IJCRR - 7(4), February, 2015
Pages: 36-47
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFECTS OF CHRONIC EXPOSURE TO 2G AND 3G CELL PHONE RADIATION ON MICE TESTIS
- A RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL
Author: N. Mugunthan, J. Anbalagan, A. Shanmuga Samy, S. Rajanarayanan, S. Meenachi
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objective: The aim of our study is to evaluate possible effects of chronic exposure to 900 - 1800 MHz radiation emitted from 2G cell phone and 1900 -2200 MHz from 3G cell phone on the testis of mice and to compare the effects of 2G and 3G radiation on testis at the histological level. Methods: Mice were exposed to 2G and 3G ultra-high frequency radiation, 48 minutes per day for a period of 30 to 180 days. The sham control mice were exposed to similar conditions without 2G or 3G exposure. Animal's weight of 2G and 3G cell phone exposed group were recorded before sacrificing at the end of 30, 60, 90,120,150 and 180 days. Same numbers of control animals were sacrificed on the same period. Blood samples were collected to measure plasma testosterone. Both the testes were dissected and its size, weight and volume were measured. The testes were processed for histomorphometric study. Results: Following chronic exposure of 2G and 3G cell phone radiation in mice, there was significant reduction of animal weight at first, second and fourth month. The mean testis weight and volume of 2G and 3G radiation exposed mice were significantly reduced in the first three months. The comparison between 2G and 3G exposed groups, showed no significant changes in mean body weight, mean testis weight and mean testis volume. The mean density of seminiferous tubule, mean seminiferous tubule diameter, mean number of Sertoli and Leydig cells of 2G and 3G exposed groups had significantly lower value than the control. The following microscopic changes were observed in the 2G and 3G radiation exposed mice testis over control. 1. Wide interstitium 2. Detachment of Sertoli cells and spermatogonia from the basal lamina. 3. Vacuolar degeneration and desquamation of seminiferous epithelium. 4. Peripheral tubules showed reduced thickness of seminiferous epithelium and maturation arrest in the spermatogenesis. 5. Seminiferous tubules scored 7 to 9 using Johnson testicular biopsy score count. The mean total serum testosterone level of first, second, third, fourth and sixth month 2G and 3G exposed mice had significantly lower serum testosterone level than control. However, comparison between 2G and 3G showed no significant difference in the mean serum testosterone level.
Conclusion: Chronic exposure to ultra-high frequency radiation emitted from 2G and 3G cell phone could cause microscopic changes in the seminiferous epithelium, reduction of serum testosterone level, reduction in the number of Sertoli cells and Leydig cells.
Keywords: 2G cell phone, 3G cell phone, Mice testis, Testosterone, Ultra-high frequency radiation
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The increasing use of cell phone and handset devices emitting radiofrequency electromagnetic fields, particularly by children and teenagers, raises a great concern about the interactions of radiofrequency radiation on the male reproductive organs. Electromagnetic radiation emitted from the cell phone could be absorbed by testis when they are carried in belts. Most of the cellular phones work on the ultra-high frequency bandwidth of 900- 2200 MHz’s. Ultra high frequency (UHF) electromagnetic radiation or radiofrequency radiation (RFR) with a frequency range of 300- 3000 MHz is “non-ionizing”. The present inquest is concerned this form of radiation either to incriminate it as potentially hazardous or absolve it as absolutely harmless. The second generation cell phone (2G) network operates in the 900-1800 MHz frequency and third generation cell phone (3G) network operates in the 1900-2200 MHz frequency for GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications)1 . Mobile phone in operation emits a pulsed radiofrequency electromagnetic field (RF-EMF). Most of the energy is found to be absorbed into user’s body particularly in the head region, which can produce heat stress and non-thermal stress in the form of releasing free radicals, alter the enzyme reaction and thereby compromises immune system2 . Specific absorption rate (SAR) is a unit of Watt per kilogram to measure the amount of electromagnetic radiation absorbed by body tissue whilst using a mobile phone3, 4. The higher the SAR the more radiation is absorbed. International Commission on Non-Ionising Radiation Protection (ICNIRP Guidelines 1998) recommendations has set a SAR limit of 2.0 W/Kg in 10 grams of tissue. Whole body average SAR of 0.4W/Kg is widely adopted in most guidelines, which were based on the threshold of the observed effects due to whole-body heating to cause significant elevation of core temperature (>1°C)1 . Review of literature shown that exposure to mobile phone radiation could induce damage to tissues which include an increase in single and double strand DNA breakages5 , increased risk of acoustic neuroma associated with mobile phone use of at least ten years duration6 , genotoxic effects in human peripheral blood leukocytes7 , reduction of Purkinje cell number in the adult female rat cerebellum8 , and disturbance of short term memory in mice9 . Authors have reported that short term exposure to mobile phone radiation induced damage to kidney10-14. Keeping a cell phone on or close to the waist can decrease sperm concentration15, decrease in sperm viability and motility due to direct exposure of semen to cell phone radiation16. Long term exposure to mobile phone radiation could lead to reducing sperm motility, serum testosterone levels17-20, increased ROS (reactive oxygen species) 21-24, reduction in seminiferous tubule diameter and thickness of epithelium25 and vacuolisation in the cytoplasm of Sertoli cell 26 In contrary to above findings some researchers reported that no adverse biological effects of exposure to non-ionizing radiation emitted from the cell phone, such as no double stranded DNA breaks or effects on chromatin of rat brain27, no effect on mouse embryonic lens development28, psychomotor performance was not influenced by brief repeated exposures to mobile phones29.The lack of histological changes on rat testis30, 31 and no alterations in serum testosterone32 were cited. The present study is undertaken because of the contradictory findings on the effects of exposure to non-ionizing radiation emitted from the 2G and 3G cell phone on testis. The aim of our study is to evaluate possible effects of chronic exposure to 900 - 1800 MHz radiation emitted from 2G cell phone and 1900 -2200 MHz from 3G cell phone on the testis of mice; and to compare the effects of 2G and 3G radiation on testis at microstructure level.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Our study was approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee of Mahatma Gandhi Medical College and Research Institute, Puducherry.Fifty four male neonatal albino mice were obtained from the King Institute of Preventive Medicine and Research, animal section, Guindy, Chennai. New born mice (with the mother for twenty one days) were randomly divided into three independent groups; control, 2G exposed and 3G exposed. Animals were kept in mice cages at the temperature of 22 ± 1°C, 60% relative humidity and housed in the central animal house provided with adequate ventilation; twelve hours of illumination alternated with twelve hours of darkness. During the study, all the animals received appropriate animal care and were fed with laboratory diet and water ad libitum. Eighteen mice were exposed to 900-1800 MHz frequency radiation emitted from 2G cell phone and eighteen mice were exposed to 1900-2200 MHz frequency radiation emitted from 3G (video call) cell phone. Eighteen mice were sham control. The roof of the mice cage was designed to hang the 2G and 3G (video call) cell phone from the distance of five centimetres from the floor; which allow the mice to move freely and to avoid direct thermal injury in mice. 2G and 3G (video call) mobile phone in non-vibrating, silent, do not disturb (DND) and auto answer mode activated was kept hanging inside the mice cage. EMF emitted from a 2G and 3G standard handset with a frequency bandwidth of 900-1800 MHz and 1900 – 2200MHz respectively with the power of 2W/Kg. The highest specific absorption rate (SAR) value for this standard handset was 1.69 W/Kg (10gm).The mobile phone which was kept inside the mouse’s cage was rung upon from other 2G and 3G (video call) cell phone for every half an hour, each call lasting for two minutes. Mice were exposed forty eight minutes per day for a twelve hour periods (from 8.00AM to 8.00PM) and total duration of exposure was 30 to 180 days. RF meter was used to measure the amount of radiation exposed in 2G and 3G experimental groups. The sham control group of eighteen mice was kept under similar conditions without 2G or 3G exposure. Before sacrificing, we measured the body weights of mice in all three groups. Three mice each were sacrificed at the end of 30, 60, 90, 120, 150 and 180 days of exposures in the experimental groups after 24 hours of last exposure. Equal numbers of control mice were sacrificed on a similar time points. We sacrificed mice under anaesthesia and collected 1 ml of blood by cardiac puncture for total serum testosterone measurement and all samples were read in duplicate. Testes were dissected out and its weight and volume measured. We used Denver’s digital weighing machine (0.001gm) for measuring weight and water displacement method to calculate volume. After the morphometric analysis, testes were fixed by 4% formalin solutions for a period of twenty four hours and then tissues processed and embedded in paraffin. Tissues were sectioned at five microns, stained with Haematoxylin and Eosin. We analysed testis sections from random slide, random sections and random field under the light microscope; for histomorphometric parameters and structural changes. Diameters of 50 randomly selected essentially round seminiferous tubules from each testis were measured using calibrated ocular micrometre. We measured the seminiferous tubule diameter in both horizontal and vertical axis and the mean average was taken. The mean seminiferous tubule density per unit area was calculated by square graticule which was mounted on an eyepiece. All the testis sections were blindly reviewed by the same investigator. Each seminiferous tubule was analysed and classified into one of 10 different grades utilizing Johnson testicular biopsy score count33. The total serum testosterone measured by enzyme linked fluorescent immunoassay (ELFA) method.
Statistical analysis
We used ANOVA and Kruskal–Wallis test to compare all three groups; independent t test and Mann Whitney U test for comparing 2G and 3G groups. P value ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
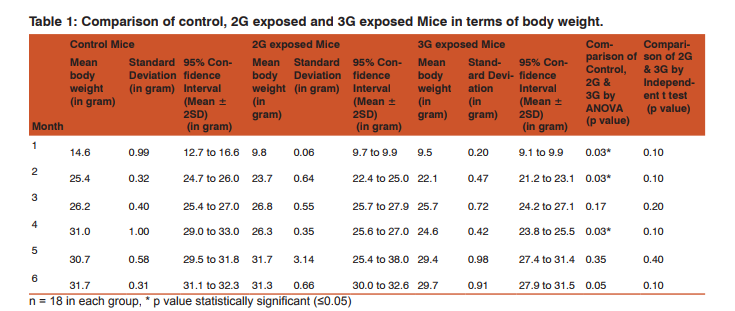
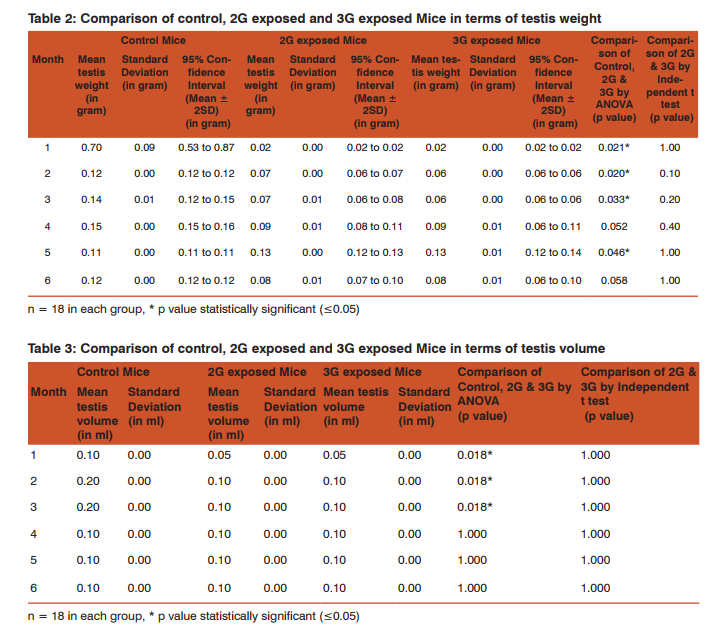
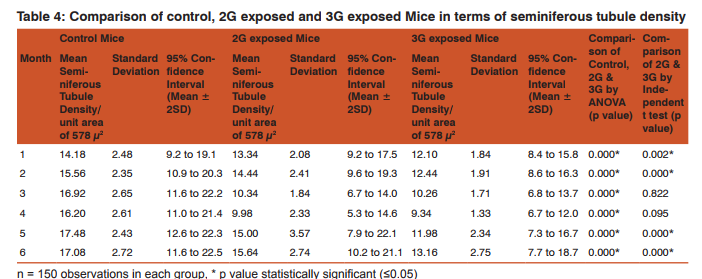
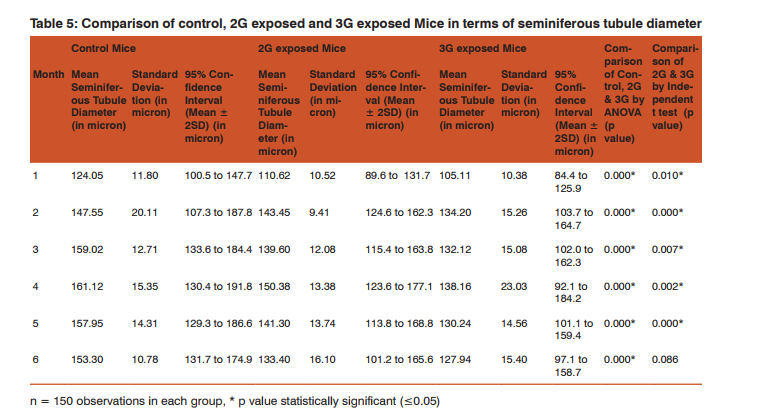
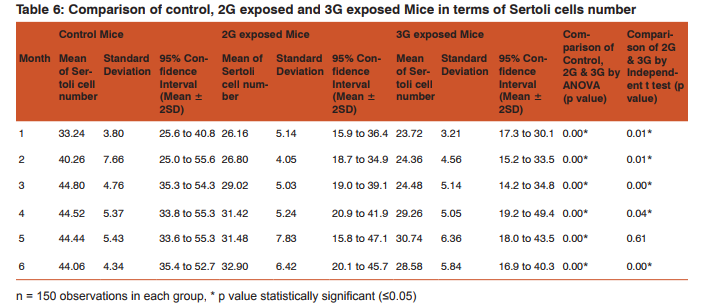
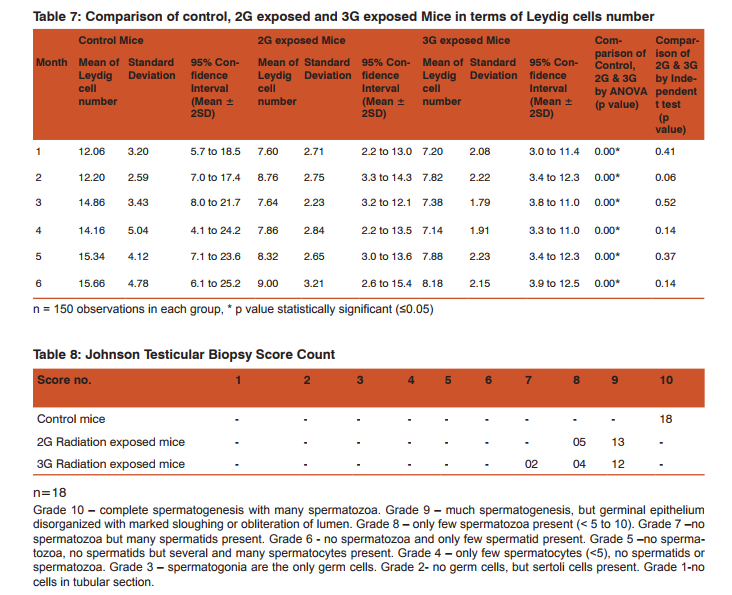
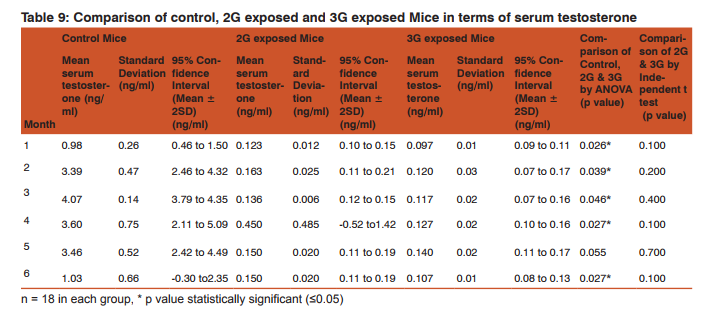
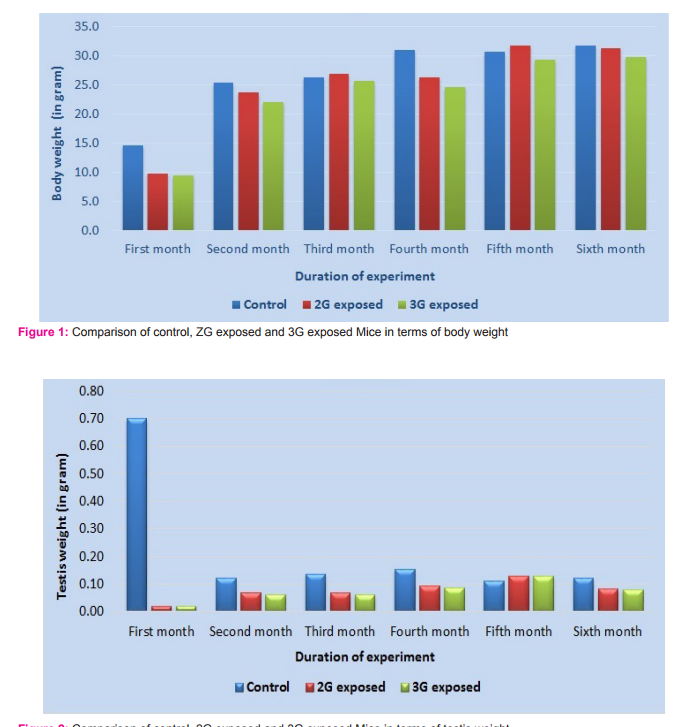
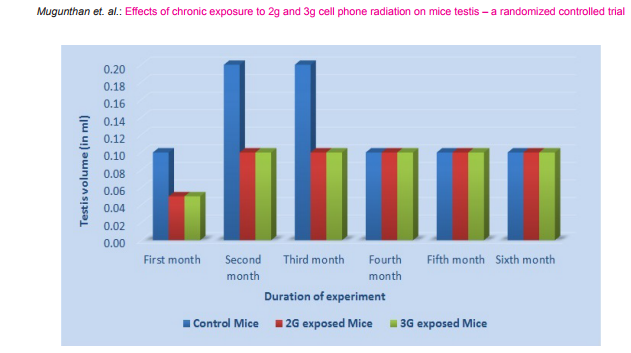
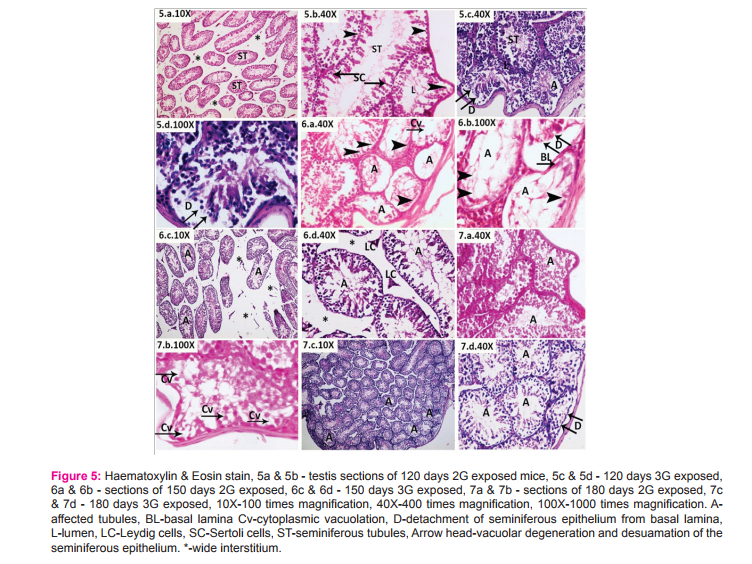
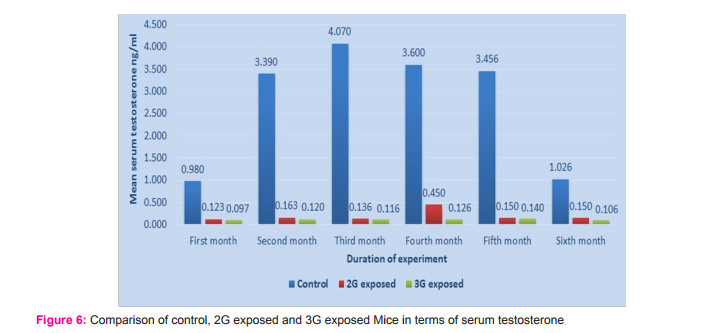
Morphometric study: The mean body weight of mice sacrificed during first, second and fourth month was significantly differing amongst three groups by ANOVA (p value 0.05) (Table 1-3). Histomorphometric study: The mean density of seminiferous tubule (per unit area of 578µ2 ), mean seminiferous tubule diameter (in micron), mean number of Sertoli and Leydig cells of mice sacrificed every month were significantly differing amongst three groups by ANOVA (p value 0.05) (Table. 7). The following microscopic changes were seen in the 2G and 3G radiation exposed mice testis over control. 1. The interstitium between tubules appeared morewide 2. Sertoli and spermatogonial cells appeared detached from the basal lamina. 3. Vacuole degeneration and desquamation of seminiferous epithelium. 4. Most of the peripheral tubules showed reduced thickness of seminiferous epithelium and maturation arrest in the spermatogenesis 5. Seminiferous tubules scored 7 to 9 using Johnson testicular biopsy score count (Table. 8) (Figure. 4 and 5). Biochemical Study: Mean serum testosterone (ng/ml) of first, second, third, fourth and sixth month mice were significantly differed amongst three groups by ANOVA (p value 0.05) (Table.9) (Figure.6).
DISCUSSION
The present study has been undertaken to investigate the effects of chronic exposure of 2G and 3G cell phone radiations on mice testis; and to compare the effects of 2G and 3G radiations on testis at the histological level. Chronic exposure of 2G and 3G cell phone radiation to mice, resulted in reduction of animal weight at first, second and fourth month. The mean testis weight of 2G and 3G radiation exposed mice was significantly reduced in the first three months, however in fifth month mean testis weight was significantly increased. Similarly mean testis volume of 2G and 3G radiation exposed mice was significantly reduced in the first three months. The mean density of seminiferous tubule, mean seminiferous tubule diameter, mean number of Sertoli and Leydig cells of 2G and 3G exposed groups were significantly lower than control group. When compared to control group mean serum testosterone level of 2G and 3G exposed mice was significantly lower. Sections of 2G and 3G radiation exposed mice testis showed wide interstitium, detachment of Sertoli cells and spermatogonia from the basal lamina, vacuolar degeneration and desquamation of the seminiferous epithelium. Most of the peripheral tubules showed reduced thickness of seminiferous epithelium and maturation arrest in the spermatogenesis. Seminiferous tubules scored 7 to 9 in Johnson testicular biopsy score count. In earlier studies of Ozguner M et al (2005)34 and Hanci H et al (2013)25, rat was exposed to 900MHz cell phone radiation and found there was a significant decrease in seminiferous tubular diameter, mean height of the seminiferous epithelium and serum total testosterone level. Our study agreed with Ozguner M et al and Hanci H et al study with the above mentioned parameters in mice testis indicating that there was no species difference. Our study agreed with S Dasdag et al study (1999)35 on rat exposed to microwaves emitted by cell phone The author reported significant reduction of mean seminiferous tubular diameter and Johnson testicular biopsy score count was between 8 to 10. In the study of LatifaIshaqKhayyat (2011)12 and Pradeep Kumar (2014)36, the electromagnetic field of cell phones induced Leydig cell hypoplasia, wide interstitium, atrophied seminiferous tubules, maturation arrest in the spermatogenesis, decreased germ cell population, pyknotic nuclei in germ cell and vacuolisation in spermatogenic cells. They also observed detachment of spermatogonia and Sertoli cells from the basal lamina, shrinkage, residual cytoplasm and debris of degenerating cells in the seminiferous tubules. The present study conducted with mice was in agreement with Latifa Ishaq Khayyat12 and Pradeep Kumar study36. Our study agreed with the findings of Ali H.M.Omer et al (2009)37 who observed reduction of serum testosterone level inthe rat after exposure of 900MHz electromagnetic radiation. Similar reduction in serum testosterone level have been cited by Salem Amara et al (2006)38, Mugunthan et al (2014)39 and Wang S M et al (2003)20. H.OzlemNisbet et al (2011)40 found that exposure of the rat to 900 to 1800 MHz radiations produced severe vacuolar degeneration, necrosis and desquamation of the seminiferous epithelium; they also reported high level of mean plasma testosterone in experimental group than the sham control group. Our study showed significant reductions in mean serum total testosterone level in mice. Study conducted by ZsoltForgacs et al (2006)41 on mice exposed to 1800 MHz GSM like microwave observed significant increase in serum testosterone without any structural changes in testis. The present study showed structural changes in mice seminiferous epithelium and lower serum testosterone level.The present study disagreed with Ji Yoon Kim et al (2007)42 who observed long term exposure of rats to 2.45 GHz radiations induced increase in the number of Leydig cells and increased serum total testosterone level. Leydig cells are most susceptible to electromagnetic radiation. Radiation might be detrimental to the structure and function of Leydig cells and thereby reduce the serum testosterone level20. This could be responsible for the significant reduction in the mean number of Leydig cells and serum testosterone level of 2G and 3G exposed mice in our study. Cell phone radiation could cause increased vascular permeability and thereby interstitial oedema43. We observed wide interstitium in the sections of 2G and 3G radiation exposed mice testis and it could be the reason for the significantly low mean density of seminiferous tubules per unit area in 2G and 3G radiation exposed mice testis. The surface organ such as testis could be more affected by the radiation emitted from the cell phone. Even though mice testis movesto abdomen through the inguinal canal (abdomino-scrotal), energy absorbed (SAR) by testis could be more as it is predominantly surface organ. This could be probable reason for the predominant damages observed on the peripheral tubules of testis exposed to 2G and 3G cell phone radiations.
CONCLUSION
Chronic exposure of mice to ultra-high frequency radiation emitted from 2G and 3G cell phone could cause a reduction in body weight, testis weight and volume. Microscopic changes in the testis such as reduction in mean seminiferous tubule density, seminiferous tubule diameter, vacuolar degeneration and desquamation of the seminiferous epithelium; reduction in the thickness of seminiferous epithelium and maturation arrest in the spermatogenesis of the peripheral tubules could occur. Decreased serum testosterone level, reduction in the number of Sertoli and Leydig cells could also occur following chronic exposure to 2G and 3G cell phone radiation. Thus long term exposure of cell phone radiation could cause male infertility in mice.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors sincerely thank the Professors and Heads of the Department of Anatomy, Pharmacology and Pathology of Mahatma Gandhi Medical College and Research Institute, Puducherry, for their whole hearted support to undertake this research work. Authors thank Dr.SaravananGanesan, Director, Laboratory Medicine, Nanolab, Nammakkal, Tamil Nadu, for his support to carry out this research work. Authors also thank Mr.Chandresekar, senior histology technician at Mahatma Gandhi Medical College and Research Institute, Puducherry, for his valuable support. Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/ editors/ publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been considered and discussed.

References:
1. International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection. Review of the scientific evidence on dosimetry, biological effects, epidemiological observations and health consequences concerning exposure to high frequency electromagnetic fields (100 KHz to 300 GHz). Germany. ICNIRP 16/2009.
2. TomKosatsky,AbderrachidZitouni,MonaShum,HelenD. Ward,RichardP.Gallagher,FrancineAnselmo,RandyRoss,L isaFreeman,JoannaOda,SarahLidstone,LisaMiu,Michele Wiens,Maureen Phillips, and Terry Spock. Project - Radiofrequency Toolkit for Environmental Health Practitioners. Canada, 2013; ISBN: 978-1-926933-48-1.Page:269.
3. Federal Communications Commission Office of Engineering and Technology. Evaluating Compliance with FCC Guidelines for Human Exposure to Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields.OET Bulletin 65. Edition 97-01.August 1997: Page 5.
4. IEEE Standards Coordinating Committee 28 on Non-Ionizing Radiation Hazards.IEEE Standard for Safety Levels with Respect to Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Fields, 3 KHz to 300GHz. New York, December 1998.ISBN 0-7381-1558-4 SS94717. Page: 29.
5. Lai H, Singh NP. Single and double strand DNA breaks in rat brain cells after acute exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation. Int J Radiat Biol.1996; 69(4):513-21. 6. Lonn S, Ahlbom A, Hall P, Feychting M. Mobile phone use and the risk of acoustic neuroma. Epidemiology.2004; 15(6):653-9.
7. Zeni O, Romano M, PerrottaA, Lioi MB, Barbieri D, d’Ambrosio G, Massa R, Scarfi M.R. Evaluation of genotoxic effects in human peripheral blood leukocytes following an acute in vitro exposure to 900 MHz radio frequency fields. Bioelectromagnetics 2005; 26:258-265
. 8. OsmanFikretSonmez, ErsanOdaci, Orhan Bas and Suleyman Kaplan. Purkinje cell number decreases in the adult female rat cerebellum following exposure to 900 MHz electromagnetic field. Brain Research. 2010. Volume 1356: 95- 101
. 9. Ntzouni MP, Stamatakis A, Stylianopoulou F, Margaritis LH. Short- term memory in mice is affected by mobile phone radiation. Pathophysiology.2010: 25.
10. Al-Glaib B, Al-Dardfi M, Al-Tuhami A, Elgenaidi A and Dkhil M. A technical report on the effect of electromagnetic radiation from a mobile phone on mice organs. Libyan J Med.2007.AOP: 080107:8-9.
11. Laila K. Hanafy, Sawsan H, Karam, AnisaSaleh. The adverse effects of mobile phone radiation on some visceral organs. Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences. 2010. 5(1):95-99.
12. LatifaIshaqKhayyat. The histopathological effects of an electromagnetic field on the kidney and testis of mice. EurAsian Journal of BioSciences.2011, 5:103-109.
13. N Hanafi, F.Eid, A.El-Dahshan.Radiation emitted from mobile phone induces amyloidosis features in some tissues of infant mice. The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine.2012.Vol.47:132-144.
14. Ingole IV, Ghosh SK. Cell phone radiation and developing tissues in chick embryo: A light microscopic study of kidneys. J. Anat. Soc. India.2006, 55(2):19-23.
15. Sarah J Kilgallon, Leigh W Simmons. Image content influences men’s semen quality. Biol.Lett.2005; 1:253-255.
16. AshokAgarwal, Nisarg Desai, KartikeyaMakker, Alex Varghese, Rand Mouradi, Edmund Sabanegh, Rakesh Sharma. Effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic waves (RFEMW) from cellular phones on human ejaculated semen: an invitro pilot study. Fertil Steril.2008:1318-1325.
17. Meo SA, Al-DreesAM, Husain S, Khan MM, Imran MB. Effects of mobile phone radiation on serum testosterone in Wistar albino rats. Saudi Med J.2010; 30(8):869-73.
18. I Fejes, Z.Zavaczki, J.Szollosi, S.Koloszar, J.Daru, L.Kovacs and A.Pal. Is there a relationship between cell phone use and semen quality? System Biology in Reproductive Medicine.2005; Vol.51, No.5:385-393.
19. Erogul O, Oztas E, Yildirim I, Kir T, Aydur E, Komesli G, Irkilata HC, Irmak MK, Peker AF. Effects of electromagnetic radiation from a cellular phone on human sperm motility: an in vitro study. Archives of medical research.2006; 37(7):840-3.
20. Wang SM, Wang DW, Peng RY, Gao YB, Yang Y, Hu WH, Chen HY, Zhang YR, Gao Y. Effect of electromagnetic pulse irradiation on structure and function of Leydig cell in mice. National Journal of Andrology.2003; 9(5):327-330.
21. SrinivasBelurVeerachari, SS Vasan. Mobile phone electromagnetic waves and its effect on human ejaculated semen: An in vitro study. Int J Infertility Fetal Med.2012; 3(1):15- 21.
22. ManeeshMailankot, Anil P Kunnath, Jayalekshmi H, BhargavKoduru, RohithValsalan. Radio frequency electromagnetic radiation (RF-EMR) from GSM (0.9 / 1.8 GHz) mobile phone induces oxidative stress and reduces sperm motility in rats. Clinics. June.2009 Vol.64.No.6.
23. AshokAgarwal. Cell phones and male infertility: dissecting the relationship. Reproductive BioMedicine Online. 2007; Vol 15.No.3:266-270.
24. Ozorak A, Naziroglu M, Celik O, YukselM,OzcelikD,OzkayaMO,Cetin H, Kahya MC, KoseSA. Wi-Fi (2.45 GHz) and Mobile Phone (900 and 1800 MHz) Induced Risks on Oxidative Stress and Elements in Kidney and Testis of Rats During Pregnancy and the Development of Offspring.Biol Trace Elem Res 2013;156 (1-3): 221-229.
25. Hanci H, Odaci E, Kaya H, Aliyazicioglu Y, Turan I, Demir S, Colakoglu S. The effect of prenatal exposure to 900 megahertz electromagnetic field on the 21 old day rat testicle. ReprodToxicol. 2013; 42:203-209.
26. Celik S, Aridogan IA, Izol V, Erdogan S, Polat S, Doran S. An evaluation of the effects of long term cell phone use on the testes via light and electron microscope analysis. Urology. 2012; 79 (2): 346-350.
27. Belyaev IY, Koch CB, Terenius O, Roxstrom Lindquist K, Malmgren LO, H Sommer W, Salford LG, Persson BR. Exposure of rat brain to 915 MHz GSM microwaves induces changes in gene expression but not double stranded DNA breaks or effects on chromatin conformation. Bioelectromagnetics. 2006; 27(4):295-306.
28. Ke Yao, YiBoYu, KaiJun Wang, Juan Ye, DeQiang Lu, Huai Jiang. Absence of effect of power-frequency magnetic fields exposure on mouse embryonic lens development.Bioelectromagnetics.2007; 28 (8):628-635.
29. Curcio G, Valentini E, MoroniF,Ferrara M, De GennaroL,Bertini M. Psychomotor performance is not influenced by brief repeated exposures to mobile phones. Bioelectromagnetics.2008; 29 (3):237-241.
30. Imai N, Kawabe M, HikageT,Nojima T, Takahashi S,Shirai T. Effects on rat testis of 1.95 GHZ W-CDMA for IMT-2000 cellular phones.SystBiolReprod Med. 2011;57(4): 204-209.
31. Hae - June Lee, Jeong - Ki Pack, Tae - Hong Kim, Nam Kim, Soo - Yong Choi, Jae - Seon Lee, Sung - Ho Kim, Yun - Sil Lee. The lack of histological changes of CDMA cellular phone - based radio frequency on rat testis. Bioelectromagnetics.2010; 31 (7):528-534.
32. B. Khillare, J.Behari. Effect of amplitude –modulated radiofrequency radiation on reproduction pattern in rats. Electromagnetic Biology and Medicine.1998, Vol.17, No.1: Pages 43-55.
33. Johnsen S.G. Testicular biopsy score count – A method for registration of spermatogenesis in human testes: normal values and results in 335 hypogonadal males. Hormone Research.1970; Vol.1, No.1: Pages 2-25.
34. Ozguner M, Koyu A, Cesur G, Ural M,Ozguner F, Gokcimen A, Delibas N. Biological and morphological effects on the reproductive organ of rats after exposure to electromagnetic field. Saudi Med J. 2005; 26 (3): 405-10.
35. S.Dasdag, M.A.Ketani, Z.Akdag, A.R.Ersay, I.Sari, O.C.Demirtas, M.S.Celik. Whole-body microwave exposure emitted by cellular phones and testicular functions of rats. Urol Res. 1999; 27:219-223.
36. Pradeep Kumar, VineetaShukla.Ultrastructural changes in rat testicular tissue after whole body exposure to electromagnetic radiation emitted from mobile phones. Journal of International Academic Research for Multidisciplinary.2014.Vol.2 Issue.1: 518-526. 3
7. Ali H.M.Omer, Mahmoud S, Zakaryia, Ghada A Ishak, Samia A. El Feky, Dalia Mohamed Ali. Electromagnetic waves exposure and the possible associated some organs dysfunction.El –Minia Med Bull. 2009; Vol.20, No.1: 446-456.
38. Salem Amara, HafedhAbdelmelek, Catherine Garrel, Pascale Guiraud, Thierry Douki, Jean – Luc Ravanat, Alain Favier, Mohsen Sakly, Khemais Ben Rhouma. Effects of subchronic exposure to static magnetic field on testicular function in rats. Archives of Medical Research.2006; Vol.37: 947-952.
39. N Mugunthan, J Anbalagan, S Meenachi. Effects of long term exposure to a 2G cell phone radiation (900-1900 MHz) on mouse testis.International Journal of Science and Research. 2014; Vol.3.Issue 9:523-529.
40. H. OzlemNisbet, CevatNisbet, AysegulAkar, MesutCevik, M.OnderKarayigit. Effects of exposure to electromagnetic field (1.8/0.9 GHz) on testicular function and structure in growing rats. Research in Veterinary Science. 2012; 93:1001-1005.
41. ZsoltForgacs, ZoltanSomosy, GyorgyiKubinyi, JozsefBakos, ArankaHudak, AndrasSurjan, GyorgyThuroczy. Effect of whole – body 1800 MHz GSM – like microwave exposure on testicular steroidogenesis and histology in mice. Reproductive Toxicology.2006; 22:111-117.
42. Ji Yoon Kim, Hyun Tae Kim, Ki Hak Moon, Hyoun Jin Shin. Long – term exposure of rats to a 2.45 GHz electromagnetic field: Effects on reproductive function. Journal of Urology.2007; 48. Issue No. 12:1308-1314.
43. Robert E.Anderson, Morgan Berthrong, Louis F.Fajardo. Radiation injury. Anderson’s Pathology. 10th edition. Volume 1. Missouri. Von Hoffman Press.1996: Page.484-51.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License