IJCRR - 14(3), February, 2022
Pages: 53-59
Date of Publication: 01-Feb-2022
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Detection of COVID-19 from Chest X-ray Images using Concatenated Deep Learning Neural Networks
Author: Tharun Pranav S V, Anand Jeyasingh
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The severity of COVID-19 disease can be viewed from the massive death rate recorded worldwide so far. The majority of increase in death rate is due to late identification of disease. Aim: To detect COVID-19 from Chest X-ray images using concatenated Deep Learning Neural Networks Xception with ResNet152V2 and Xception with EfficientNet-B7. Materials and Methods: This work on Deep Learning (DL) system proposes the concatenation of two DL networks to identify COVID-19 using X-ray images. They are Xception with ResNet152V2 and Xception with EfficientNet-B7. Initially, the input X-ray images are performed with pre-processing. The pre-processed images are given to Xception with ResNet152V2 or Xception with EfficientNet-B7. Various features are extracted from these two networks. The output features from Xception and ResNet152V2 or EfficientNet-B7 are concatenated. The concatenated features are then given to the classifier for the classification of COVID-19. Results: The implementation has been performed on Google Colab using the neural networks with Keras library with a usage of upto 12.69 GB RAM. The average accuracy for COVID-19 is 62% and 60% using concatenated Xception with EfficientNet-B7 and concatenated Xception with ResNet152V2 respectively. Conclusion: The proposed concatenated nets provide better results for 15-epoch with a batch size of 5. With an increase in epoch and batch size the accuracy of the proposed method will be increased upto 99.7%.
Keywords: COVID-19, Deep Learning, EfficientNet-B7, ResNet152V2, Xception, X-ray images
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
COVID-191,2,3 roots to critical respiratory distress. Computer tomography (CT) scan, Lung ultrasound (LUS) and chest X-ray (CXR) are the commonly used imaging approaches to identify COVID-19 infections. 4 CT scan or X-ray helps to diagnose the severity information of COVID-19. Due to the involvement of the respiratory system, chest CT is firmly used to identify or find COVID-19 cases, but the cost of CT scan is high compared to X-ray.5,6
Currently, automation of severe infected regions in chest X-ray are in need of development. X-ray images helps to identify COVID-19 patients. 7 However manual delineation of X-ray images are challenging to experts. Hence a consistent automated algorithm to classify COVID-19 X-ray images are required to support the experts.
Further8, visual analysis of X-ray images may lead to misinterpretation between COVID-19 and pneumonia on a huge number of patients. Major drawback in the analysis of medical images is that, most of the X-ray images used for diagnostic purposes are not openly accessible due to privacy concerns, which means that the results from neural network training on any particular one dataset cannot be replicated or applied in other hospitals.
Deep9,10 learning approaches in medical images plays a vital role in reliable analysis. Deep learning based medical image analysis, classifies the images with highly similar features.11,12 Recently several deep learning based approaches are used for the diagnosis of COVID-19. 13 Pretrained deep learning models, classifies the test images with 0.93 validation accuracy based on DenseNet 201.
The deep learning models14,15,16 using LUS images were studied. 15 The classification based on ResNet18, ResNet50, Squeeze Net and DenseNet161 were performed for classification on Chexpert dataset.
Recently systems were developed based on deep learning techniques using different medical imaging modalities such as CT and X-ray. Research on deep learning approach with high sample efficiency based on self-supervision and transfer learning has been done for the Database of hundreds of X-ray scans of COVID-19 positive cases. 17 Furthermore, in a library of 1,521 pneumonia patients including COVID-19 X-ray images, predictions were made on COVID-19, pneumonia and normal classes. Due to the lack of availability COVID-19 patients X-ray images, detailed studies reporting solutions for automatic detection of COVID-19 from X-ray images are not available.
18 Radiologists faces a challenging issue in X-ray images to identify COVID-19 and other infections. This implies that challenges for radiologists in specifically identifying COVID-19 infections using X-ray images is a need in current scenario. In this work, the X-ray images of COVID-19 patients were distinguished and performance comparison of two concatenated nets were analyzed to identify its effectiveness.
The following are the major contribution of this work.
-
Propose a concatenated network of Xception with ResNet152V2 to identify COVID-19.
-
Propose a concatenated network of Xception with EfficientNet-B7 to identify COVID-19.
-
Analyse the performance between above two concatenated networks.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 1 discusses on introduction to the work followed by the work done in this area. Section 2 explains the proposed concatenated neural network. Section 3 elucidate the results and discussions of the proposed work. Finally, section 4 concludes the paper.
PROPOSED METHOD
Raw datasets
The images used for the experiment were taken from the kaggle data sets. An infectious disease, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) causes severe acute respiratory syndrome. The outbreak was officially recognized as a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) on 11 March 2020. Currently Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is used for diagnosis of the COVID-19. X-ray machines are hugely available to diagnose COVID-19 at early stages. Dataset is organized in two folders as train and test in Kaggle. Both train and test contain 3 subfolders including COVID19, PNEUMONIA and NORMAL X-rays.
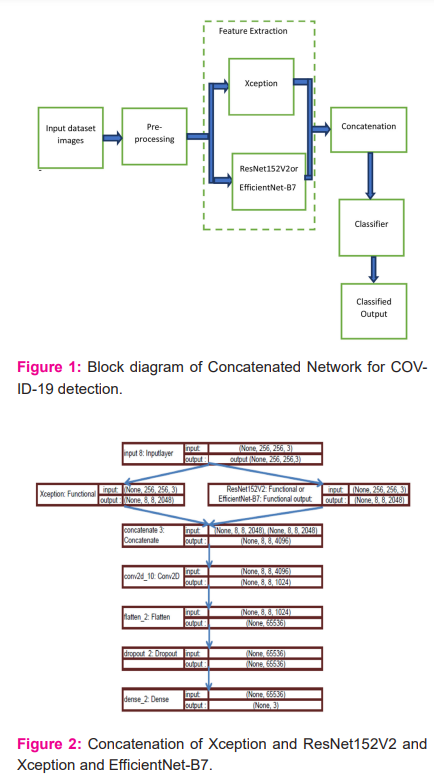
Block diagram
The overall process of the proposed concatenated network for COVID-19 detection is shown in Figure 1. Initially, the input images are performed with pre-processing operation. The output from the pre-processing is given to Xception with ResNet152V2 or EfficientNet-B7 for extracting the features.
The extracted features are concatenated and then the concatenated feature is given to the classifier to diagnose COVID-19.
The following process are carried out for the classification of COVID-19 X-ray images.
-
Experimental data analysis and pre-processing: Initially the datasets are characterized, and grouped into classes.
-
Concatenation: Xception with ResNet152V2 features are extracted from the pre-processing X-ray images. The features are concatenated to obtain the training parameters and weights from the network and applied to the training of the target data set.
-
Target dataset training: The pre-trained concatenated model is applied to the target data set to improve the classification accuracy.
-
Classification: Experiments are performed on tuned model, and then applied to the test set to obtain the classification outputs.
The above process is repeated for Xception with EfficientNet-B7.
Data analysis and pre-processing
To enhance the classification performance, the experimental data need to be pre-processed. The pre-processing of dataset includes image scaling and split the images for train and test.
i. Image scaling
X-ray images in raw format are converted to png format, and if the image is already in png format, the same format is used. The original X-ray images in dataset is performed to an image scaling before given to the training. Each image in dataset is adjusted to the resolution of 255 × 255 pixels.
ii.Grouping:
The full test dataset has 11302 images, where 31 images are COVID-19, 4420 images are pneumonia and 6851 images are normal cases. Around 6% of the total images are used for testing purposes and remaining images are used for training purposes. To improve the data identification, this work uses the expansion techniques of 360-degree rotation, zoom, horizontal flip and vertical flip.
Concatenation of neural network
To identify COVID-19 from chest X-ray, the features of lungs need to be extracted. The classification accuracy in X-ray mainly depends in the feature extraction. Generally deep feature extraction will be followed in regular learning strategies. 19,20 In this work, the features extracted from Xception with ResNet152V2are Concatenated to extract the general features and applied to the target dataset for better classification. 19,21 Also, the Xception with EfficientNet-B7 features are concatenated for classification as shown in Figure 2.
Xception generates a 10 x 10 x 2048 feature map on its last feature extractor layer from the input image, and ResNet152V2 or EfficientNet-B7 also produces the same size of feature map on its final layer as shown in figure 2. As both networks generate the same size of feature maps, the features were concatenated by using both of the inception-based layers and residual-based layers of EfficientNet-B7. Hence, the quality of the generated semantic features would be enhanced. A concatenated neural network is designed by concatenating the extracted features of Xception with ResNet152V2 and Xception with EfficientNet-B7 and then connecting the concatenated features to a convolutional layer that is connected to the classifier. The kernel size of the convolutional layer is then added after the concatenated features was 1 x 1 with 1024 filters and no activation function. This layer has been used to extract the valuable semantic feature from the features of a spatial point among all channels, where each channel is a feature map. This convolutional layer helps the network learn better from the concatenated features extracted from Xception with ResNet152V2 and Xception with EfficientNet-B7.
RESULTS
In this work, two open-source datasets were chosen. The first COVID-19 dataset, were taken from GitHub (https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset)and second dataset has been taken from (https://www.kaggle.com/c/rsna-pneumonia-detection -challenge). In this dataset, only X-ray images are considered
Parameters and functions
The following table 1, gives the parameters and functions used to train the network.
From table 1, it has been observed that, the network was trained using Categorical cross-entropy loss function and Nadam optimizer. For the concatenated network Xception with ResNet152V2 and Xception with EfficientNet-B7, the batch size chosen is 5. Each concatenated network has been trained for 15 epochs. As there are 8-training phases, the models were trained for 15 epoches. In addition, data augumentation methods are used in this work to improve the efficiency of training and to reduce the over fitting.
These concatenated Networks were implemented using Keras library on a Tesla T4 GPU with 12.69 GB that were provided by Google Collaboratory Notebooks Pro. The software used for this work is Python 3.8. This work has been validated using 11,302 images. Out-of 11,302 X-ray images, 31 images are COVID-19, 4420 images are pneumonia and 6851 images are normal cases.
Training and analysis
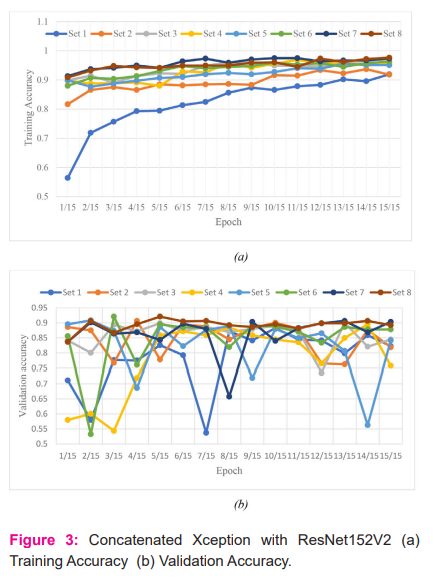
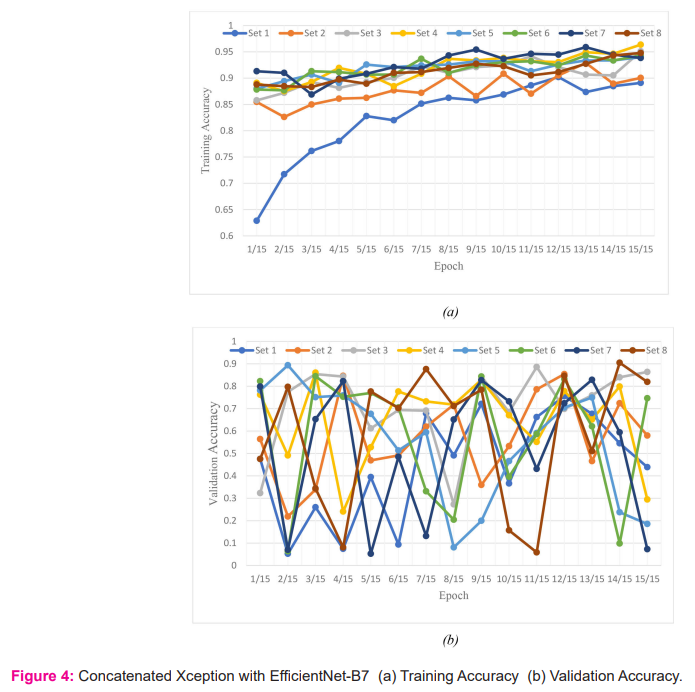
All the X-ray images in database were trained and tested. The parameters training and validation accuracy are measured initially for concatenated Xception with ResNet152V2 and Xception with EfficientNet-B7. Training accuracy is the accuracy measured when applying the model on the training data, while validation accuracy is the accuracy for the validating data. Training accuracy and validation accuracy for each epoch for all the sets are measured and is shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4 for concatenated Xception with ResNet152V2 and Xception with EfficientNet-B7 respectively.
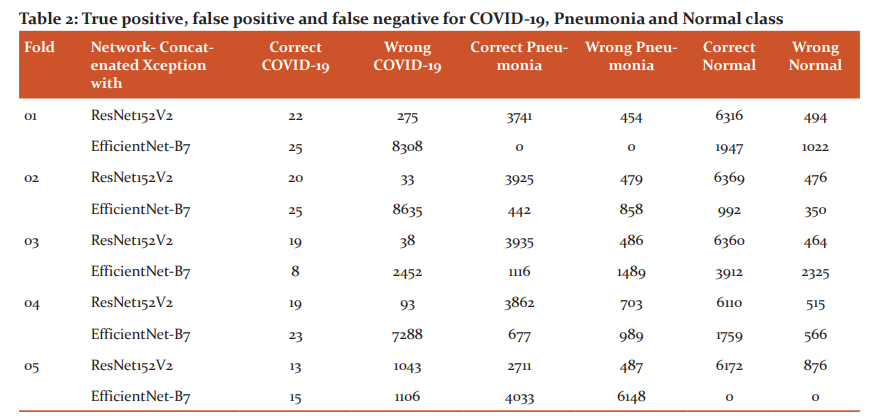
Table 2 reports the true positive, false positive and false negative for COVID-19, pneumonia and normal class using concatenated Xception with ResNet152V2 and Xception with EfficientNet-B7.
True positive is the number of correct images classified by the network, False positive is the number of wrong classified images by the network, False Negative is the number of images detected as another class by the network and True negative is the number of images not belonging to a class and network classified as not belonging to a class. From the table 2, it has been observed that, EfficientNet-B7 provides better true positive compared to concatenated Xception with ResNet152V2 except third fold for COVID-19. For pneumonia, concatenated Xception with ResNet152V2 provides better performance compared to concatenated Xception with EfficientNet-B7. Out of two networks, for COVID-19 detection concatenated Xception with EfficientNet-B7 can be used and for pneumonia, concatenated Xception with ResNet152V2 can be preferred.
The metric considered for evaluation are accuracy, sensitivity and specificity. Accuracy for all the classes is the ratio between number of correctly classified images and number of all images [ref]. Sensitivity and specificity for all classes is given in equation 2 and 3 respectively.
Sensitivity = [True Positive / (True Positive+ False Negative)] * 100 ------2
Specificity = [ True Negative / (False Positive + True Negative)] * 100 -----3
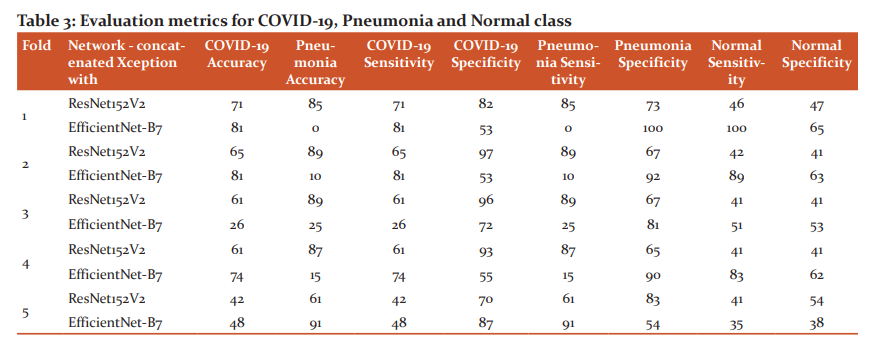
Table 3 gives the COVID-19, pneumonia accuracy, specificity and sensitivity. From the table 2, it has been observed that accuracy for concatenated Xception with EfficientNet-B7 in detecting COVID-19 is high on average compared to concatenated Xception with ResNet152V2. Eventhough the datasets are unbalanced with few COVID-19 cases, the proposed concatenated Xception with EfficientNet-B7 detects better compared to concatenated Xception with ResNet152V2.
DISCUSSION
An effort has been made in this paper, to identify COVID-19 using proposed concatenated Xception with EfficientNet-B7 and Xception with ResNet152V2. Different images like pneumonia, COVID-19 and normal X-ray images have been used in the database to identify COVID-19. Various parameters like true positive, false positive, false negative, accuracy, sensitivity and specificity for COVID-19, pneumonia and normal class X-ray images using concatenated Xception with ResNet152V2 and Xception with EfficientNet-B7 has been computed and compared. From the comparison, it has been observed that concatenated Xception with EfficientNet-B7 shows better performance than Xception with ResNet152V2. Also, the use of different images in the dataset is very effective in identifying COVID-19 using concatenated neural networks.
CONCLUSION
In this work, concatenated neural network Xception with ResNet152V2 and Xception with EfficientNet-B7 for classifying the chest X-ray images into COVID-19, pneumonia and normal were performed. Two open-source datasets were used as mentioned in the above discussions. The training sets are separated into 8-successive phases, with 633 images in each phase. Out of 633 images, each class are with approximately 149 COVID-19, 234 pneumonia and 250 normal images. For 15 epoch and 5-batch size, the average accuracy and sensitivity for COVID-19 is 62% and 62% respectively using concatenated Xception with EfficientNet-B7 which is 2% higher than concatenated Xception with ResNet152V2. Open-source code for Xception, ResNet152V2 and EfficientNet-B7 has been taken from Github and concatenation has been performed between the nets and evaluation were performed. In future, more COVID-19 X-ray images will be added in database to make it balanced and more epoch will be added to improve the accuracy.
Acknowledgement:
-
The Principal and Informatic Practices Teacher of Yuvabharathi Public School, Yuva Enclave Kanuvai, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu 641108for their support in developing the project.
-
Glada Wesley, Mathematics Teacher of Yuvabharathi Public School, Yuva Enclave Kanuvai, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu 641108 for her support in mathematics on deep learning.
Source of Funding: NIL
Conflict of Interest: NIL
Authors’ Contribution:
-
Mr. S V Tharun Pranav1: Proposed a concatenated networks of Xception with ResNet152V2 and Xception with EfficientNet-B7 to identify COVID-19.Analyse the performance between the above two concatenated networks and writing the article.
-
Mr. Anand Jeyasingh2: Interpretation of results and writing the article.
References:
-
Islam MM, Islam MZ, Asraf A, Ding W. Diagnosis of COVID-19 from X-rays using combined CNN-RNN Architecture with transfer learning. medRxiv. 2020.
-
Muhammad LJ, Islam MM, Usman SS, Ayon SI. Predictive data mining models for novel coronavirus (COVID-19) infected patients’ recovery. SN Computer Science. 2020; 1.
-
Islam MM, Karray F, Alhajj R, Zeng J. A review on deep learning techniques for the diagnosis of novel coronavirus (COVID-19). IEEE Access. 2021; 30551–30572.
-
Ning W, Lei S, Yang J, Cao Y, Jiang P, Yang Q, et al. Open resource of clinical data from patients with pneumonia for the prediction of COVID-19 outcomes via deep learning. Nature Biomedical Engineering. 2020; 4. 1197–1207.
-
Harish KB. COVID-19 Pandemic Effect on Social Life of Human. Int J Cur Res Rev. 2021; 12(7).
-
Devarajappa S, Khalida KA, Nagaraja S. Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic on Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHA) in Karnataka: A Empirical Analysis. Int. J. of Current Research and Review. 2021; 13(18).
-
Candemir S, Antani S. A review on lung boundary detection in chest X-rays. Int. J. of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery. 2019; 14. 563–576.
-
Osman AH, Aljahdali HM, Altarrazi SM, Ahmed A. SOM-LWL method for identification of COVID-19 on chest X-rays. PLoS One. 2021; 16(2).
-
Pathak A, Athavale H, Pathak T, Athavale SA. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine and Understanding its Potential for Newer Applications. Int J Cur Res Rev. 2021; 13(16).
-
Harish KB. Perspectives of Using Artificial Intelligence in Preventing and Regulating COVID-19:A Letter to the Editor. Int J Cur Res Rev. 2021; 13(15).
-
Maghdid HS, Asaad AT, Ghafoor KZ, Sadiq AS, Khan MK. Diagnosing COVID-19 Pneumonia from X-Ray and CT Images using Deep Learning and Transfer Learning Algorithms. Multimodal Image Exploitation and Learning. 2021;11734.
-
Mangal A, Kalia S, Rajgopal H, Rangarajan K, Namboodiri V, Banerjee S, Arora C. CovidAID: COVID-19 Detection Using Chest X-Ray. arXiv:2004.09803, 2020.
-
Patel S. Classification of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images using a deep convolutional neural network, Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education. 2021; 12(9). 2643– 2651.
-
Poggiali E, Dacrema A, Bastoni D, Tinelli V, Demichele E, Mateo Ramos PM, Marciano T, Silva M, Vercelli A, Magnacavallo A. Can Lung US Help Critical Care Clinicians in the Early Diagnosis of Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Pneumonia?. Radiology. 2020; 295(3).
-
Fiala MJ. Ultrasound in COVID-19: a timeline of ultrasound findings in relation to CT. Clinical Radiology. 2020; 75(7). 553–554.
-
Peng QY, Wang XT, Zhang LN. Findings of lung ultrasonography of novel coronavirus pneumonia during the 2019-2020 epidemic. Intensive Care Medicine. 2020; 46(5). 849–850.
-
Rahimzadeh M, Attar A. A modified deep convolutional neural network for detecting COVID-19 and pneumonia from chest X-ray images based on the concatenation of Xception and ResNet50V2. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked. 2020; 19.
-
Bressem KK, Adams LC, Erxleben C, Hamm B, Niehues SM, Vahldie JL. Comparing different deep learning architectures for classification of chest radiographs. Nature Scientific reports. 2020.
-
Chollet F. Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions.arXiv:1610.02357. 2017.
-
Elshennawy NM, Ibrahim DM. Deep-Pneumonia Framework Using Deep Learning Models Based on Chest X-Ray Images. Diagnostics. 2020;10(9). 649.
-
Agarwal V. Complete Architectural Details of all EfficientNet Models. towards data science. 2020.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License