IJCRR - 7(17), September, 2015
Pages: 01-06
Date of Publication: 11-Sep-2015
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
CYTOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF SEROUS BODY FLUIDS: A TWO YEAR EXPERIENCE IN TERTIARY CARE CENTRE FROM CENTRAL INDIA
Author: Preeti Rihal Chakrabarti, Priyanka Kiyawat, Amit Varma, Purti Agrawal, Shilpi Dosi, Monal Dixit
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Background: Cytological examination of serous body fluids is extremely important since it throws light on the cause, presence of metastatic cells, typing of unknown cases, staging and prognosis of cancer. Aims and Objectives: 1) To study and evaluate current trends in cytological evaluation of serous effusions for various pathological conditions in a tertiary care centre. 2) To analyse their frequency in relation to diagnosis. Material and Methods: Our Study was cross-sectional study performed in Department of Pathology, Sri Aurobindo Medical College and Post Graduate Institute from 1st January 2013 to 31st December 2014. Serous effusions included in the study were pleural, pericardial and peritoneal in origin. All other fluids were excluded from the study. The clinical history and relevant parameters were noted and correlated clinically. Conventional smears and cytospin method were performed on all fluids. Both air dried and wet fixed smears in methyl alcohol were used and stained with Papanicolaou(PAP) and May-Grunwald-Giemsa(MGG) stain. Results: Out of 902 cases, 400(44.3%) were pleural fluid, 485(53.7%) were peritoneal fluid and 17 (1.9%) were pericardial fluids. 820 (90.9%) were of benign effusion and 82(9.1%) were of malignant effusion. Total transudate cases in our study were 622 (68.9%) and exudates were 280 (31.04%). Male to female ratio was 1.5:1 with youngest patient 20 years old and eldest was 85years old. Conclusion: Benign effusions are common in younger age group and malignant in older age group. Combined approach to morphology with May-Grunwald-Giemsa (MGG) and Papanicolaou (PAP) helped in better interpretation than either methods used individually. Preliminary fluid analysis for cytology in resource limited settings, still remains the most convenient and cost effective method in arriving at the diagnosis, thereby reducing the need for invasive investigations and their related complications. Presence and absence of malignant cells at times can be the only clue to the presence of malignancy thereby affecting the prognosis and treatment outcome of the patient.
Keywords: Serous effusion, Transudate, Exudate, Adenocarcinoma
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
The three body cavities (pleura, peritoneum, pericardial) have a common embryologic origin in the mesenchymal embryonic layer. They are lined by mesothelial cells and are supported by appropriate connective tissue, vascular and nervous apparatus. Parietal and visceral layer are separated by thin layer of lubricating fluid that provides the movement of two membrane against each other in the absence of disease.[1] However, in pathological states the serous cavities develop spontaneous effusions and hence provide useful specimen for cytological evaluation. Cytomorphological examination of exfoliated cells in effusions may also provide information of various inflammatory conditions of serous membranes, infection with bacteria, fungus, viruses and parasitic infestations. It can also provide evidence of fistulous connection with a serous cavity. [2] Cytological examination of exfoliated cells in serous cavity effusions is challenging in clinical cytopathology. Twenty percentage of all effusions examined are directly or indirectly related to the presence of malignant disease, with carcinoma of lung as the most common underlying cause.[3] Cytological examination of serous effusion is important for the diagnosis of cancer, for staging and the prognosis of the patient. It is better than biopsy of the serous cavity lining for the diagnosis of malignancy affecting any of the cavities as focal lesion on a serous surface may be missed by biopsy. This leads to false negative results. But in effusions malignant cells exfoliate and accumulate from all the surfaces lining that cavity which represent entire serous cavity. Hence, the diagnostic performance of the cytomorphological study of effusion may be attributable to the fact that the cell population present in the sediment is representative of a much larger surface area than that obtained by needle biopsy.[4,5] The rate of detection of malignant cells is increased further if multiple effusion specimens are evaluated consecutively. This study was conducted to assess the trends of various types of effusions for pathological conditions diagnosed in a tertiary care centre in Central India.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
The present study was performed to analyse serous effusions for various pathological conditions submitted for evaluation in the Department of Pathology, Sri Aurobindo Medical College and Post Graduate Institute, Indore, Madhya Pradesh from 1st January 2013 to 31st December 2014. All the cases of neoplastic and non neoplastic diseases with serous effusion from pleura, pericardium and peritoneal cavity were included. All other fluids were excluded. Clinical details and relevant history were noted and correlated accordingly. The samples of serous effusions were received in the rubber stopper labelled glass bottles, sterile containers as well as in properly closed large jars in case of large volumes with properly filled requisition forms. Whenever delay was anticipated in processing the sample, sample was store at temperature of 2-60 C. Smears were prepared using the sediment obtained by routine centrifugation at 2000-3000 rpm for 5 minutes and by cytospin method. Both wet fixed (methyl alcohol) and air dried smears were used. They were stained with Papanicolaou (PAP) and May-Grunwald- Giemsa (MGG). Papanicolaou (PAP) stain helped in better interpretation of nuclear features and May-Grunwald- Giemsa (MGG) stain for cytoplasmic features.
RESULTS
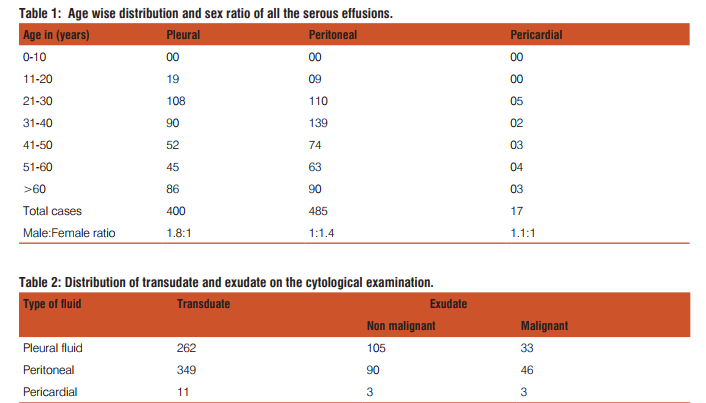
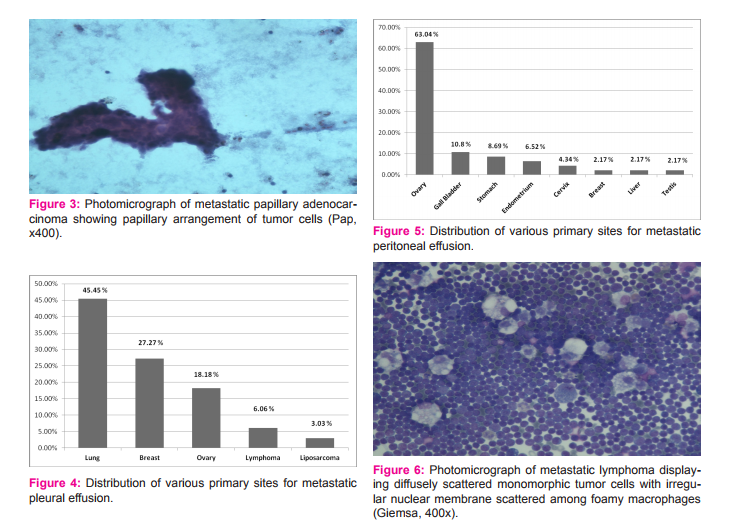
In the present study, total 902 serous fluid samples were studied. Out of 902 fluids, 400 were pleural fluids, 485 were peritoneal fluids and 17 were pericardial fluids. The maximum number of cases (25.6%) were observed in the 4th decade and minimum number (3.10%) were observed in 2nd decade with none in 1st decade of life. Age range of the patients in the present study was from 20 to 70 years. Male preponderance was noted with the ratio of male to female being 1.5:1. [Table 1] Out of 400 cases of pleural effusion, maximum number of cases(108) were observed in the age group of 21-30 years with male preponderance; male to female ratio being 1.8:1. Total 262 cases were transudate in nature and 138 were exudate in nature. Transudate effusions had protein level less than 3 gm% and exudate effusions had more than 3 gm%. Out of 138 cases of exudate in nature, cytological examination revealed, 33 cases were of malignant effusion and 105 cases were of non malignant causes of exudative effusion [Table 2]. Of all the 33 cases of malignant effusion, male preponderance was observed; with male to female ratio 1.2:1 and lung carcinoma being the most common primary site. Of all the pleural effusions, 240 cases were straw coloured, 103 were turbid, 45 were haemorrhagic and 12 were clear in nature.[Table 3] Out of total 485 cases of peritoneal effusion, maximum number of cases(139) were observed in the age group of 31-40 years with female preponderance; male to female ratio was 1:1.4. Total 349 cases were transudate in nature and 136 were exudate in nature. Cytological examination revealed, out of 136 cases of exudate in nature, 46 cases were of malignant effusion and 90 cases were non malignant causes of exudative effusion [Table 2]. Of all the 46 cases of malignant effusion, female preponderance was observed; male to female ratio was 1:5 and ovarian carcinoma being the commonest primary site. Of all the peritoneal effusions, 300 cases were of straw coloured, 70 cases were turbid, 66 cases were haemorrhagic and 49 were clear in nature [Table 3]. Out of 17 cases of pericardial effusion, maximum number of cases(5) were observed in 21-30 years with slight male preponderance; male to female ratio being 1.1:1. Total 11 cases were of transudate in nature, 6 cases were of exudate in nature [Table 2]. On cytological examination of total 6 cases of exudative pericardial effusion, 3 cases were of malignant effusion and 3 were non malignant cause of exudative effusion. Of all the pericardial effusions, 5 were straw coloured, 3 were turbid, 7 were haemorrhagic and 2 were clear [Table 3]. Cytological examination of benign effusions showed singly scattered and sheets of reactive mesothelial cells with clear spaces or windows in between them scattered among macrophages and inflammatory cells [Figure 1]. In malignant effusions, three dimension balls, aggregates forming gland like structures with lumen, and papillary structures were commonly observed [Figure 2,3]. Adenocarcinoma was the most common morphological pattern observed in our study.
DISCUSSION
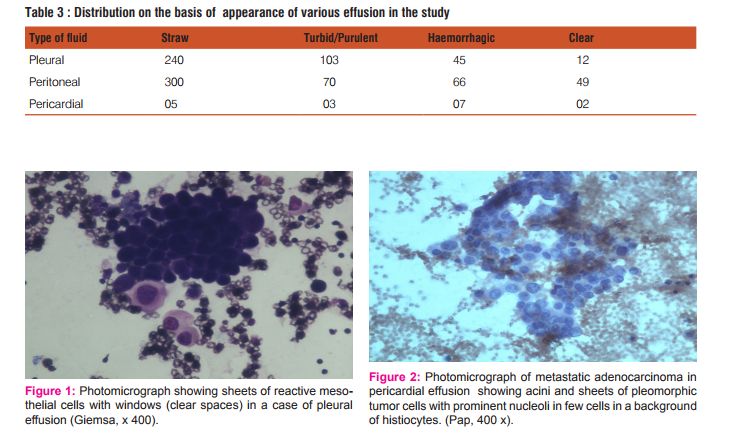
The cytological examination of body effusion is a complete diagnostic modality which aims at pointing out the etiology of effusions. The diagnostic performance of the cytologic study of fluid may be attribute to the fact that the cell population present in representative of a much larger surface area than that obtained by needle biopsy.[4,5] Examination of effusion cytology is sometimes tricky as morphology of reactive mesothelial cells may mimic malignant cells. Hence, distinction between reactive mesothelial cells and malignant cells on cytological examination of fluid cytology is a diagnostic challenge. The present study was undertaken to analyse the trends of various serous effusions in Central India and to study the significance of fluid cytology in the diagnosis of various non-neoplastic and neoplastic conditions. In the present study, the most common effusion was peritoneal followed by pleural effusion. Our study correlated with finding of Sherwani R et al. [5] In pleural fluid examination, male preponderance was seen with male to female ratio 1.8:1. Our study show concordance with study by Romero et al [6] and Rasik Hathila et al. [7] However, maximum number of patients with pleural effusion were seen in the 4th decade in the present study. Out of 400 cases of pleural effusions of which maximum number of cases (262) were transudate in nature. Differentiation from transudate on routine examination of fluid is mainly based on levels of protein (Transudate less than 3 gm% and exudate more than 3gm %), Rasik Hathila et al [7] had similar finding. On the cytological examination, transudative effusions are usually characterised by a majority of lymphocytes or other mononuclear cells. In present study, all the transudative effusions had more than 50% lymphocytes which was comparable with study of Kushwaha et al [8] which showed 83.33% of samples of transudative effusion had more than 50 % of lymphocytes. The pattern of predominantly polymorphonuclear cells were observed in most cases of exudative effusion and clinically suspected cases of pneumonia, post myocardial infection and emphysema. Of all the 138 cases of exudative pleural effusion, 33 cases were malignant effusion with male preponderance and lung carcinoma was the most common primary site which is in agreement with study of Lim et al.[9] Breast carcinoma followed by ovarian carcinoma was the next most commonest primary site in the pleural effusion group [Fig 4]. On the basis of cytomorphology, metastatic adenocarcinoma was the most common finding in malignant pleural effusion. Di Bonito et al [10] studied on cytomorphological diagnosis in pleural effusion with autopsy confirmation and found most cases were of adenocarcinoma. Hallman et al,[11] also did a comprehensive study on cytology of fluid from different cavities in children and found lymphoreticular neoplasm to be the cause of almost all malignant effusion in children. Here we found two cases of Non Hodgkins Lymphoma, both were seen in children. In peritoneal fluid examination, female predominance was observed with male to female ratio 1:1.4 and ovarian malignancy was the most common primary site. Jha R et al [12] reported gastric malignancy as the commonest primary in their study, however in female patients ovarian malignancy was the commonest which correlated with our study. Parson et al,[13] Wilailak et al,[14] Monte SA et al [15]and Karoo et al [16] also found ovarian malignancy as commonest primary site, shedding malignant cells in peritoneal fluid. In peritoneal effusion, out of 485 cases, maximum number of cases(349) were transudate in nature. Rasik Hathila et al [7] had similar findings. Of all the 136 cases of exudative effusion, 46 were malignant in nature. Of all the malignant peritoneal effusions, ovarian carcinoma was commonest followed by gall bladder carcinoma and other gynaecological cancers. [Fig 5] In pericardial fluid examination, male predominance was observed; male to female ratio being 1.1:1, maximum number of cases were transudate in nature which was in concordance with the finding of Rasik Hathila et al. [7] Of all the 6 cases of exudative effusion, cytological examination revealed 3 cases were malignant effusion of metastatic adenocarcinoma showing a female predominance. Out of 3 cases, 2 cases had primary in the breast and one was case of unknown primary and succumbed to death. In a study by Robert E et al, [17] metastatic adenocarcinoma with primary from the breast was the commonest finding which correlated with our study. The most common transudate causes were clinically suspected cases of pericarditis, post myocardial infarction, rheumatic heart disease and exudative causes were pericardial inflammation and infection. Pericardial fluid cytology is not of value in making an early diagnosis of cancer, although on several occasion positive fluid cytology did expose an underlying undiagnosed malignancy. Most commonly, it provides the information that a known or suspected cancer has metastasized, in which case corrective surgery is contraindicated. [17] On the basis of tumor cell morphology and its arrangement, diagnosis of different types of malignancy were made. Adenocarcinoma was the most common morphological pattern observed in present study. Breast carcinomas of the medium or large cell type are easily recognized as malignant in effusion because cells have classical features of metastatic adenocarcinoma. The most characteristic feature is presence of large, three-dimensional clusters of round, oval or irregular configuration wherein cells are superimposed on each other. Nuclear features of cancer cells are usually classic and comprise of nuclear enlargement, granularity of chromatin, prominent nucleoli and abnormal mitosis. Lung adenocarcinoma also showed similar cytomorphological features. Sometimes papillary configuration were also seen. However, there remains a group of poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma which can be easily recognized as malignant but fail to display any of the features that make recognisation of tumor type possible. Metastatic ovarian carcinomas also showed adenocarcinoma as commonest cytomorhological pattern. The exact identification of tumor type may be possible in some cases, although in most women a histological diagnosis of tumor type was available. Irrespective of the type of malignant lymphoma, the cancer cells never form cohesive clusters, instead lie singly. Tumor cells have spherical to oval nuclei with irregular contour, nuclear indentation with prominent nucleoli and scant cytoplasm [Figure 6]. Cytological evaluation of body fluid helps in evaluating presence or absence of cancer cells and hence affecting staging, prognosis and treatment plan for the patients.
CONCLUSION
Benign effusions are common in younger age group and malignant in older age group. Reactive mesothelial cells with window effect were commonly observed in benign effusions. Papillary structures and three dimensional balls were observed in malignant effusions. Combined approach to morphology with May-Grunwald- Giemsa (MGG) and Papinicolaou (PAP) helped in better interpretation than either methods used individually. Preliminary fluid analysis for cytology in resource limited setting still remains the most convenient and cost effective method in arriving at the diagnosis, thereby reducing the need for invasive investigations and their related complications. Cytological analysis of serous effusions have a better diagnostic performance vis-a-vis needle biopsy as the population of cells obtained in a sediment is representative of a larger surface area than the latter. Serous effusions may be present in a case of malignancy either as a manifestation of progression of disease or maybe attributable to any other cause except malignancy. This results in the upstaging or downstaging of tumour and thereby affects treatment plan and prognosis for the patient. Therefore cytological analysis of various effusions should be requested along with its clinicopathological correlation.
References:
1. LG Koss, MR Melamed. 5th Edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Williams; 2005. Editors. Koss’ Diagnostic Cytology and Its Histopathologic Bases; 919-22.
2. Shidham VB, Falzon M. Serous effusions. In: Gray W, Kocjan G: editors. Diagnostic Cytopathology, 3rd Edition. Churchill Livingstone, Elsevier 2010; 115-175.
3. Ali SZ, Cibas Es. Serous cavity fluid and cerebrospinal fluid cytopathology. New York Springer ;2012:77-131.
4. Frist B, Kahan AV, Koss LG. Comparison of the diagnostic values of biopsies of pleura and cytological evaluation of pleural fluids. Am J Clin Pathol 1979;72:48-5.
5. Sherwani R, Akhtar K, Naqvi AH, Akhtar S, Abrari A, Bhargava R. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of cytology in effusions. J cytol 2005;22:73-7.
6. Romero S, Candela A, Martin C, Hernandez L, Trigo C, Gil J. Evaluation of different criteria for the separation of pleural transduates and exudates. Chest 1993;104:399-404.
7. Hathila RN, Dudhat RB, Saini PK, Italiya SL, Kaptan KR, Shah MB. Diagnosyic importance of serous fluid examination for detection of various pathological conditions- A study of 355 cases. Int J Med Sci Public Health 2013;2:975-979.
8. Kushwaha R, Shasikala P, Hiremath S, Basavraj HG. Cells in pleural fluid and their fluid in differential diagnosis.J Cytol 2008;25:138-43.
9. Lim MH, Garrettc J, Mowlem L, Yap E. Diagnosing malignant pleural effusions: how do we compare? N Z Med J 2013;126:42- 48
10. Luigi DiBonito, Giovanni Falconieri, Isabella Colautti, Daniela Bonifacio, Sandra Dudine: The Positive Peural Effusion. Acta Cytol 1992;36:329-32.
11. James R. Hallman, Kim R.Geisinger: Cytology of fluids from Pleural, Peritoneal, Pericardial cavities in children. Acta Cytol 1992;36:329-32.
12. Jha R, Shrestha HG, Sayami G, Pradhan Sb. Study of effusion cytology in patients with simultaneous malignancy and ascitis. Kathmandu university medical journal 2006;4:483-487.
13. Parsons SL, Lang MW, Steele RJ. Malignant ascitis: a 2-year review from the teaching hospital. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1996;22:237- 9.
14. Wilailik S, Linasmita V, Srivannaboon S. Malignant Ascitis in female patients, a seven year review. J Med Assos Thai 1999;82:15-9.
15. Monte SA, Ehya H, Lang WR. Positive effusion cytology as the initial presentation of malignancy. Acta Cytol. 1987;4:448-52.
16. Karoo RS, Lyold TDR et al, Garcea G, Redway HD, Robertson GSR. How valuable is ascitic fluid cytology in detection and management of malignancy. Post graduate medical journal 2003;79:291-299.
17. Robert E. Zipf, William W.johnston. The role of cytology in the evaluation of Pericardial effusions. Chest 1972;62:593-96
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License