IJCRR - 7(19), October, 2015
Pages: 65-70
Date of Publication: 10-Oct-2015
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
EFFECT OF SUPPORTED STANDING ON FUNCTIONAL ABILITY IN PATIENTS WITH ACUTE STROKE: A SINGLE-BLINDED RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL
Author: Rehani Dhara Rakesh, Mahesh Hegde, Purusotham Chippala
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Early Mobilization improves the functional ability and the balance in acute stroke subjects. Supported standing is a common adjunct treatment procedure in early mobilisation of acute stroke individuals who have insufficient lower limb strength, poor trunk to stand actively. Objectives of the Study: To determine the effect of supported standing on functional ability in patients with acute stroke. Study design: Single-blinded Randomized Controlled Trial. Study setting: University teaching hospital in Mangalore. Methodology: Fifty stroke subjects were equally randomized to either the intervention or the conventional group. The Intervention group received the support standing along with the conventional therapy. Supported standing was done with the help of assistive devices like tilt table, standing frame. Thirty minutes of supported standing (based on the tolerance of the patient) with frequent rest periods were given, once in a day for 5 days per week for 2 weeks. Outcome Measures: Functional ability was measured by the River mead Motor Assessment Gross Function Subscale and the Berg Balance Scale. Results: The results of this study showed that the River mead Motor Assessment Gross Function Subscale and the Berg Balance Scale were statistically significant for both within and between group comparison (p< 0.05). Conclusions: The present randomized controlled trial study concludes that the supported standing along with the conventional therapy is more effective than the conventional physiotherapy alone in improving functional ability in patients with acute stroke.
Keywords: Supported standing, Functional ability, Motor recovery, Stroke, Early mobilization
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Stroke is the second leading cause of mortality and morbidity in India.The overall age adjusted prevalence rate of stroke in India is estimated range of 44-843/100,000 population and the age adjusted annual incidence (per 100,000 population) is 152.1 Stroke often results in problems of the weakness of one side of the body part, postural instability and immobility related complications like pressure sores, shoulder pain, urinary tract infection, chest infection, deep vein thrombosis, fall and depression may impair the function ability and balance. 2-4 During the acute stroke phase, 70 to 80% of subjects demonstrate mobility problems in ambulation. In such cases early and frequent out of bed activities like, sitting, supported standing with the use of supportive devices may be included in the acute stroke patients. 5 Supported standing is a common adjunct treatment procedure in early mobilization of acute stroke individuals who have insufficient lower limb strength, poor trunk to stand actively. 5-7 Supported standing reinforces the antigravity muscles and can be used to retrain trunk control, to improve or maintain standing ability and in preparation for gait training. 8-11 Supported standing also provides a prolonged weight-bearing stretch to the hip, knee and ankle flexors and is often used to manage muscle length and spasticity. 12, 13 Supported standing has a few harmful effects that include hip fracture, increased pain and spasms and symptoms of hypotension. 8-10 It also places additional demands on individuals, therapists and caregivers. Supported standing requires great commitment, time and availability of resources and ease of use of standing equipment impact on its success. 9-11 Based on the study outcomes from Bagley et al 14 and Ferrarello et al, 6 there is fair evidence to suggest that supported standing treatment in conjunction with traditional physical therapy for post stroke, does not improve functional ability including mobility and balance compared to traditional physical therapy alone.
Need for the Study
Very few Randomized control trials were conducted to address the effect of supported standing on functional ability in acute stroke subjects. Most of the published randomized control trial states that the supported standing practice is not above and beyond beneficial than the conventional physiotherapy for improving the motor function and mobility in subjects with acute stroke. 15 The need of this study is therefore to determine whether the provision of supported standing practice will increase the functional ability post stroke.
Objectives of the Study
To determine the effect of supported standing on functional ability in patients with acute stroke.
Methodology
The study was a single blinded, randomized controlled trial. The subjects were selected from the stroke population group satisfying the inclusion criteria from the Department of Medicine and Neurology of Justice K S Hegde Charitable Hospital, Mangalore.
Inclusion Criteria
The subjects included were above 18 years. Adults with acute stroke, subjects with both ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke, they were able to react to verbal commands, both the sex, medically stable subjects.
Exclusion Criteria
The subjects were excluded if they had unstable cerebral perfusion, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus and hypertension, associated cardiac problems, associated problems in the lower limb (e.g., deep vein thrombosis), any orthopaedic conditions (e.g., arthritis, fractures, etc.), if the physiological variables (blood pressure, oxygen, heart rate, temperature) go beyond set safety limits and patients with severe fatigue.
Method of Data Collection
The total number of fifty subjects fulfilled the inclusion criteria were randomly allocated equally to either of two groups by the computer generated randomization procedures using concealed opaque envelopes. Where group one received the supported standing along with the conventional therapy and group two received the conventional therapy. The Intervention group received the supported standing and conventional therapy. Supported standing was done with the help of supportive devices like tilt table, standing frame, brace or walker. Protocol Involved physiological monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and temperature before, during and after making the patient stand. 6, 14-16 The subjects were given thirty minutes of supported standing (based on the tolerance of the patient) with frequent rest periods in between. Thirty minutes of supported standing (based on the tolerance of the patient) with frequent rest periods were given, once in a day for 5 days per week for 2 weeks. The Conventional therapy group received routine stroke unit care, including, positioning, active and passive movements, activities within the bed (strengthening exercises, balance exercises in sitting), postural awareness and education. Both the group, subjects were received thirty minutes of the conventional therapy, once in a day for 5 days per week for 2 weeks.
Outcome Measures
The River mead Motor Assessment Gross Function Subscale and the Berg Balance Scale were selected as an outcome measure for this study. The River mead Motor Assessment Gross Function Subscale is one of the most commonly used quantitative measure of the functional ability in stroke subjects.It has excellent intraand inter-rater reliability and constructs validity. It contains a 13-point measure of gross function which can be completed by direct observation and include a range of activities from turning over in bed to running. 17 The Berg Balance Scale is considered a psychometrically sound measure of balance impairment in stroke subjects. It is a 14 item scale; it measures both the static and dynamic components of balance in various functional mobility activities. 18, 19 Outcome measures were taken before starting of the study at baseline, at the end of the first week and at the end of the second week.
Ethical clearance
The study was approved by the Central Ethical Committee of the Nitte University (Ref: NU/CEC/P.G.44/2013). Signed informed consent was obtained from all subjects, or their representatives at the beginning of the study
Statistical Analysis
Descriptive statistics were used to provide information about the subject’s baseline and clinical characteristics and to assess River mead Motor Assessment Gross Function Subscale, Berg-Balance Scale in acute stroke subjects. Continuous data were presented as mean and standard deviation and categorical data were presented as number and percentage. The differences of these characteristics among the group were analysed by using the Independent Student t-test for continuous and the chi-square test for ordinal and categorical variables respectively. Non-parametric analysis of the intra-group and between group comparison of admission, at the end of the first week, at the end of the second week for the River mead Motor Assessment Gross Function Subscale and Berg-Balance Scale were analysed by the Wilcoxon signed rank test and the Mann-Whitney U-test, respectively. All analyses were performed using the Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS), version 16.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The significance level was set at P 0.05).
RESULTS
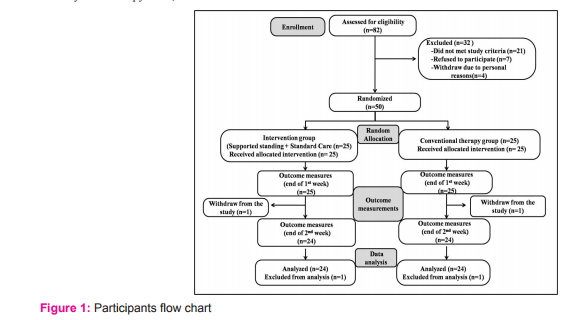
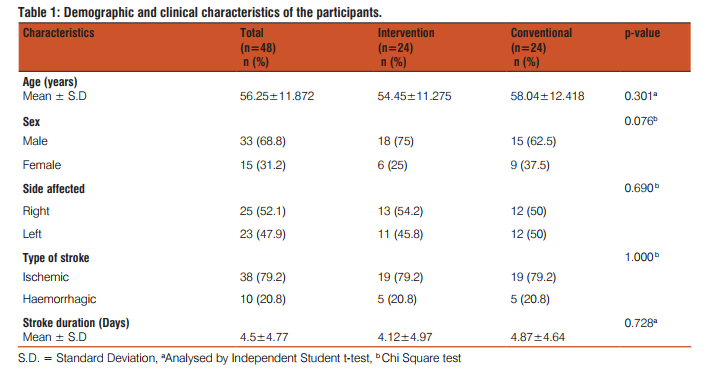
A total of eighty-two stroke subjects were screened for eligibility during the period of August 2013 to March 2014. Fifty stroke subjects were randomized (mean age = 56.25 years, standard deviation (SD) = 11.872) into two groups with equal numbers in each group. Two subjects were withdrawn from the study (one in each group) due to personal reasons. Recruitment and participant flow chart is given in figure 1. Descriptive statistics of the characteristics were represented in table-1, all demographic and clinical characteristics were equally distributed among the groups (p>0.05).Table 2 shows the change scores (1st week - admission) in the River mead Motor Assessment Gross Function Subscale obtained similar scoring for the Intervention group (median=2, Inter quartile range (IQR) =2-3) and the Conventional group (median=2, IQR=1-2) and change scores (2nd week - admission) in River mead Motor Assessment Gross Function Subscale obtained higher scores for the Intervention group (median=4, IQR=3.25-5.75) and the Conventional group (median=3, IQR=3-4). In between-group comparison, showed that improvement in the River mead Motor Assessment Gross Function Subscale scores were statistically high significant (P<0.05) for the Intervention group than the Conventional group. Table 3 illustrates the change scores (1st week - admission) in Berg Balance Scale measurements were higher for the Intervention group (median=13.5, Inter quartile range (IQR) =11-23) than the Conventional group (median=8, IQR=3.25- 8) and change scores (2nd week - admission) in Berg Balance Scale measurements were higher for the Intervention group (median=38, IQR=37-41.5) than the Conventional group (median=23.5, IQR=14.25-32.75). In between-group comparison, showed that the Intervention group obtained statistical high significance for the Berg Balance Scale measurements (p<0.001).
DISCUSSION
The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of supported standing on functional ability in patients with acute stroke. The results of this study show that the functional ability and the balance are statistically significant for both within and between groups. Therefore, we can say that supported standing is effective on functional ability in patients with acute stroke. The current study doesn’t support the findings of the most recent randomized controlled trial conducted by Ferrarello and colleagues (2015), the authors stated that supported standing practice is not above and beyond beneficial than conventional physiotherapy for improving the motor function and mobility in subjects with acute stroke. 6 The current randomized controlled trial study is not in line with the Bagley and colleagues, their study result states that both the standing frame with conventional physical therapy group and the conventional physical therapy group resulted in outcomes that were equally effective. 14 The current study supports the findings of Rhoda Allison et al. 15 did a Pilot randomized controlled trial to investigate whether supported standing enhances functional ability in post stroke patients. The study results demonstrated that the gross functional tool section of the River mead Motor assessment achieved higher median scores. In addition the Berg Balance Scale reflected higher scores at the completion of study. So it is possible that the differences, which were detected, can be the reflection of the sample bias. We can infer that making the stroke subjects mobilizing out of the bed reduces most of the secondary complications like pressure sores and contractures which might be the reason for early functional recovery. 20-22 It also has an impact on better communication as well as increased confidence which adds on early recovery. Moreover, standing is the pre-requisite for walking, so achieving independent standing must have improved the functional outcome. In the present study, step-wise process to gradually raise the patient into standing position on tilt-table was used which may have served effective in the treatment of orthostatic intolerance, thereby increasing the time of weight-bearing and influencing balance and functional ability. Lastly, as per the results of the present study, the findings of within and between-group differences analysed through the Wilcoxon sign test and the Mann Whitney U-test shows statistical significance. Hence, we accept our experimental hypothesis which states that the supported standing (in addition to the conventional therapy) is more effective than the conventional therapy alone in improving functional ability in acute stroke patients.
Strengths: Randomization, concealed allocation, blind subjects, between group comparisons with adequate sample size. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics were distributed equally among the groups.
Limitations: Assessor blinding, blinded therapists, Agestrata and adequate follow-up and dominance factor were not considered.
Future Studies Suggestions
Similar studies can be carried out with the other neurological conditions such as multiple sclerosis and spinal cord injuries, standing may be carried out with other aims considering its potential effects on other parameters (e.g. respiration, bladder and bowel function, skin integrity, psychological wellbeing, arousal, sleep, oxygen saturation, etc.)
CONCLUSIONS
The present randomized control trial study concludes that the supported standing along with the conventional physiotherapy is more effective than the conventional physiotherapy alone in improving functional ability and balance in patients with acute stroke.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank and appreciate all of the stroke subjects and their family members who has given voluntary consent and participated in this study. The investigators of this study would like to acknowledge the support of the clinical staff at the KS Hegde Charitable Hospital, Mangalore, Nitte University; we also would also like to thank Dr. Sanal, Ph.D. for Statistical Analysis. The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Source of Funding This research received no specific grant or source of financial support from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflict of Interests The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and /or the publication of this article.

References:
1. Wasay. M, Katri IA, Subhash Kaur. Stroke in South Asian countries. Nature Reviews Neurology 2014; 10:135-143.
2. Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M, Davis SM; Stroke. Lancet 2008; 371:1612-23.
3. Pandian JD, Kaur A, Jyotsna R, Sylaja PN, Vijaya P, et al. Complications in Acute Stroke in India (CAST-I): A Multicenter Study. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases 2011:21:695-703.
4. Langhorne P, Stott DJ, Robertson L, MacDonald J, Jones L, McAlpine C, Dick F, Taylor GS, Murray G. Medical complications after stroke: a multicenter study. Stroke 2000; 31:1223-9.
5. Bernhardt J, Dewey H, Thrift A, Collier J, Donnan G: A Very Early Rehabilitation Trial for Stroke (AVERT) –phase II safety and feasibility. Stroke 2008; 39: 390-396.
6. Ferrarello F, Deluca G, Pizzi A, Baldini C, Iori F, Marchionni N and Di Bari M. Passive standing as an adjunct rehabilitation intervention after stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Physiotherapy 2015; 5: 2. DOI 10.1186/s40945-015-0002-0.
7. Chang AT, Boots R, Hodges PW and Paratz J. Standing with assistance of a tilt table in intensive care: A survey of Australian physiotherapy practice. Aust J Physiother 2004; 50: 51-54.
8. Meredith Newman, Karen Barker. Systematic review on the effect of supported standing in upper motor neuron disorders. Clin Rehabil 2012; 26: 1059-1077.
9. Glickman LB. A systematic review of supported standing programs. J Pediatr Rehabil Med. 2010; 3:197-213.
10. Garland SJ, Willems DA, Ivanova TD, Miller KJ. Recovery of standing balance and functional mobility after stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2003; 84:1753-9.
11. Yocheved Laufer, Dalia Sivan, Rachel Schwarzmann and Elliot Sprecher. Standing balance and functional recovery of patients with right and left hemiparesis in the early stages of rehabilitation. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 2003; 17: 207-213.
12. Singer B, Dunne J, Singer K, Jegasothy G and Allison G. Nonsurgical management of ankle contracture following acquired brain injury. Disabil Rehabil 2004; 26: 335-345.
13. Richardson D. The use of the tilt-table to effect passive tendoachillis stretch in a patient with head injury. Physiother Theory Pract 1991; 7: 45-50.
14. Bagley P, Hudson M, Forster A, Smith J, Young J. A randomized trial evaluation of the Oswestry Standing Frame for patients after stroke. Clin Rehabil 2005; 19: 354-364.
15. Allison R and Dennett R. Pilot randomized controlled trial to assess the impact of additional supported standing practice on functional ability post stroke. Clin Rehabil 2007; 21: 614–619.
16. Baltz M, Lietz HL, Trott-SausserI, Kalpakjian C, Brown D. Tolerance of a tilt table protocol in an in-patient stroke unit setting: a pilot study. Journal of Neurologic Physical Therapy 2013; 37: 9-13.
17. Yesim Kurtais, Ayse Kucukdeveci, Atilla Elhan et al. Psychometric properties of the river mead motor assessment: Its utility in stroke. J Rehabil Med 2009; 41: 1055-1061.
18. Lisa Blum, Nicol Korner- Bitensky. Usefulness of the Berg Balance Scale in Stroke Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review. Physical Therapy 2008; 88: 559-566.
19. Stevenson TJ. Detecting change in patients with stroke using the Berg Balance Scale. Aust J Physiother 2001; 47: 29-38.
20. Diserens K, Moreira T, Hirt L, Faouzi M, Grujic J, Bieler G, et al: Early mobilization out of bed after ischemic stroke reduces severe complications but not cerebral blood flow: a randomized controlled pilot trial. Clin Rehabil 2011; 26: 451-459.
21. Bernhardt J, Dewey H, Thrift A, Collier J, Donnan G: A Very Early Rehabilitation Trial for Stroke (AVERT)–phase II safety and feasibility. Stroke 2008; 39: 390-396.
22. Chippala P, Sharma R. Effect of Very Early Mobilisation on Functional Status in Patients with Acute Stroke: A Singleblind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin Rehabil 2015. DOI: 10.1177/0269215515596054.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License