IJCRR - 14(1), January, 2022
Pages: 119-123
Date of Publication: 03-Jan-2022
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Comparison of Ultrasound-Guided Versus Nerve Stimulator Guided Technique of Supraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block in Patients Undergoing Upper Limb Surgeries
Author: Shanthan Kumar Repalle, B Srinivas Rao, Sudhalaxmi Anusha Parimi
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Brachial plexus block is an integral part of the regional anesthetic technique employed in orthopedic surgeries of hand, arm, and shoulder. It is used to circumvent the need for general anesthesia. Aim: The present study aimed to compare the efficacy of ultrasound guidance and nerve stimulation technique for supraclavicular brachial plexus block. Methods: Based on the inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria n=60 patients were identified and selected for the study. They were randomly allocated in two groups of n=30 each by computer-generated random allocation. Group A (US group) will receive ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus block and Group B (NS group) will receive nerve stimulator-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus block. Results: The average number of attempts taken to locate supraclavicular brachial plexus in Group A (US) was 1.33 and in Group B (NS) was 5.56 which is statistically significant (p< 0.001). The block performance time (BPT) is the time spent for detecting supraclavicular brachial plexus and injecting a local anesthetic (0.75 % Ropivacaine) around it. The mean time taken by Group A(US) was 4.8 \? 1 minute, while it was 10.3 \? 1.5 minutes in Group B the p-value calculated was p < 0.001 which is statistically significant. Conclusion: Compared to nerve stimulator-guided technique ultrasound-guided technique has more advantages like a lesser number of attempts required, less block performance time, lesser onset time for sensory and motor block, and longer duration of sensory and motor block, more patient satisfaction and fewer complications.
Keywords: Ultrasound guided technique, Nerve stimulator guided technique, Brachial plexus block, Regional anesthesia, Su�praclavicular brachial plexus, Upper limb surgeries
Full Text:
Introduction
Brachial plexus block is an integral part of the regional anesthetic technique to circumvent the need for general anesthesia and its side effects as well as safe in patients with comorbidities making them unsuitable for general anesthesia. It is a frequently employed technique in orthopedic surgeries of hand, arm, and shoulder by using an appropriate and accurate needle location in the vicinity of the nerves of the brachial plexus. Thorough knowledge of applied anatomy, pharmacological properties of local anesthetics, working principles of the equipment, and importantly dexterity required for the performance of the safe block. The commonly employed techniques to position the needle accurately in a brachial plexus block are transarterial, eliciting paresthesia, use of a peripheral nerve stimulator/ locator, or an ambulatory sonological device.1 The initial technique of Brachial plexus blocks was blindly hitting the first rib by a wandering technique or using the adage "No Paresthesia-No Anesthesia" before the availability of Nerve locators. 2 The introduction of peripheral nerve locator was a landmark achievement in the field of regional anesthesia providing objective evidence of needle proximity to target nerves. Their main advantages being lightweight and compact, visual and audible signals with a bright display, providing a safe circuit between the stimulator, needle and the patient with an adjustable impulse duration of 0.1 and 1 millisecond with an adjustable current from 0 to 5 mA at increments of 2 Hz impulse frequency.
The nerve stimulation technique using nerve locator carried doubt regarding its sensitivity, particularly while detecting the needle position in the intraneural space (requiring high current intensity to elicit a motor response) and keeping the needle extra neural posed more challenging for nerve injury. Ultrasonography is a useful state-of-the-art tool in the armament of regional anesthesia. 3, 4 By comparison with nerve stimulation techniques, ultrasound guidance offers some advantages of direct visualization of anatomic structures, helping to minimize vascular punctures, and a dynamic vision of needle advancement and local anesthetic spread in the per neural area. 5 Although no signi?cant differences in the incidence and severity of postoperative neurological symptoms have been reported, 6 ultrasound guidance has been shown to reduce the number of needle redirections 7 and to enhance block success rate, particularly when performing inter scalene block. 8 US guidance has also been shown to improve peripheral nerve block onset times when compared with a neurostimulation technique, 9 although very few studies showed up speci?cally when this issue was addressed for inter scalene block. 10 Hence, we conducted a prospective randomized study to test whether Ultrasonography (USG) guidance can improve the success rate and can shorten the onset time of supraclavicular brachial plexus block as compared with nerve stimulation guidance.
Material and Methods
This prospective controlled study was done in the Department of Anesthesiology, Mahatma Gandhi Medical Hospital Warangal, Telangana from June 2018 to August 2019. Institutional Ethical committee permission was obtained for the study (No.2003035D 24/06/2018) after following the due protocol. Written consent was obtained from all the patients in the study.
Inclusion criteria
-
American Society of Anesthesiologists grades I, II, and III physical status.
-
Patients of either sex between 18-60 years.
-
Elective upper limb surgery
Exclusion criteria
-
-
Those who do not fit in inclusion criteria
-
Preexisting nerve damage (sensory or motor) in the extremity to be blocked
-
Peripheral neuropathy
-
Significant cardiovascular disease
-
Body Mass Index (BMI) > 35
-
Uncontrolled diabetes
-
Renal Impairment (Creatinine> 2.0 mg/dl)
Based on the inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria n=60 patients were identified and selected for the study. They were randomly allocated in two groups of n=30 each by computer-generated random allocation. Group A (US group) will receive ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus block and Group B (NS group) will receive nerve stimulator-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus block.
In the US group (Group A), A 10 MHz Transducer probe covered with a sterile Tegaderm was placed in a transverse plane just superior to the clavicle and tilted appropriately to locate the subclavian artery. After local anesthetic skin infiltration of skin with 2% lignocaine 2 ml one cm lateral to the transducer to reduce discomfort to the patient, a 25G, 5cm, the needle was inserted and 20 ml of 0.75% Ropivacaine solution was injected all around the nerve trunks in a lateral to medial direction by hydro locating the tissue layers, with intermittently aspirating ruling out intravascular accidental entry.
In the neurostimulation group (Group B), patients were positioned similarly as described in the US group, and a 25 G, 5 cm insulated tip-free needle was used. Polarity is maintained using an appropriate electrode in proper places. The needle connected to a nerve stimulator was set to deliver a current of 1 mA the needle was inserted at an angle of 45° 2-3 CMSs depth above the clavicle with palpating fingers firmly pressed between anterior and middle scalene muscles and brachial plexus approached. Position of needle confirmed by looking for muscle contraction in the digits, hand, forearm, arm, and pectoralis with a minimal current of 0.5 mA. 0.75% Ropivacaine 20 ml was injected with intermittently aspirating ruling out accidental intravascular injections and the pressing finger pressure released finally.
Patients were kept for one hour in the post anesthesia recovery room and assessed every half an hour by the recovery nurses for the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) for pain, the motor power for elbow flexion, and any late side effects of local anesthetics.
Statistics: All the available data was entered in MS Excel spreadsheet and descriptive statistics such as Mean, Standard Deviation, Student's T-test, ANOVA were performed (p<0.05 was considered significant) was analyzed using SPSS version 21 on windows format.
Results
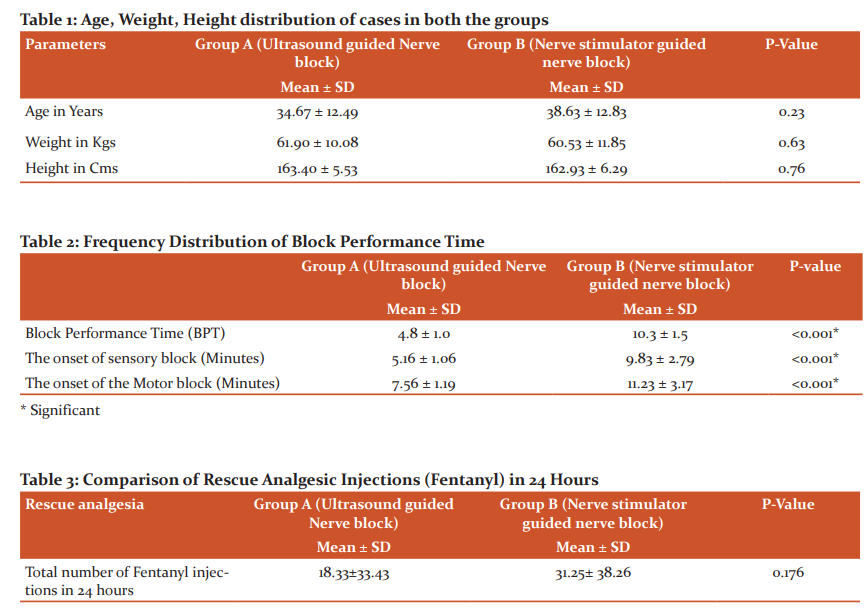
Group A (Ultrasound guided group) included n=23 males and n=7 females who ranged in age between 18 and 60 years. Group B (Nerve stimulator group) included n=18 males and n=12 females who ranged in age between 18 and 60 years. The details of the distribution of age weight and height are given in table 1.
The American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) score was nearly similar in both groups wherein Group A(US) n=11 patients had an ASA I, n=16 patients had an ASA II score and n=3 patients an ASA III score while Group B(NS) included n=13 patient with ASA I score, n=14 patients with ASA II score and n=3 patients with ASA III score (p=0.63). The average number of attempts taken to locate supraclavicular brachial plexus in Group A (US) was 1.33 and in Group B (NS) was 5.56 which is statistically significant (p<0.001). The block performance time (BPT) is the time spent for detecting supraclavicular brachial plexus and injecting a local anesthetic (0.75 % Ropivacaine) around it. The mean time taken by Group A(US) was 4.8 ± 1 minute, while it was 10.3 ± 1.5 minutes in Group B the p-value calculated was p < 0.001 which is statistically significant. There was a significant difference among both the groups regarding the onset time taken for the sensory block. In Group A (US) the meantime was 5.16 ± 1.06 minutes, while it was 9.83 ± 2.79 minutes in Group B (NS) p<0.001. There was a significant difference between both groups regarding the onset time taken for the motor block to start. In Group A (US) the meantime was 7.56 ± 1.19 minutes, while it was 11.23 ± 3.17 minutes in Group B (NS) p<0.001 (Table 2).
The comparison of doses of rescue analgesia (Fentanyl) injections required in 24 hours in the two groups. The requirement of rescue injections in 24 hours was similar in group A (US) 18.33 ± 33.43 µg and group B (NS) 31.25 ± 38.26 µg. The difference was not statistically significant p = 0.176 given in table 3.
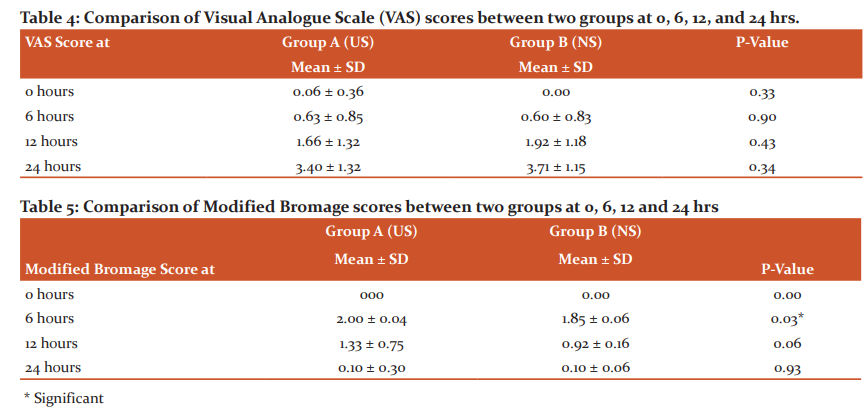
Visual analog scale (VAS) scores were recorded at 0 hr, 6th hrs, 12th hrs, and 24 hrs. ANOVA was applied for statistical analysis of VAS scores in the two groups over the various time intervals the values of p at all intervals was greater than 0.05 hence not significant given in table 4.
Modified Bromage scores for upper limb were recorded at 0 hr, 6th hrs, 12th hrs, and at 24 hrs. ANOVA was applied for statistical analysis of modified Bromage scores in the two groups at various time intervals the values at all intervals were found to be >0.05 except at 6-hour interval where the values were found to be significant (Table 5).
Discussion
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the practice of regional techniques and particular peripheral nerve blocks for surgical anesthesia and postoperative analgesia. In our study, the sample of cases selected and divided into two groups was found to be homogenous as far age, sex distribution, Height, and Weight were concerned. The ASA grades of the patients were also found to be similar in both groups. Singh G et al.;11 in their study also found a similar demographic profile as our study. In the present study, the drug selected for the brachial plexus block was Ropivacaine. In this study, it was observed that the average number of attempts taken to locate supraclavicular brachial plexus in Group A (US) was 1.33 and in Group B (NS) was 5.56 which was statistically significant (p<0.001) and the results are comparable study by Orebaugh et al.12 found that more needle insertions were required for nerve localization in the nerve stimulator-guided blocks (median = 6) than in ultrasound-aided blocks (median = 2 attempts). In the present study it was observed that the mean time taken by Group A (US) was 4.8 (± 1) minutes, while it was 10.3 (± 0.5) minutes in Group B (NS). The results were comparable with the study by Williams et al.13 in their study involving n=80 patients for supraclavicular block comparing the two-block techniques, concluded that ultrasound-guided supraclavicular block is more rapidly performed. The block was performed at an average of 9.8 min in Group NS and 5.0 min in Group US (P = 0.0001). In this study, in Group A (US) the meantime was 5.16 (± 1.06) minutes, while it was 9.83 (± 2.79) minutes in Group B (NS) (p<0.001). Kapral S et al.14 in 2008 found that Sensory, motor, and extent of the blockade were significantly better in the ultrasound group when compared with the nerve stimulation group. In the present study showed that the onset of motor block was faster in the ultrasound group, in Group A(US) the meantime was 7.56 (±1.19) minutes, while it was 11.23 (± 3.17) minutes in Group B (NS) (p<0.001). Liu et al.15 in a prospective, randomized, controlled trial comparing ultrasound versus nerve stimulator guidance for shoulder surgery and found that the use of ultrasound enhanced motor block at the 5-minute assessment (P =0.04). Leslie C et al.16 in their study where the US group achieved a significantly faster onset motor block (US group, 13.5 ± 2.3 minutes than NS group, 20.2 ± 2.1 minutes P =?0.03). In the present study, it was observed that the duration of sensory and motor block was prolonged in the ultrasound group. Maher Fawzy et al.17in their study and found that the duration of sensory block was significantly longer in US group 13 (1.4) h than in NS group 10 (1) h(P<0.001). In the present study, there was no difference in the requirement of rescue analgesia between ultrasound and nerve stimulator group. The requirement of rescue injections in 24 hours was similar in group A (US) (18.33±33.43) µg and group B(NS) (31.25± 38.26) µg (p=0.176). This agrees with the study of Leslie C et al.16 there was no difference found in need of rescue analgesics. In the present study, complications were fewer in the ultrasound group when compared with the nerve stimulator group (p-value = 0.002). Pneumothorax was observed in one patient in Group A (US) and 3 patients in Group B (NS). vascular injury observed in no patients in Group A (US) and 5 patients in Group B (NS). Our results were comparable Ullah et al.18concluded that there was a lower incidence of complications when interscalene block is performed under ultrasound guidance rather than without it. Thus, our results are comparable to the findings in these studies. The patients' satisfaction scores in group A (US) and group B (NS) were 1.43±0.67 and 2.33±0.97 respectively, the difference was statistically significant (p-value 0.001) and was comparable to study conducted by Fawzy et al.17concluded that the degree of patients satisfaction showed a significant difference favoring ultrasound guidance group (86.6%) compared to nerve stimulator group (53.3%).
Conclusion
The present study concluded that compared to nerve stimulator guided technique ultrasound-guided technique has more advantages like less number of attempts required, less block performance time, lesser onset time for sensory and motor block and longer duration of sensory and motor block, more patient satisfaction and fewer complications. So, we recommend regular use and inclusion of ultrasound-guided technique for supraclavicular brachial plexus block.
Acknowledgment: The authors wish to thank the Department of Anesthesiology, MGM Hospital Warangal for the support in the conduction of this study.
Conflict of interest: Nil
Source of support: Nil
References:
-
Winnie, AP. Perivascular techniques of brachial plexus block. Plexus anesthesia: perivascular techniques of brachial plexus block I (2nd ed.). W.B. Saunders Company Philadelphia 1990; pp. 261.
-
Perlas, Anah, Chan, Vincent W.S, Simons, martin. ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus block. Reg Anesth. 2003; 12:178-79.
-
Marhofer P, Harrop-Grif?ths W, Kettner SC, Kirchmair L. Fifteen years of ultrasound guidance in regional anesthesia: part 1. Br J Anaesth. 2010; 104:538-46.
-
Marhofer P, Harrop-Grif?ths W, Willschke H, Kirchmair L. Fifteen years of ultrasound guidance in regional anesthesia: Part 2-recent developments in block techniques. Br J Anaesth. 2010; 104:673-83.
-
Baciarello M, Danelli G, Fanelli G. Real-time ultrasound visualization of intravascular injection of local anesthetic during a peripheral nerve block. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2009; 34:278-79.
-
Liu SS, Zayas VM, Gordon MA,. A prospective, randomized, controlled trial comparing ultrasound versus nerve stimulator guidance for interscalene block for ambulatory shoulder surgery for postoperative neurological symptoms. Anesthesia Analg. 2009; 109:265–71.
-
Orebaugh SL, Williams BA, Kentor ML. Ultrasound guidance with nerve stimulation reduces the time necessary for resident peripheral nerve blockade. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2007; 32:448-54.
-
Kapral S, Greher M, Huber G,. Ultrasonographic guidance improves the success rate of interscalene brachial plexus blockade. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2008; 33:253-58.
-
Liu SS, Ngeow J, John RS. Evidence basis for ultrasound-guided block characteristics onset, quality, and duration. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2010; 35:S26-35.
-
Soeding PE, Sha S, Royse CE, Marks P, Hoy G, Royse AG. A randomized trial of ultrasound-guided brachial plexus anesthesia in upper limb surgery. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2005; 33:719-25.
-
Singh G, Mohammed YS. Comparison between conventional technique and ultrasound guide supraclavicular brachial plexus block in upper limb surgeries. IJSS. 2014; 2(8):169-76.
-
Orebaugh SL, Williams BA, Kentor ML. Ultrasound guidance with nerve stimulation reduces the time necessary for resident peripheral nerve blockade. Reg Anesth painted. 2007; 32:448-54.
-
Williams SR, Chouinard P, Arcand G,. Ultrasound guidance speeds execution and improves the quality of supraclavicular block. Anesth Analg. 2003; 97:1518-23.
-
Kapral S, Greher M, Huber G,. Ultrasonographic guidance improves the success rate of interscalene brachial plexus blockade. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2008; 33:253–58.
-
Liu SS, Zayas VM, Gordon MA,. A prospective randomized controlled trial comparing ultrasound versus nerve stimulator guidance for interscalene block for ambulatory shoulder surgery for postoperative neurological symptoms. Anesth Analg. 2009; 109:265–71.
-
Leslie C. Thomas, Sean K. Graham, Kristie D. Osteen, Heather Scuderi Porter, Bobby D. Nossaman. Comparison of Ultrasound and Nerve Stimulation Techniques for Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block for Shoulder Surgery in a Residency Training Environment: A Randomized, Controlled, Observer- Blinded Trial. Ochsner J2011;11: 246-52.
-
Fawzy M, Nevan M. Mekawy, Ahmed Abd Elaziz Aref, GomaaZahry Hussin, Mohamed Mourad. Interscalene brachial plexus block (a comparative study between nerve stimulator and ultrasound guidance in shoulder surgery). Ain-Shams Anesthesiology J. 2012;5-2:238-42.
-
Ullah H, Samad K, Khan FA. Continuous interscalene brachial plexus block versus parenteral analgesia for postoperative pain relief after major shoulder surgery (Review). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014; 2:CD007080.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License