IJCRR - 14(3), February, 2022
Pages: 48-52
Date of Publication: 01-Feb-2022
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Utility of Direct Detection of MEC a Gene in Clinical Specimen for Detection of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Author: Sevitha Bhat, Gopalkrishna Bhat K, Shalini Shenoy M, Archana Bhat K, Pooja Rao
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: MRSA: Major cause of health care associated infections (HA-MRSA). The alarming rise in the rates of HA-MRSA reported from this region necessitates the need for a DNA based assay. Real-time PCR: rapid platform or detection of MRSA. The study plans to compare culture to real-time PCR for the detection of MRSA directly in the clinical specimen Objectives: The present study aimed to isolate and identify MRSA from clinical specimen, to detect mec A gene in the clinical specimen and to compare direct detection of mec Agene with culture for Staphylococcus aureus Methods: Cross-sectional hospital based study was undertaken noninvasive samples (blood, deep tissue, aspirated pus, sterile body fluids) received for culture. The results of PCR and culture were compared in terms of sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV. Results: 110 non-duplicate clinical samples were included. MRSA rate: 29%. The rates of isolation were 74.6%: skin and soft tissue infections, 11% from blood stream infections, 10.4% from osteomyelitis cases, 4% respiratory secretions. Antibiotic resistance rates of MRSA ciprofloxacin(75%), clindamycin (51.1%), trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole (59.1%) and erythromycin (62.5%). 100% of the isolates were sensitive to Vancomycin. PCR for MRSA detection: Sensitivity: 97%, Specificity: 98% Discussion: This study demonstrates the utility of a rapid platform: real-time PCR for the detection of MRSA from clinical samples directly on the same day. The results of Gram stain were used as criteria for selection of samples.
Keywords: MRSA, Real time PCR, Direct detection, Antibiotic resistance, Invasive samples, Molecular methods
Full Text:
Introduction
MRSA has emerged as a common healthcare-associated pathogen and is implicated in infections ranging from superficial skin infections to sepsis. HA-MRSA have limited therapeutic options and can be transmitted among patients. The detection of MRSA by conventional methods like culture requires 2 or more days. The real-time PCR platform offers the advantage as a rapid test for detecting MRSA in clinical samples within 2 hours. Thus real-time PCR would enable early detection of MRSA. This approach would supplement the infection control practice by rapidly identifying MRSA strains in clinical specimens directly.
The proposed study was done to compare culture with real-time PCR, using primers specific for S. aureus and MRSA (femA, mecA).
Present knowledge/Background
Staphylococcus aureus is implicated in skin, soft tissue infections and invasive infections like cellulitis, pneumonia, endocarditis, bacteremia, septic shock.1
Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) strains have emerged as a global threat to Infection control. MRSA infections are associated with higher morbidity, mortality and higher costs.
Health care-associated infections (HA -MRSA) are a cause of concern because they are often resistant to multiple classes of antibiotics.2,3
The mechanism of resistance to Methicillin in staphylococcus aureusis by insertion of staphylococcal cassette chromosome carrying mec A gene which encodes for PBP 2 a.4
The overall HA-MRSA prevalence reported in previous studies were 41.9 % in 2008 (Pakistan), 53% in 2011(Thailand).5,6 The INSAR study reported 42% MRSA rates in 2008.7 HA-MRSA rates have increased from 23.9% in 2013 to 30.2% in 2016 in a tertiary care centre in Mangaluru.8
Clindamycin, tetracycline(doxycycline and minocycline), trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole, rifampicin, linezolid and Vancomycin are the antibiotics of choice to deal with MRSA.
The conventional methods employed for MRSA detection are Oxacillin agar screen, Cefoxitin disc diffusion method and Oxacillin broth dilution method. These conventional methods yield false negative and positive results.9, 10
The alarming rise in the rates of HA- MRSA reported from this region necessitates the need for a DNA-based assay, which would provide a solution the detection of MRSA. Rapid detection of MRSA infections would help in better implementation of Infection control practices.11,12
The investigation compares culture with real-time PCR for direct detection of MRSA in the clinical specimen.
Preliminary work
A study was conducted in this setup on HA-MRSA. The prevalence of HA-MRSA in our center was reported as 30.2%. Among these, 54.6% of the HA-MRSA were isolated from skin and soft tissue infections, 8.6% from bloodstream infections and 5.2% from osteomyelitis cases. The antibiotic resistance rates of HA- MRSA were clindamycin (51.1%), trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (59.1%) ciprofloxacin (75%), and 95.5% of the isolates were sensitive to Vancomycin .13
The rate of HA-MRSA is high in this region. Thus there is a need for further studies on rapid detection of MRSA in hospitals.
Aim
To study the usefulness of direct mec A gene detection in clinical samples in the identification of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
Objectives
-
To isolate and identify MRSA from clinical specimen
-
To detect mec A gene in the clinical specimen
-
To compare the results of PCR with culture for the detection of MRSA
Methodology
STUDY SETTING: Department of Microbiology, KMC Hospital, Ambedkar Circle, Mangalore
STUDY DESIGN: Cross-sectional study.
Sample collection
Inclusion criteria: Invasive samples (blood, deep tissue, aspirated pus, bronchoalveolar lavage, sterile body fluids) received for culture with Gram stain suggestive of presence of Staphylococcus
Exclusion Criteria: Samples: swabs, sputum, urine,
STUDY DURATION: 1 year (prospectively).
SAMPLE SIZE: 110 based on the following calculations:
Formula used is N = ( Zα2 pq )/E2 .Z is at 95% confidence, p is the relative precision;
p=37, q is the confidence interval; q=63, E = 20% of the relative precision (p),80% power15
DATA COLLECTION: The clinical details were collected using a proforma from the case sheets of the patients.
DATA ANALYSIS:
Chi-square is done for categorical variables and only those with p-value < 0.05 is statistically significant, following which analyzed data is presented in the form of tables, pie charts and bar diagrams.
Results of PCR were compared with culture in terms of positive predictive value, negative predictive value, sensitivity and specificity
SAMPLE COLLECTION:
Gram stain was performed and the samples were plated onto culture plates and incubated at 370C overnight. Blood culture was done by BacT/Alert 3 D automated system and growth from early subculture was taken. The bacterial growth was identified by standard tests.
ANTIBIOTIC SUSCEPTIBILITY TESTING:
Antibiotic sensitivity testing was done by the Modified Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method and Automated Vitek 2 system. The results were analyzed and interpreted in accordance with Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) recommendations.16 S.aureus ATCC 25923 is used for quality control.
Cefoxitin (30μg) disk diffusion method for used for MRSA detection.
PCR
DNA Extraction: modification of a QIAamp blood and tissue kit (QIAGEN), following the instructions in the kit insert.
Real-time PCR: using Microbial q PCR Assay (Qiagen)
The primer sequence of MecA1 (5´GTA GAA ATG ACT GAA CGT CCG ATAA) and MecA2 (5´CCA ATT CCA CAT TGT TTC GGTCTA A), yielding a 310-bp amplicon, FemB1 (5´TTA CAG AGTTAA CTG TTA CC) and FemB2 (5´ATA CAA ATC CAG CAC GCT CT),
The 20µl real-time PCR reaction with 1X Light CyclerFastsart DNA Master SYBR Green I (containing a modified Taq polymerase with heat-labile blocking groups), 2% DMSO (Sigma), 5 mmol/L MgCl2 and 0.25 µmol/L of each primer. The real-time PCR conditions are an initial step of 95°C for 10 minutes, an amplification program for 40 cycles of 15 seconds at 95°C(denaturation ), and 2 minutes at 60°C with fluorescence acquisition at the end of each extension. (green channel ) 17,18
Results
110 clinical non-duplicate samples were included.
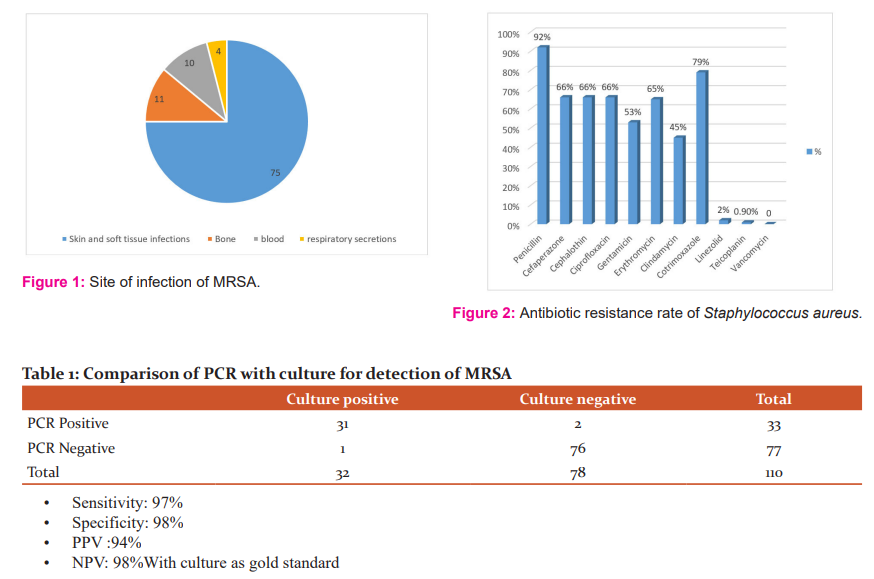
The site of infection of MRSA and the antibiotic resistance rates of Staphylococcus aureus are shown in Figures 1 and 2. The comparison of Culture with PCR is shown in Table 1.
32 out of 110 were culture positive for MRSA and 62 out of 110 were culture positive for MSSA.16 samples had no growth, could be due to antibiotic effect.
74.6%: skin and soft tissue infections,11% from bloodstream infections, 10.4% from osteomyelitis cases, 4% from respiratory secretions Antibiotic resistance rates of the 94 isolates of Staphylococcus aureus: ciprofloxacin (88%), clindamycin (45%), trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (59.1%) and erythromycin (65%), Vancomycin (0%) and MRSA rate: 29%
Discussion
Staphylococcus aureus is implicated in variety of human infections. The problem is emergence of antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. The bug is associated with Healthcare-associated infections and with the increasing rates of MRSA, empiric use of Vancomycin has increased in the past few years. Rapid test to detect MRSA would be a crucial step in restricting the use of glycopeptides as empiric therapy.19
The infections associated with Staphylococcus aureus include skin and soft tissue infections and bacteremia (62%, 42%). In our study the isolation rates of Staphylococcus aureus were, 75%: skin and soft tissue infections, 11% from bloodstream infections, 10.4% from osteomyelitis cases, 4% respiratory secretions. The findings are similar to the previous studies with skin and soft tissue as common sites of infections caused by this pathogen.20
Antibiotic resistance rates of Staphylococcus aureus reported in other studies revealed high rates of resistance to Penicillin (88%), beta-lactam (53%), macrolides (52%) and fluoroquinolones (79%). Resistance to Clindamycin was 17% and no resistance was reported to Linezolid and Vancomycin.
MRSA rate was 29%, it is similar to the studies published earlier. The rate of MRSA isolated from invasive infections was 41% in the previous studies. The prevalence of MDR Staphylococcus aureus was 54%. MRSA rates in this study on blood and invasive samples was high.21
With this rate of MRSA creeping up, especially in the health care settings, the potential utility of its rapid detection is essential.
In this study conducted, rapid detection of MRSA directly on the clinical specimen had a sensitivity of 97% and specificity of 98% respectively compared to culture.
The potential advantage of this approach would be early detection of MRSA (within hours) compared to culture (2-3 days). This test would minimize the use of Vancomycin as empiric therapy in health care settings. Thus the test could be a magic bullet in the era of Antimicrobial Stewardship.22,23
Real-time PCR for the direct detection of MRSA in clinical samples have a sensitivity of 82-100% and specificity ranging from 94-100%. The findings of our study are in par with the above findings. 24
2 samples with no growth in culture were positive for MRSA by PCR. It could either be a false-positive result in PCR or due to prior antibiotic therapy administered. 1 sample was negative by PCR and culture positive for MRSA. This fact could be attributed to PCR inhibitors in the sample.
The limitations in our study were the limited number of samples tested. Utility of this test in respiratory samples is limited as it requires clinical correlation.
The findings of the study have gathered information regarding rate of MRSA in clinical specimens using the technique proposed to adapt. Early detection of MRSA will help to identify appropriate antibiotic for early treatment which will reduce morbidity and mortality.
This approach would aid in the implementation of appropriate infection control measures to curtail the spread of MRSA in our setup.
Conclusion:
Real-time PCR is a rapid sensitive assay for the detection of antibiotic resistance genes. Rapid detection of MRSA directly in the clinical specimen is a tool for better patient care and efficient implementation of infection control practices. The appropriate antibiotic can be started at the earliest.
Acknowledgement The authors are grateful to Manipal Center for Infectious Diseases (MAC ID) PSPH, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal and Manipal Academy of Higher education for the grant and support
Source of funding: MACID seed grant 2017-18 MAC ID/SGA/2017/1
Conflict of Interest: None
Authors’ Contribution:
Dr Sevitha Bhat: idea, execution and writing of the work
Dr Gopalkrishna Bhat K: idea, execution of the study
Dr Shalini Shenoy Mulki: execution and writing
Dr Archana Bhat K: writing of the study
Dr Pooja Rao: execution of the work
References:
-
Stefani S, Goglio A. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: related infections and antibiotic resistance. Int J Infect Dis. 2010;14(4):19-22.
-
Fomda B A, Thokar M A, Bashir G, Khan A, Kour A, Zahoor D et al. Revalence and genotypic relatedness of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a tertiary care hospital. J Postgrad Med 2014; 60:386-9.
-
Sharma NK, Garg R, Baliga S, Bhat KG. Nosocomial infections and drug susceptibility patterns in methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Diagn Res 2013; 7:2178-80.
-
Navratna V, Nadig S, Sood V, Prasad K, Arakere G, Gopal B. Molecular basis for the role of Staphylococcus aureus penicillin-binding protein-4 in antimicrobial resistance. J Bacteriol 2010;192(1): 134-144.
-
Chen CJ, Huang YC. New epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus infection in Asia. Clin Microbiol Infect 2014;20:605-23.
-
Mendes RE, Mendoza M, Bangh Singh KK, Castanheira M, Bell JM, Turnidge JD et al. Regional surveillance program results for 12 Asia pacific regions (2011). Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2013 : 57: 5721-26.
-
Gopalakrishnan R, Sureshkumar D. Changing trends in antimicrobial susceptibility and hospital-acquired infections over an 8-year period in a tertiary care hospital in relation to the introduction of an infection control program. J Assoc Physicians India. 2010;58(Suppl):25–31.
-
Pai V, Rao VI, Rao SP. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus [MRSA] Isolate at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Mangalore, South India. J Lab Physicians. 2010;2(2):82-84.
-
Mohanasoundaram KM, Lalitha MK. Comparison of phenotypic versus genotypic methods in the detection of methicillin-resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Indian J Med Res 2008;127(1): 78-84.
-
Pillai MM, Latha R, Sarkar G. Detection of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus by polymerase chain reaction and conventional methods: a comparative study. J Lab Physicians 2012; 4(2): 83-88.
-
Fang H, Hedin G. Rapid screening and identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from clinical samples by selective-broth and real-time PCR assay. J Clin Microbiol 2003; 41: 2894–2899.
-
Hagen RM, Seegmuller I, Navai J, Kappstein I, Lehn N, Miethke T. Development of a real-time PCR assay for rapid identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from clinical samples. Int J Med Microbiol 2005; 295: 77–86.
-
Kumari J, Shenoy S, Baliga S, Chakrapani M, Bhat GK. Healthcare-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clinical characteristics and antibiotic resistance profile with emphasis on macrolide –lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance. Sulthan Qaboos University Med J. 2016;16:175-81.
-
Kumari J, Shenoy S, Mahabala C, Vidyalakshmi K, Bhat GK. Susceptibility pattern of healthcare-associated methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus to Vancomycin and Daptomycin. Int J Infect Dis 2016; 45 (suppl 1): 101-2
-
Huletsky A, Giroux R, Rossbach V. New real-time PCR assay for rapid detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus directly from specimens containing a mixture of staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol2004; 42: 1875–84
-
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute M100-S25: Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing – Twenty–fifth informational supplement
-
Richard IJ, Janae DL, Stephen VA, Debra M. Rapid Extraction from and Direct Identification in Clinical Samples of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococci Using the PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 2000; 38:9: 3407–12.
-
Suzanne MP, Anna CP, Donna MH, Adrienne GF, Richard BT, Jr., Karen L et al. Direct Detection of Staphylococcus aureus from Adult and Neonate Nasal Swab Specimens Using Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction. J Mol Diagn. 2004; 6:3:.191-95.
-
Holfelder M, Eigner U, Turnwald AM, Witte W, Weizenegger M, Fahr A. Direct detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in clinical specimens by a nucleic acid-based hybridization assay. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006;12(12):1163-7.
-
Tong SY, Davis JS, Eichenberger E, Holland TL, Fowler VG Jr. Staphylococcus aureus infections: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015;28(3):603-661.
-
Jonas D, Speck M, Daschner FD, Grundmann H. Rapid PCR-based identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from screening swabs. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40(5):1821-1823.
-
Mizusawa M, Carroll, K.C. Novel strategies for rapid identification and susceptibility testing of MRSA. Expert. Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2020;13:1–19
-
Ellem, J.A., Olma, T., O’Sullivan, M.V. Rapid detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-susceptible S. aureus directly from positive blood cultures by use of the BD Max StaphSR assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015; 53 :3900–04.
-
Wolk, D.M, Struelens M.J, Pancholi P, Davis T, Della-Latta P, Fuller D et al. Rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) in wound specimens and blood cultures: Multicenter preclinical evaluation of the Cepheid Xpert MRSA/SA skin and soft tissue and blood culture assays. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009; 47:823–826.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License