IJCRR - 7(8), April, 2015
Pages: 28-33
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
THE STUDY OF PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY AND AUTONOMIC NEUROPATHY PREVALENCE IN TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
Author: Bezwada Srinivasa Rao, Madu Anu Radha M. D., Matta Sree Vani M. D.
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Type 2 diabetes and its complications are major causes of morbidity and mortality with decreased quality of life. Distal symmetrical poly neuropathies affecting sensory more than motor nerves are common long term micro vascular complications. Prevalence of both peripheral and autonomic neuropathy increases with increased duration of type 2 diabetes. Tight glycemic control and lowering of glycosylated hemoglobin levels are associated with improvement of symptoms and slowing the progression of diabetic neuropathy. Aim: The aim is to study the prevalence of peripheral neuropathy and autonomic neuropathy and their relation with duration of type 2 diabetes. Materials and Methods: The present study enrolled 100 patients of type 2 diabetes with age > 30 yrs. Gestational and type1 diabetes patients were excluded from the study. Screening of neuropathy was done by monofilament and vibration tests. Nerve conduction studies were done to confirm neuropathy. Standard tests for autonomic dysfunction like orthostatic hypotension, pulse rate response to deep breaths test, hand grip and valsalva manoeuvre were performed. Results: In this study, the prevalence of neuropathy was 57% in diabetic patients. Out of 57 patients with neuropathy, 25 patients (43.85%) had only peripheral neuropathy, 6 patients (10.53%) had only autonomic neuropathy and 26 patients (45.62%) had both peripheral and autonomic neuropathy. Prevalence of both peripheral and autonomic neuropathy increased with increased duration of type 2 diabetes. Conclusions: The most common form is the distal symmetrical poly neuropathy than autonomic neuropathy. Both peripheral and autonomic neuropathies do not invariably coexist in diabetes. Peripheral and autonomic neuropathy increased with increased duration of type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Autonomic neuropathy, Glycosylated hemoglobin, Micro vascular complications, Nerve conduction studies, Symmetrical poly neuropathy, Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Disorders of the nervous system associated with diabetes have long been recognized by Rollo in 1978. Marchal de Calvi in 1864 first suggested that diabetes might be the cause rather than the effect of neuropathy.[1] International Diabetes Federation projects 285 million diabetics in 2010 to 438 million by 2030.The increased prevalence of diabetes in both developed and developing countries is associated with significant rise of health care costs. The prevalence of diabetic neuropathies is rising with global burden of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes and its complications are major causes of morbidity and mortality with decreased quality of life. The diabetic neuropathies are broadly classified into symmetric and asymmetric neuropathies. Symmetric neuropathies may be proximal or distal neuropathy, small or large fiber neuropathy and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy [CIDP]. Asymmetric neuropathy may be mono or poly neuropathy, radiculopathy and radiculoplexopathies. The most common diabetic neuropathy is predominantly sensory or sensorimotor poly neuropathy producing the typical stocking and glove pattern of sensory deficit in lower limbs. Features characteristic of a small fiber peripheral neuropathy include deficits in pain, temperature perception and dysesthesias are often described as like walking on pebbles or having cotton bunched up under the toes which predis pose to foot ulceration. Features of large fiber peripheral neuropathy include loss of position, vibration perception and deep tendon reflexes with nerve conduction abnormalities. Charcot joint or diabetic osteoarthropathy and foot ulcers are dreaded complications of diabetic neuropathy. Anorexia, weight loss, depression are prominent in neuropathies and the term diabetic neuropathic cachexia was coined by Ellenberg[2] to this syndrome. Treatment induced neuropathy due to improved glycemic control may initiate regenerating axonal sprouts which generates ectopic nerve impulses.[3] The majority of diabetic neuropathies affect 3rd and 6th cranial nerves. Facial paralysis due 7th nerve palsy occurs with increased frequency in diabetics. [4] Mono neuropathies occur due to focal ischemia, entrapment, compression or trauma to superficially placed nerves. When several nerves are involved simultaneously the condition is termed as mono neuropathy multiplex. The pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy is multi factorial. Various mechanisms involved are genetic, ischemia, oxidative stress, over activity of polyol pathway, increased advanced glycation end products, deficiency of γ-linolenic acid, protein kinase C, growth factor deficiency and dysimmune mechanisms. Reduced endoneural capillary density [5] in capillary basement membrane [5] and significantly impaired total diffusion barrier are the pathological alterations that occur in peripheral nerves. Oxidative stress in diabetes may cause reduction in antioxidant enzymes as evidenced by increase in glycoxidation and lipoxidation products.[6] The key enzymatic scavengers like superoxide dismutase[SOD], catalase, reduced glutathione[GSH], glutathione peroxidase and ascorbic acid [7] are reduced in the peripheral nerves of diabetic patients. Glucose indeed a neurotoxin is central in pathogenesis. Glycation and formation of advanced glycosylation end products [AGE] followed by binding with its receptor [RAGE] results in generation of reactive oxygen species [ROS] and inflammatory response. Over activity of polyol pathway results in generation reactive oxygen species. Activation of Protein kinase C results in inhibition of Na, K–ATP ase which slows the conduction. Inhibition of protein kinase C will reduce oxidative stress. [8] Reduction in nerve growth factor will reduce and its administration will restore glutathione peroxidase and catalase.[9] Screening for diabetic neuropathy done by SWME (the l0-g Senimes-Weinstein monofilament examination) and vibration testing. Action potentials of muscle and sensory nerves elicited in nerve conduction studies confirms neuropathy. The autonomic nervous system subserves physiological functions of cardiac muscle, gastrointestinal smooth muscle and glandular tissues. Subclinical autonomic nerve damage has greater importance because of implications for mortality and morbidity.[11] Disturbances of autonomic nervous system in gastro intestinal system leads to abnormal esophageal motility, gastro paresis diabeticorum [10] with diminished gastric motility and delayed gastric emptying. Involvement of small intestine results in intermittent diabetic diarrhea which manifests as painless and frequent watery stools without weight loss. Parasympathetic denervation [11] of cardiac muscle in autonomic neuropathy causes tachycardia which is unresponsive to postural changes, six slow maximal deep breaths test and valsalva manoeuvre. When sympathetic denervation supervenes the heart rate slows to fixed unresponsive rate [12] similar to a denervated transplanted heart. In postural hypotension systolic fall of > 30 mm Hg or diastolic fall of > 20mm Hg on standing is due to sympathetic denervation of arterioles in splanchnic bed, muscles and skin. Autonomic dysfunction of genitourinary system causes difficulty in initiation of micturition, dribbling and urinary retention with over flow. Impotence is common in diabetes and incidence ranges from 30% to 75%.[13] Autonomic neuropathy causes impotence, retrograde ejaculation and absence of nocturnal erections. Gustatory sweating with profuse facial sweating usually beginning shortly after eating and extending to scalp and shoulder symmetrically is typically seen in diabetic autonomic neuropathy.[14] Management of diabetic neuropathy begins with tight glycemic control and lowering of glycosylated hemoglobin levels with oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin which reduces pain threshold and an improvement in motor but not sensory nerve conduction velocities. The tricyclic antidepressants, anticonvulsants like gabapentin, carbamazepine and tramadol are the agents of first line therapy in the treatment of neuropathic pain which is characteristically worse at night.
Aim of Study
The aim is to study the prevalence of peripheral and autonomic neuropathy in type 2 diabetic patients and their relation with the duration diabetes.
Materials and Methods
This is a prospective and observational study. Ethical clearance was obtained from the institution. Informed consent was taken from patients in their own language before collecting data. The present study enrolled 100 patients of type 2 diabetes with age > 30 yrs. Patients with type 1 diabetes and gestational diabetes were excluded from the study. The duration of the study was over a period of two years. Detailed clinical examination and routine blood investigations like hemoglobin, total leukocyte count with differential count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, blood urea, serum creatinine, fasting blood sugar, postprandial sugar, glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1C] levels were done. Screening of neuropathy was done by monofilament and vibration tests. Nerve conduction studies done to confirm neuropathy. Standard tests for autonomic dysfunction like fall of blood pressure in supine position, pulse rate response to deep breaths test, hand grip, and valsalva test were performed.
Results
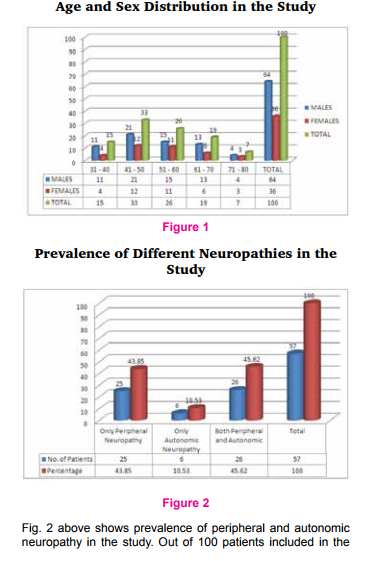
The present study enrolled 100 patients of type 2 diabetes. The results of the study were shown in tables and figures given below. Fig. 1 below shows age and sex distribution in the study. Out of 100 patients, 64 patients were males and 36 patients were females. Male to female ratio is 1.7: 1. Out of 100 patients majority of patients (33%) were in the age group between 41-50 yrs followed by 26 patients (26%) in 51-60 yrs, 19% in 61-79 yrs, 15% in 31-40 yrs and 7% in 71-80 yrs age group.
. Out of 100 patients included in thestudy, only 57 patients showed evidence of neuropathy. Out of 57 patients with neuropathy, 25 patients (43.85%) had only peripheral neuropathy, 6 patients (10.53%) had only autonomic neuropathy and 26 patients (45.62%) had both peripheral and autonomic neuropathy. Out of 100 patients, 55 patients (55%) had diabetes < 5 yrs duration and 45 patients (45%) had diabetes > 5 yrs duration.
Fig. 3 below shows prevalence of peripheral neuropathy in relation to duration of type 2 diabetes. Out of 51 patients with peripheral neuropathy, 7 patients (13.7%) had diabetes < 5 yrs duration and 44 patients (86.3%) had > 5 yrs duration of diabetes.

Fig. 4 above shows prevalence of autonomic neuropathy in relation to duration of type 2 diabetes. In this study out of 32 patients with autonomic neuropathy, the duration of diabetes < 5 yrs in 8 patients (25%) and in 24 patients (75%) the duration of diabetes > 5 yrs. Table 1 below shows frequency of neuropathic symptoms and signs.
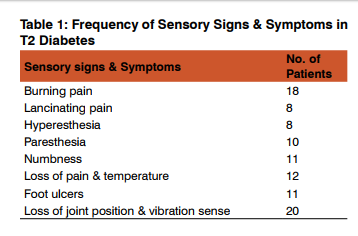
Fig. 5 below shows frequency of sensory and motor symptoms in the study. Out of 100 patients included in the study, 54 patients had only sensory symptoms, only motor symptoms in one patient and both sensory and motor symptoms were seen in 55 patients.
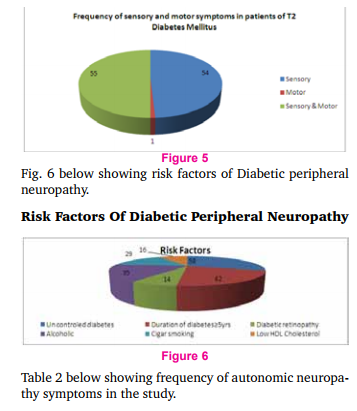
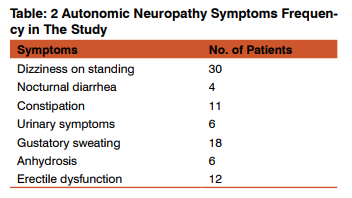
Fig. 7 below shows correlation of simple tests with nerve conduction studies in the study. In this study simple tests like monofilament, vibration tests and nerve conduction studies were done to confirm diabetic peripheral neuropathy. The study showed both monofilament and vibration tests were positive in 38 patients and nerve conduction studies were abnormal in 51 patients.
DISCUSSION
Diabetes and its complications are major causes of mortality, morbidity and decreased quality of life. The complications include both micro vascular (neuropathy, nephropathy and retinopathy) and macro vascular (atherosclerotic). Neuropathies are among the most common long-term micro vascular complications. The prevalence of diabetic neuropathies is rising with global burden of type 2 diabetes. Screening of diabetic neuropathy was done by monofilament tests, vibration tests and confirmed by nerve conduction studies tests. Autonomic dysfunction related tests were also done. With early detection and meticulous treatment of diabetes mellitus, neuropathic complications can be prevented along with decrease morbidity and mortality. In this study, out of 100 patients 64 patients were males and 36 patients were females. Male to female ratio is 1.7: 1. Majority of the patients 33% were in the age group between 41-50 yrs as shown in Fig 1. In this study of 100 patients with type 2 diabetes, prevalence of neuropathy was 57% which correlated with study done by Prasad Katulanda et al[15] and studies done in Malaysia and Saudi Arabia [16] which showed the prevalence of 59.1% and 54.3% respectively. Moreover peripheral and autonomic neuropathy do not invariably coexist in diabetes as per study by Tentolouris et al.[17] Out of 57 patients with neuropathy, 25 patients (43.80%) had only peripheral neuropathy, 6 patients (10.60%) had only autonomic neuropathy and 26 patients (45.60%) had both peripheral and autonomic neuropathy as shown in Fig 2. A population based study by Phillip et al [18] showed 73% prevalence of autonomic neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. The present study showed increased prevalence of both peripheral and autonomic neuropathy as the duration of type 2 diabetes increases. Out of 51 patients with peripheral neuropathy, 7 patients (13.7%) had diabetes < 5 yrs duration and 44 patients (86.3%) had > 5 yrs duration of diabetes as shown in Fig; 3. In the present study autonomic neuropathy was seen in 8 patients (25%) with < 5yrs duration of diabetes and in 24 patients (75%) with > 5yrs duration of diabetes as shown in Fig: 4. In this study, frequency of symptoms in peripheral neuropathy observed were shown in Table 1. Prevalence of sensory symptoms in this study correlated with study done by Schandry et al. [19] Out of 100 patients in the study, only sensory symptoms were observed in 54 patients, only motor symptoms in one patient and both sensory and motor symptoms were seen in 55 patients as per Fig 5. Risk factors of neuropathy like uncontrolled diabetes in 58 patients, >5yrs duration of diabetes in 42 patients, diabetic retinopathy in 14 patients, alcoholic in 35 patients, history of smoking in 29 patients and low high density lipoprotein[HDL] cholesterol in 16 patients observed were shown in Fig: 6. The frequency of symptoms observed in relation to autonomic neuropathy in this study were shown in Table:2. In this study , monofilament and vibration tests in type 2 diabetic patients were positive in 38 patients but nerve conduction studies were positive in 51 patients as per Fig. 7 Nerve conduction studies not only confirms but also identifies subclinical peripheral neuropathies which may be helpful in treatment planning.
CONCLUSION
The prevalence of diabetes is increasing dramatically in both developed and developing countries. Neuropathies are common long-term micro vascular complications and the most common form is the distal symmetrical poly neuropathy affecting sensory more than motor nerves. Prevalence of both peripheral and autonomic neuropathy is increasing with increased duration of type 2 diabetes. Both peripheral and autonomic neuropathies do not invariably coexist in diabetes. Tight glycemic control, lowered glycosylated hemoglobin levels with effective treatment by oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin are associated with improvement of symptoms and slowing the progression of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes and its complications are major causes of mortality, morbidity and decreased quality of life. Limitations of the study: Patients < 30 yrs and Type 1 diabetes mellitus patients were not included in the study.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors are thankful to Postgraduate students in Department of Medicine for their co-operation in the study. Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/ editors/ publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Marchal de Calvi CJ. Recherchessur les accidents diabetiques P Asselin, 1894\
2. Ellenberg M. Diabetic neuropathic cachexia. Diabetes 1974;23:418-423.
3. Tesfaye S, Malik R, Harris N, et al. Arterio-venous shunting and proliferating new vessels in acute painful neuropathy of rapid glycaemic control (insulin neuritis). Diabetologia 1996; 329-335.
4. Korczyn AD. Bell’S palsy and diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1971;1:108-109.
5. Malik RA, Newrick PG, Sharma AK, et al. Microangiopathy in human diabetic neuropathy : relationship between capillary abnormalities and the severity of neuropathy Diabetologia 1989; 32 : 92-102
6. Baynes JW, Thorpe SR. Role of oxidative stress in diabetic complications : a new perspective on an old paradigm. Diabetes 1999; 48:1-9.
7. Jennings PE, Chirico S, Lunec J, et al, Vitamin C metabolites and microangiopathy in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res 1987; 6: 151-154.
8. Matinez – Blasco A, Bosch – Morell F, Trenor C, et al. Experimental Diabetic neuropathy: role of oxidative stress and mechanisms involved. Biofactors 1998; 8: 41-43.
9. SampathD, Jackson GR, Werbach – Perez K, et al., Effects of nerve growth factor on glutathione peroxidase and catalase on PC 12 cells J N eurochem 1994; 62: 2476-2479.
10. Kassander P. Asymptomatic gastric retention in diabetics (gastroparesis deabeticorum). Ann Intern Med 1958; 48 : 797-812.
11. Ewing DJ, Campbell IW, Clarke BF, Heart rate changes in diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1981; 1: 183-186.
12. Lloyd-Mostyn RH, Watkins PJ. Defective innervations of heart in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. BMJ. 1975; 3 : 15- 17.
13. Mc Culloch Dk, Campbell IW, Wu FC, et al. The prevalence of diabetic impotence. Diabetologia 1980; 18 : 279-283.
14. Stuart DD. Diabetic gustatory sweating. Ann Intern Med 1978; 89 : 223-224.
15. The prevalence, patterns and predictors of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in a developing country, Diabetology and Metabolic Syndrome 2012, 4:21, Prasad Katulanda, Priyanga Ranasinghe, RanilJayawardena, Godwin R Constatine, M H R Sheriff and David R Matthews.
16. Explorative study on diabetes neuropathy among type II diabetic patients in UniversitiSains Malaysia Hospital, SalwaSelim Ibrahim Abougalambou, Ayman SelimAbougalambou, Discipline of Clinical Pharmacy, School of Phar-maceutical Sciences, UniversitiSains Malaysia (USM), Malaysia, King Abdhullah Medical City, Saudi Arabia.
17. Peripheral neuropathy does not invariable coexist with autonomic neuropathy in diabetes mellitus by N. Tentolouris, S. Pagoni, A. Tzonou, N. Katsilambros, First Department of Propaedeutic Medicine, Athens University Medical School, ‘Laiko’ Epidemiology, Athens University Medical School, Athens, Greece.
18. A population-based study by Philip A. Low, MD, Lisa M. Benrud-Larson, PHD, David M. Sletten, Tonette L. OpferGehrking, Stephen D. Weigand, MS, Peter C. O’Brien, PHD, Guillermo A. Suarez, MD and Peter J. Dyck, MD.
19. R Schandry, M Lobisch, Importance of sensory symbptoms in identifying patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, published in Practical Diabetes International, January/February 2007.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License