IJCRR - 7(9), May, 2015
Pages: 61-65
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
PREVALENCE OF MALARIA AND HEPATITIS B VIRUS INFECTION IN FEBRILE PATIENTS IN KANO NORTHWEST NIGERIA
Author: Sharif A. A, Dabo N. T., Getso M. I.
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background and Objectives: Malaria and Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) infections are co-endemic throughout much of the tropical and Sub-Saharan Africa and both present major threat to public health. Nigeria is endemic for both Malaria and Hepatitis B virus infections. Presence of both infections concurrently in an individual might have significant clinical and public health implications. Hence the present study was undertaken to detect the prevalence of Hepatitis B-Malaria co-infections in a tertiary health center in Northwestern Nigeria. Methodology: The study was carried out on 200 patients presenting with fever to the General Outpatient Department (GOPD) of the Murtala Muhammed Specialist Hospital (MMSH) Kano using Gold Standard microscopy and rapid diagnostic test (RDT). Results: Fifty one (25.5%) out of the total subjects studied were malaria positive. Females presented with higher rate of malaria infection with 18% prevalence than males with 7.5%. Age group 15-24 had the highest malaria prevalence (11%), followed by age group 25-34 with 6.5%. Thirteen (6.5%) subjects were HBsAg positive. Males had higher rate of infection with 4.5% prevalence than females with 2.0%. Nine individuals representing 4.5% of the total population had co-infection with higher prevalence observed among the males with 3.0%. Age groups 25-34 were observed to have high co-infection rate of 1.5% and the least prevalence was observed among the age group 15-24 with 0.5% prevalence for both males and females. Conclusion: These findings ware discussed in the light of the prevalence of co-infection with the two ailments and showed a decreasing trend of the infections.
Keywords: Malaria, Hepatitis B, co-infection, MMSH, Kano
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Fever is a non specific symptom that manifests due to many conditions of infectious origin such as malaria and hepatitis. It is a common presentation and accounts for most consultations in general outpatient units of major hospitals in tropical and sub-tropical regions (Igharo 2012). Both Malaria and HBV infections can present with febrile illness associated with generalized body ache, weakness, headache and yellowish sclera as their first symptoms. Malaria still remains a burden globally particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa. The World health organization (WHO) reported an estimated 219 million cases of malaria in 2010 with an estimated 660,000 death mostly affecting the African population where 90% of malaria infection occurs and also reported that 99 countries worldwide have an ongoing malaria transmission in 2012. Nigeria was first among the six most endemic countries for malaria which altogether account for 103 million cases. Southeast Asia is the second most affected region in the world with India taking the highest cases among the countries (WHO 2012). As a result of efforts mounted towards control and prevention there was decline in transmission, limited to 97 countries only with an estimated 207 million cases and 627,000 deaths. Pathetically however, 90% of these cases occur in Sub Saharan Africa and children less than five being worst affected (WHO 2013). HBV infection though a vaccine preventable disease remains a global health problem. An estimated 2 billion people have been infected with HBV (WHO 2012) and more than 300 million people worldwide suffer from persistent infection. It is estimated that about 600, 000 people die every year due to the acute or chronic consequences of the disease (Lee 1997, Ekanem 2013, WHO 2013,). Again the prevalence rate of the infection is highest in the Sub-Saharan Africa and Eastern parts of Asia. The infection is largely acquired during childhood with 5-10% of the adults developing a chronic disease. Malaria and HBV infection co-endemic throughout much of the tropical and Sub-Saharan Africa and they both present major threat to public health (Mazie 2002, Paulyn 2010, Jeya 2010, WHO 2011). Co-infection of Malaria with HBV may occur in areas where both infections are endemic and because of their geographical coincidence (Freimanis 2012, Andrade 2011). These two infections live some of their developmental stages within the liver and hepatocyte damage in HBV infection may cause poor liver handling of malaria parasites (Thurz 1995, Paulyn 2010) thus culminating in increased morbidity. In line with this, co-infection with Plasmodium parasite and HBV virus in individual may possibly influence progression of both agents and associated severity.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Before commencement of the study, ethical clearance was obtained from the Ethical committee of the Kano State Hospital Management Board (KSHMB). The study was conducted between July and December 2013, in General Outpatient Department (GOPD) of the MMSH in Kano. The study was carried out among patients presented with febrile illnesses. Two hundred informed and consented subjects aged between 15- 64 were recruited for the study. Exclusion criteria were patients with an established clinical condition other than malaria and/ or HBV infection such as obstructive jaundice, cirrhosis, renal diseases, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, sickle cell disease, pregnancy, cancer and patients already on course of chemotherapy or who had it in the last two weeks for treatment of an earlier diagnosed illnesses were also excluded.
Sample Collection
From each individual subjects, 5 ml of blood sample was obtained via venopuncture from the subjects using vacoutainer needle (Cheesbrough 2005). Two milliliters of the blood was placed in ethylenediethyltetra acetic acid (EDTA) bottles for parasitological analysis. The remaining 3 ml placed in universal bottle and centrifuged at 3000rpm for 5 minutes to obtain the serum for serological detection of the HBsAg.
Parasitological examination
Incidence of malaria parasites in the blood samples was established using the gold standard microscopic procedure using Giemsa staining technique on thin and thick film smears were made from the 2ml collected above for specie determination and the level of parasiteamia respectively. Level of parasiteamia was expressed as number of parasite/µl of blood. (Alperex 1932, WHO 1991, Cheesbrough 2005)
Hepatitis B serology
Hepatitis B infection was diagnosed using serology. The 3ml portion of the blood sample was used for the detection of HBsAg. The blood was centrifuged and the serum obtained from which HBsAg was detected using Micropoint ELISA commercial Kits technique following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Statistical Analysis
Results obtained were analyzed using SPSS software (version 20) for both the descriptive and inferential analysis. Results were expressed as means and standard deviation. One way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to determine the level of significance between the parameters.
RESULTS
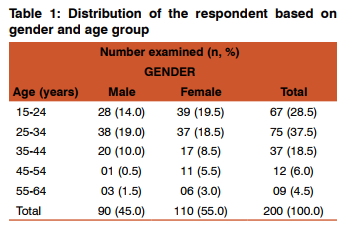
The distribution of the subjects based on gender and age is presented in Table 1 below. Of the 200 studied, 90 (45.0%) were males and 110 (55.0%) were females. Subjects aged 15-34 constitute 66% of the population studied.
Malaria Assessment
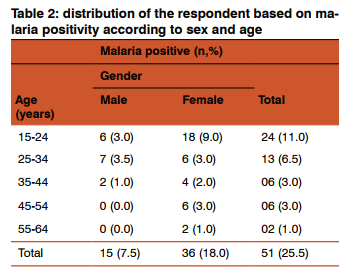
Fifty one (25.5%) of the subjects studied were positive for malaria (Table 2). This comprises of 15 (7.5%) males and 36 (18.0%) females, thus the females had greater burden than the male, however, statistical analysis showed no significant difference (P>0.05) in infection rates between male and female. Males aged 15-34 had the highest 13(6.5%) malaria infection than the other groups. A similar observation was also made among the females aged 15-34 constituting 24(12%) of the total infected. Fifty one (25.5%) of the subjects studied were positive for malaria (Table 2). This comprises of 15 (7.5%) males and 36 (18.0%) females, thus the females had greater burden than the male, however, statistical analysis showed no significant difference (P>0.05) in infection rates between male and female. Males aged 15-34 had the highest 13(6.5%) malaria infection than the other groups. A similar observation was also made among the females aged 15-34 constituting 24(12%) of the total infected.
HBsAg Serology
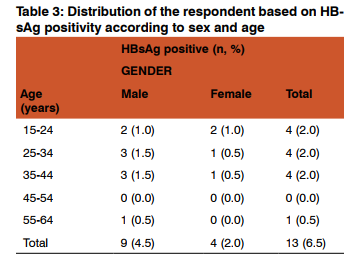
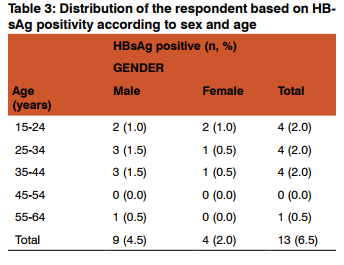
Thirteen persons (6.5%) out of the 200 subjects studied were positive for HBsAg (Table 3). Higher infection was observed among the males with 9 (4.5%) infection rate than the females with 4(2.0%). Higher infection rate was observed within 25-34 and 35-44 age groups each with 3(1.5%) among the male population. This was followed by 2 (1.0%) observed within 15-24 age group for both male and female population. Least infection rate 1(0.5%) was seen within the age group 55-64 among male population and within 25-34 and 35-44 age groups among female population.
Malaria/HBV Co-infection
Nine individuals (4.5%) were observed to have co-infection of malaria and HBV infection. Again, the males had higher co-infection rate 6 (3.0%) than their female counterparts 3 (1.5%). Male patients within the age group 25-34 were observed to have higher co-infection rate 3(1.5%). This is followed by 2(1.0%) each for both female and male patients within the age groups 35-44 and 25-34 respectively. The least co-infection rate was observed among age group 15-24 1(0.5%) for both male and female population.
DISCUSSION
Malaria and HBV infection are both endemic and life threatening diseases in this part of the world. This study presents 25.5% prevalence rate of malaria infection among the study population which is less than 30.59% reported by (Gobir 2014) from kano metropolis and 77.6% reported by (Igwe 2014) from Enugu, South-East Nigeria. The reduction in trend as observed in this study may be due to adequate measures taken in malaria prevention and prompt diagnostic measures (WHO 2012, 2013). Female population in this study is more affected with 18.0% prevalence. This may point to high vulnerability of women especially when they are pregnant. This finding is not consistent with the findings by (Gobir 2014) who reported a prevalence rate of 61% in female than their male counterparts with a 38%. These results showed continuous decline in malaria prevalence as stated by WHO (2013). Age group affected in both females and males were within 15-24 and 25-34. This study presents a 6.5% prevalence of HBsAg which differs from the results obtained from other studies within the same state and from other geopolitical zones of Nigeria. Recent report on the prevalence of Hepatitis B infection on adolescent in Kano puts the rate at 12.5% (Yunusa, 2014). The figure is also lower than 11% (Sule 2010) reported from studies in Anyingba, kogi state, 11.5% (David, 2012) from Ekiti State and 10.6% (Esumeh, 2003) from South-South region is also lower than 12.3%, (Hamza, 2013) and 18.2% (Luka, 2008) obtained among HIV infected population in Aminu Kano Teaching Hospital and among pregnant women in Zaria, respectively. It is also lower than 47.2% and 20% re-ported from Benue State among blood donors and Borno State among primary school pupils respectively. (Nneka, 2007) also reported a 17.1% from Nasarawa State among commercial sex workers. Several studies also reported values similar or less than this. (Dawaki and Kawo, 2006) reported 7.3% prevalence among pregnant women in Kano, 6.8% (Ndako, 2011) among secondary school students in north central Nigeria. 4.2% (Mukhtar, 2005) in Zaria, 4.1 % (Ugwuja, Okonko, 2010). Age specific prevalence rate was found to be 1.5% which is higher among 25-34 and 35-44 age groups followed by 1.0% each among 15-24 age groups. Least infection rate was observed among 55-64 age groups at 0.5%. These findings agree with that reported by (Gambo, 2012, okonko 2010) indicating the high rate of hepatitis B infection among these age groups 25-34 and 35-44. They constitute the sexually active population among the study group and they are at high risk of engaging in several ways through which one can contract the infection. The study figured out no significant difference (p=0.94) in Hepatitis B infection among the two sex groups with male patients having 4.5% while females recorded 2.0% prevalence rate. Higher rate of HBV infection and coinfection (3.0%) among males, though lower than the previously reported findings of 12.1% and 32% prevalence of HBsAg among male population reported from Kano, North west and North east by respectively (Nwokedi,2010 ,Gambo 2012) can probably be explained by unequal exposure to risk factors of contracting the infection. Male population in this part of the country are more engaged in one form of risk behavior or the other while the female population are always under close monitoring by parents. In this area the ratio of men to women that are engaged in business occupation, civil service, schools and other outdoor activities is significant going by their tradition, culture and religion.
CONCLUSION
The low rate of co-infection presented by this study proves that, there is decrease in the trend of malaria and HBV infections as reported by the World Health Organization. It also shows that the effort at containment of these two infections is reaching the target as the study shows reduction in prevalence of the twin infection. However, the prevalence of HBV infection has shown a fluctuating trend in the area.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors are grateful to the Bayero University, Kano for providing assistance and enabling atmosphere to do the study and to the management of the MMSH, Kano for permission to use their facility and for the ethical clearance to carry out the investigation. The authors also acknowledge the help received from scholars whose articles are sited and included in the references of this manuscript. They are also grateful to authors, editors and publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed
References:
1. Andrade BB, Santos CJN, Camargo LM, Souza-Neto SM., Reis-Fiho A: Hepatitis B infection is associated with asymptomatic malaria in the Brazilian Amazon. PLoS ONE, 2011, 6(5): e19841
2. Cheesbrough, M: District laboratory practice in tropical countries, part 1. Cambridge University Press. Cambridge, 2005, Pp 239-245
3. David OM, Oluduro AO, Ariyo AB, Ayeni DI, and Famurewa OI: Sero-epidemiological survey of hepatitis B surface antigenemia in children and adolescents in Ekiti State, Nigeria. J of pub health and Epid, 2012, 5(1): 11-14
4. Dawaki SS and Kawo AH: Seroprevalence of HBsAg in pregnant women attending urban maternity hospital in Kano: Nig J of microb, 2006, 20:705-709
5. Esumeh FI, Ugbomoiko D, and Isibor JO: Seroprevalence of HIV and Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) among blood donors in central hospital Benin City, Nigeria. J of med lab sci,2003, 12(2): 52-55
6. Earle, WS, Perex M: Enumeration of parasites in the blood of malaria patients: J of lab and clinical med, 1932, 1(7): 1124
7. Friemanis GL, Owuso-Ofori S, Allain JP: Hepatitis B virus Infection does not significantly influence plasmodium parasite density in asymptomatic infections in Ghanian transfusion recipients. PLoS ONE, 2012, 7(11):e49967
8. Gambo IM, Rabiu AM Muhammad MB, Shugaba AI: Seroprevalence of HBsAg among Fulani Nomads in Toro North Eastern Nigeria. Global adv research J of Medicine and Med Sciences, 2012, 1(8): 214-217
9. Gobir Z, Tukur Z: Prevalence of Malaria parasitemia using rapid diagnostic test among apparently healthy children in Kano, Nigeria. Journal of Medical Trop, 2014, 1(6):1-4
10. Hamza M, Samaila AA, Yakasai AM, Babashani M, Borodo MM, Habib AG: Prevalence of Hepatitis B and C virus infections among HIV-infected patients in a tertiary hospital in North western Nigeria. Nig J of Basic Clin Sci, 2013, 10: 76-81
11. Igwe NM, Joannes UO, Chukwuma OB, Chukwudi OR, Oliaemeka EP, Maryrose AU, Joseph, A: Prevalence and parasite density of asymptomatic malaria parasiteamia among unbooked paturients at Abakaliki, Nigeria. J of Basic Clin and Repro Sci ,2014, (3):44-8
12. Jeya, DB., Botelho de suza, RA., Batista da Silva, E: Cohuman infection by plasmodium and hepatitis B: Clinical aspect, Immunological and Serological: Tropical medicine foundation of amazon, 2010.
13. Mazie JB, Barcus TT, Nicholas JW, Kantilaras JF, Schwartz, IK, Andrew C, Baird JK, :Hepatitis B infection and severeplasmodium falciparum malaria in Vietnamese adults: Amer J of tropical medicine and hygiene, 2002, 66(2), 140- 142
14. Mukhtar HM, Sulaiman AM, Jones M: Safety of blood transfusion: Prevalence of HBsAg In donor in Zaria: Nig J of Surgical research, 2005, 7(4): 290-292
15 Ndako JA, Nwankiti OO, Echeonwu GON, Junaid SA, .Anaele O, Anthony TJ: Studies on prevalence and risk factors for hepatitis B surface antigen Among secondary school Students In North central Nigeria. Serria leone journal of Biomedical research, 2011, 3(3): 163-68
16. Nneka O: Seroprevalence of Hepatitis B virus infection among commercial sex workers in Keffi, Nigeria. Nassarawa State University, 2007, 1-18 [Dessertation]
17. Nwokedi EO, Odimayo MS, Emokpae AM, Yahaya IA, Sadiq MN, Okwori EE: Seroprevalence of HBsAg among patients attending Aminu Kano Teaching Hospital, Kano. Nigerian journal of medicine, 2010, 19(4):423-6
18. Okonkwo, Soleye FA, Alli JA, Ojezele MO, Udeze AO, Nwanze JC, Adewale OG, Iheanyi,O: Seroprevalence of HBsAg Antigenemia among patients in Abeokuta, South Western Nigeria.Global journal of medical research,2010, 10(2): 140-149
19. Paulyn TA, Terdzungwe TS: Prevalence of plasmodia and HBV co-infection in blood donors at Bishop Murray Murray Medical Centre, Markurdi, Benue State, Nigeria: Asian pacific Journal of tropical medicine, 2010, pp 22- 226
20 Sule WF, Okonko IO, Ebute AJ, Donbraye E, Fadeyi A, Udeze AO, Alli JA : Farming and non farming individuals attending grimard catholic Hospital Anyingba Kogi State Nigeria, were Comparable in Hepatitis B surface antigen Seroprevalence. Current reaserch journal of Biological sciences, 2010, 2(4): 278-282
21. Thurz, MR Kwiatkowski D, Torok ME. Allsopp CE, Greenwood BM: Association of hepatitis B surface antigen carriage with severe malaria in Gambian children: Natural Medicine, 1995, (1), pp 374-375.
22. Ugwuja E, Ugwu N: Seroprevalence of HBsAg and liver function test among adolescents in abakaliki, south eastern Nigeria. The internet journal of tropical medicine, 2010, 6(2)
23. World health organization (2010): A global strategy for Malaria control, Geneva. www.who.int/malaria/publication/ world-malaria-report-2010/en/ (accessed on 13/10/2013)
24. World health organization (2012): world malaria report fact sheet www.who.int/malaria/media/world-malaria-report-2012/en/ (accessed on 12/09/2013)
25. World health organization (2013): world malaria report fact sheet www.who.int/malaria/publication/world-malariareport-2013/en/ (accessed on 15/02/2014)
26 Yunusa I, Minjibir AI, Ahmad IM, Madobi AL, Abdulkadir RS, Huzaifa U, Kabir N, Ezeanyika LU: Low body Mass index does not correlate with HBsAg infection in Female adolescents: British journal of Applied Science and technology, 2014, 4(8):1230-1237.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License