IJCRR - 7(7), April, 2015
Pages: 10-17
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL EGG QUALITY CHARACTERISTICS OF THREE VARIETIES OF HELMETED GUINEA FOWL (NUMIDAMELEAGRIS) IN NIGERIA
Author: Onunkwo D. N., Okoro I. C.
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:An investigation of the egg quality characteristics of three varieties of guinea fowls was studied. The experimental varieties were Pearl (Sake), Lavender (Hurudu) and Black (Angulu). Base populations of 180 guinea fowls were used to generate 144 F1 females comprising 48 birds per variety. Each variety was divided into three randomized replicates containing 16 birds per replicate. Data were collected fortnightly on egg quality traits. Parameters collected for egg quality traits include: Egg Weight (EW), Egg Length (EL), Egg Width (EWD), Egg Index (EI), Shell Thickness (ST), Shell Weight (SW), Albumen Height (AH), Albumen Weight (AW), Albumen Diameter (AD), Yolk Length (YL), Yolk Height (YH), Yolk Weight (YW), Yolk Diameter (YD), Yolk Index (YI), and Haugh Unit (HU). The egg quality data were treated statistically. The Pearl, Lavender and Black varieties showed great
similarities in two important indices for assessing egg quality traits, namely: Haugh unit (88.95, 89.04, and 88.56) and yolk index values (0.40, 0.41, and 0.42) respectively. Based on the mean internal egg quality values, Differences were observed in albumen weight (18.23, 19.79 and 17.36) and yolk diameter (32.31, 31.91 and 31.50) of the Pearl, Lavender and Black varieties respectively. The Lavender and Pearl varieties recorded higher values in both traits than the Black. The result of the mean external egg quality traits showed that the Pearl and Lavender varieties are similarly longer and wider than the Black variety. The Black
variety however outperformed the Pearl variety in shell thickness. The Pearl and Lavender varieties showed more similarity in performance than the Black. However, since, the Lavender variety performed better than the Pearl variety in albumen weight and shell thickness, it is thus recommended.
Keywords: Egg quality, Egg characteristics, Guinea fowl, Varieties
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Guinea fowl (Numida meleagris) are indigenous to WestAfrica North of the Equatorial forest where there is an estimated population of about 4.7 million (FDLPS/RIM, 1991). It got the name ‘Guinea’ because it was believed to have originated from Guinea in West Africa. Among domestic types which the peasant farmers have long identified and given local names based on their coloration are Pearl (Sake), Lavender (Hurudu), Black (Angulu) and White (Faren Zabi). The Pearl is the most common and probably the first developed from the Wild West African birds (Ikani and Dafwang, 2004). Guinea fowls are seasonal breeders which has been recognized as one of the major drawbacks to large scale guinea fowl production. In the wild, production starts at 28-42 weeks with 15-20 eggs being laid each season while in captivity, production starts at 28-32 weeks with 50- 100 eggs being produced in the first year and more eggs (180) are laid in the second year of production(Ayorinde, 1990). Laying may continue for 7 or more years. The eggs and to a lesser extent the meat of guinea fowl are widely eaten by Nigerians because of the distinctive flavor they produce (Dudusola, 2010). According to Ayorinde (1990), guinea fowl meat has higher protein content (about 28%), an eviscerated yield of over 80% and a yield of edible carcass of between 50% and 80%. The good keeping quality of guinea fowl eggs and the hardy disease resistant nature of the stock contribute to the prominent position of this species in Nigeria. Egg quality is composed of those characteristics of an egg that affects its acceptability to consumers such as cleanliness, freshness, egg weight, shell quality, yolk index, albumen index, Haugh unit and chemical composition (Song et al., 2000). In other countries like India, it is the more important price contributing factor in table and hatching eggs and as such the economic success of a laying flock solely depends on the total number of quality eggs produced (Parma et al., 2006). Chicken eggs has been very well studied for its external and internal qualities as well as for its composition; however such information are not so abundantly documented in other poultry species (Dudusola, 2010). Certain traits of economic importance in egg production include the egg number, egg quality traits, and other egg indices (Oluyemi and Robert, 2000).
MATERIALS AND METHOD
Location of Study
This study was carried out in the Teaching and Research Farm of Michael Okpara University of Agriculture, Umudike, located at about ten kilometers from Umuahia, the Abia State capital. Umudike bears the coordinate of 5°281 North and 70 321 East, and lies at an altitude of 122 meters above sea level. The environment of study was situated within the Tropical Rainforest zone and is characterized by an annual rainfall of about 2177 mm. The relative humidity during the rainy season is well over 72 %. Temperature ranged from 22 0 C - 36 o C with March being the warmest month, while July to October represents the coolest period with a temperature range of 22 0 C – 30 o C (Nwachukwu, 2006).
Acquisition and Mating of Base Population
One hundred and eighty adult guinea fowls of three varieties were procured from several markets in Zaria. The base population consisted of 36 adult males, and 144 adult females. Each variety had 12 males and 46 females each. These adults were quarantined for two weeks. A mating ratio of 1 male: 3 females were maintained and the mating scheme adopted was as shown below:
• Pearl male X Pearl female - Homozygous Pearl variant main cross
• Lavender male X Lavender female - Homozygous Lavender variant main cross.
• Black male X Black female - Homozygous Black variant main cross.
Experimental Animals and Management
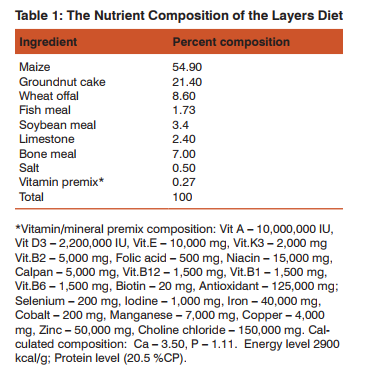
The eggs laid by the base population were set and hatched at Kanem Hatcheries off Aba-Owerri Road, Aba. A total of two hatches which were one week apart yielded 350 F1 keets. All F1 male keets hatched were culled leaving only 165 F1 female keets which were used for the experiment. The keets were brooded for six weeks and subsequently reared until the 28th week when they started laying eggs. At the 28th week, 144 adult females were randomly selected out of the 165 females and wing-banded. The 144 adult females consisted of 48 females of Pearl, Lavender and Black each. Each variety was replicated three times, which gave a total of 9 replicates (B1, B2, B3, P1, P2, P3, L1, L2, and L3) for all the varieties, with 16 females per replicate. The guinea fowl varieties were raised in deep litter pens under natural daylight. Feed and water was provided ad-libitum. During the laying phase, layers mash containing 2900 kcal/kgME and 20.5 % CP according to Oguntona (1983) was introduced to the guinea fowl varieties. The nutrient composition of the layers diet is shown in table 1 below:
Data collection
Data was collected for egg quality traits fortnightly. With the aid of a scalpel, the eggs were broken and the content emptied into a Petri-dish. The following parameters were determined:
• Egg Weight (EW): This was measured using an electronic sensitive scale.
• Egg Length (EL): This was determined using Vernier Caliper.
• Egg Width (EWD): This was determined using Vernier Caliper
. • Egg Index (EI): This was computed from the ratio: EI = Mean Egg Width Mean Egg Length
• Shell Thickness (ST): This was determined using a micrometer screw gauge. The average of the three readings at the broad, narrow and mid sections was taken as the shell thickness for each bird in the group.
• Shell Weight (SW): This was measured using electronic scale
• Albumen Height (AH): This was measured with a Spherometer.
• Albumen Weight (AW): The albumen was placed in a Petri-dish on an electronic scale and the weight of the albumen was determined by difference
. • Albumen Diameter (AD): This was computed as follows: AD = Long diameter + short diameter 2
• Yolk Length (YL): This was determined using Vernier Caliper
• Yolk Height (YH): This was measured with a Spherometer
. • Yolk Weight (YW): The yolk was separated from the albumen and then placed in a weighed Petridish on an electronic scale and the weight of the yolk was determined by difference.
• Yolk Diameter (YD): This was measured using a Vernier Caliper as the width of the yolk.
• Yolk Index (YI): This was computed from the ratio YI = Yolk height Yolk diameter
• Haugh Unit (HU): This was estimated using the equation according to Haugh (1937): HU = 100Log {H+7.57-1.7 W0.37} Where, H = Observed Albumen Height (mm) W = Observed Weight of Egg (g).
Statistical Analysis
Data collected for the egg quality traits were subjected to Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) in Completely Randomized Design (CRD) using the general linear model described by Steel and Torrie (1980) and significant means were separated using Duncan’s Multiple Range Test (Duncan, 1955).The statistical model used is as shown below:

RESULTS
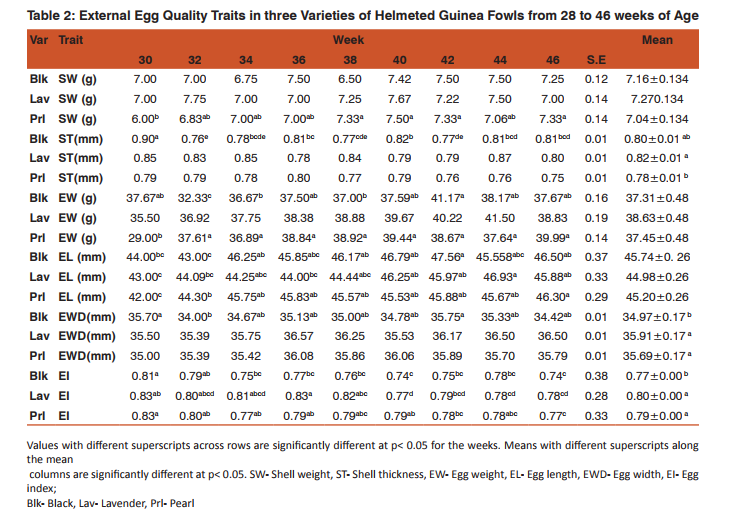
External Egg Quality Traits in Three Varieties of Helmeted Guinea Fowl from 28 to 46 Weeks of Age The external egg quality traits in three varieties of helmeted guinea fowls from week 28 to 46 weeks of age is presented in Table 2. Non-significant differences (P> 0.05) were found in the shell weight values of Black and Lavender whereas a significant difference (P< 0.05) was found in Pearl. The shell thickness values were observed to vary (P< 0.05) in Black whereas no significant differences (P> 0.05) were observed in Pearl and Lavender. Black and Lavender showed fluctuating trends whereas the Pearl variety showed a decreasing trend with slight fluctuations. Chineke (2001) reported similar trends in the shell thickness of the Olympia Black laying variety. Oke et al. (2004) reported values which portrayed a decreasing trend in Pearl which agrees with our present report in Pearl variety. The egg weight values varied (P< 0.05) for Black and Pearl whereas no significant difference (P>0.05) was observed in Lavender as shown in Table 2. The three varieties showed very slight increases in egg weight. However, some decreases were noticed in the Black and Lavender towards the end of lay. The egg length values of each of the three varieties varied (P< 0.05) as shown in Table 2.Significant difference (P< 0.05) was observed in the egg width values in Black whereas no significant differences (P> 0.05) were observed in Pearl and Lavender as shown in Table 2. The Black and Lavender variety showed a fluctuating trend whereas the Pearl variety showed an increasing trend up to the 36th week and fluctuated thereafter. Chineke (2001) reported an increasing trend for the first three weeks which fluctuated thereafter in Olympia Black laying variety; this agrees with the present report for Pearl variety. The following Researchers have also reported increases in egg width: Gerstmayr and Horsi (1990); Olori and Sonaiya (1992; Austic and Neslieim (1990); and Asuquo (1994). The three varieties recorded significant differences (P0.05) was observed in Black va riety. The three varieties showed a decreasing trend up to the 38th week and the Pearl and Lavender varieties thereafter maintained a slightly increasing trend with slight fluctuations whereas the Black increased with a big trough in week 44. The decreasing trend suggests some level of similarities which could have resulted by genetic or non-genetic reasons (Chineke, 2001). The albumen height (AH) values were observed to vary significantly (P0.05) were observed for Pearl and Lavender. Significant difference may be due to non-genetic factors and due to variations in physiological status of the animal. The three varieties showed a somewhat increasing trend from at least the 36th week. Oke et al. (2004) reported values that showed somewhat increasing trend which agreed mostly with the present report for Pearl variety. It is noteworthy that the Black and Lavender showed initial decreases whereas the Pearl variety maintained its increasing trend. Yolk diameter (YD) varied (P< 0.05) in each of the three varieties. The three varieties maintained a decreasing trend. Normally, a higher yolk height associated with a lower yolk diameter, results in better quality of the egg. Yolk index (YI) varied (P< 0.05) in each of the three varieties. The three varieties showed a fairly increasing trend with slight fluctuations. This increasing trend implies that the yolk height increased as the yolk diameter decreased over time. This is to say that yolk quality increases with age in the wet season. The similarity in trend may again be due to genetic reasons (Chineke, 2001). None significant difference (p> 0.05) was found in the mean yolk index values of the three varieties. Obike et al. (2011) obtained a mean yolk index value of 38.90 and 38.65 in Pearl and Black varieties of guinea fowl which were slightly lower than the 40.00 and 42.00 obtained in this study for Pearl and Black varieties respectively. Significant differences (P0.05) was observed in the mean Haugh unit values of the three varieties which again suggest similarities. The Haugh unit values obtained in this study is higher than the 70% benchmark noted for quality eggs (Adeogun and Amole 2004). They also reported that the higher the yolk index and Haugh unit, the higher the quality of the egg.
DISCUSSION
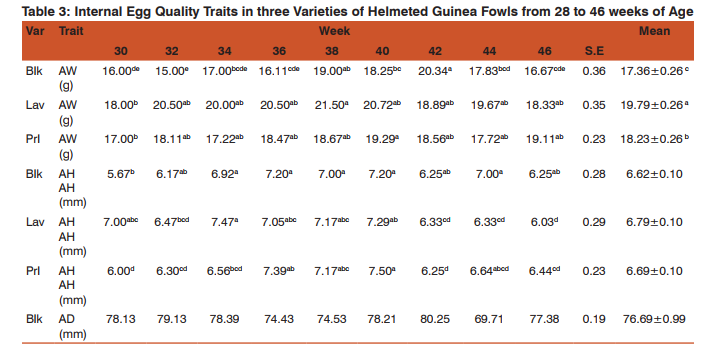
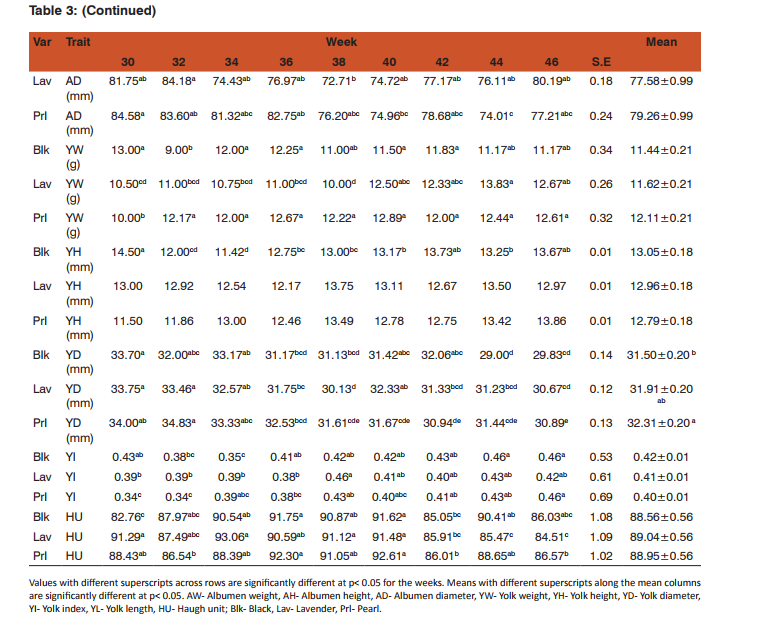
In shell weight values, Black and Lavender varieties showed similar trends with slight fluctuations which might be due to fluctuations in calcium metabolism. Onyeanusi (2007) noted that calcium has significant effect during egg production in guinea fowls. The Pearl variety portrayed an increasing trend up to the 40th week. The mean shell weight of the three varieties did not vary significantly (P> 0.05). Obike et al. (2011) obtained a mean shell weight values of 7.27 g and 7.12 g in Pearl and Black varieties of guinea fowl which compares with the values obtained in this study. Significant differences (P< 0.05) were observed in the mean shell thickness of the three varieties. The higher values obtained in this study may be because the shell thickness was obtained from the shells with their membranes intact. The slight increases in egg weight values of the three varieties agrees with the report of Chineke (2001) in Olympia Black laying variety, and Oke et al. (2004) who reported values that showed increases as production advanced. Obike et al. (2011) and Oke et al. (2004) obtained a mean egg weight of 37.67 g and 36.24 g respectively in Pearl variety of Guinea fowls which is slightly lower than the value (39.99 g) obtained in this study. These investigators also obtained a value of 37.91 g in Black variety which agrees with the present report for Black variety (37.67 g) The three varieties showed increasing trend which again may be due to genetic reasons (Chineke, 2001). Chineke (2001) and Oke et al.,(2004) reported an increasing trend in egg length. The following Researchers have also reported increases in egg length: Gerstmayr and Horsi (1990); Olori and Sonaiya (1992); Austic and Neslieim (1990); Asuquo (1994). Non-significant difference (P>0.05) was observed in the mean egg length values of the three varieties. Obike et al. (2011) obtained a mean egg length of 46.84 mm and 47.40 mm in Pearl and Black variety of Guinea fowls respectively which almost agrees with the present report of 45.20 mm in Pearl and 45.74 mm in Black variety Significant differences (P< 0.05) were observed in the mean egg width of the three varieties. The Pearl and Lavender varieties were the most significant while the Black variety was the least. Obike et al. (2011) obtained a mean egg width of 36.60 mm and 36.83 mm in Pearl and Black guinea fowls respectively which almost agrees with the present report for Pearl (35.69 mm) but slightly higher than the value 34.97 mm reported for Black. Significant differences (p< 0.05) were observed in the mean egg index value of the three varieties. Significant differences (P< 0.05) were observed in the mean albumen weight of the three varieties. The Lavender variety had the highest albumen weight (19.790 g) followed by the Pearl (18.236 g), and lastly the Black variety (17.355 g). Obike et al. (2011) obtained a mean albumen weight values of 17.38 g and 17.48 g respectively in Pearl and Black varieties of Guinea fowls which compares with the values obtained in this present study. Non-significant difference (P>0.05) was observed in mean albumen diameter in the three varieties of guinea fowl studied which suggests similarity. Obike et al. (2011) obtained a mean albumen diameter values of 61.27 mm and 66.97 mm in Pearl and Black varieties of guinea fowls which are lower than the values 79.26 mm and 76.69 mm obtained for Pearl and Black varieties respectively in this study. The three varieties showed an increasing trend in the Albumen Height up to the 40th week and thereafter showed a decreasing trend. The decrease may be associated with non-genetic factors (Chineke, 2001) such as the increasing humidity and higher rainfall which probably affected intake and metabolism thus resulting in increased fluidity of the albumen. Genetic or non-genetic factors (Chineke, 2001) like nutrition, and changing environmental conditions (Bernacki, 2003) could be responsible for the significant differences in the Yolk Weight. Oke et al. (2004) however, reported values that show an increasing trend in Pearl variety of Guinea fowl which concurs mostly with the present report for Pearl variety and to some extent, the Lavender variety but contrasts with the Black variety. Non-significant difference (P>0.05) was found in the mean yolk height values of the three varieties. The mean yolk height values obtained for the three varieties are lower than the value (15.89 mm) obtained by Oke et al. (2004) but compared with the values 13.09 mm in Pearl variety and 13.70 mm in Black variety of Guinea fowl reported by Obike et al. (2011). Significant differences (P0.05) was observed in the mean Haugh unit values of the three varieties which again suggest similarities. The Haugh unit values obtained in this study is higher than the 70% benchmark noted for quality eggs (Adeogun and Amole 2004). They also reported that the higher the yolk index and Haugh unit, the higher the quality of the egg.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
CONCLUSION
The three varieties of guinea fowl showed similarities in their external traits but differed in egg width and egg index. The Pearl and Lavender recorded higher values than the Black guinea fowl. The three varieties performed similarly well in Haugh unit (88.95, 89.04, and 88.56) and yolk index values (0.40, 0.41, and 0.42) in Pearl, Lavender, and Black respectively, which are very important indices for assessing egg quality. Considering the mean values, the three varieties showed similarities in most of the parameters except in albumen weight and yolk diameter. The result of the mean external egg quality traits showed that the Pearl and Lavender varieties are similarly longer and wider than the Black variety. The Black variety however outperformed the Pearl variety in shell thickness. The Pearl and Lavender varieties showed more similarity in performance than the Black. From the foregoing, the Pearl and Lavender varieties showed more similarity in performance than the Black variety and thus may be more genetically related than the Black. However, since, the Lavender variety performed better than the Pearl variety in albumen weight and shell thickness, it is thus recommended.
References:
1. Adeogun, I. U. and Amole, F. O. (2004). Some quality parameters of exotic chicken eggs under different storage condition. Bulletin for Animal Health andProduction in Africa (Kenya). Vol.52 (1): 43-47.
2. Asuquo, B.O. (1994). Some production parameters of Lohmann Brown broiler parent lines in the humid tropics. Nigeria Journal of Animal Production.
3. Austic, R.E. and Nesheim, M.C. (1990). Poultry production. Lea and Febiger, 13th ed. London.
4. Ayorinde, K. L. (1990). Problems and prospects of guinea fowl production in the rural areas of Nigeria. In: Rural Poultry in Africa (Proceedings of an International Workshop on Rural Poultry Development in Africa), (Ed. Sonaiya, E.B.), African Network on Rural Poultry Production Development, pp.106-115.
5. Bernacki Z. and Heller, K. (2003). Ocean jakosci jaj perlic szarych w roznych okresach niesnosci. Pr. Kom. Nauk. Roln. Boil. BTN 51: 27-32.
6. Chineke, C.A. (2001). Interrelationships existing between bodyweight and egg production traits in Olympia BlackLayers. Nigeria Journal of Animal Production. 28 (1): 1-8.
7. Dudusola, I.O. (2010). Comparative evaluation of internal and external qualities of eggs from quail and guinea fowl. International Research Journal of Plant Science. Vol.1 (5). Pp.112-115.
8. Duncan, D.B. (1955). Multiple Range Test. Biometrics. 11: 1-42
. 9. FDLPS/RIM (1991). Nigerian National Livestock Survey Report. Federal Department of Livestock and Pest Control Services, Abuja Nigeria.
10. Gerstmayr, S. and Horsi, R. (1990). The relationship between bodies, egg and oviduct weight in laying hens. Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics, 107: 149-158.
11. Ikani, E.I. and Dafwang, I.I. (2004). The production of guinea fowl in Nigeria. Extension Bulletin No.207 Poultry Series No. 8 National Agricultural Extension and Research Liaison Services, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria.
12. Nowaczewski, S., Katarzyna, W., Maciej, F., Helena, K., Andrzej, R., Stanislawa, K. and Andrzej, R. (2008). Egg quality from domestic and French guinea fowl. Nauka Przyr. Tachnol. 2.2. 8.
13. Nwachukwu, E.N. (2006). Evaluation of growth and egg production potential of main and crossbred normal feathered, naked neck and frizzle chickens. Michael Okpara University of Agriculture, Umudike. PhD dissertation.
14. Obike, O.M., Oke, U.K. and Azu, K.E. (2011). Comparison of egg production performance and egg quality traits of Pearl and Black strains of guinea fowl in a humid rainforest zone of Nigeria International Journal of Poultry Science, 10(7): 547-551.
15. Oguntona, T. (1983). Current knowledge of nutrient requirements of the grey breasted helmet guinea fowl. In: The Helmet Guinea Fowl (Eds Ayeni, J. S. O, Olomu, J. M. and Aire, T.A.), Kainji Lake Research Institute, New Bussa, Nigeria, pp.121-128.
16. Oke, U.K., Herbert, U. and Nwachukwu, E.N. (2004). Association between bodyweight and egg production traits in the guinea fowl (Numida meleagris galleata pallas). Livestock Research for Rural Development 16 (9).
17. Oluyemi, J. A. and Roberts, F. A. (2000). Poultry production in warm wet climates. Spectrum Books Limited; 2nd ed., Nigeria. Pp 202-233.
18. Onyeanusi, B.I. (2007). Calcium and phosphorus levels in Nigerian guinea fowls. International Journal of Poultry Science, 6(8): 610-611.
19. Parmar, S. N. S., Thakur, M. S. Tomar, S. S. and Pillai, P. V. A. (2006). Evaluation of egg quality traits in indigenous Kadaknath breed of poultry. Livestock Research for Rural Development. 18 (9).
20. Song, K.T., Choi, S.H. and Oh, H.R. (2000). A comparision of egg quality ofpheasant, chukar, quail and guinea fowl. Asian-Australian Journal of AnimalScience, 13: 986-990.
21. Steel, R.G.D. and Torrie, J.H. (1980). Principles and procedures of statistics. A Biometrical Approach. Second edition, MC GRAW-Hill Book Coy. Inc. New York.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License