IJCRR - 7(17), September, 2015
Pages: 39-44
Date of Publication: 11-Sep-2015
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
PARASITIC WORMS FOUND IN THE COLON WHILE DOING COLONOSCOPY AND STUDY OF THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HOOKWORMS AND WHIPWORMS
Author: Govindarajalu Ganesan
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Objective: To diagnose parasitic worms during colonoscopy in our patients. There have not been many studies in India which discuss about the presence and the type of parasitic worms present in the colon while doing colonoscopy. Hence this present study was carried out to study about the presence and the type of parasitic worms present in the colon while doing colonoscopy in our institute. Methods: A study of 72 patients who had undergone colonoscopy in our institute for a period of 5 years from November 2009 to October 2014 was carried out in order to find out the presence of parasitic worms during colonoscopy in these patients. Results: Out of these 72 patients, parasitic worm was found in the colon in only one patient. But the stool examination of the patient was negative for ova or cyst. The parasitic worm found in this patient was identified as whipworm or trichuris trichiura by its characteristic whip like shape. In this patient, the tail or the posterior end of the whipworm is straight and bluntly round without any coil or corkscrew shape and hence can be identified as the female whipworm. The tail or the posterior end is highly curved and coiled like a corkscrew only in the male whipworm. Thus, while doing colonoscopy we can easily distinguish between male and female whipworm by looking at the tail or posterior end of the whipworm. But unlike hookworms which suck blood from the small intestinal wall and is red in colour, whipworms do not feed on blood and is white in colour as it feeds only on the tissue secretions of the large intestinal wall. Thus the whipworm in this patient was white in colour. Conclusion: Whipworms are the most common nematodes or roundworms found in the large intestine of human beings while doing colonoscopy. Our patient was also found to have whipworm in the colon while doing colonoscopy. The patient who had whipworm in our study had negative stool examination for ova or cyst. Hence colonoscopy is a very useful investigation to diagnose whipworm infection especially when the stool examination is negative for its eggs.
Keywords: Adult whipworm, Trichuris trichiura, Colonoscopy
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Hookworms are the most common nematodes or roundworms found in the duodenum of human beings while doing upper gastro-intestinal endoscopy. Similarly whipworms are the most common nematodes or roundworms found in the large intestine of human beings while doing colonoscopy. Our patient was also found to have whipworm in the colon while doing colonoscopy. There have also been reports of finding whipworm in the large intestine of human beings while doing colonoscopy in many parts of the world. (1 to 9,11 to 15). Usually whipworms are most commonly found in the caecum and in the right colon (2, 4). Only rarely whipworms are found in the left colon ( 4 ). But in our patient whipworm was found in the sigmoid colon which is the rare site to find the whipworm. The important differences between the hookworms inhabiting the small intestine and the whipworms inhabiting the large intestine of human beings are also highlighted in this article.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study was conducted in the department of general surgery, Aarupadai Veedu Medical College and Hospital, Puducherry. A study of 72 patients who had undergone colonos copy in our institute for a period of 5 years from November 2009 to October 2014 was carried out in order to find out the presence of parasitic worms during colonoscopy in these patients. In each of these patients, presence of any parasitic worm was carefully looked for during the procedure of colonoscopy and the colonoscopic pictures of each patient were carefully studied and analysed.
RESULTS
Out of these 72 patients, parasitic worm was found in only one patient. The parasitic worm found in this patient was identified as whipworm or trichuris trichiura by its characteristic whip like shape. This patient was an eighty year old male patient. In one study, the patient with whipworm in the colon was a 84 year old female (16) and in another study the patient with whipworm in colonoscopy was a 75 year old male (12). Our patient presented with history of lower abdominal pain for 1week, constipation for 2 days and vomiting for 1day. On abdominal examination, his abdomen was soft, mildly distended and mild tenderness was present in the hypogastric region. His haemoglobin was 14.4g%, white blood cell count was 10,900 and his differential white blood cell count was polymorphs 80%, lymphocytes 16% and eosinophils 4% . His stool examination was negative for ova or cyst. His X-ray abdomen and ultrasound abdomen showed gas filled bowel loops and was diagnosed as having mild subacute intestinal obstruction .When he was subjected to diagnostic colonoscopy, one adult whipworm was found in the sigmoid colon while doing colonoscopy despite negative stool examination for ova or cyst. The patient was treated with a single dose of 400mg of albendazole and started showing clinical improvement.
1. Absence of anaemia in whipworm infection In our patient anaemia was not present (haemoglobin 14.4 g%). In another study also (5), all the three patients with whipworm in colonoscopy did not have anaemia (haemoglobin 13.7 g %, 14.1 g%, 13.9 g%).
2. Absence of eosinophilia in whipworm infection In our patient, eosinophilia was not present. Eosinophilia was also not found in whipworm infection in various other studies (5, 7,12,16).
3. Negative stool examination in whipworm infection In our patient, stool examination was negative for ova or cyst. In various other studies also, adult whipworms were found while doing colonoscopy even when the stool examination is negative for its eggs (2, 3,5,6,7,14).
4. Site of whipworm in the colon Usually whipworms are most commonly found in the caecum and in the right colon (2, 4). Only rarely whipworms are found in the left colon (4). But in our patient whipworm was found in the sigmoid colon which is the rare site to find the whipworm. The worm can be overlooked particularly if colon preparation is imperfect ( 1) . Only in one more study, adult whipworms were found in the sigmoid colon and also in the rectum while doing colonoscopy (15). In another study, whipworm was found in the left colon in one patient (4). In all the other studies, adult whipworms were found in the caecum ( 2,3,4,5,7,13,14,16)or in the ascending (right) colon ( 2,3,5,12,13) while doing colonoscopy
5. Number of whipworms and gender of the whipworm found in the colon In our patient, only a single whipworm was found in the colon while doing colonoscopy and it was identified as female whipworm since the tail or the thicker posterior end of the whipworm is straight and bluntly round without any coil or corkscrew shape (fig 2). In one more study, single whipworm was found in the colon while doing colonoscopy (3) but this whipworm was identified as male whipworm since its tail or the posterior end is highly curved and coiled like a corkscrew. Thus, while doing colonoscopy we can easily distinguish between male and female whipworm by looking at the tail or the thicker posterior end of the whipworm. Few other studies have also shown single whipworm in the colon while doing colonoscopy (5,14). Many studies have shown the presence of multiple whipworms in the colon while doing colonoscopy (7,9,13,15,16).
6. Lower abdominal pain and tenderness in whipworm infection Our patient presented with lower abdominal pain for 1week and mild tenderness in the lower abdomen . In various other studies also, patients have presented with lower abdominal pain and tenderness in the lower abdomen (2to5 ,12to14).
7. Constipation or dysentery in whipworm infection Our patient presented with constipation for 2 days. Only in one study, a 75 year old male patient presented with constipation (12). But in many studies, patients have presented with diarrhea ( 2,5,13 )or with dysentery causing anaemia (Trichuris dysentery syndrome) which is common in children when there is a heavy load of whipworms ( 4,7,9,15).
8. Intestinal obstruction in whipworm infection Our patient presented with vomiting for 1day, constipation, mild abdominal distention and thus with mild subacute intestinal obstruction which was relieved with conservative man-agement, enema and anti worm treatment. Heavy whipworm or trichuris trichiura infection can lead to colonic obstruction producing vomiting, constipation and abdominal distention (16) and when very severe due to very heavy load of whipworms may require surgical resection of the right colon (16).
9. Mild, moderate and severe whipworm infection
a. Mild whipworm infection Whipworm infection is clinically silent in the vast majority of cases, since the worm load tends to be low (14 ) and these patients require only anti worm treatment. Our study and also some other studies ( 3,5,14) have shown only a single whipworm in the colon while doing colonoscopy which represents the least load of whipworms and very mild whipworm infection in these fortunate patients.
b. Moderate whipworm infection
Howewer, when worm load approaches 50 to 150 worms, clinical disease becomes evident with either chronic or acute symptoms (14). Most patients exhibit chronic nonspecific disease (14). Many studies referred in this article (1,2,6,7,11,12,13) had patients only with few or moderate number of worms and hence these patients did not have any serious complications and could be treated only with supportive and anti worm treatment.
c. Severe whipworm infection
Fortunately, only very few number of patients –especially only poorly nourished children and very old people living in unhygienic conditions-have a very heavy load of whipworms and present with serious complications like Trichuris dysentery syndrome (4,9,15) causing anaemia requiring intensive medical treatment and prolonged antiworm treatment. Colonic obstruction and perforation occur especially in very old people living in very bad conditions (16) requiring surgical resection of the right colon.
DISCUSSION
1. Parasitic worms occurring in the large intestine of human beings Various studies from many parts of the world have also clearly shown that whipworms are the most common nematodes or roundworms found in the large intestine of human beings while doing colonoscopy( 1to9,11to15). Our study has also shown the presence of whipworm in the sigmoid colon of a patient while doing colonoscopy. In almost all the studies, whipworm or trichuris trichiura was almost the only intestinal helminth or roundworm found in the large intestine of human beings while doing colonoscopy (1,3to9,11to15). Only rarely intestinal helminths other than whipworm or trichuris trichiura were found in the large intestine of human beings while doing colonoscopy such as ascaric lumbricoides and enterobius vermicularis ( 2). Very rarely anisakis simplex larva can be found in the large intestine of human beings while doing colonoscopy (2). But only stomach is the commonest site of infection by anisakiasis (2). Colonic anisakiasis is a very rare condition (2). Hookworms were also rarely found in the large intestine of human beings while doing colonoscopy(17, 18).
2. Blood loss and anaemia in whipworm and hookworm infection Unlike hookworm which sucks blood from the small intestinal mucosa, whipworm (trichuris trichiura) does not suck blood and causes only minimal oozing of blood at the site of its attachment to the colonic mucosa. Hence in trichuris infection, the daily blood loss is only 0.005 ml per worm per day which only accounts for about 10-15% from the blood loss due to Necator americanus and only 2-3% of that attributed to Ancylostoma duodenale. Also most people in endemic areas of Trichuris trichiura infections are colonized only by a small number of worms (usually less than 15) unlike large number of hookworms present commonly in hookworm infection. Hence severe anaemia is not common in whipworm infection, but is common in hookworm Infection. Our patient also did not have any severe anaemia (haemoglobin 14.4 g%).
3. Eosinophilia in whipworm and hookworm infection Eosinophilia is also not common in whipworm infection (5, 7,12,16), but is common in hookworm infection.
4. Whipworm eggs in the treatment of crohns disease Helminthic Infection like whipworm infection is known to decrease the incidence of inflammatory bowel disease like crohns disease (8,10) and ulcerative colitis (10). Crohns disease involves overactive Th 1 pathways and helminthes blunt Th 1 responses ( 8). Treatment with trichuris suis ova or pig whipworm eggs is shown to be effective in the treatment of active crohns disease (8,10) and to a lesser extent, ulcerative colitis (10) .
5. Shape of whipworm and its extremely long, thin oesophagus(stichosome) Whipworm has a short posterior thick part resembling the short handle of the whip and a long, thin anterior part resembling the distal long, thin part of the whip. The short posterior thick part of the whipworm constitutes 1/3rd part and thelong anterior thin part constitutes 2/3rd part of the whipworm. The short posterior thick part is occupied by intestine and reproductive organs and the long anterior thin part is occupied almost entirely by oesophagus and a very small mouth. Hence its oesophagus is an extremely long and thin tube occupying 2/3d of the body length. The anterior portion of the oesophagus is a thin walled muscular tube and its posterior portion is a thin tube surrounded by a column of unicellular glandular cells termed stichocytes. The entire oesophagus is termed as stichosome (16).
6. Size of whipworm and its life cycle The head or the anterior part of the whipworm having the esophagus needs to be narrow so that it can easily burrow through the tissue of the intestine (15) while the larger tail end having the reproductive organs ensures that the worm can still produce many eggs. The male whipworm is 3to 4.5cm and the female whipworm is 3.5 to 5cm in length (12 ). Adults can live for years and deposit thousands of eggs per day (8). Infective eggs are ingested form eating contaminated soil (8,14). Upon ingestion the eggs hatch into larvae in the small intestine (8,12,14,15) .The larvae eventually migrate to the large intestine and complete maturation to adult worms in 1to3 months (8,12,14,15).
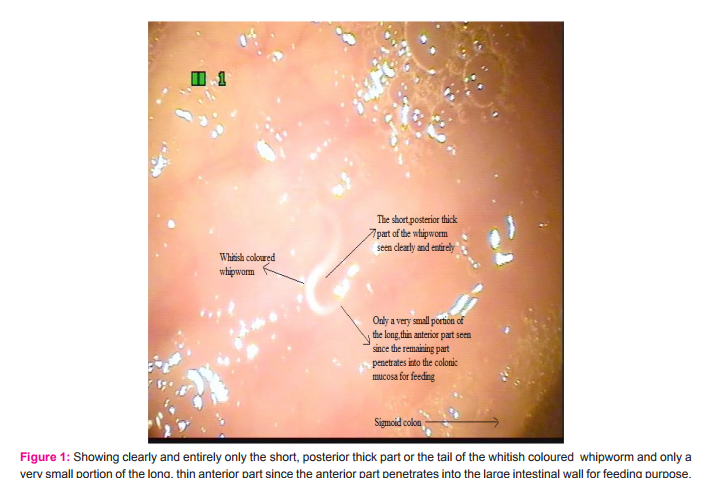
7. White colour of whipworm and red colour of hookworm Unlike the hookworms which suck blood from the small intestinal wall , whipworms do not feed on blood and feeds only on the tissue secretions of the large intestinal wall. Hookworm appears red coloured immediately after sucking blood. But the whipworm is always whitish in colour (5) (fig 1) as it does not feed on blood.
8. Only a very small portion of the long anterior part of whipworm seen during colonoscopy We can see only the short posterior thick part or the tail entirely in the lumen of the large intestine (14,15) but only a very small portion of the long ,thin anterior part while doing colonoscopy since most of the anterior part penetrates into the large intestinal wall in order to feed on the tissue secretions of the large intestinal wall (14,15) . Hence in fig 1, we can see only the short posterior thick part or the tail of the whitish coloured whipworm entirely in the lumen of the sigmoid colon but only a very small portion of the long, thin anterior part since most of the anterior part penetrates into the large intestinal wall for feeding purpose. But in the highly magnified view in fig 2, we can see clearly both the short posterior thick part or the tail and also the anterior thin part clearly due to the higher magnification.
9. Tail or the posterior end of male and female whipworm The tail or the posterior end of the male whipworm is highly curved and coiled and has corkscrew shape. Its corkscrew tail has a single spicule for copulation. But the tail of the female whipworm is straight and bluntly round without any coil and is not corkscrew shaped (5). In fig 2, we can see clearly that the tail or the posterior end of the whipworm is straight and bluntly round without any coil or corkscrew shape and hence can be identified as the female whipworm. Thus, while doing colonoscopy we can easily distinguish between male and female whipworm by looking at the tail or posterior end of the whipworm.
10. Mouth and oesophagus of whipworm In whipworm the esophagus in the anterior end is extremely long and thin in order to penetrate into the wall of the large intestine in order to feed on the tissue secretions of the large intestinal wall. Hence only a very small portion of the long, thin esophagus can be seen while doing colonoscopy (fig 1) since most of the esophagus burrows through the tissue of the large intestine for feeding purpose. The extremely small mouth of the whipworm has a minute spear which helps to suck the tissue secretions of the large intestinal wall.
CONCLUSION
1. Hence colonoscopy is a very useful investigation to diagnose whipworm infection especially when the stool examination is negative for its eggs.
2. Whipworm has a short posterior thick part resembling the short handle of the whip and a long, thin anterior part resembling the distal long, thin part of the whip.
3. But we can see only the short posterior thick part entirely in the lumen of the large intestine but only a very small portion of the long ,thin anterior part while doing colonoscopy since most of the anterior part or esophagus penetrates into the large intestinal wall in order to feed on the tissue secretions of the large intestinal wall.
4. We can also easily identify between the male and female whipworm by looking at its tail or its posterior end which is highly curved and coiled only in the male whipworm .In the female whipworm, the tail or its posterior end is straight and bluntly round without any coil or corkscrew shape.

ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The author sincerely thanks the staff nurse Nithya who was assisting while doing endoscopy and for her immense help rendered to the author while conducting this work. The author acknowledges the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The author is also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. The author is extremely grateful to IJCRR editorial board members and IJCRR team of reviewers who have helped to bring quality to this manuscript.
References:
1. Joo JH, Ryu KH, Lee YH, Park CW, Cho JY, Kim YS, Lee JS, Lee MS, Hwang SG, Shim CS. Colonoscopic diagnosis of whipworm infection Hepatogastroenterology. 1998 NovDec;45(24):2105-9.
2. Do KR1, Cho YS, Kim HK, Hwang BH, Shin EJ, Jeong HB, Kim SS, Chae HS, Choi MG Intestinal helminthic infections diagnosed by colonoscopy in a regional hospital during 2001- 2008. Korean J Parasitol. 2010 Mar;48(1):75-8.
3. Yoshida M, Kutsumi H, Ogawa M, Soga T, Nishimura K, Tomita S, Kawabata K, Kinoshita Y, Chiba T, Fujimoto S. A case of Trichuris trichiura infection diagnosed by colonoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996 Jan;91(1):161-2.
4. Khuroo MS, Khuroo MS, Khuroo NS Trichuris dysentery syndrome: a common cause of chronic iron deficiency anemia in adults in an endemic area (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2010 Jan;71(1):200-4.
5. Ok KS1, Kim YS, Song JH, Lee JH, Ryu SH, Lee JH, Moon JS, Whang DH, Lee HK Trichuris trichiura infection diagnosed by colonoscopy: case reports and review of literature. Korean J Parasitol. 2009 Sep;47(3):275-80.
6. Wang DD, Wang XL, Wang XL, Wang S, An CL Trichuriasis diagnosed by colonoscopy: case report and review of the literature spanning 22 years in mainland China. Int J Infect Dis. 2013 Nov;17(11): e1073-5.
7. Tuan Sharif SE, Ewe Seng C, Mustaffa N, Mohd Shah NA, Mohamed Z Chronic Trichuris trichiura Infection Presenting as Ileocecal Valve Swelling Mimicking Malignancy. ISRN Gastroenterol. 2011;2011:105178. doi: 10.5402/2011/105178. Epub 2010 Oct 31.
8. Chang CW, Chang WH, Shih SC, Wang TE, Lin SC, Bair MJ Accidental diagnosis of Trichuris trichiura by colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008 Jul;68(1):154.
9. Diniz-Santos DR, Jambeiro J, Mascarenhas RR, Silva LR. Massive Trichuris trichiura infection as a cause of chronic bloody diarrhea in a child. J Trop Pediatr. 2006 Feb;52(1):66-8.
10. Büning J, Homann N, von Smolinski D, Borcherding F, Noack F, Stolte M, Kohl M, Lehnert H, Ludwig D Helminths as governors of inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 2008 Aug;57(8):1182- 3
11. Lorenzetti R1, Campo SM, Stella F, Hassan C, Zullo A, Morini S An unusual endoscopic finding: Trichuris trichiura. Case report and review of the literature. Dig Liver Dis. 2003 Nov;35(11):811- 3.
12. Tokmak, N., Koc, Z., Ulusan, S., Koltas, I. S., and Bal, N. Computed tomographic findings of trichuriasis World Journal of Gastroenterology, 2006; 12(26), 4270
13. Lee, S. H., Kwon, J. E., and Cheong, Y. S. Two cases of Trichuris trichiura infection diagnosed by colonoscopy. Korean Journal of Family Medicine, 2010; 31(8), 622-629.
14. Herman, M. A., Ukawa, K., and Sugawa, C. CASE REPORT: Diagnosis and Removal of Cecal Whipworm Infection. Digestive diseases and sciences, 2000; 45(8), 1639-1643
15. Azira, M. S., and Zeehaida, M Severe chronic iron deficiency anaemia secondary to Trichuris dysentery syndrome-a case report. Trop Biomed, 2012; 29(4), 626-631.
16. Bahon, J., Poirriez, J., Creusy, C., Edriss, A. N., Laget, J. P., and Dei Cas, E Colonic obstruction and perforation related to heavy Trichuris trichiura infestation. Journal of clinical pathology, 1997; 50(7), 615-616
17. Thomas, V., Harish, K., Tony, J., Sunilkumar, R., Ramachandran, T. M., and Anitha, P. M. (2005). Colitis due to Ancylostoma duodenale. Indian J Gastroenterol 2006; 25(4), 210-211.
18. Wang, C. H., Lee, S. C., Huang, S. S., and Chang, L. C. Hookworm infection in a healthy adult that manifested as severe eosinphilia and diarrhea. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection, 2011 6(44), 484-487.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License