Raghupathi K et al, Comparative Analysis of Coordinative and Balancing Abilities Among 10-15 Years of Rural and Urban School Boys, Volume: 2, Issue: 5, May 2013, ISSN No 2277-8160.
10. Maria Nida c. et al, Development of Lower Extremity Kinetics for Balance Control in Infants and Young Children, Journal of Motor Behavior,20011,Vol.33, No.2,180-192.
11. Carolyn A Emer et al, Development of a Clinical Static and Dynamic Standing Balance Measurement Tool Appropriate for Use in Adolescents, Physical Therapy, Volume 85, Number 6, June 2005
12. V. Hatzitak et al, Perceptual-Motor Contributions to Static and Dynamic Balance Control in Children, Journal of Motor Behavior, 2002,Vol. 34, No. 2, 161–170.
13. Stanley N. Graven et al , Auditory Development in the Fetus and Infant, VOLUME 8, NUMBER 4, www.nainr.com.
14. Oya Erkut At?lgan et al, The effects of postural control to gender differences in children, Volume: 9 Issue: 2 Year: 20.
15. Eva D’Hondt et al, Relationship Between Motor Skill and Body Mass Index in 5- to 10-Year-Old Children, Physical Activity Quarterly, 2009, 26, 21-37.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License