IJCRR - 7(8), April, 2015
Pages: 14-18
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
PROCESS PERFORMANCE AND OUTCOME AS USEFUL CONSTRUCTS OF MEASUREMENT IN DEFINING THE QUALITY IN EYE CARE
Author: Akilan Arunkumar A., C. A. K. Yesudian
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objective: The study was designed with an objective to understand quality in eye care by studying the relationships among process compliance and outcome in outpatient and inpatient ophthalmic processes. Methods: The exploratory study focuses on finding out the relationship between process performance and treatment outcomes. It was based on primary and secondary data. Frequency distribution, chi square analysis, correlation and regression analysis were used to analyse the data. Results: A strong association between the process conformance and outcome in terms of visual acuity was observed in cataract ((r = -.682, p
Keywords: Process performance, Quality improvement, Quality in eye care
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
For years health care has been discussing about improving the quality of treatments, however, the system has failed in its ability to deliver quality healthcare to all consistently. A reason for this inefficiency may be the healthcare system focusing and acting on the parts than the whole. Taking a systems perspective, and orienting systems for the delivery and improvement of quality, are fundamental to progress and to meeting the expectations of the populations. Healthcare systems across the world have largely, realized this, and are in pursuit of improving the quality. Comparing to the other disciplines of medicine, Ophthalmology adopted quality assurance since 1980s. The first mention of quality assurance in ophthalmology appeared in medical journals in Australia, and USA in the 1980s (Carver, 1985). In the late 1990s, studies of the quality of life as outcome measures of ophthalmic conditions, and patients’ perspectives of their eye care were published. In India, more than 15 million people are visually impaired (Dandona et. al., 2003), with cataract (62.6 %) and refractive errors (19.7 %) as the leading causes of visual impairment (Jose, 2008). India has achieved a tremendous success in solving the problem of blindness, especially cataract, which was the high prevalence blinding disease. The number of cataract operations has increased five- fold over the last 20 years. Today, Indian eye care systems are promulgated as models for high volume eye surgeries. Although significantly reducing the prevalence of blindness to 1.0 percent, and reducing cataract blindness by 40 percent, there are alarming concerns about the quality of eye care (Limburg et.al, 2005). Dandona et al, (2003) estimates that the 3.5 million cataract surgeries performed in India in 2000 are to result in 0.3 million persons having irreversible blindness induced due to poor quality of surgeries. Policy makers and providers are shifting their focus from quantity to quality as the targets are achieved, and continuum of quantity is ensured. In the absence of nationwide data on outcome, these revelations pose great challenge to eye care providers. Eye care systems in India increasingly started deliberating on improving the quality of care over quantity in the last decade. Ravi Thomas (2000) points out that if outcomes and quality are ignored, the Indian eye care system is not only converting curable blindness to incurable, but also create adverse publicity to the national programme. Over the years, eye care has placed greater emphasize on post-procedural visual outcome as an indicator of quality. However, when poor quality is observed, the providers always get back to see what went wrong in the treatment process. In other words, the root cause analysis pertaining to a deficiency in the outcome always leads the providers to the see how the processes are being implemented. This underscores why processes becomes the center of attraction in any quality improvement initiative. In a system perspective, a process is defined as a sequence of interdependent and linked procedures. Activities of a hospital fully comprise of processes. Improving processes offers a tremendous opportunity for hospitals to improve the quality of patient services and overall organizational performance. Unmanaged processes produce random results and high amount of variation from the standard, since protocols or guidelines are not in place. In these cases, the quality of care differs from patient to patient. Therefore, a system-based approach to measure process variations and improve them consistently is required for better quality of services. While choosing indicators of measurement, outcome indicators are considered more stringent quality indicators than structural or process indicators because deviations from appropriate care should influence residents’ health outcome; however they are difficult to define and infer. On the other hand, process indicators are often easy to interpret. Many are also easy to enumerate and do not require adjustment. Donabedian (1983) notes, “outcomes are no more valid a measurement of quality than process, since validity resides not in the outcomes or processes themselves but the causal linkages between outcome and processes”. The core ideas behind this facet of total quality are that organizations are sets of interlinked processes, and that improvement of these processes is the foundation of performance improvement (James W. Dean, 1994).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study was designed with an objective to understand quality in eye care by studying the relationships among process performance in terms of compliance and outcome, in outpatient and inpatient ophthalmic processes. A causal chain linking interventions to outcome drawn from Donabedian’s theory is the basic framework of this study. The study explored the relationship between one factor with the other. Cataract and refraction were identified as the two processes under the study since one is an outpatient process and the other one is an inpatient process. In addition, these two processes constitute 3/4th of the patient load of any eye hospital. This study was conducted at a tertiary care eye hospital in South India. Excluding patients having co-morbidity, the valid samples included in the study were 323 and 343 from cataract and refractive error patients respectively; systematic random sampling was used to recruit respondents. Based on the process map, a tool to measure the level of compliance to process elements was developed. To improve the validity of the process tools, first, a process map was developed in consultation with the ophthalmologists, and later the process map was converted to a schedule. Ophthalmologists and experts evaluated and approved the tools. While developing this tool, standard protocols prescribed by the national and international eye care organizations were considered. The processes relating to the technical (clinical) aspects were grouped to the technical section and the processes relating to the functional aspects of the care delivery were grouped under functional section. Secondary data, such as process compliance, visual acuity was collected from the medical records of patients identified as samples over a period of six months. Data analysis was done using statistical analysis software SPSS 20.0. Frequencies and cross tabulation were used for descriptive analysis; correlations, and regression analysis were used in identifying relationships. Informed oral consent was taken from the patient to participate in this study and it was assured that participation in this study would not influence their care delivery.
RESULTS
Cataract treatment process
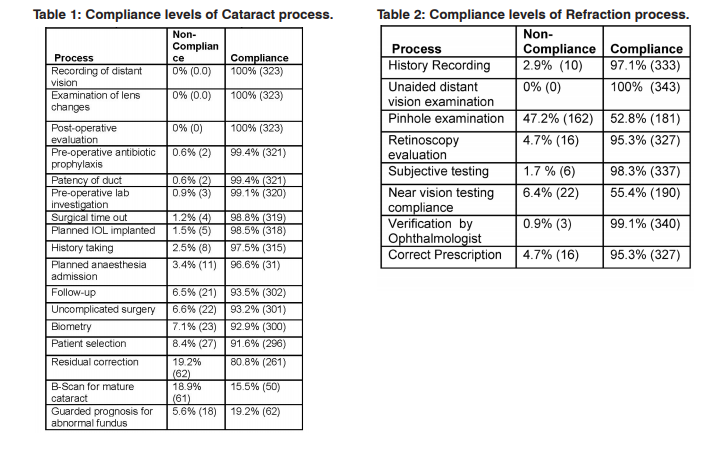
The frequency distribution of gender showed although the access to cataract treatment was equal, women have less access comparing men. A large majority of respondents (76%) were above the age of fifty. Patients operated under PHACO technique showed higher non-compliance (11.8%) as against respondents operated with small incision cataract surgery (4.8 %) for the criteria of patient selection (p<.05). While measuring compliance to Biometry, 19.0% belonging to non-paying category had noncompliance with the requirement of biometry followed by a very small proportion of respondents in paying and subsidized categories showing non-compliance (5.0 % and 2.2 %). This suggests that the non-paying patients have higher non-conformance to biometry comparing to the other groups (P<.001). The difference between categories of payment and level of compliance with follow-up was statistically significant at P<.001 as 19.0% of non-paying patients, 6.5% of subsidized category patients and 3.2% paying patients had non-conformances to follow-up. While Table.1 shows the conformances of individual processes, the analysis of overall process compliance showed that the level of compliance was above 70% in all samples. Further, interpreting the levels of compliance with technical and functional processes, in 50% opportunities, the system has demonstrated full compliance, which implied, that protocols are followed rigorously in most of the time in cataract surgical treatment. A Pearson correlation coefficient was computed to assess the relationship between post-operative visual outcome and overall process compliance which suggested a statistically significant strong correlation between overall process compliance and post-operative visual outcome (r = -.682, n=323, p<.01.). The negative correlation was an effect of the logMAR (Logarithm of the Minimum Angle of Resolution) scale used to assess the visual outcome. Increase in process compliances was correlated with better visual outcome of cataract surgery. In an effort to identify the processes that could probably influence the outcome, the frequency distribution of non-conformances supported by regression analysis, suggested that processes such as patient selection, biometry, uncomplicated surgery, follow-up, b-scan for mature cataract and residual correction were crucial in achieving better post-procedural outcome (p<.05).
Refractive error correction
Compliance levels of technical processes are presented in Table 2. Among the processes, unaided distant vision examination was performed for all patients without any deviation. Pinhole examination was a process, which had high levels of non-compliance, suggesting co-morbidity was not ruled out when improvement in vision was not found. Comparing pinhole examination with age groups, the compliance inversely progressed with age groups (p<.001); this may be attributed to the general perception among optometrists that only aged patients may have other ocular diseases that are hindrance to the refractive error correction. It was revealed that while in the young age group optometrists relied on autorefractor’s findings; in the older aged group they were more careful to perform the subjective refraction (p<.01). The review patients had higher non-compliance, which may be attributed to optometrists not verifying the age of the respondents at the time of examination as the registered age might be obsolete at the time of examination. Higher non-compliance was observed in the review patients regarding prescribing correct values. Comparing technical processes, the level of compliance with the functional dimensions was less. Among the functional variables, initial assessment received lowest compliance (73.7%) followed by counseling (82.5%) and overall process time (82.2%). Age and counseling showed significant association as lesser-aged patients did not receive counseling compared to old-aged patients (p=.001). When attempted to identify variables that are significant to cause an association with the outcome, it was found that pinhole examination, retinoscopy examination, subjective vision testing, near vision screening and correct prescription were significant causing an association (P<.001). The results, confirm the hypothesis that better processes compliance results in better outcome, as a strong positive correlation was observed between compliance and outcome (r= -.680, n=343, p<.001). This is a significant finding, suggesting eye care to concentrate on complying with processes to ensure the desired outcome.
DISCUSSION
The study reiterated the gender imbalance prevailing in cataract treatment uptake. Although the gap has been narrowed down, the eye care delivery systems need to provide necessary impetus to ensure women have better access to cataract treatment. The process compliances levels were marginally less with non-paying patients. This may be attributed to the influence of the camp method of cataract treatment, which is relatively simpler than the screening process of walk-in patients. However, in the growing concern towards quality in cataract, any such discrepancies between patients will not be acceptable and in the world of standardization, every patient should receive the same kind of treatment. Further, the study revealed that non-paying patients not tend to maintain the follow-up plan, as they perceive some improvement in the vision postoperatively, as the end of cataract care. In addition, since most of them were brought through outreach, the follow-up may be lost due to access difficulties. Since the residual correction is an important, deterministic factor in receiving best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) providers should develop follow-up systems to ensure compliance with the same. Overall, both the cataract and refraction technical processes had a high level of conformances. However, in the cataract process, while most of the respondents had conformance above ninety percent, only half of the respondents of refraction services showed conformance in this range. It may be reasoned that cataract being a surgical process, the level of conformance was higher comparing the non-surgical refraction process. Hospital staffs tend to follow protocols with great rigor when the risk is also high. At the same time, when the risk associated with errors or implications of the lapses are insignificant, the adherence to protocols is found to be less rigor. When the risk profile is high, the system responds with much carefulness hence fewer non-conformances and when the risk profile is less, there are more non-conformances. Although the findings explain the reason for varying conformance levels, the variation in the level of conformance may not be acceptable to the patients since their objective of the hospital visitation may not have fulfilled. In other words, every patient would like to receive the appropriate care in the same manner every other patient had received. The findings suggested that processes that were well integrated in to the system had no chance of not being complied. For example, the recording of distant vision, which had a full conformance, is a fundamental process without which no further examination could be performed. In addition, the system is so designed that no patient moves further in the process without having conformance to this. Performing critical tasks, the same way every time can reduce the kind of lapses that all human beings are subject to, especially when fatigue is a factor and in high workload environments. Well-adhered processes results in producing anticipated outcomes. When variation occurs in adherence, it affects the outcome of the treatment process. In the cataract and refraction treatment procedure, a strong association between process performance (conformance) and outcome was observed, which suggests that if processes were complied in line with the standards, its conformance would result in better outcome. This is in line with Donabedian’s theory of quality improvement. Peterson et al (2006) have observed an association between composite adherence and in-hospital morbidity in a cardiac care setting. Similarly, in an outpatient care, Kane et al, (1977), found that good outcomes had better process scores than those with bad outcomes. A significant association between care process and outcomes supports the use of process-based performance as a means of assessing and helping improve hospital quality. Likewise, Eagle et al., (2005) found that centers that routinely use standardized care processes, such as patient care algorithms, admission order sets, and discharge checklists, tend to have higher adherence to guidelines. Strengthening the argument for combined process-outcome models of quality measurement, Brook (2000) suggested that health care professional show less and unenthusiastic response when the ‘process only’ results were presented. On the contrary, when ‘process-outcome’ audit results were presented, concerns over the outcomes predominated and suggestions for action emphasized. It would be easier to drive the quality improvement agenda at this stage, since the target audiences are already sensitized and willing to change. Besides identifying the relationship between the processes and outcome, a further exploration of the processes that had a significant bearing on the outcome revealed that six of the cataract process and five of the refraction processes were significantly associated with the outcome. The study revealed that processes like patient selection, biometry, uncomplicated coherence surgical process, and residual correction were crucial in attaining best visual outcome. In some processes (time-out, patency examination, pre-operative antibiotic prophylaxis), even though an obvious association could not be seen, non-conformance to these may have catastrophic outcomes such as sentinel events (wrong site surgery, endophthalmitis, etc). Since there was no significant association was established with the outcome, it cannot be said that compliance to these processes may not as important in attaining the best possible outcome. It may be due to inadequate variation (less non-conforming samples), the statistical significance may have not observed. Further focused research on these processes and their non-conformances, may strengthen the reason for including them in the cataract care bundle. In the refraction process, it was found that pinhole examination, retinoscopy examination, subjective vision testing, near vision screening and prescribing process was significant to the outcome. History recording and verification by ophthalmologist were the only two processes were not found to be associated with the outcome. It suggests history recording may not be as critical as other processes in improving the visual outcome. In addition, since most of the processes relating to refractive error correction are carried out by optometrists, the ophthalmologist only confirms the power arrived by the optometrists hence it is a duplication.
CONCLUSION
Process performance management offers key insights into the way protocols are being followed in care delivery. As the performance of these processes impact the outcome of the treatment, it becomes pertinent for the healthcare professionals to give greater attention to improving processes. In addition, when healthcare professionals understand that the way their healthcare delivery system functions, the reality touches the bottom-line of the business interests of the hospital. In a competitive environment, quality becomes the single most deterministic factor in the sustainability of the organization and process performance management offers a practical way of implementing a quality improvement program.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
With immense gratitude, Authors acknowledge the financial support in the form of scholarship for the study program by the Lutheran World Federation (LWF), Geneva. Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Avedis Donabedian. Quality assessment and monitoring – Retrospect and prospect. Eval Health Prof 1983; 6: 363- 375.
2. Brook R, H.E. Mc Glynn, and Shekell. Defining and Measuring Quality of care: A perspective from US researchers, Int J Quality in Healthcare 2000; 12:281-95.
3. Carver AM. Development and implementation of a hospital- wide quality assurance program at the King Khaled Eye Specialist Hospital in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Aust Clin Rev 1985; 5:188-90.
4. Dandona L, Dandona R, Anand R, Srinivas M, Rajashekar V. Outcome and number of cataract surgeries in India: policy issues for blindness control. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthal 2003; 31:23-31.
5. Eric D. Peterson, Matthew T. Roe, Jyotsna Mulgund, Elizabeth R. DeLong, Barbara L. Lytle et. al. Association between hospital process performance and outcomes among patients with acute coronary syndromes. JAMA 2006; 295:1912-1920.
6. Idvall E, Rooke L, Hamrin E. Quality indicators in clinical nursing: a review of the literature. JAN 1997; 25:6-17.
7. James W. Dean, Jr., David E. Bowen. Management Theory and Total Quality: Improving Research and Practice through, The Academy of Management Review 1994; 19(3): 392-418.
8. Jose R, Bachani D. Performance of cataract surgery between April 2002 and March 2003. NPCB-India 2008.
9. Limburg H, Foster A, Gilbert C, Johnson GJ, Kyndt M, Myatt M. Routine monitoring of visual outcomes of cataract surgery. Part 2: results from 8 study centres. Br J Ophthalmol 2005; 89: 50–52.
10. Thomas R. Surgical Techniques for a Good Outcome in Cataract Surgery: Personal Perspectives. Community Eye Health 2000; 13: 38–39.
11. Robert L Kane, Gardner J, Wright DD, Snell G, Sundwall D, et.al. Relationship between Process and Outcome in Ambulatory Care. Med Care 1977; 15: 961-965.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License