IJCRR - 7(17), September, 2015
Pages: 07-14
Date of Publication: 11-Sep-2015
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
MANAGEMENT OF IPSILATERAL FRACTURE OF HIP AND SHAFT OF FEMUR
Author: Vetrivel Chezian Sengodan, S. Elangovan, J. Saravana Kumar
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Ipsilateral fractures of the hip with fracture of shaft of femur are rare injuries. They warrant special diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. Various techniques and implants have been developed to manage these fractures. No single device has been proved to be superior to others. Material and Methods: 8 patients (6 male and 2 female) with ipsilateral hip and shaft of femur fractures were treated with various fixation devices. Among the hip fractures there were 2 femoral neck and 6 peritrochanteric fractures. Functional outcome was assessed using the Friedman and Wyman classification. Results: All the 8 hip fractures united in a mean duration of 3 months. No osteonecrosis of the femoral head was noted. Of the femoral shaft fractures 5 united in a mean of 8.5 months, 3 were non-unions. One patient developed deep infection, which resolved with debridement and antibiotic treatment. Functional results were good in 4 patients, fair in 2 and poor in 2. Conclusion: Early diagnosis of all injuries and operative treatment are important to improve the functional outcome in ipsilateral hip and shaft fractures. Basically, each technique has individual advantages and disadvantages, and all are technically demanding. Most important factor determines the outcome is the anatomical reduction and stable internal fixation of both fractures.
Keywords: Hip fracture, Reconstruction nail, Long proximal femoral nail, Compression screw
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Ipsilateral femoral hip and shaft fractures are rare injuries. It was reported by Delaney and Street in 1953. [1] The incidence is 5-6% of all femoral fractures. [2] Increase in the incidence may be due to better data reporting, better recognition of the injury pattern and better resuscitation efforts. Normally, this type of injury is caused by high energy trauma like a motor vehicle accident, fall from height and industrial accidents. Associated injuries are very common.[3] The attributed mechanisms include axial compression against the acetabular roof, when the hip in flexion and abduction. Trauma force found to cause buckling of the shaft and shearing the neck of femur. Hence hip fractures are non-displaced or minimally displaced and shaft factures are severely comminuted. Therefore, hip fractures are easily missed and shaft fractures bear significant healing problems. [4] Isolated femoral neck fractures may have high rates of head osteonecrosis and neck nonunion, but combined neck and shaft fractures are reported to have a relatively better outcome. [3-5] This is attributed to the fact that the majority of energy sustained in this type of trauma is dissipated in the shaft of the femur. No single device has been shown to be absolutely superior to others. Swiontkowski (1 987) suggested that there had been nearly 60 recommended methods of managing this fracture combination in his 176 cases collected from 20 series.[6] A variety of management modalities have been described to treat this complex fracture pattern ranging from conservative approach to recently introduced reconstruction nails. These techniques include simultaneous transcervical screwing and shaft plating, intramedullary fixation with additional transcervical fixation, [7, 8] retrograde intramedullary nailing with femoral neck-lag screws,[2] reversed intramedullary fixation with cephalo medullary locking,[9] Ender pins with percutaneous Knowles pins,[10,11] Gamma (long) nailing, and recently introduced reconstruction nailing.[3, 12] All these approaches have their own surgical difficulties. But the ultimate goal of treatment is anatomical reduction and stable fixation of both fractures so that the patient can be mobilized early.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study period ranged from June 2012-December 2014. The total number of patients was eight. The study was conducted in Coimbatore medical college hospital after ethical committee approval. Ipsilateral fracture of the hip and shaft of the femur were included in our study. All the patients had plain radiographs of the pelvis including both hips, thigh including knee and hip joint. Both orthopaedic and non orthopaedic associated injuries are documented. Hip fractures were classified into two main groups, neck and peritrochanter. They were further classified into Garden (neck fractures) and Boyd and Griffin (trochanter). The femoral shaft fractures were also classified with Winquist classification of comminution, [13] site and also into open or closed fractures. Once the patient’s general condition stabilized, they were treated with various operative procedures like reconstruction nail, long proximal femoral nail. (PFN), long dynamic hip screw (DHS) plate and cancellous screws with retrograde intramedullary nailing. In our series, other systemic injuries were found in 4 patients. Two patients had more than three bone fractures. One patient had head injury. Spinal and epidural anesthesia were used in 6 and 2 patients respectively. Reconstruction nails were used for 3 of our patients. While using reconstruction nail, the proximal fracture is fixed first with cephalic screws followed by distal femoral locking. Internal rotation may be necessary to reduce the hip fracture into anatomical position, [14] and this can be done by first fixing the femoral shaft fracture. [15] Dynamic hip screw (DHS) and Long DHS plate fixation was used in 2 patients. Both of them had femoral shaft fractured at the level of proximal 3rd of the femur. Hence we decided to use DHS to fix both fractures. In one case DHS was used for trochanteric fracture fixation, and compression plate for femoral shaft fracture fixation. Minimally displaced trochanteric fracture was fixed first and the shaft was fixed next. Long proximal femoral nail was used in one patient to fix both the fractures. In one patient wound debridement and external fixation was done. Once constitutional symptoms, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C- reactive protein were normal, femoral neck fracture was fixed with AO cancellous screws. While the soft tissues around the shaft fracture site healed, external fixator was removed and later fixation done with retrograde intramedullary interlocking nailing. After the operation, patients were allowed to ambulate with partial weight bearing as early as possible. Quadriceps strengthening and knee-motion exercise were encouraged. Patients were followed-up in the outpatient department at 4-6 week intervals to assess the clinical and radio graphical fracture healing processes. Protected weight bearing was advised until bony union. Radio graphical union was defined as bridging trabeculae across the fracture site or solid callus with cortical density connecting both fracture fragments. Nonunion was defined as a fracture site which remained unhealed one year after treatment or a fracture which required a second surgery to achieve union. [4, 16] Functional results (Table 1) were assessed according to the Friedman and Wyman classification.[7]
RESULTS
The diagnosis of neck fracture was not delayed in our series. Hip fractures were classified into two main groups, neck (n = 2) and peritrochanter (n = 6). Among the femoral shaft fractures 3 were open fractures. The data of shaft fracture pattern and grading of comminution are described below [Table 2 and 3] Mean duration of surgery is 140 min. Average blood loss is 450 ml. The mean union time was 3.0 months (range 1.5- 7.0 months) for hip fractures and 8.5 months (range 6-11 months) for shaft fractures. Time of fixation was generally within 7 days, expect one patient who was operated on 10 th day due to head injury. Complications were knee stiffness (two patients) and one deep wound infection. Three patients had non-union of the shaft of the femur. In our series on two year follow up, femoral head osteonecrosis was not encountered even in a single case. Fat embolism was also not encountered in our series. Results (Table 4) were evaluated based on the criteria adopted by Friedman and Wyman classification.[7] Four patients (50%) had a good functional result, two patients (25%) had fair result and in two patients the result (25%) was poor.
DISCUSSION
Ipsilateral femoral hip and shaft fractures are a challenge to the orthopaedic surgeons. High velocity injury like traffic accidents accounts for majority of cases. Most of the patients were young men and had multi-system injuries. Associated injuries are quite common, because of the high velocity impact, [7, 8, 10 and 15]. The diagnosis of hip fracture can be easily missed, if an anteroposterior radiograph of pelvis or hip is not taken. Early recognition of all fractures is of paramount importance in planning the surgical treatment, and is the first step towards good results. A careful examination and proper roentgenograms of the hip are necessary. In our opinion, entire shaft, hip and knee-joint X-rays are mandatory, to minimize the late detection of these injuries. Three major issues in this type of fracture management are 1) optimal timing of fracture stabilization, 2) deciding which fracture should be stabilized first neck or shaft 3) optimal hardware combinations for fixation. Polytrauma patients with long bone fractures are advised to undergo surgical ducted in Coimbatore medical college hospital after ethical committee approval. Ipsilateral fracture of the hip and shaft of the femur were included in our study. All the patients had plain radiographs of the pelvis including both hips, thigh including knee and hip joint. Both orthopaedic and non orthopaedic associated injuries are documented. Hip fractures were classified into two main groups, neck and peritrochanter. They were further classified into Garden (neck fractures) and Boyd and Griffin (trochanter). The femoral shaft fractures were also classified with Winquist classification of comminution, [13] site and also into open or closed fractures. Once the patient’s general condition stabilized, they were treated with various operative procedures like reconstruction nail, long proximal femoral nail. (PFN), long dynamic hip screw (DHS) plate and cancellous screws with retrograde intramedullary nailing. In our series, other systemic injuries were found in 4 patients. Two patients had more than three bone fractures. One patient had head injury. Spinal and epidural anesthesia were used in 6 and 2 patients respectively. Reconstruction nails were used for 3 of our patients. While using reconstruction nail, the proximal fracture is fixed first with cephalic screws followed by distal femoral locking. Internal rotation may be necessary to reduce the hip fracture into anatomical position, [14] and this can be done by first fixing the femoral shaft fracture. [15] Dynamic hip screw (DHS) and Long DHS plate fixation was used in 2 patients. Both of them had femoral shaft fractured at the level of proximal 3rd of the femur. Hence we decided to use DHS to fix both fractures. In one case DHS was used for trochanteric fracture fixation, and compression plate for femoral shaft fracture fixation. Minimally displaced trochanteric fracture was fixed first and the shaft was fixed next. Long proximal femoral nail was used in one patient to fix both the fractures. In one patient wound debridement and external fixation was done. Once constitutional symptoms, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C- reactive protein were normal, femoral neck fracture was fixed with AO cancellous screws. While the soft tissues around the shaft fracture site healed, external fixator was removed and later fixation done with retrograde intramedullary interlocking nailing. After the operation, patients were allowed to ambulate with partial weight bearing as early as possible. Quadriceps strengthening and knee-motion exercise were encouraged. Patients were followed-up in the outpatient department at 4-6 week intervals to assess the clinical and radio graphical fracture healing processes. Protected weight bearing was advised until bony union. Radio graphical union was defined as bridging trabeculae across the fracture site or solid callus with cortical density connecting both fracture fragments. Nonunion was defined as a fracture site which remained unhealed one year after treatment or a fracture which required a second surgery to achieve union. [4, 16] Functional results (Table 1) were assessed according to the Friedman and Wyman classification.[7] RESULTS The diagnosis of neck fracture was not delayed in our series. Hip fractures were classified into two main groups, neck (n = 2) and peritrochanter (n = 6). Among the femoral shaft fractures 3 were open fractures. The data of shaft fracture pattern and grading of comminution are described below [Table 2 and 3] Mean duration of surgery is 140 min. Average blood loss is 450 ml. The mean union time was 3.0 months (range 1.5- 7.0 months) for hip fractures and 8.5 months (range 6-11 months) for shaft fractures. Time of fixation was generally within 7 days, expect one patient who was operated on 10 th day due to head injury. Complications were knee stiffness (two patients) and one deep wound infection. Three patients had non-union of the shaft of the femur. In our series on two year follow up, femoral head osteonecrosis was not encountered even in a single case. Fat embolism was also not encountered in our series. Results (Table 4) were evaluated based on the criteria adopted by Friedman and Wyman classification.[7] Four patients (50%) had a good functional result, two patients (25%) had fair result and in two patients the result (25%) was poor. DISCUSSION Ipsilateral femoral hip and shaft fractures are a challenge to the orthopaedic surgeons. High velocity injury like traffic accidents accounts for majority of cases. Most of the patients were young men and had multi-system injuries. Associated injuries are quite common, because of the high velocity impact, [7, 8, 10 and 15]. The diagnosis of hip fracture can be easily missed, if an anteroposterior radiograph of pelvis or hip is not taken. Early recognition of all fractures is of paramount importance in planning the surgical treatment, and is the first step towards good results. A careful examination and proper roentgenograms of the hip are necessary. In our opinion, entire shaft, hip and knee-joint X-rays are mandatory, to minimize the late detection of these injuries. Three major issues in this type of fracture management are 1) optimal timing of fracture stabilization, 2) deciding which fracture should be stabilized first neck or shaft 3) optimal hardware combinations for fixation. Polytrauma patients with long bone fractures are advised to undergo surgical.
Reconstruction nailing
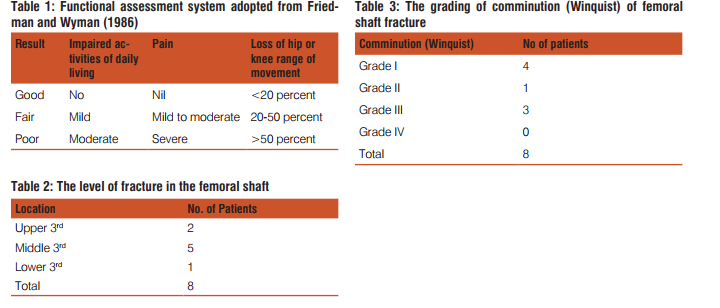
Reconstruction nailing is a technically demanding procedure with a steep learning curve. The advantages of recon nails include using one incision to treat the combined fractures and saving the bony stock for the insertion of proximal screws for hip fractures. [4, 17] If the reduction is performed in a closed manner, the infection rate and blood loss can be reduced. Other advantages are better cosmetic appearance and shorter hospital stay. Biomechanically, they are load-sharing devices and early rehabilitation is possible. [18] Two-dimension stabilization provided by recon nails. [19] Technical problems include placement of screws into the neck. This can be achieved by significant internal rotation of femur. Figure 1a showed the pre operative x ray of a 22 year old female with ipsilateral shaft and trochanter fracture. Figure1 b showed immediate post operative x ray with good reduction. Figure 1c showed 1 year follow up X-ray showing no visible callus at the fracture site. The reconstruction nails available are theoretically and practically the best option when done by closed means and locked at the either ends. The studies carried out in the anatomic specimens for the suitability of the femoral neck fixation revealed the strength of the reconstruction nail to be 2.5 times superior to the strength of screw fixation of the femoral neck.[20] The two sliding screws for stabilization of the femoral neck with distal locking capability aids the strength and stability. But the central placement of the screw is difficult. Introduction of 135° nail dictates that the screws often come to lie in a superior position on the antero-posterior view. The lack of radiolucent jig for proximal screw insertion makes visualization of the screws on the lateral projection difficult. Introduction of nail requires excessive adduction and flexion which can pose difficulty in fatty and obese patients. The risk of avascular necrosis of the femoral head looms largely due to the damage of the blood vessels at the base of the femoral neck as the nail is driven through the pyriform fossa has been reported by Swiontowski et al[2] Bose et al [21] reported high complication rate after Russel Taylor reconstruction nails. In their series of 11 patients, there were two delayed union, two cases of shortening of the femur, one had a mal-alignment, and three technical errors during the surgery leading to fracture complications.
Retrograde nailing
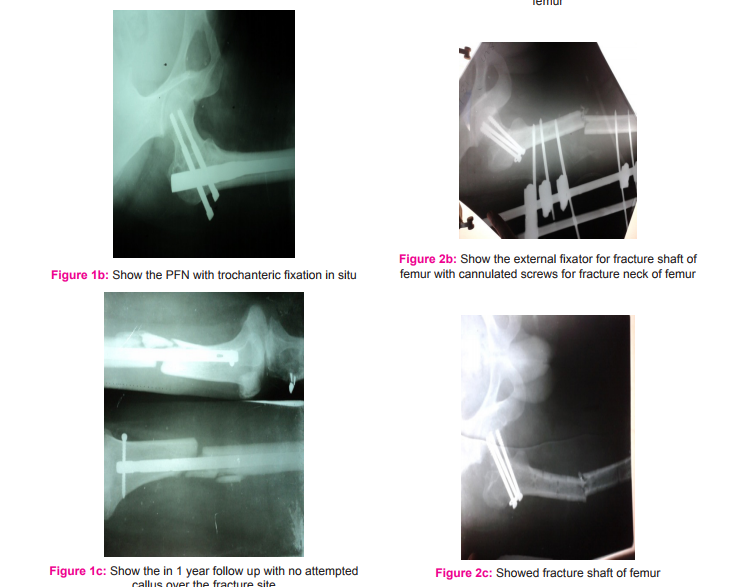
Retrograde nailing for the femoral shaft fractures, ipsilateral femoral neck fractures fixation by cancellous screws as suggested by Oh et al [22] can provide easy fixation and favorable results are reported. Theoretically, this seems to be an attractive treatment modality, reducing the incidence of damage of blood supply to the femoral head and fixation of the hip fracture independently. This treatment strategy may involve morbidity associated with an arthrotomy, and sometimes difficulty in removing the nail, as the entry point for the nail is the knee joint. Other disadvantages are knee stiffness, more blood loss and large operative scar. Knee stiffness was seen in our patient who undergone this treatment modality. Figure 2 a showing x-ray of 30 year old man with compound fracture of shaft and neck of femur with external fixator. Fig b shows AO cancellous screw fixation for fracture neck fracture. Fig c showing the radiograph after external fixator removal. Fig 4 showing retrograde nailing for fracture shaft of femur.
Proximal Femoral Nailing (PFN)
The PFN is available in 130-135° and has a 6° proximal mediolateral angle to facilitate easy insertion from the trochanter. The entry portal of the PFN through the trochanter limits the surgical injury predominantly to the tendinous hip abductor musculature only, unlike those nails which need the entry through the pyriform fossa. The stabilizing and the compression screws of the PFN adequately compress the fracture leaving between them a bone block for further revision of the proximal hip should the need arises. PFN allow the biologically viable fragments to heal around the nail. [24] Almost all the load is transferred to the nail and negligible portion to the medial femoral cortex. Hence intra medullary implant itself acts as a buttress to prevent excessive fracture collapse and shaft medialization. We feel that the long PFN rigidly stabilizes both the factures adequately leading to osseous healing. It also offers the advantage of a reamed and unreamed implantation technique, high rotational stability of the head-neck fragment, and the possibility of static or dynamic distal locking.
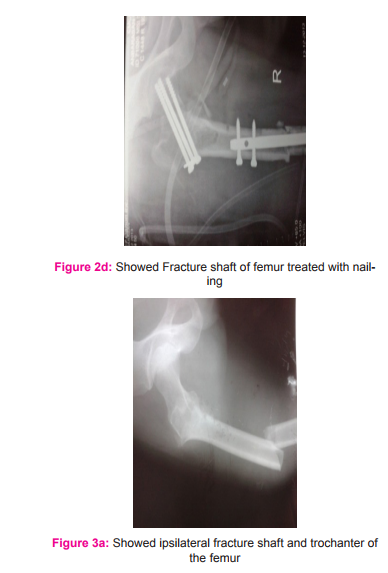
Figure 3 a showing ipsilateral fracture shaft and trochanter in a 52 year old man. Fig b showing the x ray following fixation with long PFN Douša et al [25] reported good results of ipsilateral fractures of the proximal femur and the femoral shaft treated by the long PFN in 147 cases. They found results do not differ from those reported by other authors. Our patient operated with this technique the functional result was good.
Dynamic Hip Screw Device (DHS)
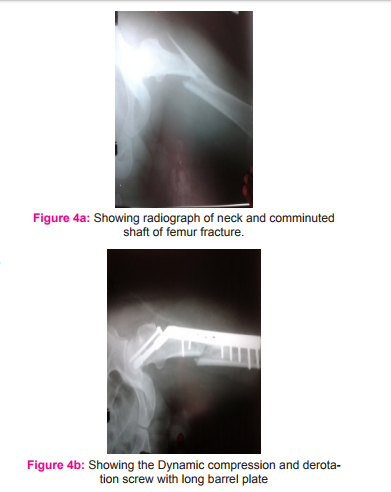
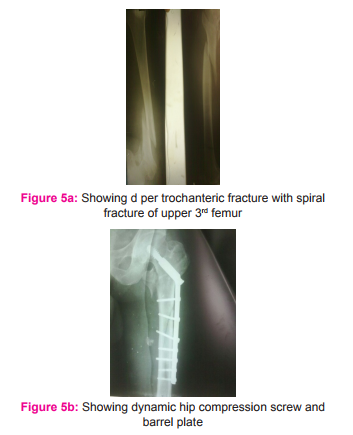
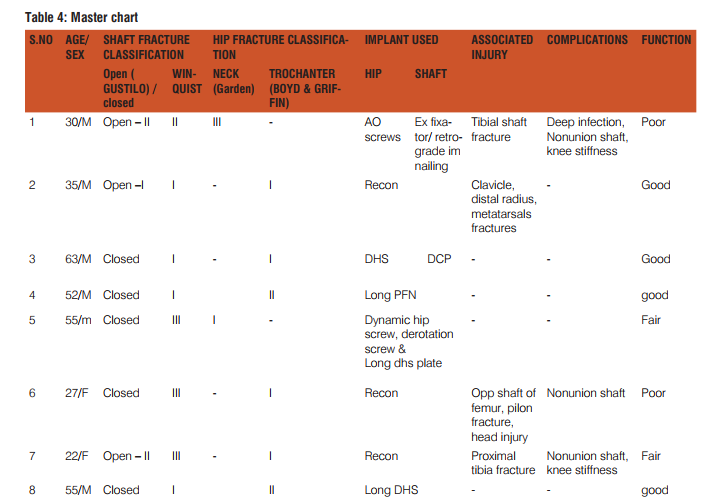
Technically, it is much easier to fix such fractures with a plate plus screws or DHS (than an intramedullary nail with screws or a reconstruction nail). It achieves a union rate of 77 to 93% in the femoral shaft and 93 to 100% in the femoral neck, with 77 to 93% of patients achieving good outcomes. [26] The advantages of this technique include reliable and familiar methods of fixation for each fracture. The disadvantages include increased blood loss and periosteal stripping of the femoral shaft, extensive surgical dissection, with potential need for bone graft. A high incidence of infection was reported after plating for femoral shaft fractures. [9] But in our patients who was operated with this technique no infection was noted. Figure 4 a showing radiograph of a 55 yr old man with minimally displaced neck and comminuted shaft of femur fracture. Figure b showing the same patient treated with Dynamic compression and derotation screw with long barrel plate Figure 5 a showing radiograph of a 55 year old man radiograph showing left sided peritrochanteric fracture with spiral fracture in the upper third of femur. Fig b showing the same patient treated with dynamic hip compression screw and barrel plate.
Complications
The two major complications are nonunion and osteonecrosis. Osteonecrosis represents perhaps the most devastating complication, especially in a young adult. Wiss et al. [9] reported a 6% incidence of osteonecrosis at an average follow up of 32 months. Swiontkowski et al. [2] reported that 2 of 9 (22%) patients who were followed for a minimum of 3 years developed osteonecrosis. Alho [3] found that the incidence of osteonecrosis in ipsilateral femoral neck shaft fractures is less than that in simple femoral neck fracture. Clinical examination and radiographs were reviewed in this study and no head osteonecrosis occurred after a median of nearly two years of follow-up. No further studies such as bone scan, tomography, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging were used to assess the viability of the femoral head. Though numerous authors report a union rate of 100% for both fracture, nonunion of the femoral neck and shaft remains a potential serious complication. Wiss [9] and co-workers reported an 18% incidence in his patients. In our serious there were three cases of the femoral shaft nonunions which required revision surgery. Missed neck The world literature reveals an incidence of 19-31% of hip fractures missed during the initial presentation.[2,3 ] Conventional nails in conjunction with cancellous screws by the miss-a-nail technique are appropriate for fractures detected intraoperatively or postoperatively. “Miss a nail technique”: Antegrade nailing for the comminuted femoral shaft fractures and the cancellous screw fixation around the nail for the fixation of the hip fracture. Closed reamed antegrade IM nailing with supplemental screw fixation of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures did not produce uniformly successful results because of the high rates of varus malunion of the femoral neck fracture. [9]
CONCLUSION
Early diagnosis and surgical treatment are important for the better functional outcome in the management of ipsilateral fracture of the hip and shaft of the femur. Basically, each technique has individual advantages, disadvantages and is technically demanding. Most important factor determines the outcome of this combined injury is the anatomical reduction and stable internal fixation of both fractures.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.


References:
1. Delaney W M, Street D M. Fracture of femoral shaft with fracture of neck. Treatment with medullary nail for shaft and Knowles pins for neck. J Int Coll Surg 1953; 19: 303-12.
2. Swiontowski M, Hansen S, Kellam J. Ipsilateral fractures of the femoral neck and shaft- a treatment protocol. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66:260–8.[PubMed: 6693453]
3. Alho A. Concurrent ipsilateral fractures of the hip and femoral shaft. A meta-analysis of 659 cases. Acta Orthop Scand 1996;67:19-28.
4. Wu CC, Shih CH. Ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures: retrospective study of 33 cases. Acta Orthop Scand 1991;62:346- 51. [PubMed: 1882674]
5. Jain P, Maini L, Mishra P, Upadhyay A, Agarwal A. Cephalomedullary interlocked nail for ipsilateral hip and femoral shaft fractures. Injury 2004;35:1031-8.
6. Swiontkowski M F. Ipsilateral femoral shaft and hip fractures. Orthop Clin North Am 1987; 18 (I): 73-84.
7. Friedman R J, Wyman E T Jr. Ipsilateral hip and femoral shaft fractures. Clin Orthop 1986; 208: 188-94.
8. Zettas JP, Zettas P. Ipsilateral fractures of the femoral neck and shaft. ClinOrthop. 1981;160:63–73. [PubMed: 7285439]
9. Wiss DA, Sima W, Brien WW. Ipsilateral fractures of the femoral neck and shaft. J Orthop Trauma. 1992;6:159–66. [PubMed: 1602335]
10. Casey MJ, Chapman MW. Ipsilateral concomitant fractures of the hip and femoral shaft. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979;61:503– 9. [PubMed: 438236]
11. Barquet A, Femandez A, Leon H. Simultaneous ipsilateraltrochenteric and femoral shaft fracture. ActaOrthop Scand. 1985;56:36–9. [PubMed: 3984701]
12. Russell TA. Ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures.ClinOrthopRelat Res. 1986;208:188–94. [PubMed: 3720122]
13. Winquist R A, Hansen S T, Clawson D K. Closed intramedullary nailing of femoral fractures. A report of five hundred and twenty cases. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 1984; 66: 529-39.
14. Leung KS, So WS, Leung PC (1993) Treatment of ipsilateral femoral shaft fractures and hip fractures. Injury 24(1):41–45.
15. Bernstein SM (1974) Fractures of the femoral shaft and associated ipsilateral fractures of the hip. Orthop Clin North Am 5:799–819.
16. Wu CC. Treatment of femoral shaft aseptic nonunion associated with plating failure: emphasis on the situation of screw breakage. J Trauma 2001;51:710-3.
17. Hossam EM, Adel MH, Emad EY. Ipsilateral fracture of the femoral neck and shaft, treatment by reconstruction interlocking nail. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2001;121:71- 4.
18. Rahul Kakkar, Kumar S, Singh AK (2005) Cephalomedullary nailing for proximal femoral fractures. Int Orthop (SICOT) 29 (1):21–24.
19. Rehnberg L, Olerud C. The stability of femoral neck fractures and its influence on healing. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1989;71:173-7.
20. Ramser JR, Mihalko WM, Carr JB, Beaudoin AJ, Kruse WR. A comparison of femoral neck fixation with the reconstruction nail versus cancellous screws in anatomic specimens. ClinOrthopRelat Res. 1993;290:189–96. [PubMed: 8472448]
21. Bose WJ, Corces A, Anderson LD. A preliminary experience with the Russel Taylor reconstruction nail for complex femoral fractures. J Trauma. 1992;32:71–6.[PubMed: 1732578]
22. Oh CW, Oh JK, Park BC, Jeon IH, Kyung HS, Kim SY, et al. Retrograde nailing with subsequent screw fixation for ipsilateral femoral shaft and neck fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2006;126:448–53. [PubMed: 16810555]
23. Abalo A, Dossim A, OuroBangna AF, Tomta K, Assiobo A, Walla A. Dynamic hip screw and compression plate fixation of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures. J Orthop Surg. 2008;16:35–8.
24. Gadegone WM, Salphale YS.Proximal femoral nail-an analysis of 100 cases of proximal femoral fractures with an average followup of 1 year. Int Orthop.2007;31:403–8. [PMCID: PMC2267603] [PubMed: 16823585]
25. Douša P, Bartoníek J, Pavelka T, Lunácek L. Ipsilateral fractures of the proximal femur and the femoral shaft. ActaChirOrthopTraumatolCech. 2010;77:378–88.[PubMed: 21040649]
26. Chen CH, Chen TB, Cheng YM, Chang JK, Lin SY, Hung SH. Ipsilateral fractures of the femoral neck and shaft. Injury 2000;31:719–22.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License