IJCRR - 14(13), July, 2022
Pages: 52-59
Date of Publication: 05-Jul-2022
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Anti-diabetic Effect of Ethanolic Extracts of Cissus Quadrangularis linn Fruits and Michelia Champaea Leaves in Alloxan Induced Hyperglycaemic Rats and in 3T3L1 Cell Lines
Author: Jasti Deepthi, D. V. R. N Bhikshapathi, Palanati Mamatha, Puttaswamy Nirmala
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that results in increased blood sugar. This study came up with a search for alternative medicines with no or fewer side effects for antidiabetic therapy. Materials and methods: The plants are extracted and screened for the phytochemical study of crude extracts. Anti-diabetic activity in alloxan-induced hyperglycaemic rats, in a single-dose study, multiple-dose treatment was investigated. In vitro cellular assay using 3T3L1 cell line was performed to check the cell viability with increasing plant extract treatment. Results: Phytochemical investigation reveals the presence of alkaloids, flavonoids, saponins, tannins, steroids, triterpenoids, carbohydrates, and glycosides in both plant extractions. In acute toxicity studies, no mortality was observed with either of the extracts even at a dosage of the level of 5000 mg per kg of body weight. The ethanolic extracts showed a noteworthy decline in blood glucose level in alloxan-induced rats in both single and multiple dosage methods. Significant changes were observed in the serum glucose and body weight from day 0 to day 14. The cell viability of the extracts was also comparable with the standard. Conclusion: Our results report that CQ fruits and MC leaves have potent antidiabetic action and on further studies, can be a credible resource in antidiabetic therapy.
Keywords: Cissus Quadrangularis Linn Fruits, Michelia Champaea Leaves, Anti-diabetic activity, 3T3L1 cell line, Cyototoxicity, Wistar rats.
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a syndrome characterized by chronic hyperglycemia and disturbances of carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism associated with absolute or relative deficiencies in insulin secretion and/or insulin action1. It is a metabolic disorder comprising of micro and macrovascular complications that result from insignificant morbidity and mortality. It is a major cause of death worldwide 2. There are an estimated 143 million people worldwide diagnosed with DM and this number will probably double by the year 2030 3.
Despite significant advancement in the treatment of DM using oral hypoglycemic agents, exploration for newer drugs continue due to several limitations of synthetic drugs. In recent times, there has been a renewed interest in plant remedies 4-5.
The medicinal properties of CQ were known since the distant past. Cissus was also used in ayurvedic medicines for treating injured bones, ligaments, and tendons. In Siddha medicine CQ finds its application as an analgesic, and in treating broken bones. The Magnoliaceae belong to the fossil plant family dated back to 95 million years. These are characterized by large, cup-shaped flowers with no distinct petals. Some species, including the champak (Michelia champaca) and Michelia doltsopa are grown for their flowers, both on the tree and as cut flowers. Champak flowers are also used to produce essential oil for perfume. A few species have been introduced to gardens or as street trees outside of the Indomalaya region, including Michelia figo, M. doltsopa, and M. champaca6-8.
The current paper deals with a screening of Cissus quadrangularis linn fruits and Michelia champagne leaf extracts for anti-diabetic activity in alloxan-induced hyperglycaemic rats.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Experimental Animals
Adult Wistar albino rats (150-200 g), housed in the institutional animal house and used for the study. Animals caged in polypropylene cages in a controlled environmental condition (22± 30C, 55 ± 5% humidity, and a 12 h light/ dark cycle). The animals were provided with a regular rodent diet and water ad libitum. The animals were allowed to adapt to these conditions for a week.
Methods
Plant collection and authentication
The CQ fruits and MC leaves were obtained from the local places of Tirupati, AP. The CQ fruit was authenticated by Dr. K. Madhava Chetty, M.Sc., M.Ed., M.Phil., Ph.D., PG DPD., Assistant Professor, Department of Botany, Sri Venkateswara University, Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh.
Extraction by maceration
Fresh leaves of MC and fruits of CQ were washed with water to get rid of contaminants like dirt and other impurities and were shade-dried. These dried leaves and fruits were ground and sieved to get a uniform, coarse powder. Powdered plant material was weighed (1Kg) and immersed in 95% ethanol and kept for maceration for 7 days with occasional stirring. On the 8th day, the solvent was filtered by pressing with a muslin cloth and was evaporated in a rotary evaporator at 40oC. The resultant extract was put in a desiccator to remove any ethanol left in it. The dried ethanolic extract of Michelia Champaea (EEMC) and ethanolic extract of Cissus Quadrangularis (EECQ) were packed in an air-tight bottle and put in a dry place for further studies.
Qualitative evaluation of phytoconstituents
The EECQ were screened for the presence of various phytoconstituents like carbohydrates, flavonoids, polyphenolic compounds, saponins, tannins, triterpenoids, etc.
Cell culture
3T3L1 cell line was procured from the National Centre for Cell Science, Pune. Cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) (high glucose) with 10% FBS (Invitrogen, Canada), 10,000 U Penicillin G, 10,000 μg/mL streptomycin sulfate (Invitrogen), and 10 mM 4? (2?hydroxyethyl)?1?piperazineethanesulfonic acid. Cultures were maintained at 37°C in 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator.
3?(4, 5?dimethylthiazol?2?yl)?2,5?diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay
3?(4, 5?dimethylthiazol?2?yl)?2, 5?diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay is a colorimetric assay to determine the toxicity of a compound on the cells based on the conversion of MTT to formazan crystals by the lactate dehydrogenase present in live cells 17,18. The 3T3L1 cells were seeded at an initial density of 20 × 104 cells per well/200 µL in 96 “well” plate and cultured overnight. The cells were then treated with desired concentrations of plant extract (25–400 µg/mL) for 24 h in the same culture conditions. Post-treatment, the medium was aspirated, 0.5 mg/mL of MTT reagent was added to cells and incubated at 37°C for 2 h. MTT reagent was then removed, and formazan crystals were dissolved with 20 µL of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Absorbance at 570 nm was measured by a microplate reader. Percentage viability was determined using the formula:
.png)
Evaluation of anti-diabetic activity 9, 10
For the study of the anti-diabetic activity of various extracts of EEMC and EECQ, the study was divided into two phases
I) Activity in normoglycaemic animals
II) Activity in alloxan induced hyperglycaemic rats
a) Single-dose study
b) Multiple-dose study (14 days treatment)
Activity in normoglycaemic animals
Method of oral administration of extracts
An 18-gauge needle was suitably covered with flexible polythene tubing, where the edge was made blunt. The needle was fixed to a 1ml tuberculin syringe. The rat was held firmly in the left hand. The tubing was moistened with glycerin and inserted right into the oesophagus and gently pressing plunger for drug administration, and this was followed by 0.2ml of distilled water to ensure administration of the correct dose of the drug.
Experimental design
Twenty-four animals were categorized into four equal groups. Animals (Wister rats) were fasted for 18 h but were allowed free access to water before and throughout the experiment. The study was approved by the institutional animal ethical committee with No: 1447/PO/Re/S/11/CPCSEA/15/A.
Group-I: Administered with vehicle (distilled water) & served as Normal control.
Group-II: Administered with standard drug Glipizide (5mg/kg).
Group III : Administered EECQ (100mg/kg).
Group IV : Administered EECQ (200mg/kg).
Group V : Administered EEMC (200mg/kg).
Group VI : Administered EEMC (400mg/kg).
Blood samples were withdrawn from the retro-orbital venous plexus with capillary tubes under ether anesthesia and with Sodium citrate as an anticoagulant. Serum was separated by centrifugation. The glucose level in blood was measured after 0, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12& 24 h of administration of the single dose of test samples.
Estimation of serum glucose by GOD/POD method11
This method utilizes two enzymes Glucose Oxidase (GOD) and Peroxidase (POD) along with chromogen-4-amino antipyrine, phenol and is intended for in vitro quantitative determination of glucose in serum, plasma, and cerebrospinal fluid. There was no interference due to the creatinine, fructose, galactose, reduced glutathione, ascorbic acid, and xylose. Hemoglobin or bilirubin up to 10mg does not affect the test.
Single Dose Study 12
Induction of diabetes
The animals were allowed to fast for 24 h and rendered diabetic by injecting a single dose of alloxan at 150mg/kg body weight administered as a 5% w/v in distilled water by i.p. route. It produces diabetes by selected necrosis of b - cells of islets of Langerhans of the pancreas.
After 48 h of injecting alloxan, diabetes was confirmed by testing blood sugar with Erba CHEM 5 Plus Auto analyzer.
The animals with a sugar level of more than 250mg/dl were selected. Animals were maintained for four days in diabetic conditions for good establishment of diabetes.
Standard: Glipizide at the dose of (5mg/kg) was used as a standard drug.
Experimental Design: Animals were categorized into 5 different groups of six animals each. The animals (Wister rats) were fasted for 18 h but were allowed free access to water before and throughout the experiment.
Blood samples were collected from the retro-orbital venous plexus with capillary tubes under ether anesthesia and with sodium citrate as an anticoagulant. Serum was separated by centrifugation.
Multiple-dose treatment (14 days treatment)
The animals used for this study are the same animals used for the single-dose study, had free access to feed and water during this period.
The chronic study involved repeated administration of extracts of EEMC, EECQ, and Glipizide for 14 days(once a day) to the groups used for single-dose study at a prefixed time and the glucose levels in blood estimated in samples withdrawn after 2 h on day 0,7th and 14th day.
Statistical analysis
The result analysis was carried out by the one-way ANOVA method followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison tests.
RESULTS
Preliminary phytochemical screening
Results of phytochemical screening were elucidated in Table-1.
The preliminary phytochemical screening indicated the presence of various phytoconstituents like flavonoids, phenolic compounds, triterpenoids, tannins, saponins, amino acids, proteins, and carbohydrates in EECQ. The preliminary phytochemical screening showed the presence of various phytoconstituents like flavonoids, phenolic compounds, triterpenoids, tannins, saponins, amino acids, proteins, and carbohydrates in EEMC.
Cytotoxicity assay on 3T3 L1 cell line
3T3?L1 cells were treated with different concentrations (25 μg–400 μg/mL) of EECQ and EEMC were assayed for their cytotoxic effect. The extract displayed no cytotoxic effect on cells. The concentrations of the extract used and the respective percent cell viability were tabulated and plotted [Table 2 and Figures 1].
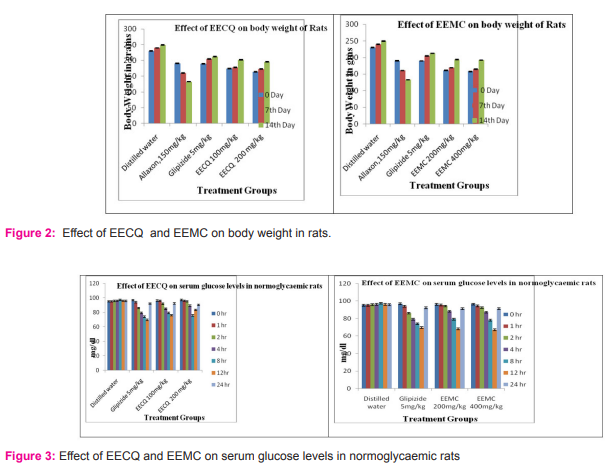
Body weight
The changes in body weight of the different groups of animals during the period of study was given in Table 3 and represented in Figure 2 which shows an increase in the mean body weight (± SEM) of normal rats from 230.33 ± 1.47g on day 0 to 240.00 ± 1.06g on day 7, 249.2 ± 0.94g on day 14. This shows that the group of normal rats gained body weight during the treatment period of 14 days.
Effect on normoglycemic rats
The fasting serum glucose of the different groups of animals during the single-dose treatment period of study is given in Table 4 and presented in figure 3. which shows that the mean (±SEM) fasting serum glucose values of the normal group of rats was 95.16 ± 1.81, 95.16 ± 1.078, 95.83 ± 1.49, 96 ± 1.00, 97.33 ± 1.60, 96 ± 0.85 and 95.83±0.60 mg/dl, on 0, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12 and 24 h respectively.
Effect on alloxan-induced hyperglycaemic rats
The fasting serum glucose of the different groups of animals during the single-dose treatment period of study is given in Table 5. and presented in figure 4, which shows that the mean (±SEM) fasting serum glucose values of the normal group of rats was 95.76 ± 3.248, 96.2 ± 3.21, 96.86 ± 3.47, 97.3 ± 3.26, 97.96 ± 3.29, 98.65 ± 3.15 and 97.68±3.44 mg/dl, on 0, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12 and 24 h respectively.
Multiple-dose study
The fasting serum glucose of the different groups of animals during the chronic study is given in Table 6 and presented in figure 5. which shows that the mean (±SEM) fasting serum glucose values of the normal group of rats was 94.63±3.54,96.27 ±3.60, 97.29±3.09 mg/dl on day 0, day 7, and day 14 respectively. The above values show that the fasting serum glucose in the normal group of rats was maintained within the normal range throughout the study.
DISCUSSION
In cytotoxicity assay on 3T3 L1 cell line, the lowest concentration of EECQ and EEMC (25 µg/mL) showed 98.6% and 99.7% viability respectively, and the highest concentration (400 µg/mL) showed 89.45% and 88.9% of viability respectively after 24 h of exposure. These results indicated that EECQ and EEMC are not toxic to mammalian cells even at higher concentrations and could be used to analyze other parameters of antidiabetic studies. Metformin (100 µM) treatment – positive control – also had a percent viability of 97.4% post 24?h exposure13,14. During the period of treatment, the diabetic group of rats has shown a change in body weight from a mean (± SEM) value of 190.5 ± 1.2g on day 0, 160. ± 1.28g. On day 7 and which decreased further to 132.8 ±1.07g on day 14. The glipizide (5 mg/kg) treated group body weight was found to have been increased. The body weight gain in this group of rats from day 0 through day 7 to day 14 was relatively less when compared with the normal group15-17. The EECQ (100 mg/ kg) treated group of diabetic rats was found to have a mean body weight (± SEM) of 174.3±2.30 g on day 0, 178.00±1.4 g on day 7, 202.3±0.9 g on day 14 . The EECQ (200 mg/kg) treated group of diabetic rats shows mean (± SEM) body weight of 164 ±1.25 g on day 0, 172.80 ± 1.9 g on day 7, 195.80 ± 1.13 g. on day 14. The EEMC (200 mg/kg) treated group of diabetic rats shows mean (± SEM) body weight of 161±1.12g on day 0, 169±2.21g on day 7, 194±2.11g on day 14. The EEMC (400 mg/kg) treated group of diabetic rats shows mean (± SEM) body weight of 158±1.23g on day 0, 165±1.43g on day 7, 192±1.44, on day 14.
Effect on normoglycaemic rats was studied by measuring glipizide (5 mg/kg) treated normal rats show a mean (±SEM) fasting serum glucose of 96.83 ± 0.60, 94 ± 1.29, 86 ± 1.29, 79.16 ± 0.94, 74 ± 1.03, 69.66 ± 0.33 and 92.16 ± 0.83mg/dl on 0, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12 and 24h respectively. The EECQ and EEMC treated normal rats showed mean fasting serum glucose of reduced levels respectively with doses. These changes in fasting serum glucose values illustrate that the normoglyceaemic rats treated with EECQ and EEMC show a progressive and significant reduction. 18
Effect on alloxan induced hyperglycaemic rats was studied by measuring mean fasting serum glucose (±SEM) in the diabetic control group of rats was found to be 262.16 ± 07.96, 266.5 ± 7.39, 275.5 ± 7.20, 285 ± 7.42, 296.16 ± 6.84, 316.5 ± 4.61 and 326.16 ± 4.76mg/dl on 0, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12 and 24 h respectively, which was found to be significantly (p≤0.01) higher when compared with the normal rats. 19
In the multiple dose study the mean fasting serum glucose (±SEM) in the diabetic control group of rats was found to be 269.64±2.89, 337.73±9.899 and 386.5±17.92 mg/dl on 0th, 7th and 14th day respectively, which was found to be significantly (p≤0.01) higher when compared with the normal rats. These elevated fasting serum glucose levels were found to have been maintained throughout the 14 days of the treatment period indicating that the rats are rendered diabetic. The glipizide (5 mg/kg) treated diabetic rats show a mean (±SEM) fasting serum glucose was reduced from day 0 to day7 and then to day 14, a similar reduction was also observed with multiple doses treated groups.20
CONCLUSION
Phytochemical evaluation of EECQ and EEMC showed the presence of carbohydrates, flavonoids, tannins, terpenoids, saponins, proteins, amino acids, and phenolic compounds. According to the literature, EECQ and EEMC were found to be safe in the dose used and there was no mortality up to 5000 mg/kg dose.
The results indicate that the EECQ fruits and EEMC leaves have good anti-diabetic activity. The ethanolic extracts of CQ fruits and MC leaves displayed noteworthy anti-hyperglycaemic activity in alloxan-induced hyperglycaemic rats without any major variation in body weight; they also enhanced the condition of DM that was indicated by body weight, serum creatinine, serum urea, and serum alkaline phosphatase. The study also displayed damage of the pancreas in alloxan-treated diabetic control rats and leads to regeneration of cells by glipizide and extract treatment group.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors sincerely thank Professor Dr. D V R N Bhikshapathi for rendering his suggestions and helping them in each and every step of completing this research paper successfully.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No conflict of interest
FUNDING INFORMATION
Self financed
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTION
Jasti Deepthi developed the theoretical formalism, performed the analytic calculations and numerical simulations. Both Jasti Deepthi and D V R N Bhikshapathi contributed to the final version of the manuscript.
.png)
.png)
.png)


.png)
References:
1. Barar FS. Essentials of pharmacotherapeutics. S. Chand Publishing; 2000.
2. Ahmed MF, Kazim SM, Ghori SS, Mehjabeen SS, Ahmed SR, Ali SM, Ibrahim M. Antidiabetic activity of Vinca rosea extracts in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Int J Endocrinol 2010:841090.
3. Aiman R. Recent research in indigenous anti-diabetic medicinal plants, An overall assessment. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1970;14(2):65-76.
4. Dinesh P, Mohapatra TK. New oral hypoglycemic agents: merits and demerits. Ind J Clin Pract 1997;7:34-56.
5. Ratnakar P, Murthy PS. Preliminary studies on the antitubercular activity and the mechanism of action of the water extract of garlic (Allium sativum) and its two partially purified proteins (Garlic defensins?). Indian J Clin Biochem 1996;11(1):37-41.
6. Muhammad A, Sirat HM. COX-2 inhibitors from stem bark of Bauhinia rufescens Lam.(Fabaceae). EXCLI journal 2013;12:824.
7. Anushia C, Sampathkumar P, Ramkumar L. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities in Cassia auriculata. Glob J Pharmacol 2009;3(3):127-30.
8. Sutar NG, Sutar UN, Behera BC. Antidiabetic activity of the leaves of Mimosa pudica Linn. in albino rats. J of Herb Medi and Toxi 2009;3(1):123-6.
9. Bussa SK, Jyothi P. Antidiabetic activity of stem bark of Neolamarckia cadamba in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. IJPT 2010;2(2):314-24.
10. Chaudhuri RK, Mukherjee M, Sengupta D. Limitation of glucose oxidase method of glucose estimation in jaundiced neo�nates.Indian J Exp Biol 2006;44(3):254-55.
11. Babu V, Gangadevi T, Subramoniam A. Anti-hyperglycemic activity of Cassia kleinii leaf extract in glucose fed normal rats and alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Indian J Pharmacol 2002;34(6):409-15.
12. Ahmed SM, Swamy V, Gopkumar P, Dhanapal R. Anti-diabetic activity of Terminalia catappa Linn. leaf extracts in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. IJPT 2005;4(1):36-0.
13. Skehan P, Storeng R, Scudiero D, Monks A, McMahon J, Vistica D, Warren JT, Bokesch H, Kenney S, Boyd MR. New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. JNCI 1990;82(13):1107-12.
14. Patel S, Gheewala N, Suthar A, Shah A. In-vitro cytotoxicity activity of Solanum nigrum extract against Hela cell line and Vero cell line. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 2009;1(1):38-46.
15. Tiwari BK, Pandey KB, Abidi AB, Rizvi SI. Therapeutic potential of Indian medicinal plants in diabetic condition. Ann Phytomed 2013;2:37-43.
16. Rana CS, Ballabha R, Tiwari JK, Dangwal LR. An ethnobotanical study of the plant resources in the Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve (a world heritage site), Uttarakhand, India. J Ethnobio Trad Med 2013;120:591-601.
17. Rana CS, Tiwari JK, Dangwal LR, Gairola S. Faith herbal healer knowledge document of Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve, UttaraKhand, India. IJTK 2013;12(2):308-14.
18. Poretsky L. Principles of diabetes mellitus. Springer Science & Business Media; 2010.
19. Scott LJ, Spencer CM. Miglitol: A review of its therapeutic potential in type 2 diabetes. Drugs 2000;59(3):521-49. 20. Zaid H, Antonescu CN, Randhawa VK, Klip A. Insulin action on glucose transporters through molecular switches, tracks and tethers. Biochemical Journal 2008;413(2):201-15.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License