IJCRR - 7(8), April, 2015
Pages: 23-27
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
FUNCTIONAL ANNOTATION OF PROTOCADHERIN BETA GENES HYPERMETHYLATION AND THEIR SIGNIFICANCE IN NEONATAL SEPSIS
Author: Benet Bosco Dhas D., Hiasindh Ashmi A., Vishnu Bhat B., Subhash Chandra Parija
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Apart from genetic factors, epigenetic mechanisms like DNA methylation are now being established for their association with human diseases. Despite advance in medical research, sepsis still remains the major cause of neonatal mortality. In this study, the role of DNA methylation in neonatal sepsis was studied in an epigenome wide scale and the candidate genes were functionally annotated. Methods: The methylation status was analyzed in babies with and without sepsis in epigenome wide scale using Illumina Infinium Human Methylation 450K methylation microarray. The microarray data was functionally annotated and interpreted for their biological significance using the bioinformatics softwares and databases like DAVID v6.7, GeneMania, KEGG, etc.
Results: Functional annotation of methylation microarray data revealed that the protocadherin beta group of genes was hypermethylated in babies with neonatal sepsis. Protocadherin beta genes was found to be associated with calcium dependent cell to cell adhesion which is important in signaling pathways like leukocyte migration during sepsis. Conclusion: DNA methylation might play critical roles in neonatal sepsis which was obvious from differential methylation of candidate genes like protocadherins, modifying the associated biological pathways.
Keywords: EWAS, CpG methylation, Neonatal sepsis, Protocadherins, Leukocyte adhesion molecules
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Neonatal sepsis is associated with high mortality despite the advancement in medical field. Diagnosis of neonatal sepsis still remains one of the major problems. Researchers often came up with novel or improved diagnostic techniques but none predetermines the disease susceptibility or severity so as to help with the treatment and management of sepsis. Inherited genetic behavior of the host plays vital role in disease susceptibility and immune response against infections. Recent studies showed that human diseases or behaviors, not only depend on their genetic code but also non-genetic factors. DNA methylation, one of such epigenetic factor, is a heritable form of gene modification without any changes in the underlying nucleotide sequence. The changes in gene expression originated by hyper- and hypo- methylation of DNA and its association with disease physiology are still a mystery and no epigenome wide studies had been done so far in neonatal sepsis. In this study, an epigenome wide search was carried out to explore the differential methylation of candidate genes associated with neonatal sepsis.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
This study was conducted in the Department of Neonatology in a tertiary care referral hospital during the period of March to April, 2014. This study was approved by Institute Scientific Advisory and Human Ethics Committees. Six preterm newborns belonged to Dravidian population of South India were enrolled following inclusion and exclusion criteria for sepsis. Newborns of age less than 28 days and blood culture positive sepsis were re cruited as cases. Newborns with no sepsis and endured blood sampling for minor ailments were enrolled as controls. Babies with surgical conditions, congenital malformations, maternal history of infections / inflammations and Apgar score < 6/10 at five minutes were excluded.
Methylation Microarray
The detailed methodology has been described previously [1]. In brief, 200µL of peripheral venous blood was collected from the newborns and genomic DNA was extracted using QIAmp DNA Blood Mini kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). The DNA was then subjected to heat based bisulfite treatment using EZ DNA methylation kit (Zymoresearch, USA). After bisulfite treatment, the DNA samples were amplified, fragmented by enzymes and hybridized to the Illumina Infinium Human Methylation450 BeadChip kits (Illumina, Inc., San Diego, CA). Then allele specific single-base extension and staining was performed, followed by imaging of BeadChips on Illumina BeadArray Reader and analyzed using Illumina’s BeadScan software (Illumina iScan scanner). Microarray data was processed and analyzed Illumina GenomeStudio v2011.1 (Methylatioin Module v1.9.0) and the statistical computing package R 3.0.2 (http://www.r-project. org). The microarray service was provided by Macrogen Inc., South Korea. The complete microarray data can be accessed from the public domain, Gene Expression Omnibus of NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/). The accession number is GSE58651.
Filtering of biologically insignificant CpGs
The statistically significant CpGs were filtered using the threshold values of difference in methylation level > 0.2 and p-value > 0.05. The significant CpGs filtered also included CpGs in sex chromosome, CpG-SNPs, CpGs in known repeats, non CpG methylation. The microarray data was further analyzed manually and filtered to remove these biased CpGs to find out the biologically significant and valid CpGs.
Gene Clustering Analysis
The differentially methylated genes identified through microarray data analysis were then subjected to clustering analysis in order to find out the biological roles. This was done with the bioinformatic online software DAVID v6.7 (Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery) (SAIC-Frederick Inc., Maryland, USA). The list of genes was selected from microarray data and pasted in the query dialog box, followed by selection of data type and clustering. The cluster with high enrichment score represents more biological value.
Biological Network and Pathway
Analysis The biological networks of the differentially methylated genes and their associated pathways were identified by GeneMANIA database (University of Toronto, Canada) which is based on the Cytoscape plugin. The false discovery rate (FDR) indicated the significance of analysis. The pathways regulated by the gene were identified and analyzed using KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) pathway database (Kanehisa Laboratories, Japan).
Gene Panel Analysis
The characteristics of the differentially methylated genes were analyzed using UCSC Genome browser (University of California, Santa cruz). The CpG islands in the genes and literatures involving the gene were analyzed for biological and clinical interpretation. The clinical significance of the genes was retrieved from the database, Online Mendelian Inheritance of Man (OMIM) developed by NCBI.
RESULTS
The newborns enrolled in our study were homogenous with regard to general demographic characteristics. All cases were positive for Klebsiella pneumoniae and similar sepsis risk factors like prematurity, premature rupture of membrane, etc.
Distribution of DNA methylation
The Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation450 is capable of analyzing about 4,85,350 CpGs throughout the genome. The distribution of DNA methylation level among the cases and controls were shown in Figure 1. The cases and controls were significantly distinguished both by hypomethylation and hypermethylation. Obviously the hypermethylation frequency of cases was predominantly higher compared to the controls.
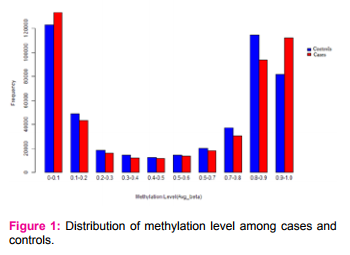
The difference in methylation level of majority of the CpGs (4,73,081) among the cases and controls lied in the range of -0.1 to +0.1 (negative sign indicates hypomethylation and positive sign indicates hypermethylation). After filtering the CpGs for statistical and biological significance, 91 CpGs were found differentially methylated including 57 hypermethylated and 34 hypomethylated(Figure 2)
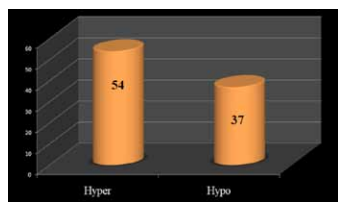
Figure 2: Graph showing the number of hyper- and hypomethylated CpGs.
Functional Location
The functional location of hypermethylated and hypomethylated CpGs are shown in Figure 3. Almost 40 % of the significant hypermethylated CpGs were found in the promoter region that includes TSS150, TSS 200 and 1st Exon, in contrast to 16 % of hypomethylated CpGs. Most of the hypomethylated CpGs were found in the gene body (65 %).
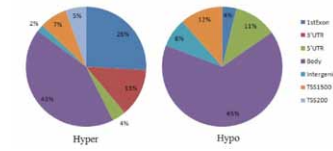
Figire 3: Functional location of significant hyper- and hypomethylated CpGs
Clustering Analysis
The differentially methylated 64 genes containing the 81 CpGs were subjected to bioinformatic analysis in order to find out the biologically significant genes and their functions. DAVID analysis was done to find out the functional gene clusters based on gene enrichment score among the differentially methylated genes. The complete details of DAVID analysis along with the corrected bonferroni values are shown in Figure 4. DAVID analysis revealed a cluster of protocadherin beta (PCDHB) genes that were differentially methylated with annotation score of 4.44.
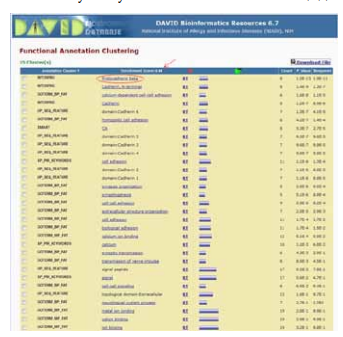
Figure 4: Results of DAVID analysis showing significant gene clusters
Biological networks and functions
This cluster comprised of five biologically important PCDHB genes which were PCDHB11, PCDHB12, PCDHB5, PCDHB6, PCDHB16. PCDHB17 was also found to be included in the cluster but it is a pseudogene, which has no biological function. This cluster of genes was then analyzed for their biological roles and networks using GeneMania database (Figure 5).
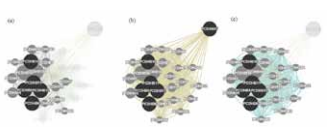
Figure 5: Gene ontology annotation of PCDHB gene cluster.
(a) Physical interactions; (b) Co-expression; (c) Biological interactions
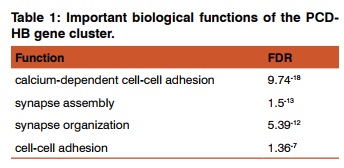
The network lines connecting the circles of genes, represents the relationship between them. The dark circles correspond to the genes in the cluster and brighter circle denotes related genes. Since PCDHB17 is a pseudogene, it was not found to be involved in physical and biological interaction, except that it is co-expressed. The biological functions of the genes were also found by GeneMania and the most important of them are listed in the table.
DISCUSSION
The significance of DNA methylation in relation with microbial infections is increasingly explored. The best example is abnormal methylation of DNA, especially in the promoters regions of underlying genes, that was induced by H. pylori infection in human gastric cancer cells [2]. Hypermethylation associated with H.pylori infection was found to occur in the genes such as E-cadherin gene – CDH1 [3], DNA repair gene – MLH1 [4], tumor suppressor genes like WWOX [5]. A recent study also showed methylation of LPS receptor gene, TLR4 in epithelial cells of intestine by commensal bacteria during non – inflammatory conditions [6]. Jelinek et al. observed that the gene PRV-1 which is expressed in neutrophils is epigenetically controlled by CpG methylation. During sepsis, PRV-1 expressing neutrophils increase significantly [7]. On the other hand, during endotoxin tolerance, TNF-α expression was found to be silenced via synergistic effect of DNA methylation and histone methylation, resulting in pro-inflammatory gene silencing associated severe systemic inflammation [8]. In contrast to these studies, Bierne et al., hypothesized that the pathogen itself can acts as epimutagens affecting the gene expression of host immune system in various infections with H.pylori, P.gingivalis, C. rectus and E.coli stating that the bacterial products like lipopolysaccharide may trigger these epigenetic changes [9]. In this study, we attempted to explore the genes that are differentially methylated in babies with sepsis through methylation microarray analysis. We found an immense variation in DNA methylation level in both extremes, hypo- and hyper-, among newborns with sepsis and without sepsis. This variation reveals that in sepsis, some CpGs are hypomethylated that may allow expression of genes and some are hypermethylated, suppressing the gene expression. Out of 4,85,350 CpGs analyzed in the whole epigenome, only 91 CpG sites belonging to 64 genes were found significantly varied among cases and controls. To our surprise, 35% of the significant CpGs (both hypo- and hyper-methylated) were found in the promoter region, giving hint to their association with gene expression. The functional analysis of these genes showed their association with sepsis pathophysiology. The functional clusters given by DAVID algorithm exposed the incredible fact of PCDHB hypermethylation in neonatal sepsis. Cadherin family of proteins play vital role not only in cell adhesion but also in cell recognition and sorting, maintenance of structural and functional cell polarity [10]. Protocadherins are calcium dependent cell-cell adhesion molecules, previously thought to be functional mainly in nervous system synapse organization. Recent studies showed that PCDHB genes were also expressed in peripheral blood cells and PCDHB10 gene was epigenetically regulated [11]. Hypermethylation of PCDHB genes found in our study, may restrain adhesion efficiency of leukocytes via suppressed expression of cell adhesion molecules. Leukocyte cell adhesion, an essential innate immune response is seized in healthy individuals by shear forces, but infection or inflammatory signals up regulate the expression of adhesion molecules leading to accumulation of leukocytes at the site [12]. In sepsis, suppression of leukocyte extravasation may exaggerate disease severity and poor outcomes like multiple organ dysfunctions [13]. The cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) play vital role in leukocyte migration during microbial infections. Differential expression of leukocyte adhesion molecules was found to be associated with varying biological functions of lymphocyte and monocytes in sepsis [14]. This varying expression of CAMs is mediated by nitric oxide produced by the enzyme, cytokine induced nitric oxide synthase [15]. We also found that oxidative stress regulators like AGER, SCARA3 were differentially methylated in sepsis cases. AGER gene encodes the receptor for AGE molecules which are the end products of advanced glycation capable of activating pro-inflammatory response [16]. Ying et al. have reported downregulation and hypermethylation of SCARA3 in prostate cancer [17].
CONCLUSION
Differential methylation of immune related genes regulates differential immune response during sepsis. Hypermethylation of protocadherin beta genes can be correlated with dysregulation of biological pathways like leukocyte migration. This understanding will help in the development of novel epigenetic based biomarkers and therapeutic targets for neonatal sepsis.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Authors thank Indian Council of Medical Research for providing research fellowship to the first author. Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
ACCESSION NUMBER The complete microarray data can be accessed from the public domain, Gene Expression Omnibus of NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/). The accession number is GSE58651.
CONTRIBUTORSHIP: BBD, AH and VB designed the study. BBD and AH done data analysis and bioinformatics analysis. BBD, AH, VB and SCP prepared the manuscript. VB and SCP finalized and proofread manuscript.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors declare no conflicts of interest
SOURCE OF FUNDING: JIPMER Intramural research fund
References:
1. BB Dhas, Ashmi AH, Bhat BV, Kalaivani S, Parija SC. Comparison of genomic DNA methylation pattern among septic and non-septic newborns - an Epigenome wide association study. Genomics Data 2015;3:36–40.
2. Maekita T, Nakazawa K, Mihara M, Nakajima T, Yanaoka K, Iguchi M, et al.. High levels of aberrant DNA methylation in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosae and its possible association with gastric cancer risk. Clin Cancer Res 2006; 12: 989–995.
3. Chan AO, Lam SK, Wong BC, Wong WM, Yuen MF, Yeung YH, et al. Promoter methylation of E-cadherin gene in gastric mucosa associated with Helicobacter pylori infection and in gastric cancer. Gut 2003; 52: 502–506.
4. Yao Y, Tao H, Park DI, Sepulveda JL, Sepulveda AR. Demonstration and characterization of mutations induced by Helicobacter pylori organisms in gastric epithelial cells. Helicobacter 2006; 11: 272–286.
5. Yan J, Zhang M, Zhang J, Chen X, Zhang X. Helicobacter pylori infection promotes methylation of
6. Takahashi K, Sugi Y, Nakano K, Tsuda M, Kurihara K, Hosono A, et al. Epigenetic control of the host gene by commensal bacteria in large intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 35755–35762.
7. Jelinek J, Li J, Mnjoyan Z, Issa JP, Prchal JT, AfsharKharghan V. Epigenetic control of PRV-1 expression on neutrophils. Exp Hematol 2007;35:1677–83.
8. El Gazzar M, Yoza BK, Chen X, Hu J, Hawkins GA, McCall CE. G9a and HP1 couple histone and DNA methylation to TNFalpha transcription silencing during endotoxin tolerance. J Biol Chem 2008;283:32198–208.
9. Bierne H, Hamon M, Cossart P. Epigenetics and bacterial infections. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2012;2:1–24.
10. Halbleib JM, Nelson WJ. Cadherins in development: cell adhesion, sorting, and tissue morphogenesis. Genes Dev 2006;20:3199–214.
11. Ying J, Gao Z, Li H, Srivastava G, Murray PG, Goh HK, et al. Frequent epigenetic silencing of protocadherin 10 by methylation in multiple haematologic malignancies. Br J Haematol 2007;136:829–32.
12. Zarbock A, Ley K. Neutrophil adhesion and activation under flow. Microcirculation 2009;16:31–42.
13. Liu L, Kubes P. Molecular mechanisms of leukocyte recruitment: organ-specific mechanisms of action. Thromb Haemost 2003;89:213–20.
14. Mühl D, Woth G, Drenkovics L, Varga A, Ghosh S, Csontos C, et al. Comparison of oxidative stress and leukocyte activation in patients with severe sepsis and burn injury. Indian J Med Res 2011;134:69–78.
15. Benjamim CF, Silva JS, Fortes ZB, Oliveira MA, Ferreira SH, Cunha FQ. Inhibition of leukocyte rolling by nitric oxide during sepsis leads to reduced migration of active microbicidal neutrophils. Infect Immun 2002;70(7):3602–10.
16. Bierhaus A, Schiekofer S, Schwaninger M, Andrassy M, Humpert PM, Chen J, et al. Diabetes-associated sustained activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB. Diabetes 2001;50:2792–808.
17. Yu G, Tseng GC, Yu YP, Gavel T, Nelson J, Wells A, et al. CSR1 suppresses tumor growth and metastasis of prostate cancer. Am J Pathol 2006;168:597–607.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License