IJCRR - 7(8), April, 2015
Pages: 07-13
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
CELL PHONE DEPENDENCE AMONG MEDICAL STUDENTS AND ITS IMPLICATIONS - A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY
Author: Anuj Mittal, Vedapriya Dande Rajasekar, Lavanya Krishnagopal
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Context: The rising use of cell phone made people dependent on cell phone, to an extent that with usual disruption of services people feel disturbed. Cell phone dependence can be considered as a new diagnostic entity. Current literature proves that there is cell phone dependence among youth but not many studies highlight its implications and magnitude in developing Nations. Methods and Material: A cross-sectional study was planned to evaluate dependence on cell phone among medical under graduate students and its implications. Total of 309 students studying in second to eighth semester had responded on self administered questionnaire. Results: Among 309 participants, 131 were males and 178 were females. There was no significant difference between call patterns of males and females. Students were restless when they were unable to contact desired person (3.9+1.47) and when they forget to bring the cell phone (restlessness observed significantly among very frequent users). Total 54% students were angry with cell phone; the common reasons were software problems (29.3%), unavailability of network (23.4%), annoying messages and calls (22.8%). 25% students attend call while driving. False perception of ring was reported by 64.4% users and it was twice more common among students with emotional bonding score greater than 18.
Conclusions: As observed unjustified use of cell phone may result in problems, therefore health education should be targeted to youth to prevent harmful effect of this great invention.
Keywords: Mobile phone, Dependence, False perception of ring
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Currently cell/mobile phone is considered an important accessory, which has been carried by all. The charm of cell phone is more among youth and they spend a good amount of their pocket money on cell phone1 . This rising use of cell phone made people dependent on cell phone, to an extent that with usual disruption of services people feel disturbed. A study conducted among medical students reveals that 19% males and 18% females suffers from nomophobia (fear of being out of contact through cell phone)2 . According to psychiatrist3 cell phone dependence can be considered as a new diagnostic entity as it has properties of excessive use, withdrawal, tolerance and negative repercussions. Major studies done on problems arising due to cell phones are done in developed countries4,5,6,7. Present literature proves that there is cell phone dependence among youth but not many have highlighted its implications and magnitude in developing Nations. Realizing the urgency and importance of situation, present study is planned to evaluate dependence on cell phone among medical under graduate students and its implications. It also focused to assess relationship between dependence, duration of cell phone use and gender preferences.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A cross-sectional study was planned and a research instrument was developed, which was pretested and validated to achieve study objectives. Considering findings of a study conducted among youth in Mumbai which reported that 58% of the respondents could not manage without a cell phone even for a day8 , minimum sample size for present study was estimated to be 290 with allowable error of 10% and 95% confidence interval. Additional 10% of sample was drawn considering attrition, so sample size was estimated to be 320. Sample was drawn out of 500 students randomly through attendance registers with help of Random Allocation Software. Students were given self administered questionnaire and assured that their confidentiality will be maintained, to get unbiased response. Total 320 students were selected for the study but three students didn’t consented to be part of study and six questionnaires were rejected as they were not completely filled. Out of 311 students two didn’t use cell phone so the final sample size was 309. Data collection was done during August 2011. After data collection, students were briefed regarding Do’s and Don’ts about cell phone use. The data thus collected was entered on Ms Excel and analyzed on SPSS 11.5 software. Chi square test, ANOVA (analysis of variance), post hoc test were applied to derive p values. Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to derive adjusted odds ratio.
RESULTS
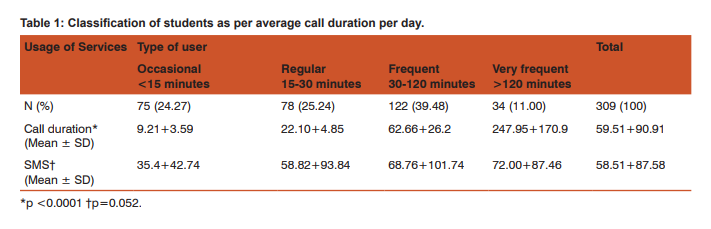
Students were selected from second to eighth semester and their mean age being 20.2 years (range 17 to 26 years). Out of 309 participants, 131 were males and 178 were females. As students were having variation in use of cell phone they were divided into four categories: Occasional, regular, frequent and very frequent user (Table 1). There was no significant difference between call patterns of males and females, mean and SD (standard deviation) being 52.62+80.85 and 64.65+97.67 minutes per day. While males were more inclined to use SMS (short message service) with mean and SD of 75.86+115.35 which was significantly different (p=0.003) from females 47.74+56.48. Majority of students preferred call (51.1%) as mode of communication rest of them (48.9%) preferred sending SMS.
Emotional bonding
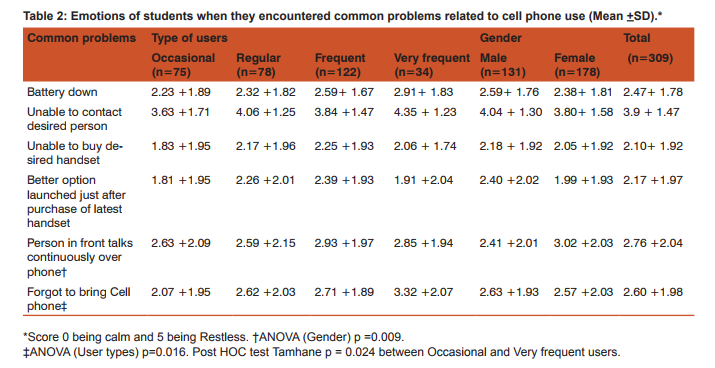
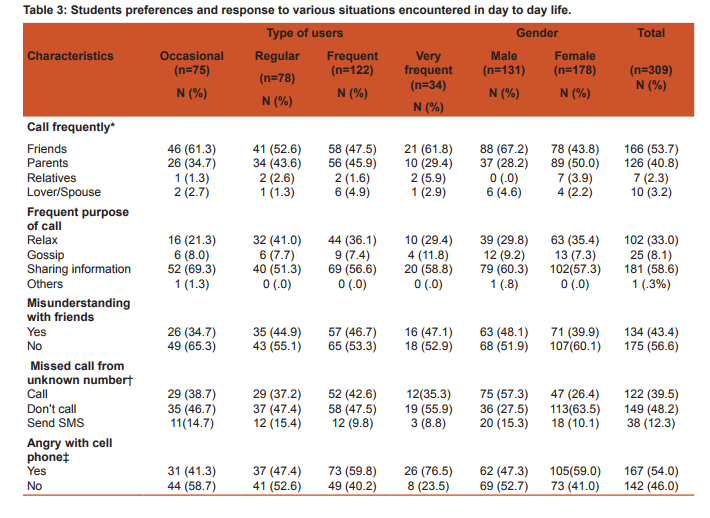
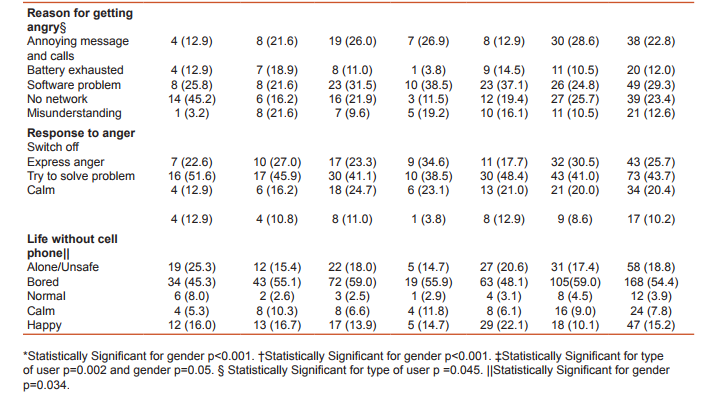
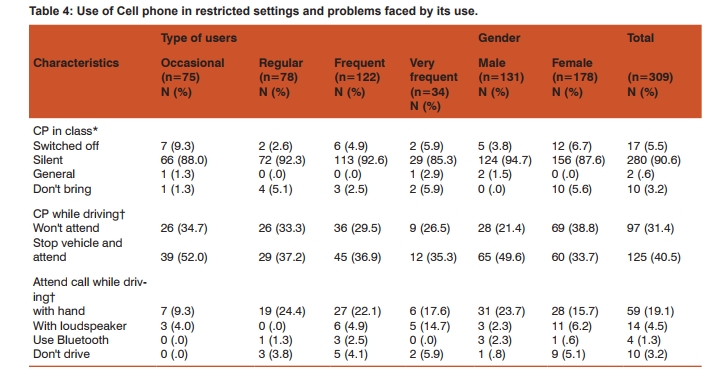
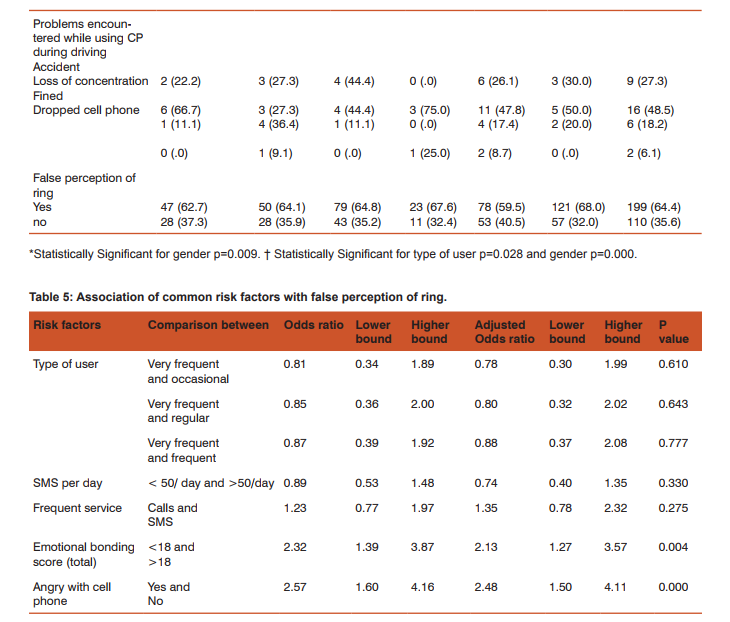
To assess emotional bonding for cell phone, students were asked to grade their feelings between score of zero to five (zero being calm and five being restless) for circumstantial problems encountered in day to day life. Students became restless when they were unable to contact desired person (3.9+1.47), while stress with other situations mentioned in table 2 were less. Though the score was higher among very frequent users as compared with occasional users but it was not significantly different except when individual forgot to bring his/her cell phone (Post hoc Tamhane test: p=0.024). Stress score was higher among males but it was not significantly different. Females becomes restless when person in front talks continuously over phone, this attitude was significantly different from males (p=0.009). Students preferred to call their friends (53.7%) and parents (40.8%). Call pattern was significantly different among males and females (p<0.001), where 67.2% males call their friends while 50% females call their parents. Majority (58.6%) of students call frequently to share information, while 33%, 8.1% calls to relax and gossip respectively. Misunderstanding with friends while talking on cell phone was reported by 43.4% users. The chance of misunderstanding was higher among very frequent users and males, but it was not statistically significant. Forty eight percent students ignored missed call from unknown numbers, whereas 39.5% students call back and 12.3% send SMS to verify their identity. Fifty four percent of students were angry with cell phone. Very frequent users (76.5%) and females (59%) getting angry with cell phone was significantly different having p=0.002 and p=0.05 respectively. Common reasons for getting angry were software problems 29.3%, unavailability of network 23.4% and annoying messages and calls 22.8%. Occasional users most commonly got angry because of unavailability of network while frequent and very frequent users became angry due to software problems (phone hangs) and this pattern was significantly different p = 0.045. Most of the students 43.7% expressed their anger by throwing or by shouting on cell phone; expression of anger was more common among occasional users and gradually reducing among very frequent users (due to adaptation). In such situations, 25.7% students switched off their cell phones, 20.4% tried to solve the problem and 10.2% were calm. As observed that there is love-hate relationship for cell phone among its users, so we asked how life would be without cell phone, we had many responses describing their feelings but we summarized it in broad categories (table 3). Nearly 73% students responded that life would be boring (54.4%) and unsafe/lonely (18.8%), while 26.8% considered other way; life would be happy (15.2%), calm (7.8%) and normal (3.9%). There was no significant difference in feelings among user types, but 22.1% males would be relatively more happier without cell phone as compared with 10.1% females (p=0.034). Use of Cell phone in restricted settings and problems faced by its use Students who brought cell phone to class were 96.8%, among them 90.6% kept it silent, 5.5% switched it off and 0.6% kept on normal mode. All the males who own cell phone bring it to class, while 5.6% females don’t bring it (p=0.009). On being asked how they respond when they receives a call while driving 31.4% students won’t attend the call, 40.5% stop vehicle and attend while 25% students attended the call while driving. This practice was significantly less (p=0.028) among occasional users (13.3%) as compared to regular (25.7%), frequent (29.5%) and very frequent (32.3%) users. Thirty three (10.7%) users admit that they had faced problems on attending a call while driving, it constitutes 17.5% of males and 5.6% females, problems faced by males was significantly higher as compared to females (p=0.001). Among 33 users who had faced problems most common were loss of concentration 48.5%, accident 27.3%, fined by policeman 18.2% and dropping of cell phone 6.1%. False perception of ring is a feeling that cell phone is ringing when actually it is not and it was reported by 64.4% users. This phenomenon was lower among occasional users and gradually increasing among very frequent users. False perception of ring was more common among 68% female users as compared with 59.5% males but it was not significantly different. To ascertain whether there was any possible association between students’ behaviour and false perception of ring, we calculated odds ratio and adjusted odds ratio by multiple logistic regression analysis. In table 5 odds ratio was estimated for possible risk factors; type of users, frequency of SMSs’ sent per day, preferred service (call/sms), emotion bonding score more than 18 and angry with cell phone. Further adjusted odds ratio was computed to control the impact of confounders and we observed that students whose emotional bonding score was more than 18 and those who got angry with cell phone were approximately twice more prone to have false perception of ring.
DISCUSSION
In present study we observed that cell phone use among medical students was high as compared to Malaysian medical students whose average talk time was 32 minutes9 and 47 minutes10 as compared to 59 minutes among our students. Students in present study called frequently to their friends for sharing information which was not the case in other South Indian study11, where students called frequently to their parents. The latest function of sending group SMSs’ and low tariffs may have resulted in increased SMSs sent per day in our study. Emotional bonding and problem of nomo-phobia are two sides of coin which describes attachment of students towards cell phone; present study highlights 41.1% students have stress score more than 60% in normally encountered situations while nomo-phobia was reported among 19% students in other study2 . Even 58% of Mumbai youth could not manage a single day without cell phone8 . Dependency on cell phone was more among very frequent users, their chances of getting angry with cell phone was also more. Most common reason stated was software problem which is commonly encountered with multimedia phones. Male (31.3%) and female (23.6%) students responded that life will be normal or happy without cell phone; this suggests that though youth are inclined towards cell phone gradually their interest is declining. Accidents due to cell phone are common among car drivers, pedestrian and even trains which causes mass casualty12,13. A recent train accident in Spain was due to over speeding of train at turn resulting in derailment of train because driver was on phone at the time of crash14. In present study 25% students attend call while driving, whereas in other studies in India it was reported as 24.1%8 and 17.9%11. Though students were aware of hazards of using cell phone while driving still the impulse or urgency to attend call forces them to use cell phone while driving and 10% students in our study had experienced problem in doing so. False perception of ring also called ringxiety or phantom ringing has been experienced by 64.4% of students in our study and 36.4% of students in other south Indian study11. The proportion of the phenomenon is greater in our study as compared to other study which may be because of more emotional bonding with cell phone among our students. Study by Sonu H. Subba et al 11 observed that ringxiety was significantly more among students who use cell phone during class, library, eating, cut down sleep for talking and borrow money for recharge but there was no difference between gender and call duration. Our findings also suggests that there was no association of false perception of ring with gender and call duration, but false perception of ring was twice more common among students who got angry with cell phone and higher emotional bonding.
CONCLUSION
As observed use of cell phone is increasing and unjustified use may result in problems. Further studies should be conducted to have foresight on problems arising due to excess cell phone use. Prevention is better than cure therefore health education strategies should be targeted to youth to prevent harmful effect of this great invention.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the support of students for sharing their valuable information in this study and sparing their time. Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Mittal Anuj, Vedapriya Dande Rajasekar, Lavanya Krishnagopal. A study to assess economic burden and practice of cell phone disposal among medical students. J Clin Diagn Res 2013;7:657–60. PMID:23730640.
2. Sanjay Dixit, Harish Shukla, AK Bhagwat, Arpita Bindal, Abhilasha Goyal, Alia K Zaidi, et al. A study to evaluate mobile phone dependence among students of a medical college and associated hospital of central India. Indian J Community Med. 2010;35:339–41. PMID:20922119.
3. Bhatia Manjeet Singh. Cell Phone Dependence — a new diagnostic entity. Delhi Psychiatry Journal 2008;11:123-4.
4. Braune SA, Riedel J, Schulte-Monting J, Raczek J. Influence of a radiofrequency electromagnetic field on cardiovascular and hormonal parameters of the autonomic nervous system in healthy individuals. Radiat Res. 2002;158:352-6.
5. Eliyahu I, Luria R, Hareuveny R, Margaliot M, Meiran N, Shani G. Effects of radiofrequency radiation emitted by cellular telephones on the cognitive functions of humans. Bioelectromagnetics 2006;27:119-26.
6. Oftedal G, Wilen J, Sandstrom M. Mild Symptoms experienced in connection with mobile phone use. Occup Med (Lond) 2000;50:237-45.PMID:10912374.
7. Rubin GJ, Hahn G, Everitt BS, Cleare AJ, Wessely S. Are some people sensitive to mobile phone signals? Within participants double blind randomised provocation study. BMJ 2006;332:886-91.PMID:16520326.
8. Database on the Internet: Macro - market analysis and consumer research organization. A report on study of mobile phone usage among the teenagers and youth in Mumbai, April-May-2004 page 1-24. [Cited 2013 Oct 1] Available from:http://www.itu.int/osg/spu/ni/futuremobile/socialaspects/ IndiaMacroMobileYouthStud.y04.pdf
9. Kumar L, Chii K, Way L, Jetly Y, Rajendaran V. Awareness of mobile phone hazards among university students in a Malaysian medical school. Health 2011;3:406-15.
10. Zulkefly SN, Baharudin R. Mobile Phone use Amongst Students in a University in Malaysia: Its Correlates and Relationship to Psychological Health. European Journal of Scientific Research 2009;37:206-18.
11. Sonu H. Subba, Chetan Mandelia, VaibhavPathak, Divya Reddy, Akanksha Goel, Ayushi Tayal, et al. Ringxiety and the mobile phone usage pattern among the students of a medical college in south India J Clin Diagn Res 2013;7:205- 9. PMID:23542709.
12. Website- timesofindia.com [Internet]. Chennai: Times of India, Chennai, Bennet, Colman and Co. Ltd; c2013, [updated 2011 Sept 18; cited 2013 Oct 1]. Available from: http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2011-09-18/chennai/30171796_1_mobile-phones-train-accident-hand-heldphones
13. Website– nbcnews.com [Internet]. Washington: NBC News, Washington;c2013 [updated 2009 March 3, cited 2013 Oct1]. Available from: http://www.nbcnews.com/ id/29494331/ns/us_news-life/t/train-crash-probe-focuses-cellphone-use/
14. Website- latintimes.com [Internet]. Newyork: Latin times, IBT Media;c2013, [updated 2013 June 30, cited 2013 Oct1]. Available from: http://www.latintimes.com/articles/6892/20130730/spain-train-crash-cell-phone-speedingderailment.htm
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License