IJCRR - 13(22), November, 2021
Pages: 129-132
Date of Publication: 20-Nov-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Application of Lepidium sativum Seed Mucilage as a Disintegrant in Pharmaceuticals Formulations: Exploring the Myth vs. the Reality
Author: Mahapatra Abikesh Prasada Kumar, Gupta Niraj, Panigrahy Subodhkant, Paul Basudev, Ekambaram Vijay Kumar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The uses of Lepidium sativum seed mucilage (LSSM) as a disintegrant in various pharmaceutical formulations were already discussed. Researchers claimed that the different functional properties of the seed mucilage of Lepidium sativum enable it to use as a natural disintegrant. Furthermore, scientific research on the disintegrant activity of the LSSM has revealed that it could be effectively used as an alternative to synthetic disintegrants. However, certain factors restrict its use as a disintegrant on the large scale. Aim: In the current scientific discussion, we technically analyzed the prospective obstacles that limit the use of Lepidium sativum seed mucilage as a natural disintegrant in pharmaceuticals. Discussion: In the present discussion, the real case scenario of the functional use of LSSM as a disintegrant on the large scale in different pharmaceutical formulations was summarized. Diligence effort was given to evaluate the different factors associated with the isolation process as well as the intrinsic functional properties that restrict its use as a disintegrant. Conclusion: In conclusion, we opined that Lepidium sativum seed mucilage (LSSM) can be used as a disintegrant. However, before its use in the pharmaceutical industry on a commercial scale, a lot of research and development must be done.
Keywords: Lepidium sativum, Seed mucilage, Disintegrant, Pharmaceutical formulations, Pharmaceutical excipient, Intrinsic functional properties
Full Text:
Introduction
Lepidium sativum is a readily available medicinal herb. The Lepidium sativum seeds, roots, and leaves have medicinal properties. However, the plant is well recognized for its seeds.1 Several researchers are investigating the use of Lepidium sativum-derived products as a disintegrant, binder, control release polymer, gelling agent, oxidizing, and as viscosity-enhancing agent due to their extensive functional properties.2,3 Based on its popularity many researchers explored the use of Lepidium sativum seed mucilage in different pharmaceutical dosage forms.2,4 There is an increasing interest in using seed mucilage from Lepidium sativum in pharmaceutical formulations, which plays distinct roles in tablet and liquid dosage forms.4 Lepidium sativum mucilage has become more popular as a disintegrant. Though several studies have been focused on the development of a cost-effective isolation and extraction process of mucilage from Lepidium sativum seeds; however, there is very little information available on how to efficiently extract the mucilage from seeds.
The extraction and isolation of Lepidium sativum seed mucilage by using cost-effective and easily accessible solvents is critical for its commercial viability. The factor which contributes most is the yield of extraction process. Due to low yield, the cost of extracted mucilage may shoots up. In an attempt to get maximum yield Karazhiyan et al.5 and Kilor et al.6 proposed several extraction processes. In a recent advancement, Mahapatra et al.7 reported a modified method produced a yield of approximate 20% which was relatively higher compared to other reported yields. Mucilage is present around the seeds and an effective solvent, and a simple economic, and user friendly method needed to extract the mucilage from the seeds efficiently. Even if an effective method was utilized, a higher amount of input seeds was needed to get the desired amount of mucilage. Therefore, due to this reason, the observed yield was always found less. Hence, this shall not function as a cost-effective approach and is a tedious task for the manufacturer to produce on a large scale.
Maintaining an alkaline condition during extraction of mucilage from seeds of Lepidium sativum could increase yield by hydrolyzing insoluble constituents into soluble which increases the extraction yield. The effect of alkaline condition on the yield of mucilage from seeds of Lepidium sativum was discussed by Karazhiyan et al.5 and Mahapatra et al.7. Karazhiyan et al.5 extracted mucilage from cress seed (Lepidium sativum) by optimizing pH (alkaline pH), temperature, and water: seed ratio by using response surface methodology. Mahapatra et al. in their research work improved the yield of the seed mucilage of Lepidium sativumby optimizing pH (alkaline pH) and water: seed ratio by using a quality by design (full factorial design) approach. The pH modification proposed by both authors was not justified by solid scientific evidence like why pH was adjusted to alkaline (pH 10). As the extracted mucilage will be used in the finished product as a disintegrant the alkaline pH would affect the pH of the finished product which might affect the finished dosage form stability. Thus, getting a higher percentage yield by maintaining an alkali condition (pH 10) and utilizing the obtained disintegrant in the finished product in the lab scale may be possible. However, reproducing the result on a commercial scale for stability is quite difficult.
Settling (or swelling) volume is considered an essential functional related characteristic of disintegrants.8 This test has been used for several decades. The greater the swelling volume, the greater the capacity of that material to accommodate adsorbed water molecules.9,10 The swelling index of seed mucilage of Lepidium sativum by Mahapatra et al.7 and Archana et al. 10 was found to be 10.3 % and 11 % respectively. Based solely on the swelling volume, the most used synthetic disintegrants used in the pharmaceutical formulations having a swelling index in between 10-30 ml and are follows the order: SSG > CCS > XPVP SSG.11 Among the 3 disintegrants SSG yields faster disintegration times than CCS and XPVP. However, the reported swelling index of the extracted seed mucilage of Lepidium sativum is very much less as compared to the other synthetic disintegrants (SSG / CCS/ XPVP) used in pharmaceuticals. This contributes to a lower disintegrant activity of seed mucilage of Lepidium sativum as compared to the other synthetic disintegrant. The particle size of the disintegrant also contributes rate and extent of swelling. A group of a researcher by Rudnic et al.12 investigated the role of particle size on the rate and extent of swelling and demonstrated higher particle size endorses disintegrant activity. Studies have shown that the particle size is mainly controlled by the extraction process and there is a need of higher control in the extraction process to control the particle size of mucilage.12 Controlling the particle size by extraction process without using any milling step is a tedious process on a larger scale and thus limit its use as a substitute for other marketed synthetic disintegrants.
The determination of ash values, as well as contaminants such as heavy metals and aflatoxins, always represents qualitative standards for naturally extracted materials and these tests determine the authenticity and purity of the material. The determination of ash values (total ash, acid insoluble ash, and water-soluble ash), heavy metals (Cd/Pb/As/Hg) and aflatoxins from a natural source like Lepidium sativum seed mucilage is critical and may need a sophisticated instrument which again may not be economic. Moreover, limited information available in the literature database for these contaminates and showed that the values were very high.13 Due to high chance of contaminants there is a higher probability of lower purity level which signifies that the extracted mucilage is not pure and may not be good for use as an excipient or adjuvant in pharmaceutical formulations for human consumption. Many authors reported the extraction and characterization of Lepidium sativum seed mucilage. It is reported that a large number of organic solvents belonging to classes 1, 2, and 3 such as ethanol, acetone, and chloroform are used for the extraction process. However, residual solvents removal as per Q3C (R6) was not confirmed by any of the authors which restricts the use for human consumption in regulated markets such as the United State America, Canada, Europe, and Australia where the requirement of residual solvent is highly stringent and considered as an organic impurity which needs to be taken into consideration for human consumption. Moreover, the extracted mucilage was from a natural source. Thus, consideration of pesticides or microbiological levels is highly essential. However, this aspect was ignored by the researchers, and consideration of any pesticides or microbiological levels should have been studied as it might represent a major drawback for its use. It was reported that the appearance of the extracted mucilage was brownish red or pale brown in color.13 If it is used as a disintegrant in pharmaceutical formulations, it may cause unacceptable appearance for the final formulation and it will be more critical for uncoated tablets. Moreover, getting a longer shelf life will be always a challenging task owing to its natural source.
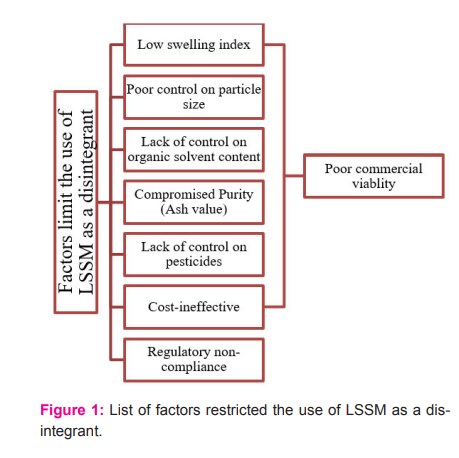
Many scientific studies have been published on the extraction of seed mucilages of Lepidium sativum by using cost-effective methods however have poor yields. Researchers also evaluated various physico-chemical properties and demonstrated their potential use as disintegrants in pharmaceutical formulations. It was claimed that the seed mucilages of Lepidium sativum can be established as a potential new excipient that can suffice the requirement of novel disintegrants for pharmaceuticals. However, we emphasized that reality is different. The use of seed mucilages of Lepidium sativum as a disintegrant in pharmaceuticals is a very much challenging task owing to its low disintegrating efficacy, not being cost-effective, poor control over its particle size and other quality standards such as compromised purity, pesticide content and microbial load (figure 1). Any dosage form in pharmaceuticals must pass through several quality control tests. The same applies to excipients also. Due to the stringent regulatory requirements, it seems an even tougher assignment.
Conclusion
In this summary, we discussed the potential hurdles that enable the use of seed mucilages of Lepidium sativum on a commercial scale as a disintegrant in pharmaceuticals. We also acclaimed that it can be used on small scale i.e. laboratory scale. It could be used in pharmaceuticals, however, for a viable use a lot of work and research needs to be done before it can be used in the pharmaceutical industry on a commercial scale.
Acknowledgements
The authors express their sincere thanks to the management of OPJS University, Churu, Rajasthan, INDIA for providing the necessary support. Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles and journals from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare
Source of funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval is not required for this study
Author’s contributions
We declare that this work was done by the authors named in this article: APKM conceived, drafted and designed the manuscript. SKP and BP collected and analyzed the data. . SBP supervised the work and assisted in the data analysis. VKE contributed to the final revision of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
References:
1. Tosif MM, Najda A, Bains A, Kaushik R, Dhull SB, Chawla P and Walasek-Janusz M. (2021). A comprehensive review on plant-derived mucilage: Characterization, functional properties, applications, and its utilization for nanocarriers fabrication. Polymers, 13,1066
2. Sonawane MS, Supdu APS, Sonawane RO, Ige PP, Patil PG. (2019).Lepidium Sativum characteristics and as a multifaceted polymer: An overview. Indo Am. JP. Sci, 06(05), 9470-9480
3. Gangane PS, Ghughuskar SH, Mahapatra DK and Mahajan NM. (2020). Evaluating the Role of Celosia argentea Powder and Fenugreek Seed Mucilage as Natural Super-Disintegrating Agents in Gliclazide Fast Disintegrating Tablets. Int J Cur Res Rev. 12(7), 101 – 108
4. Bergama C, Goyal A. (2019). Phytoconstituents, pharmacological activity, and medicinal use of Lepidium Sativum Linn.: A review. Asian J Pharm Clin Res,12(4), 45-50
5. Karazhiyan H, Razavi SM and Phillips GO. (2011). Extraction optimization of a hydrocolloid extract from cress seed (Lepidium Sativum) using response surface methodology. Food Hydrocolloids, 25(5), 915–920.
6. Kilor V, Bramhe NN. (2014). Development of an effective extraction method for Lepidium Sativum seed mucilage with a higher yield. J Adv Pharm Edu & Res, 4, 354-360.
7. Mahapatra APK, Murthy PN, Panda N, Gupta A, Paul B, Malla S and Panigrahy S. (2021). Extraction of Lepidium sativum Seed Mucilage: Optimization of Extraction Process with Maxi�mum Yield by using Full Factorial Design. J. Pharm Res Int, 33(64B), 720-735.
8. Wyawahare NS, Mishra MU and Bhongade SL. (2020). Fast dispersing tablets of diclofenac sodium with natural super disintegrant. Int J Cur Res Rev. 2(4), 20 – 29
9. M Soundaranathan, P Vivattanaseth, E Walsh, K Pitt, B Johnston and D Markl. (2020). Quantification of swelling characteristics of pharmaceutical particles. Int. J. Pharm, 590,119903.
10. Archana KS, Mahalaxmi R, Shirwaikar AA and Shirwaikar A. (2012) Physico-chemical characterization and evaluation of disintegrating property of Lepidium Sativum seed mucilage. J. Pharm Res, 5(1), 61-65.
11. Bauhuber S, Warnke G and Berardi A. (2021). Disintegrant selection in hydrophobic tablet formulations. J. Pharmacol. Sci, 110.
12. Rudnic EM, Rhodes CT, Welch S and Bernardo P. (1982). Evaluations of the mechanism of disintegrant action. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm, 8, 87–109.
13. Ahmad R, Mujjeb M, Anwar F, Hussain F et al. (2015). Pharmacognostical and phytochemical analysis of Lepidium sativum L. seeds. Int. Cur. Phar. J, 4(10), 442-446.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License