IJCRR - 14(3), February, 2022
Pages: 01-05
Date of Publication: 01-Feb-2022
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Dental Practice Adaptations in Response to COVID-19 Pandemic in Delhi-National Capital Region
Author: Singh Neelam, Gupta Natasha, Singh Shradha, Sybil Deborah
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Today the world seems to have turned topsy turvy due to unwanted and unseen circumstances owing to the contagious SARS-COV-2 virus. Everybody's life seems to have altered. Dental professionals were impacted too by this. In this study, our aim was to assess dental practice modifications made by dentists practicing in Delhi and nearby National Capital Regions. Aim: The study aimed to understand the changes that were adapted to routine practice in order to fight the deadly virus and not compromise the dental care that was required by the patients at the time of the pandemic. Methodology: This study was based on Google form objective pattern, validated questionnaire, and disseminated using various online communication means among 200 dentists practicing in Delhi. The survey included MCQ questions enquiring about the mode of the dental practice, patient flow per day, services provided, adherence to evolving infection control measures, effectiveness and usage of teledentistry, and duration of restricted services in response to a lockdown of 2020. Results: Overall, 105 dentists contributed to this survey. In this survey, we found that periodontal and esthetic services like implantology were most affected. The most rendered service was Oral Medicine during the lockdown owing to Covid 19. All the practicing dental professionals tried to implement all the guidelines given by WHO and IDA. Personal protective methods were preferred by 81% of professionals followed by sanitation methods. Various means to prevent infection were resorted to by most of the dentists while others maintained a time gap between the patients along with cross ventilation methods to stop the spread. Moreover, 52.4% of them preferred online patient scheduling and others have favored teleconsultation as most useful for catering patients during this pandemic. Conclusion: This study highlights the scope and usage of newer methods of dental consultation such as teledentistry or teleconsultations in the routine dental practice and especially during the hours of need like at the times of lockdown so that the dental concerns of all classes of people can be addressed too without increasing the risk of spread of the disease.
Keywords: COVID-19, Dental Health Survey, Dental Services, Questionnaire, Preventive Guidelines, Teledentistry
Full Text:
Introduction
Healthcare services have had to adapt to new systems in response to the covid-19 pandemic. A new normal had to be attained in adherence to the recommendations of WHO. Changes were seen in the patient triaging system, infection control measures, rotational staffing of hospitals, workflow patterns and modes of patient care and communication.1 A major factor in the prompt delivery of healthcare services was the speed at which medical practices adapted to the evolving information of the disease.
Dental practice has been one of the most severely affected healthcare services during this pandemic. Oro-dental care was considered non-essential and routine dental practice had to be shut with the provision of only emergency services.2 Dental practitioners had to adapt to the emerging situation and bring about extreme changes to the way they catered to patients. Some of the recommended adaptations that required implementation were structural changes in the clinic and waiting area, improved and enhanced ventilation systems, evolving infection control measures, strict patient triaging, reduced number of patient appointments and teledentistry among others.3
The National capital region is one of the highly affected areas in this pandemic. As on 30th April 2021, total number of people affected by SARS- CoV-2 in Delhi was 11,49,333.4 Dentists in Delhi have had to face adverse conditions with restriction of dental services second time.5
This study aimed to assess dental practice adaptations/modifications by dentists practicing in Delhi at the time of first lockdown of the country. The study evaluated adherence to recommendations of IDA and the changes brought about in individual dental practice during the pandemic to sustain the spread of the disease and provide emergency dental services.
Methodology
Study design and population
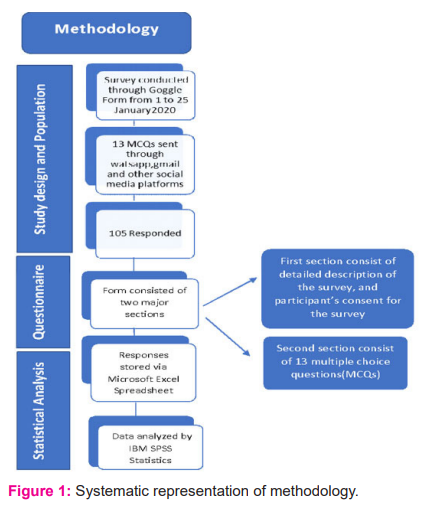
A cross-sectional observational study was conducted online between January 1st to 25th 2021 (almost 25 days) among the (specialist and non-specialist) dentists practicing in Delhi-NCR region. Participants were asked to fill a survey form titled “Adaptations in dental practice during Covid 19 pandemic” which was created using an online platform of google forms. The form was circulated among dentists via various social media platforms like email, whatsapp, instagram and could be easily filled on a smartphone, tablet or a PC. It was kept concise and to the point so as to not take much time and not deviate the dentist from the topic. The questionnaire was sent to 200 dentists whose contact details were obtained from a district-wise list of dentists available on various websites. An effort was made to include roughly equal numbers of participants from each of the 8 districts of Delhi and surrounding NCR region (Figure1).
Questionnaire
A pretested self -administered questionnaire was set. The questionnaire consisted of two sections, the first section consisted of a detailed email that was self-explanatory for the purpose of the study and informed consent. The participants were assured that no personal information was required. The only inclusion criterion was that the dentist should have a private practice in Delhi. There were no incentives offered to dentists to participate in the study.
The second section consisted of 13 multiple choice questions with 5 close-ended and 7 open-ended questions. Each MCQ had a provision for the dentist to describe his/her opinion if the choices were not suitable. The first 5 questions were related to location, years of practice, mode and zone of dental practice and duration of restricted services in response to lockdown of 2020. Next 4 questions were regarding patient flow per day, services provided and adherence to evolving infection control measures. The rest were in relation to changes in the system of practice, effectiveness and use of teledentistry tools and willingness to implement teledentistry in routine practice.
Pre-test was done with the collaborators to ensure proper working, submission and validity of the survey. The questions that were incomprehensive were modified and irrelevant sections were removed. All data was collected and stored in excel form and descriptive analysis of the data was carried out.
Result
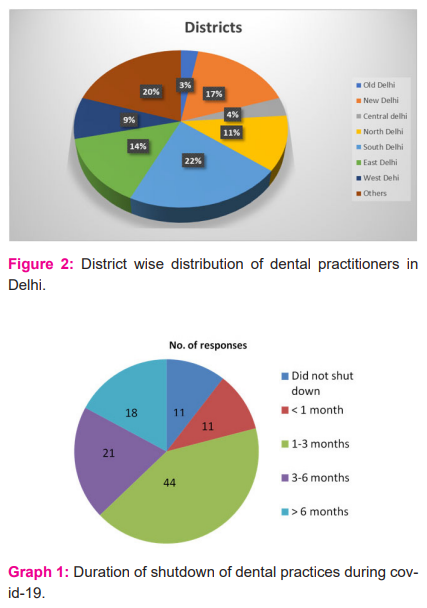
105 dentists responded to the questionnaire. District-wise distribution of participants and their containment zones is presented in Figure 2. Among the different modes of practice, 61.9% (n=65) of participants had a private dental practice, 21% (n=22) had a multispecialty practice, 18.1% (n=19) had a college-based practice while the rest practiced in a hospital-based setup.
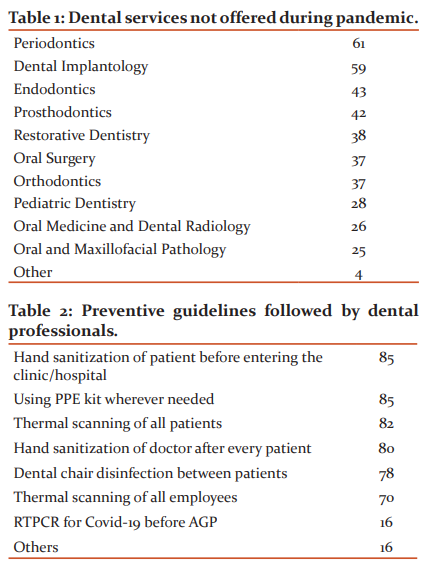
More than half of the participants, (56%, n= 59) were practicing dentistry for less than 5 years. It was seen that during COVID-19 lockdown in Delhi, the majority (41.9% n= 44) of dental professionals had shut down their services for 1 to 3 months. Moreover, 10.5% (n= 11) did not stop their services at all. (Graph 1).
Out of all the total respondents, more than half (59.6% n= 62) of the dentists had examined less than 10 patients per day. Periodontics (58.1%, n=61) and Dental implantology (56.2%, n=59) were the most affected while Oral Medicine was the most offered services to the patients during Covid-19 pandemic (Table 1).
Of all the guidelines given by WHO and IDA, 81% (n=85) of dental professionals have preferred personal protective methods. Additionally, 80% have followed various sanitization methods to prevent the spread of COVID-19 in their practice in Delhi. (Table 2).
Contributors, resorted to different means to prevent the infection but more than half of them (81% n= 85) tried to maintain a time gap between the patients and 48.6% (n=51) had utilized cross ventilation to stop the spread or cross-infection in their clinical setups (Table 3).
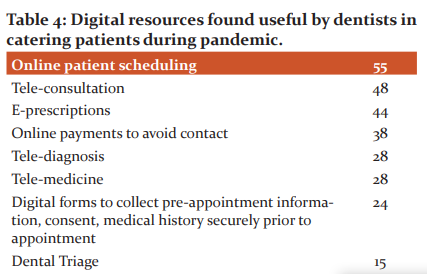
It was observed that 41% (n= 43) dentists were willing to use of tele-dentistry in their routine dental practice while, 52.4% (n= 55) of them preferred online patient scheduling and 45.7%(n=48) have favored teleconsultation as most useful for catering to patient during this pandemic (Table 4).
Discussion
Covid 19 has become a public health concern due to its high transmissibility. After the reporting of the first case in January 2020 in India, all the measures were adapted to control its spread. The transmission was so rapid that a lockdown of the entire nation was announced. This shutdown led to further increase in the bridge between dental healthcare services and population due to its proximity to patients and aerosol formation during the dental treatment.6 Oral health requires regular screening. Oral diseases like caries are very high prone with high carbohydrate intake and unfortunately, the lockdown led to increase in the consumption of convenience food, tasty treats and alcohol which further worsens the pre-existing dental condition.7 The pandemic urged dental professionals to look for and adapt newer means to continue providing dental healthcare services along with minimizing the risk of spread of virus.
In this survey, we tried to develop a correlation of the impact of lockdown on dental professionals and on the patients who required dental services. This survey showed that about 10.5% of the total clinics did not stop functioning and continued to provide emergency dental care whereas all other clinics had to shut down services for 1 to 3 months. This survey revealed that 59.6% of dental practitioners felt the volume of patients that were seen per day was reduced to approximately 10. Unfortunately out of these 10 also only a few were given treatment and others were just screened. This showed the extent to which dental health was neglected and this could only worsen the pre-existing oral health condition affecting the overall health of the patient and also impacting the dental practitioners financially.8
This survey showed us that periodontics and implantology were the most affected services. Non-surgical periodontics had been worldwide impacted, probably due to the need of use of ultrasonic/piezoelectric devices generating aerosols.9 The esthetic dental implants is an elective procedure, the pandemic had a major impact on this due to it being postponed either by patients or by professionals to protect the health care providers and save the system from completely falling down.
This was followed by endodontics, prosthodontics and restorative dentistry. The progression of dental pathology leads to pain, infection and sepsis. In early stages, if the pathological condition is diagnosed and intervened if needed the disease can either be reversed or arrested.10 The OSHA considered the Aerosol Generating Procedures as very high risk for known or suspected COVID 19 patients.11 The two procedures that are considered very high in aerosol generation are the one involving the high-speed handpiece with its water spray coolant and the ultrasonic scaler used to remove hard deposits on teeth.12 These both procedures are considered as an advancement in the field of dentistry as they are not just faster but reduce pain for the patient.13
Around 80% of the participants strongly agreed with the suggested measure of revised PPE protocols and others along with this resorted to thermal screening, hand sanitisation, decontamination procedures, good ventilation and fumigation of clinics. Whenever a need for AGPS (Aerosol generated procedures) occurred the participants preferred to go ahead with the RTPCR report. A new guideline was issued by MOHFW in May 2020 amidst the pandemic and lockdown announced in the country which divided the city in zones as per the contaminations. They also gave a guideline to modify the dental clinic into three phases. The preparatory phase, implementation and follow-up phase.14 All the dental treatments were divided among urgent procedures and emergency procedures as per age group (Geriatrics, adults, adolescents and children). The urgent treatments could only be undertaken after teleconsultation as prevention is the cornerstone of public health. Dental care paradigm was shifted to a more preventive approach.15 The only means as of now to fight this deadly virus is to follow the prevention protocols and be very careful while carrying out disinfection procedures.16
Tele dentistry was introduced when face-to-face consultation was not feasible. It is a developing practise for caring patients online and without physical contact.17 This method became the most suited means to address lack of access during the times of pandemic.18 The respondents of these studies had adopted teledentistry in various ways. Online patient scheduling and Tele Consultation were most commonly adopted means followed by E prescriptions.
Tele dentistry has many advantages. It can be used for consultation, triage and understanding whether the dental concern requires urgent or emergency care. It helps in-patient counselling when the condition can be temporarily resolved at home and the treatment can be postponed. This decreased the burden on emergency departments that are functioning during the pandemic and also avoided overcrowding and helped maintain social distance. This can continue to provide dental education and the importance of oral health care and diet during lockdown.19 The other aspects of it are electronic health records, electronic referral systems, digitizing images, teleconsultations, and telediagnosis.20
Tele dentistry is a means which can bridge the gap between urban and rural areas of the country. 21 It proved to be the cheapest and fastest way of delivering specialised dental services during the lockdown.22
Though this method has proved to be very helpful during the tough times of pandemic there are some shortcomings associated with it. During this survey, 67% participants felt that the socio-economic condition of people really impacted the success of this method implementation in India followed by lack of funding, infrastructure and manpower. Other shortcomings which may be encountered are the patient not being satisfied and apprehensive with the advice as lack of face-to-face consultation may make him feel his main problem has not been addressed. This survey concluded by showing that 43 % of our participants were willing to use teledentistry as a routine practice whereas 30% were not sure.
This study had its limitations. It had a limited sample size and was restricted to only Delhi NCR region only.
Conclusion
In these testing times teledentistry has been able to reach out to patients, resolve concerns associated with dental health, address dental conditions and categorize them into emergency and urgent by just a phone call or social media. It has helped minimise the spread of Covid 19 and also reduced the use of PPE which is needed in life saving procedures.
The scope of teledentistry is vast and is yet to become an integral part of the dental health care technique but the pandemic has pushed the professionals to reach out and try this means. It can reshape the dynamics of the dental care system. The current condition worldwide can be an opportunity for tele-dentistry to be adapted on a larger scale and hence impart dental health to every sector of society.
Acknowledgement
I wholeheartedly thank all the authors for contributing in making this article a success.
Declaration of interests: None
Conflict of Interest: None
Funding Resource: None
Auther’s contribution
Concept and design – Dr Neelam Singh
Dr Natasha Gupta
Data Collection and maintenance of record – Shradha Singh
Critical analysis and editing - Dr Sybil Deborah
Total Number of references cited in main body of the manuscript- 21

References:
References
-
Yaffee A, Peacock E, Seitz R, Hughes G, Haun P, Ross M et al. Preparedness, Adaptation, and Innovation: Approach to the COVID-19 Pandemic at a Decentralized, Quaternary Care Department of Emergency Medicine. West. J. Emerg. Med.2020;21(6):63-70.
-
Benzian H, Beltrán-Aguilar E, Mathur M, Niederman R. Pandemic Considerations on Essential Oral Health Care. J. Dent. Res.. 2020;100(3):221-225.
-
Meng L, Hua F, Bian Z. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Emerging and Future Challenges for Dental and Oral Medicine. J. Dent. Res.. 2020;99(5):481-487.
-
#IndiaFightsCorona COVID-19 [Internet]. MyGov.in. 2021 [cited 16 November 2021]. Available from: https://www.mygov.in/covid-19/
-
Delhi Govt Portal: Home [Internet]. Delhi.gov.in. 2021 [cited 16 November 2021]. Available from: https://www.delhi.gov.in/
-
Izzetti R, Nisi M, Gabriele M, Graziani F. COVID-19 Transmission in Dental Practice: Brief Review of Preventive Measures in Italy. J. Dent. Res.. 2020;99(9):1030-1038.
-
Campagnaro R, Collet G, Andrade M, Salles J, Calvo Fracasso M, Scheffel D et al. COVID-19 pandemic and pediatric dentistry: Fear, eating habits and parent’s oral health perceptions. Children and Youth Services Review. 2020;118:105469.
-
Coulthard P, Thomson P, Dave M, Coulthard F, Seoudi N, Hill M. The COVID-19 pandemic and dentistry: the clinical, legal and economic consequences - part 2: consequences of withholding dental care. Br. Dent. J.. 2020;229(12):801-805.
-
Nibali L, Ide M, Ng D, Buontempo Z, Clayton Y, Asimakopoulou K. The perceived impact of Covid-19 on periodontal practice in the United Kingdom: A questionnaire study. J. Dent.. 2020;102:103481.
-
Jepsen S, Blanco J, Buchalla W, Carvalho J, Dietrich T, Dörfer C et al. Prevention and control of dental caries and periodontal diseases at individual and population level: consensus report of group 3 of joint EFP/ORCA workshop on the boundaries between caries and periodontal diseases. J. Clin. Periodontol.. 2017;44:S85-S93.
-
[Internet]. Acfd.ca. 2021 [cited 16 November 2021]. Available from: https://acfd.ca/wp-content/uploads/Members/COVID-19/RTPs/Non-Canada/National/US-OSHA-COVID-19%20Control%20and%20Prevention-Dentistry%20Workers%20&%20Employers-20-04-22.pdf
-
Harrel S, Molinari J. Aerosols and splatter in dentistry. J Am Dent Assoc J AM DENT ASSOC. 2004;135(4):429-437.
-
Chen Y, Chang H, Chiang Y, Lin C. Application and development of ultrasonics in dentistry. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. J FORMOS MED ASSOC. 2013;112(11):659-665.
-
Mehta V, Gid A, Thakur R, Jangid M, Bagwe S, Mathur A. Dentist preparedness regarding novel coronavirus disease: An insight. 2021.
-
Nimbulkar. Dental practice guidelines in the precariousness of covid-19: a review. Int J Cur Res Rev | Vol 12 • Issue 19 • October 2020 82
-
Ghai S. Teledentistry during COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews. 2020;14(5):933-935.
-
Villa A, Sankar V, Shiboski C. Tele(oral)medicine: A new approach during the COVID?19 crisis. Oral Diseases. 2020;27(S3):744-745.
-
Bhanushali P, Katge F, Deshpande S, Chimata V, Shetty S, Pradhan D. COVID-19: Changing Trends and Its Impact on the Future of Dentistry. Int. J. Dent.. 2020;2020:1-6.
-
Khan S, Omar H. Teledentistry in Practice: Literature Review. Telemedicine and e-Health. 2013;19(7):565-567.
-
Reddy K. Using teledentistry for providing specialist access to rural Indians. Indian J. Dent. Res.. 2011;22(2):189.
-
Deshpande S, Patil D, Dhokar A, Bhanushali P, Katge F. Teledentistry: A Boon Amidst COVID-19 Lockdown—A Narrative Review. Int. J. Telemed. Appl.. 2021;2021(8859746).
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License