IJCRR - 7(11), June, 2015
Pages: 08-12
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
A STUDY ON ECONOMIC TREATMENT OF DISTILLERY EFFLUENT
Author: Nusrat Ali, Sohail Ayub, Juned Ahmad
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:The present study was conducted to find out the economic pollution reduction technique of distillery effluent that possesses a serious environmental problem. The distillery effluent is generally highly acidic (pH 3.8 - 4.4) with high rates of BOD 45000- 60000 mg/l and COD 70000 \? 98000 mg/l and also suspended solids (2000 -14000 mg/l). Currently different treatment techniques are used to treat distillery effluent which includes fungal treatment, adsorption techniques, Electrosorption, filtration, biological treatment, etc. but no treatment method alone give the desired goal to treat the distillery effluent effectively and efficiently therefore further research study in this area should be carried out to prevent surface and ground water pollution.
Keywords: BOD, COD, Adsorption, Electrosorption, Filtration etc.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Water is one of the most important compounds required for every existing of life therefore adequate supply of fresh and clean water is a basic need for all human beings but According to the Natural Environmental Engineering and Research Institution (NEERI) Nagpur about 70% of all available water in India is polluted and therefore two third of all ailments in India such as Typhoid, Jaundice, Cholera, Diarrhea and Dysentery system is caused by contaminated water. These water borne diseases claims 1.5 million lives in India every year, which means three people die every 10 minutes due to contaminated water. [9] The fact behind this is rapid industrialization which is one of the major causes of water pollution. The discharges of untreated and partially treated wastewater from various industries like chemical, pesticides, fertilizer, pulp and paper and sugar, etc., have polluted the aquatic bodies such as a river, pond and ditches. [10] Alcohol production from sugarcane molasses is an important distillery industry posses a high load of water pollution. In India there are around 295 distilleries with a total installed capacity of 3198 million liters per annum and a current yearly production of 1587 million liters alcohols [1]. Liquid wastes from breweries and distilleries possess a characteristically high pollution load and have continued to pose a critical problem of environmental pollution. The high temperature of the waste waters may instantaneously kill fish and other aquatic organisms, thus destroying the flora and fauna of a river, when the wastewater is discharged into it. The spent wash gen- The spent wash generated is highly Acidic in nature (pH 4.0-4.3), Due to decomposition of soluble and suspended organic matters present in the wastewaters, high BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) (45000-60000 ml/l) and COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) (750000-98000 mg/l) (750000-98000 mg/l) of the waste- of the waste- of the wastewaters results, causing rapid depletion of the oxygen content of the water, thus creating a foul smell [2 and 9]. This required that the effluents of the distillery are either treated or utilized profitably.
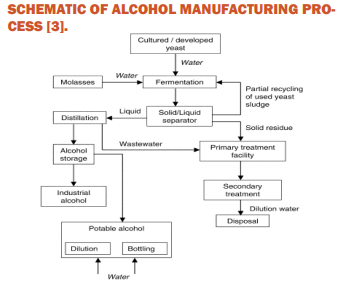
SCHEMATIC OF ALCOHOL MANUFACTURING PROCESS [3].
IMPACT OF DISTILLERY EFFLUENT ON ENVIRONMENT [8]
1. Discharge of wastewater with high TDS would have an adverse impact on aquatic life and to make unsuitable water for drinking purposes, if used for irrigation reduce the crop yield, corrosion in the water system and pipeline.
2. Suspended solids in wastewater reduce the light penetration and plant production as a result, in receiving water by increasing turbidity it can also clog the fish gills.
3. High amount of BOD in the wastewater leads to the decomposition of organic matter under the anaerobic condition that produces highly objectionable products including Methane (CH4), Ammonia (NH3), and Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S) gas.
4. Low Dissolved Oxygen (DO) in water bodies affect the aquatic life as DO drops fish and other species are threatened and may get killed.
5. Fall in DO levels causes undesirable odors, tastes and reduce the acceptability of water for domestic purpose.
6. In steam generation, DO is one of the most important factors causing corrosion of the boiler material.
7. Generally, industrial wastewater changes pH level of the receiving water body. Such changes can affect the ecological aquatic system; excessive acidity particularly can result in the release of hydrogen sulphide (H2S) to air.
8. The alkaline nature of wastewater causes declination in plant growth and crop growth.
9. Color and odor of the effluent of the distillery were red brown in color with the unpleasant odor of Indol, Sketol and other sulphur compounds.
10. Spent wash is a complex, multi component stream that is known to cause considerable fouling.
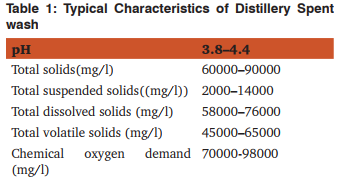
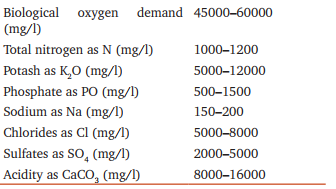
Physico-chemical characteristics: The distillery spent wash is hot, highly colored and acidic with strong and objectionable odors that presents a significant disposal or treatment problem. Physicochemical characteristics are given in Table 1. [4]
Literature Review
The current distillery wastewater treatment includes methods to remove recalcitrant compounds by physicochemical processes (Pandey et al., 2003). In one case example, the physicochemical treatment of biologically-treated wastewater using conventional coagulant iron pickling wastewater supplemented with coagulant aid generated an effluent with COD in the range 940 to 1780 mg/L and a BOD of 25 to 30 mg/L. During this study, the colour of the treated wastewater was in the range of 580 to 1100 platinum cobalt units. It was recommended that the waste sludge from this industry be utilized as a substitute for conventional coagulants. Wastewater generated after chemical coagulation could be further treated efficiently by using 8 g/L of activated carbon with a contact time of 45 min to reduce residual COD to < 250 mg/L to meet discharge limits (Pandey et al., 2003). Anodized graphite anodes were found to be suitable for the treatment of wine distillery wastewater, especially in the presence of supporting electrolytes such as sodium halide, or sodium chloride, which was found to be the most effective in the degradation of polyphenols (Manisankar et al., 2004). Nataraj et al. (2006) investigated the treatment of distillery spent wash by removing the colour and the contaminants using a combination of NF and RO processes. Due to the high fluxes obtained, significant rejection rates of total dissolved solids (TDS), COD, potassium and chloride concentrations were achieved. Water reclaimed by NF and RO is suitable for use in both municipal and industrial applications. Chemical oxygen demand was considerably reduced in distillery wastewaters in India in order to reduce the cost of wastewater disposal. This process emphasized the recovery and recycling of valuable chemicals contained in the wastewaters (Nataraj et al., 2006). As with the generation of fertilizer for direct land application, the economics of any treatment method heavily depends on the financial value that can be assigned to the resultant product. The pre-treatment of wine distillery waste water with ozone improves its kinetic behavior during anaerobic digestion, but at the same time decreases COD removal efficiencies (Benitez et al., 1999a; Martin et al., 2002). Vinasse is known to be chemically very complex because of the high content of polyphenols, which delay biological processes such as anaerobic digestion. As a result, ozonation is seen as a desirable chemical pre-treatment prior to biological treatment because it is capable of converting the inhibitory and refractory compounds into simpler, low molecular weight compounds that are more readily degradable by microorganisms. In such cases, an alternative chemical oxidant has been used, and the treatment of wine distillery wastewater in a continuous reactor using a combination of ozonation and aerobic degradation in activated sludge systems has also been investigated (Benitez et al., 2000). In this combined system, oxidation by ozone achieved a reduction in the organic substrate concentration of 4.4 to 18%, while removal of the content of phenol compounds in the range of 50 to 60% was achieved. Aerobic degradation of these vinasses by activated sludge in experiments using varying hydraulic retention time (HRT) and substrate concentration provided organic substrate removal in the range of 12 to 60% (Benitez et al., 2000). Ozonation of this aerobically pre-treated vinasse led to an increase in COD removal efficiency from 16 to 21.5%, as well as higher rate constants (Benitez et al., 2000). Schafer et al. (2001) later applied membrane filtration with chemical treatment in the management of wastewaters containing natural organic problems. COD removal efficiencies were improved in aerobically pretreated and then ozonated wastewaters (Benitez et al., 1999a).
OTHER TREATMENT AND DISPOSAL OPTIONS OF DISTILLERY WASTE WATER
During the 1970s, land disposal was practiced one of the main treatment options, since it was founded to enhance yield of certain crops. However, for the high strength molasses based spent wash, the odor, putrefaction and unpleasant landscape due to unsystematic disposal are concerns in land application. More recent investigations have indicated that land disposal of distillery effluent can lead to groundwater contamination. Deep well disposal is another option but limited underground storage and specific geological location limits this alternative. Other disposal methods like evaporation of spent wash to produce animal feed and incineration of spent wash for potash recovery have also been practiced. [5]
Fungal treatment: In recent years, fungi have been used in the decolourization of natural and synthetic melanoidin in connection with colour reduction of waste waters from distilleries. The fungus has the capability to purify the effluent by consumption of organic substances, thus, reducing its COD and BOD, and at the same time to obtain any valuable product, such as fungal biomass for protein-rich animal feed or some specific fungal metabolite. In comparison to bacteria filamentous fungi have lower sensitivity to variations in temperature, pH, nutrients and aeration and have lower nucleic acid content in the biomass. [6]
Adsorption techniques to treat wastewater: Adsorption is a natural process by which molecules of a dissolved compound collect on and adhere to the surface of an adsorbent solid. Adsorption occurs when the attractive forces at the carbon surface overcome the attractive forces of the liquid. Granular activated carbon is a particularly good adsorbent medium due to its high surface area to volume ratio. One gram of a typical commercial activated carbon will have a surface area equivalent to 1,000 square meters. Application of above-mentioned methods becomes economically unviable for the removal of heavy metals at lower concentrations. Adsorptive treatment using non-conventional adsorbents. A number of other materials have also been used to remove heavy metals from wastewater, such as peat, wool and silk. Many papers have appeared on preparation of activated carbon from cheaper and readily available materials.[7]
Electrosorption: Electrosorption is generally defined as potential polarization induced adsorption on the surface of electrodes, and is a non-Faraday process. After the polarization of the electrodes, the polar molecules or ions can be removed from the electrolyte solution by the imposed electric field and adsorbed onto the surface of the electrode. Because of its low energy consumption and environmentally friendly advantage, electrosorption has attracted a wide interest in the adsorption processes for treatment of wastewater. Although electrosorption has been shown as a promising treatment process, it has been limited by the performance of electrode material. Activated carbon fiber cloth with high specific surface area and high conductivity is one of the commonly used electrode materials. The surface chemistry of activated carbon fiber has been recognized as a key parameter in the control of the adsorption process. To increase the adsorption capacity, a number of modification methods have been employed. [7]
Biological treatment: In the wastewater treatment sector, biological processes deal primarily with organic impurities. Microbial-based technologies have been used over the last century for the treatment of liquid waste domestic stream. The development of these technologies has provided an excellent process for the destruction of waste constituents that are readily biodegradable under aerobic conditions. Therefore, processes similar to those used for conventional domestic wastewater treatment have applied successfully for the treatment of many industrial wastewaters. Aerobic degradation in the presence of oxygen is considered to be a relatively simple, inexpensive and environmentally sound way to degrade wastes. Factors that are critical in the optimal degradation of the selected substrate include the temperature, moisture, pH, nutrients and aeration rate that the bacte-rial culture is exposed.[7]
Membrane technology [7]: Membrane processes such as microfiltration (MF), Ultrafiltration (UF), Nanofiltration (NF) and reverse osmosis (RO) are increasingly being applied for treating oily wastewater. Membranes have several advantages, among them:
(1) The technology is more widely applicable across a wide range of industries.
(2) The membrane is a positive barrier to reject components. Thus, the quality of the treated water (the permeate) is more uniform regardless of influent variations. These variations may decrease flux, but generally does not affect the quality of its output.
(3) No extraneous chemicals are needed, making subsequent oil recovery easier.
(4) Membranes can be used in-process to allow recycling of selected waste streams within a plant.
(5) Energy costs are lower compared to thermal treatments. \
(6) The plant can be highly automated and does not require highly skilled operators.
Membrane processes have some limitations:
(i) Scale-up is almost linear above a certain size. Thus capital costs for very large effluent Volumes can be high.
(ii) Polymeric membranes suffer from fouling and degradation during use. Thus, they may have to be replaced frequently, which can increase operating costs significantly
DISCUSSION
Distillery wastewater is highly concentrated and cause various problems and therefore distillery industries face dengerious environmental challenges in treating their effluents. Therefore, this review put the task of passing in revue the different technologies issued to treat distillery wastewaters. Several physicochemical options and biological wastewater treatment processes are widely utilised in the successful treatment of distillery effluent but no treatment technology alone is effective in treating the distillery effluent however combined treatment methods may be use to achive the desired goal.
CONCLUSION
In Distillery Industry the spent wash generated is highly Acidic in nature (pH 4.0-4.3), high BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) (45000-60000ml/l)and COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) (750000-98000 mg/l) of the wastewaters causing rapid depletion of the oxygen content of the water, thus creating a foul smell. Current treatment includes methods to remove recalcitrant compounds by physicochemical processes. The high rate of mass transfer generated by RO showed that a large amount of clean water could be permeated economically instead of being vaporized by energy-intensive evaporation Processes or steam distillation using tall towers. The findings of the present study are encouraging and suggest that application of UF and RO processes can be successfully used for the removal of colour and other contaminants from the distillery effluents. Biological treatment is considered to be a relatively simple, inexpensive and environmentally sound way to degrade wastes, but factors such as temperature, moisture, pH, nutrients and aeration rate that the bacterial culture is exposed are critical in the optimal removal from the spent wash. The application of sand and soil in the filtration bed would always be more effective than sand and soil alone. Activated charcoal has been observed best absorbent than fly ash and wood ash to remove the pollutants from distillery spent wash, but no treatment method alone gives the desired goal to treat the distillery effluent effectively and efficiently therefore an intensive research in this area would not only help to solve the liquid waste management problem but would be effective in preventing surface and ground water pollution.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
References:
1. Sohail Ayub, Nusrat Ali, Hassan Haleem, Impact of Distillery Effluent on ground water: A review. International Conference “Emerging trends in Engineering and Technology” held at TMU, Muradabad, April 6-7 2012.
2. Z.V.P. Murthy ,L.B. Chaudhari, Treatment of distillery spent wash by combined UF and RO processes. Global NEST Journal, Vol 11, No 2, pp 235-240, 2009.
3. N.K. Saha, M. Balakrishnan, V.S. Batra, Improving industrial water use: case study for an Indian distillery. Resources, Conservation and Recycling 43 (2005) 163–174.
4. Goyal SK, Seth R, Handa BK. Diphasic fixed-film biomethanation of distillery spentwash. Bioresource Technol 1996;56:239–44.
\5. Pawar Avinash Shivajirao International Journal of Advanced Engineering Research and Studies (E-ISSN2249–8974)
.6. Removal of melanoidin present in distillery effluent as a major colorant: A Review. Radhika Agarwal, Sneh Lata, Meera Gupta and Pratibha Singh, July 2010, 31, 521-528 (2010).
7. Mohamed Osman Awaleh and Youssouf Djibril Soubaneh Waste Water Treatment in Chemical Industries: The Concept and Current Technologies Res 5: 164. doi:10.4172/2157- 7587.1000164.
8. Sohail Ayub, Shoebuddin Usmani, TREATMENT OF DISTILLERIES AND BREWERIES SPENT WASH WASTEWATER International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eISSN: 2319-1163 | pISSN: 2321-7308.
9. Sohail Ayub and Nusrat Ali Impact of wave distillery effluent on ground water : A case study of Atrauli district, Uttar Pradesh, India, ICER/642/PS/O/14.
10. Avnish Chauhan and Namita, Tewari Effect of Lysimetric Treated Effluent on Seed Germination, Radicle Length and Plumule Length of Wheat Plants. New York Science Journal, 2010;3(1)
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License