IJCRR - 14(9), May, 2022
Pages: 01-06
Date of Publication: 03-May-2022
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Negative Appendectomy Rate in a Tertiary Care Hospital of Quetta: A Cross-Sectional Study
Author: Allauddin, Muhammad Sohaib Khan, Azmat Ullah, Seemin Kashif, Gulalai Rehman, Muhammad Kashif Malik
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Acute appendicitis is the most common surgical pain that requires surgical intervention in an emergency. Diagnosis of acute appendicitis is mainly a clinical judgment but many clinical scoring systems and advanced radiology is routinely used in developed countries. The aim is to reduce unnecessary removal of the normal appendix, which is still very high up to 37% in some parts of the world. Aim: The aim of this study was to assess the Negative appendectomy rate (NAR) in a tertiary care hospital of Quetta. Method: This is a prospective observational study carried out between November 2020 and June 2021.121 cases of acute appendicitis that underwent surgical management. Results: The study data revealed a negative appendectomy rate of 59.5% Tenderness rebound tenderness and total leucocyte count (TLC) showed statistical significance with histopathology findings. Females had a high negative rate of appendectomy. Conclusion: The study showed that on clinical judgment in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis will result in a high negative appendectomy rate, it is need of time to add radiology at least ultrasonography should be mandatory in every suspected case of appendicitis in our part of the world, and diagnostic laparoscopy in equivocal cases, especially in female patients.
Keywords: Acute appendicitis, Advance radiology, Clinical judgment, Diagnostic laparoscopy, TLC, Histopathology
Full Text:
Introduction:
Acute appendicitis is 2nd most common acute emergency, after nonspecific abdominal pain in presentation to the emergency department 1. It has a rate of 7-12% in the general population. The peak age of incidence is between 16 to 40 years in adults 2.More common in males. However, in young women of childbearing age, the diagnosis of appendicitis is difficult due to the wide range of differential diagnoses 3.Acute appendicitis is a clinical diagnosis and many surgeon resorts to a clinical judgment for the management. This clinical decision has a lot of potential for improvement as reflected by the high negative appendectomy rate (NAR) up to 37%4. A major problem is overtreatment in the form of normal appendectomy (removal of the histologically normal appendix), which may be lead to high cost and postoperative complications 5, 6 There is little consensus on optimal diagnostic pathways for right iliac fossa pain diagnosis 7. Although different scoring systems are used to reduced negative appendectomy rate (NAR)., In the USA and Europe, CT scan is routinely used for appendicitis diagnosis 6, Equivocal cases Diagnostic laparoscopy is used routinely specially in female patients,7,8. which reduced the negative rate as low as 3.5 %. But in South Asia like Pakistan lack of routine CT scans and even the non-availability of routine use of U/S, the NAR is as high as up to 20—37% 9.
The negative appendectomy rate is 11-36% 8,9 in Australia and 15-33% in the United Kingdom 10,11. But in the United States the NAR rate is less than 5% 11. The availability of advance radiology and its utilization in appendicitis reducing the negative appendectomy rate. Despite this great achievement The questions remains regarding the cost-benefit of imaging verses to other clinical indicators 9. Diagnosis of appendicitis is possible only on histological examination, regardless of the gross appearance of the appendix and the clinical picture 12.
This study was conducted at a tertiary care teaching hospital where the emergency presentation of acute abdominal pain is attended by junior residents. We evaluate and diagnose acute appendicitis on clinical judgment with histopathological findings rather than a specific scoring system. Whenever needed or was available ultrasonography was done. So the objective of this study was to find out the NAR in a tertiary care hospital of Quetta and to see the positive clinical predictors in our sitting
Material and method:
The study is a prospective observational study conducted between Nov 2020 and June 2021.The study was approved by the institutional review board, informed consent was taken from all the study participants. 121 consecutive adults patients who presented with the clinical feature of acute appendicitis and underwent appendectomy were included in the study.
Inclusion criteria:
-
All patients with acute pain in right lower quadrant and with clinical features suggestive of acute appendicitis
-
All patients who underwent open appendectomy after satisfying the above mention criteria
-
Adults patients aged 15 and above
-
Patients whose appendix was sent for Biopsy with standard protocol.
Exclusion criteria:
1. Age below 15 years
2. Female patient with known gynecological conditions
3. Patient had a recent abdominal surgery minor or major
4. Interval appendectom
All patients admitted with features suggestive of acute appendicitis like right iliac fossa pain, rebound tenderness, nausea, total leucocyte count, and-in case of u/s- a high suspicion of acute appendicitis underwent appendectomy. The appendectomy specimen was sent for histopathology as the final step for diagnosis. And the histopathology report was used as the gold standard reference for the study. All the biographic and demographic data, clinical assessment and per operative finding were recorded on a proforma prospectively then analyzed.
The statistical analysis of the study was performed by using a statistical package for social sciences (SPSS version21.IBM corporation USA). In the study p-value of less than 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. The mathematical tools used in the analysis were the chi-square test and Binary regression analysis.
Results:
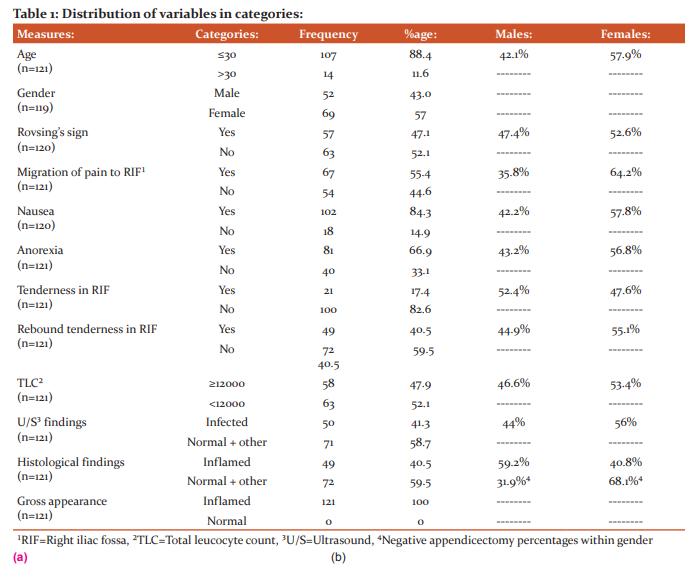
A total of 121 appendicectomies were performed. About 88.4% of the patients were 30 years old or younger. Only 11.6% of this population was older than 30 years of age (Table 1). Out of 121 patients, 43% were males, and 57% were females. Migration of pain to the right iliac fossa (RIF) was present in 55.4% of the patients. Anorexia was present in 66.9%, and nausea in 84.3% of patients. Although rebound tenderness in RIF was present in 40.5% of patients, tenderness in RIF was present in 17.4 % of the patients. Rovsing’s sign was positive in 47.1%. (Table 1). TLC was ≥12,000/mm³ in 47.9% of patients, Ultrasound abdomen showed inflamed in appendix in 41.3% of patients. Histopathology was suggestive of acute appendicitis only in 40.5% of patients (Table 1).
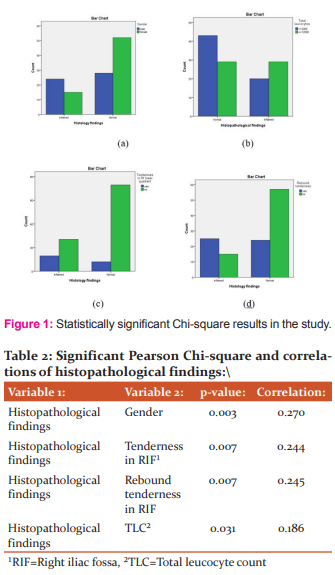
Crosstabs between histopathological findings (inflamed or normal appendix) and gender showed that they had a statistically significant (p=0.002), but weak and positive correlation (r=0.277) (Table 2; Fig 1a). Similarly, both tenderness in RIF and rebound tenderness in RIF had a statistically significant (p=0.007, r=0.244, and p=0.007, r=0.245, respectively), but weak, positive correlation with histopathological appearance (Table 2; Fig 1b, 1c). Histopathological findings and TLC also showed that they had a statistically significant (p=0.031), but weak and positive correlation (r=0.186) (Table 2: Fig 1a). No other significant correlations were found.
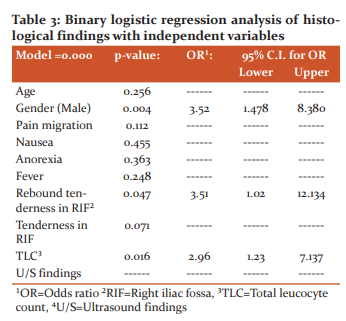
Binary logistic regression analysis was done to assess the effects of various predictors on inflammation of the appendix (through positive or negative histopathological reports) (Table 3). The model was statistically significant (p=0.000), variation in the dependent variable based on our model ranged from 22.0% to 30.0%, and the model correctly classified about 72% of patients. Results showed that only gender and rebound tenderness in RIF was the true predictors of histopathological proven inflammation of the appendix (Table 3). The odds ratio for the male gender was found to be 3.52 (95% CI [1.47, 8.38]), for rebound tenderness was found to be 3.5 (95% CI [1.02, 12.13]), and for TLC was 2.96 (95% CI [1.23, 7.13]), after adjusting for all remaining variables included, plus age, gender, and ultrasound findings. Male gender, rebound tenderness in RIF, and TLC was found to be strong predictors of inflammation of the appendix.
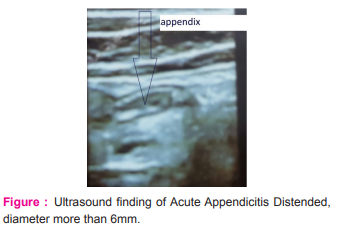
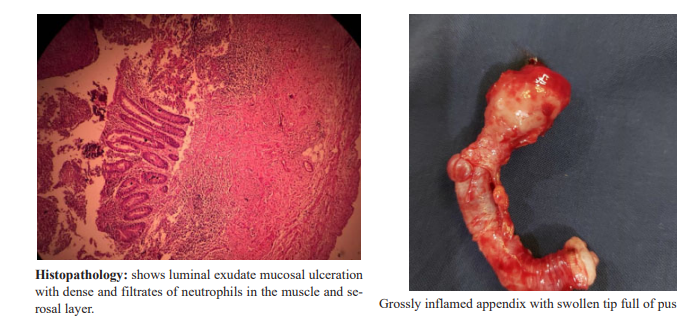
Discussion:
Acute appendicitis can often prove to be a diagnostic perplexity. More so in female patients. This is attributed to the myriad presentations, these patients can have the numerous other conditions that mimic acute appendicitis
In our study, more than 88.4% of the patients were ≤30 years of age (Table 2). In this younger age group, the males was less than females i.e. 43%. However, 59.2% of the histologically inflamed appendix belonged to the male group, only31.9% of female appendix was inflamed. These findings were comparable with the literature, where it was found that acute appendicitis was commoner in younger people, and in males, but it was falsely diagnosed twice as commonly in females2.
The negative appendicectomy rate (NAR) ranges from 19% to 34% in the UK 12. In our study, however, only about 40.5% of the appendicectomy specimens were found to be inflamed, and the rest of the samples either showed normal histopathology or some other pathology. It meant that about 59.5% of the patients had undergone negative appendicectomy. This finding was alarming.
In a study done in Australia, NAR for males was 9.0%, and for females was 12.7% 13 and in a Pakistani study, it was 7%-12.7% for males, and 7%-29% for females. In our sample, about 19% of males, and 40% of the females had undergone negative appendicectomy. Negative appendicectomy rate (NAR) is common in females due to certain gynecological conditions like ovarian cysts, pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy, etc.14 To reduce NAR among young age females, a transvaginal ultrasound would be required, in addition to abdominal ultrasound, in suspected gynecological issues15 which is not practiced routinely in our setups. Apart from gynecological causes, certain non-gynecological causes can also cause lower abdominal pain in young girls, which might mimic acute appendicitis, and lead to unnecessary surgery 16These causes might include mood disorders, depression, anxiety, eating disorders (anorexia nervosa, bulimia), or other emotional problems.
Another important reason for this sizeable NAR was a fear of appendix perforation. Perforation of appendix rate was reported to be 7% to 13% in Pakistan. Therefore, surgeons prefer to do appendicectomy as soon as possible to avoid perforation and peritonitis. But avoidable surgery is a financial burden for the patients as well as for the healthcare system.
NAR of 15 to 30% is mostly acceptable 17.However, efforts are being made to reduce it further. Different scoring systems have been developed for proper diagnosis. In a study done in India, it was suggested that this could have been prevented by using criteria of RIPASA>11 instead of 7.518. Similarly, ultrasound together with a modified Alvarado score could be a better way for better diagnosis 19. Appendicitis was histologically confirmed in more than 95% of patients with help of CT and abdominal ultrasound. About 97% of these cases were diagnosed with help of a CT scan, and 93% of the cases with ultrasonography 20 The false-positive rate for assessing appendicitis was 5.4% with ultrasound, and 2.3% with CT scan 21. Hence, the negative appendicectomy rate could be improved by preoperative imaging22. The diagnostic laparoscopy7.This could also save costs of surgery, hence avoiding wastage of resources23. However, in developing countries, like India and Pakistan, using imaging in every patient is expensive nor all time available in the hospital premises in government set up. And very expensive for patients from private systems to have u/s.24 Hence, making decisions under these circumstances can be difficult for surgeons, especially junior doctors 25According to a study in Pakistan, even imaging techniques were believed not to significantly reduce the negative appendicectomy rate26, probably due to comparatively inexperienced sonographers, because regardless of a high rate of negative appendicectomies, about 25% of the non-inflamed appendix was found to be with other pathologies which might have caused RIF painand they could not be differentiated on imaging.
Conclusion:
The Negative appendectomy rate was very high in comparison to other regional and global setups. Tenderness in right iliac fossa (RIF), rebound tenderness, total leukocyte count were found to be the positive predictor of acute appendicitis. Moreover negative appendectomy rate was found more prevalent in female population.
Recommendation:
Further studies needed to be carried out to take a deep insight and causative factors of High negative appendectomy rate in this area. Need of time to add advance radiology routinely like ultrasonography and CT Scan to avoid unnecessary removal of appendix.
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflicts of interest and no source of funding for this study.
Acknowledgement: The authors are grateful to Immaduddin Khan a 9th class student for his contribution in formatting and typing of the this article.
References:
1. GlobalSurg Collaborative. Mortality of emergency abdominal surgery in high-, middle- and low-income countries. Br J Surg. 2016 Jul;103(8):971–88.
2. Wagner P de J, Haroon M, Morarasu S, Eguare E, Al-Sahaf O. Does CT Reduce the Rate of Negative Laparoscopies for Acute Appendicitis? A Single-Center Retrospective Study. J Med Life. 2020 Mar;13(1):26–31.
3. Bhangu A, Søreide K, Di Saverio S, Assarsson JH, Drake FT. Acute appendicitis: modern understanding of pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Lancet Lond Engl. 2015 Sep 26;386(10000):1278–87.
4. Risk Stratification Using Appendicitis Inflammatory Response Score, A Useful Tool To Reduce Negative Appendicectomy Rate?: Our Experience, IJSR - International Journal of Scientific Research(IJSR), IJSR | World Wide Journals [Internet]. [cited 2022 Jan 30]. Available from: https://www.worldwidejournals.com/international-journal-of-scientific-research-(IJSR)/article/risk-stratification-using-appendicitis-inflammatory-response-score-a-useful-tool-to-reduce-negative-appendicectomy-rate-our-experience/MTkxNTE=/?is=1&b1=417&k=105
5. National Surgical Research Collaborative. Multicentre observational study of performance variation in provision and outcome of emergency appendicectomy. Br J Surg. 2013 Aug;100(9):1240–52.
6. Bijnen CL, Van Den Broek WT, Bijnen AB, De Ruiter P, Gouma DJ. Implications of removing a normal appendix. Dig Surg. 2003;20(2):115–21.
7. Mock K, Lu Y, Friedlander S, Kim DY, Lee SL. Misdiagnosing adult appendicitis: clinical, cost, and socioeconomic implications of negative appendectomy. Am J Surg. 2016 Dec;212(6):1076–82.
8. Rogers W, Hoffman J, Noori N. Harms of CT scanning prior to surgery for suspected appendicitis. Evid Based Med. 2015 Feb;20(1):3–4.
9. Hwang ME. Sonography and Computed Tomography in Diagnosing Acute Appendicitis. Radiol Technol. 2018 Jan;89(3):224–37.
10. Lim J, Pang Q, Alexander R. One year negative appendicectomy rates at a district general hospital: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Int J Surg Lond Engl. 2016 Jul;31:1–4.
11. Tseng J, Cohen T, Melo N, Alban RF. Imaging utilization affects negative appendectomy rates in appendicitis: An ACS-NSQIP study. Am J Surg. 2019 Jun;217(6):1094–8.
12. Miah M, Centea D, Cleto C, Yusuf R, Husain N, Thomas P. Negative Appendicectomy Rates and Implication of Preoperative Imaging - A Retrospective Cohort Study. Biomed J Sci Tech Res [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2022 Jan 30];28(5):22019–21. Available from: https://ideas.repec.org/a/abf/journl/v28y2020i5p22019-22021.html
13. Mackay TG, Dissanayake B, Yuide PJ, Burstow MJ, Gundara JS, Chua TC. Cohort study of 1241 patients to identify predictors of negative appendicectomy. ANZ J Surg. 2020 Oct;90(10):1984–90.
14. Alhamdani YF, Rizk HA, Algethami MR, Algarawi AM, Albadawi RH, Faqih SN, et al. Negative Appendectomy Rate and Risk Factors That Influence Improper Diagnosis at King Abdulaziz University Hospital. Mater Socio-Medica. 2018 Oct;30(3):215–20.
15. Pooria A, Pourya A, Gheini A. Appendicitis: Clinical implications in negative appendectomy. Int J Surg Open [Internet]. 2021 Feb 1 [cited 2022 Jan 30];29:45–9. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S240585722100005X
16. Lower abdominal pain as a problem in child gynecology [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2022 Jan 30]. Available from: https://imrpress.com/journal/CEOG/47/1/10.31083/j.ceog.2020.01.5091
17. Dirie J, Merali N, Macias A. 699 Does Pre-Operative Imaging Improve Negative Appendicectomy Rate? Br J Surg. 2021 Oct 11;108.
18. Mynalli S, Biradar BN, Braggs AV, Basti RS. Combined Use of High Resolution Ultrasonography and Ripasa Score in Acute Appendicitis with the Aim to Reduce Negative Appendicectomy Rate. 2018;3(1):5.
19. Samudre SS, Munde AS. Comparative study between clinical diagnosis using modified Alvarado score and ultrasound imaging in decreasing negative appendectomy rate. Int Surg J [Internet]. 2021 Mar 26 [cited 2022 Jan 30];8(4):1185–9. Available from: https://www.ijsurgery.com/index.php/isj/article/view/7323
20. 13_35687lsj161119_121_125.pdf [Internet]. [cited 2022 Jan 30]. Available from: http://www.lifesciencesite.com/lsj/lsj161119/13_35687lsj161119_121_125.pdf
21. Baguley M, Palser T. 514 Audit to Assess Negative Appendicectomy Rate (NAR) in Adult Patients in The Leicester Royal Infirmary (LRI). Br J Surg [Internet]. 2021 May 1 [cited 2022 Feb 1];108(Supplement_2):znab134.442. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/bjs/znab134.442
22. Javanmard-Emamghissi H, Hollyman M, Boyd-Carson H, Doleman B, Adiamah A, Lund JN, et al. Antibiotics as first-line alternative to appendicectomy in adult appendicitis: 90-day follow-up from a prospective, multicentre cohort study. Br J Surg [Internet]. 2021 Nov 11 [cited 2022 Jan 31];108(11):1351–9. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/bjs/article/108/11/1351/6363089
23. Chan J, Fan KS, Mak TLA, Loh SY, Ng SWY, Adapala R. Pre-Operative Imaging can Reduce Negative Appendectomy Rate in Acute Appendicitis. Ulster Med J. 2020 Jan;89(1):25–8.
24. Singh A, Parihar US, Kumawat G, Samota R, Choudhary R. To Determine Validation of RIPASA Score in Diagnosis of Suspected Acute Appendicitis and Histopathological Correlation with Applicability to Indian Population: a Single Institute Study. Indian J Surg. 2018 Apr;80(2):113–7.
25. Ramakrishnan R, Ravindrakumar C, Kannappan K, Raj R. strategies in the management of Acute Appendicitis among South Indian population - Comparison of modified Ripasa and Alvarado scores. 2021 Jul 1; International Journal of Current Research and Review Original Research DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.31782/IJCRR.2021.131414
26. T M, Gt P, A V, Ag C, D S. Incidence, Clinical Features and Complications in Patients with Appendicolith Associated Acute Appendicitis. International Journal of Current Research and Review Original Research DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.31782/IJCRR.2021.131028
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License