IJCRR - 14(1), January, 2022
Pages: 98-103
Date of Publication: 03-Jan-2022
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Utility of Fluorescence Immunoassay in Early Diagnosis of Dengue
Author: Das Rashmita, Joshi Suvarna, Palewar Meghna, Karyakarte Rajesh
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Early and prompt diagnosis of dengue infection can help in improving the clinical outcome of patients by ensuring early initiation of supportive treatment. Non-structural glycoprotein-1 (NS-1) is a useful biomarker for the early diagnosis of dengue as it is abundantly present in the serum during the early stages of infection. Several rapid diagnostic tests targeting NS-1 antigen are commercially available and many more are being developed. The present study evaluated a newly developed fluorescence immunoassay (FIA), NS-1 QUANTI CARD test, to determine its effectiveness in the early diagnosis of dengue. Methods and Material: A total of 85 serum samples from clinically suspected dengue patients were tested for NS1 antigen by ELISA, FIA and rapid immunochromatography test (ICT). The performance characteristics of FIA and ICT were calculated considering ELISA as the gold standard test. Sensitivity, specificity, predictive values, likelihood ratios and Cohen's Kappa value for the level of agreement were calculated using MedCalc\? Statistical Software version 19.6.4. Results: The overall sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values of FIA and ICT were found to be 96.5%, 96.4%, 93.3%, 98.1% and 65.5%, 83.9%, 67.8%, 82.4%, respectively. There was almost a perfect level of agreement between the ELISA and QUANTI CARD test whereas ELISA and ICT results had a moderate level of agreement. Conclusion: Owing to its shorter turnaround time (TAT), the NS1 Ag QUANTI CARD test can be a better alternative to ELISA for dengue diagnosis in resource-limited settings and critically ill patients for prompt diagnosis.
Keywords: Dengue, Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA), Fluorescence immunoassay (FIA), i-Quant Analyser, Non�structural (NS1) antigen, QUANTI CARD
Full Text:
Introduction
Dengue, the most common arboviral infection worldwide, has spread rapidly to more than 129 countries. World over, about 3.9 billion people are at risk of acquiring dengue infection, 70% of these people at risk are from Asia. Over the last two decades, the number of reported cases has increased by eight-fold from half a million cases in 2000 to 2.4 million cases in 2010 and 4.2 million cases in 2019. Similarly, the reported deaths have increased from 960 to 4032 over 15 years, from 2000 to 2015.1
The virus causes a wide spectrum of disease manifestations ranging from subclinical infection to severe disease that leads to bleeding, organ impairment and death. Therefore, early diagnosis of infection can help improve the clinical outcome of the disease by ensuring early initiation of supportive therapy and close follow-up, thus lowering the fatalities to less than 1%.2 The major obstacle in early diagnosis is the non-specific clinical presentation that may lead to delay and misdiagnosis of the disease. Therefore, all clinically suspected cases must be confirmed by laboratory tests for efficient and accurate diagnosis.3
A range of laboratory diagnostic tests have been developed for dengue diagnosis. Definitive diagnosis of dengue includes isolation of virus by culture, viral genomic RNA detection by Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR), detection of viral products like Non-Structural (NS1) protein or detection of host immune response to the virus by measuring the specific IgM/IgG antibodies against dengue virus using rapid immunochromatography test or Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay.2
Virus isolation by culture is the gold standard test for dengue diagnosis. It is time-consuming as it takes days and weeks to complete. The RT-PCR test requires specialized reagents and technical expertise. Both the tests are useful in the first five days of illness and thereafter the sensitivity of the tests decreases as the viremia decreases over time.4 Serological diagnosis is not helpful during acute illness as the antibodies remain undetectable until 3-4 days post-symptom onset and require a second sample within 14-21 days for definitive diagnosis. NS-1 protein is released during the infection and is accumulated in human serum in very high concentrations. It is detectable early during the infection. Therefore, NS1 antigen has become an attractive target for diagnostic assay development as it is more specific and shows high specificity. However, the choice of diagnostic method depends on the time of sample collection, laboratory facilities the technical expertise available, and the purpose of testing, i.e., clinical diagnosis, epidemiological studies, or vaccine development.5
The most widely used test for diagnosis of dengue is Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) which is used for the detection of viral antigen and anti-DENV IgM/IgG antibodies in patient serum. It has high specificity and sensitivity, but at the same time, it is time-consuming, labor-intensive and requires skilled manpower and equipment.4 Therefore, in the past two decades, with the growing demand for point-of-care diagnostics, many Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTs) have flooded the market. However, the available diagnostic tests vary in their sensitivity and specificity.6
With the above background, the current study aims to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy and utility of a newly developed rapid fluorescence immunoassay test, i.e., Dengue NS1 Ag QUANTI CARD test with a commercially available NS1 antigen rapid immunochromatography test and NS1 ELISA for early diagnosis of dengue infection.
Material and Methods
The present study was carried out in the Department of Microbiology at Byramjee Jeejeebhoy Government Medical College, Pune, Maharashtra.
Study Design: A diagnostic evaluation study
Specimen collection
A total of 85 serum samples from patients suspected of dengue infection with fever for less than or equal to five days were collected and tested. Following all standard precautions, 5 mL of blood sample was collected in a clean plain vacutainer. The blood was allowed to clot at room temperature for 45 minutes and then serum was separated. 10 serum samples were also collected from healthy individuals to evaluate the specificity of the newly developed test.
Methodology
The collected serum samples were tested for NS1 antigen (NS1 Ag) using fluorescence immunoassay (FIA), Rapid Immunochromatography test (ICT) and ELISA test.
Dengue NS1 QUANTI CARD (J. Mitra & Co. Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, India) is a fluorescence immunoassay test based on the principles of sandwich immunoassay. It is a cartridge-based test for the qualitative detection of Dengue NS1 Ag in human serum/plasma. On a nitrocellulose membrane, the test region is coated with specific anti-dengue NS1 antibodies. When a sample containing NS1 Ag is added, the antigen forms a complex with a conjugated antibody directed against the NS1 Ag. The antigen-antibody complex migrates along the nitrocellulose membrane to the test region and binds to immobilized antibodies forming an antibody-antigen-antibody immunocomplex. The results are read after 30 minutes using iQuant analyser. The results obtained were interpreted in terms of NS1 Ag units as reactive (> 1.1 U), equivocal (> 0.9 to < 1.1 U) or non-reactive (< 0.9 U).
Dengue NS1 rapid antigen test (RAT) was performed using Dengucheck, a rapid qualitative immunochromatographic test for detection of NS1 Ag in serum/ plasma (Zephyr Biomedicals, a division of Tulip diagnostics (P) Ltd, Goa, India) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Similarly, Dengue NS1 Ag ELISA was performed using Dengue NS1 antigen Microlisa (J. Mitra & Co. Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, India) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. It is a solid phase Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent assay based on the principles of direct sandwich ELISA.
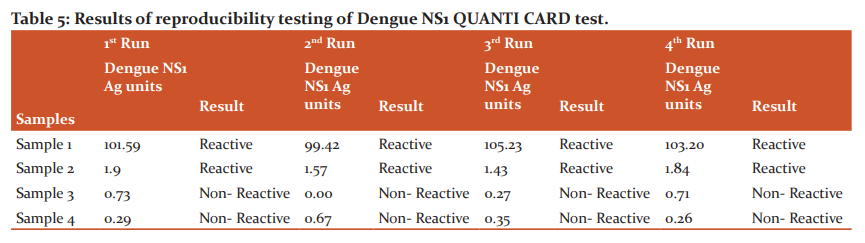
Reproducibility of the test results of the newly available fluorescence immunoassay test, NS1 QUANTI CARD, was evaluated by testing four samples (two weak positive samples and two negative samples for NS1 Ag) at four different times by the same technician.
Statistical analysis
The data obtained was compiled using Microsoft® Excel. Sensitivity, specificity, predictive values, likelihood ratios and Cohen’s Kappa value for the level of agreement were calculated using MedCalc® Statistical Software version 19.6.4.
Results
Characteristics of the study population
A total of 85 samples were collected from suspected patients of dengue. The mean age of the study population was 20.98 years and the sex ratio (male: female) was 1.7:1.
Characteristics of the diagnostic tests
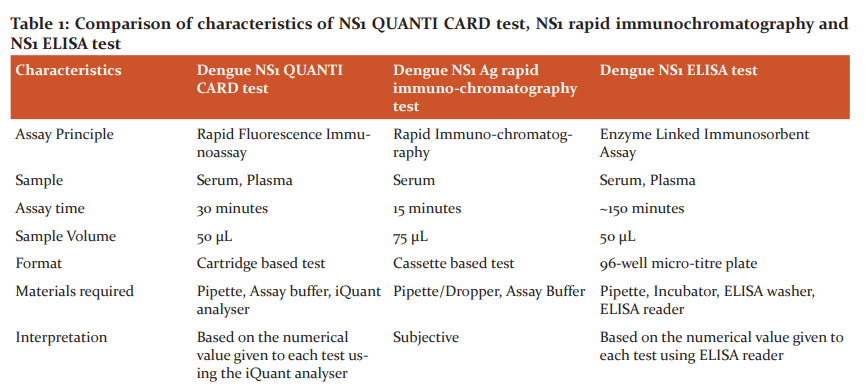
A comparison of several functional attributes of NS1 QUANTI CARD test, NS1 rapid immunochromatography and NS1 ELISA test is shown in Table 1.
Correlation between results of fluorescence immunoassay and rapid immunochromatography with NS1 ELISA test.
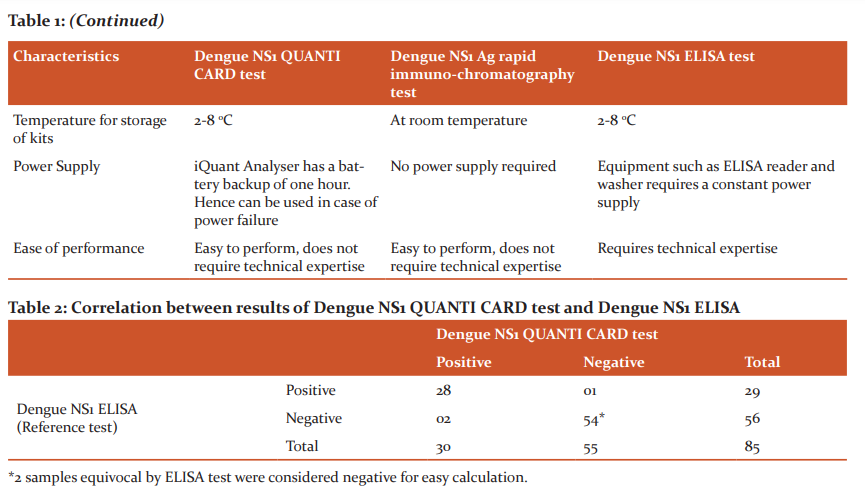
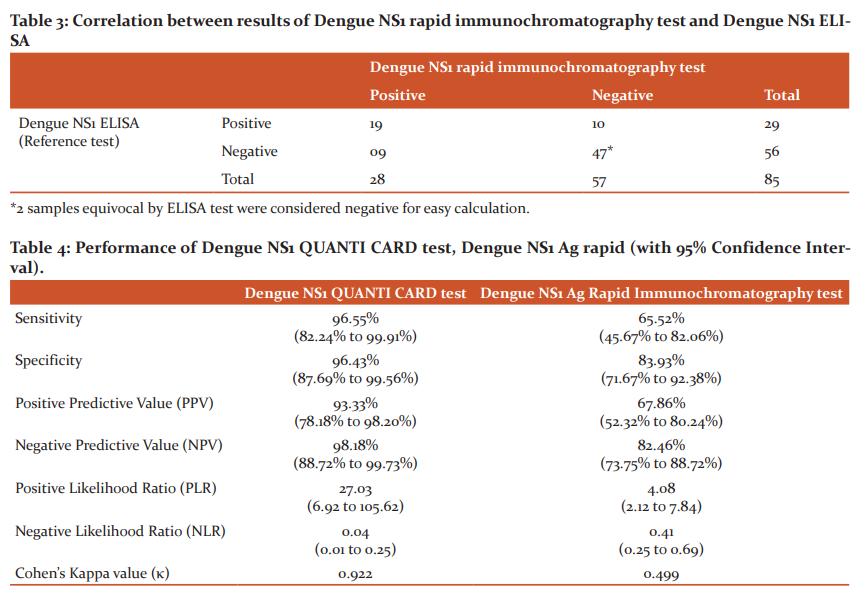
Out of 85 samples tested, NS1 ELISA was positive in 29 (34.1%) and negative in 56 (65.9%) samples; dengue NS1 QUANTI CARD test was positive in 30 (35.3%) and negative in 55 (64.7%) samples, and NS1 rapid immunochromatography test was positive in 28 (32.9%) and negative in 55 (67.1%) samples. The correlation between the results of NS1 ELISA, NS1 QUANTI CARD test and rapid immunochromatography test is shown in Table 2 and 3, respectively.
Performance characteristics of fluorescence immunoassay and rapid immunochromatography test considering ELISA as the gold standard test.
The performance characteristics of the Dengue NS1 QUANTI CARD test, Dengue NS1 Ag rapid immunochromatography test was calculated considering Dengue NS1 ELISA as the gold standard test as shown in Table 4.
To test the specificity of the newly developed test, 10 serum samples collected from healthy individuals were tested. The specificity and NPV of the Dengue NS1 QUANTI CARD test were found to be 100% and 80%, respectively.
Reproducibility testing of Dengue NS1 QUANTI CARD test.
The dengue NS1 QUANTI CARD test results were reproducible with all dengue samples (two dengue NS1 Ag positive and two dengue NS1 Ag negative) in four different runs as shown in Table 5.
Discussion:
Dengue infection usually presents with non-specific symptoms, mimicking any other viral infection. However, due to a wide spectrum of disease presentation, early diagnosis and prompt treatment are of paramount importance.1 Detection of NS1 antigen has emerged as a popular diagnostic method for early diagnosis of dengue as it becomes detectable from day 1 to day 9 after the onset of disease in both primary and secondary dengue cases.5 Therefore, many diagnostic tests have been developed using NS1 as a target and are being assessed for early diagnosis of dengue.
One such newly developed test, the Dengue NS1 Ag QUANTI CARD test, a fluorescence immunoassay test based on the principles of sandwich immunoassay was evaluated in this study. In the present study, the QUANTI CARD test produced results comparable to that of ELISA. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV of the FIA test were found to be 96.5%, 96.4%, 93.3% and 98.1%, respectively. The Cohen’s Kappa value was found to be 0.92, indicating almost total agreement between ELISA and QUANTI CARD test results. The test showed reproducible results when tested at four different times. Our findings are similar to those of Pohekar et al. where the sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV were 100%, 98.3%, 97.4% and 100%, respectively.7
The need for a simple point-of-care diagnostic test has led to the large-scale production of Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTs) using the immunochromatographic format. In this study, the sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV of RDT were 65.5%, 83.9%, 67.8% and 82.4%, respectively. The Cohen’s Kappa value was 0.499, indicating a moderate level of agreement between ELISA and rapid ICT test results. The performance of the RDT kit was lower as compared to other studies in India as various studies have reported a sensitivity of 88% to 100% and a specificity of 90% to 98%.8-11 In a study by Yow et al. (2021), the sensitivity and specificity of six RDT kits were found to be 68.5% to 87% and 100%, respectively.12 Similarly, Pal et al. (2014) in their study have highlighted that the sensitivity of NS1 antigen rapid tests that have been reported in the literature varies from 58% to 99%.4
After comparing the characteristics of the three tests, it is observed that the ELISA test requires technical expertise, is time-consuming and requires a constant power supply for its operations. It requires approximately 2-3 hours of assay time. RDTs based on the principle of FIA and ICT, on the other hand, are easy to perform with very little expertise and require 15 to 30 minutes of run time. However, the interpretation of results in the case of an ICT is subjective. This is of particular importance while interpreting tests with weak positive bands. Whereas the results of the FIA test are read using iQuant Analyser. This provides a numerical value to every test, thereby ruling out any subjectivity during the interpretation of results. The inbuilt memory of the iQuant analyser can store results that can be used for future reference. It also has a 1-hour battery backup which keeps the machine operational in case of power failure.
Conclusion
To conclude, the performance of the newly developed Dengue NS1 Ag QUANTI CARD test was superior to the rapid immunochromatographic test and was comparable to the performance of the ELISA test. Due to its superior sensitivity, the ELISA test will remain the recommended choice of test in laboratories with trained manpower and equipment. On the other hand, in resource-limited settings such as in semi-urban and rural areas, with restricted availability of skilled manpower and equipment, the fluorescence immunoassay with high sensitivity and lesser TAT can be a better alternative to ELISA. It would be a valuable tool for prompt diagnosis of dengue infection in critically ill patients as it may impact patient management by early initiation of appropriate therapy.
Acknowledgement:
We acknowledge Mrs Shobha Sabale and Mrs Sonal Kalbhor for their technical support during the study.
Source of funding: Nil
Conflict of Interest: Authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Authors’ Contribution:
This work was carried out in collaboration among all authors. Authors Rashmita Das, Suvarna Joshi, Meghna Palewarand Rajesh Karyakarte have conceptualised and designed the study. Authors Rashmita Das, Suvarna Joshiand Meghna Palewar performed data acquisition and managed the literature searches. Authors Rashmita Das, Suvarna Joshi performed the data analysis and author Rashmita Das wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Authors Rashmita Das, Suvarna Joshi, Meghna Palewar and Rajesh Karyakarte performed manuscript editing. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
References:
1. Dengue and severe dengue [Internet]. WHO 2021. [cited 29 July 2021]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dengue-and-severe-dengue
2. Dutta A, Dighade R, Malpekar K, Bisure K. Comparison of Diagnostic Modalities in Early Dengue in a Tertiary Hospital in Mumbai. Ann. Int. Med. Den. Res. 2021;7(1):MB01-MB05.
3. Chong Z, Sekaran S, Soe H, Peramalah D, Rampal S, Ng C. Diagnostic accuracy and utility of three dengue diagnostic tests for the diagnosis of acute dengue infection in Malaysia. BMC Inf Dis. 2020;20(1):1-11.
4. Pal S, Dauner AL, Mitra I, Forshey BM, Garcia P, Morrison AC, Halsey ES, Kochel TJ, Wu SJ. Evaluation of dengue NS1 antigen rapid tests and ELISA kits using clinical samples. PLoS One.2014;9(11):1-8.
5. National Vector Borne Disease Control Program. National Guidelines for Clinical Management of Dengue Fever. New Delhi: Government of India; 2015:15.
6. Raafat N, Blacksell S, Maude R. A Review of Dengue Diagnostics and Implications for Surveillance and Control. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019;113(11):653-660.
7. Pohekar J, Bhalchandra M, Ghogre H, Pathrikar T. Evaluation and Comparison of Currently Available Fluorescence Immunoassay (FIA) Test with Rapid Immuno-Chromatographic Test (ICT) Considering NS 1 ELISA as a Reference Test. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci. 2017;6(11):506-513.
8. Reddy R, Sahai K, Malik A, Shoba S, Khera A. Comparative Analysis of Rapid Dengue Testing and ELISA for NS1 Antigen and IgM in Acute Dengue Infection. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci. 2016;5(10):931-937.
9. Naidu A, Venkateswarlu P, Umadevi S, Sailaja M, Praveena B, Devi A. Detection of Dengue NS1 by a Comparative Analysis of Panbio Elisa and Rapid Diagnostic Test. Sch. J. Appl. Med. Sci. 2017;5(3B):816-820.
10. Hassan S, Khare V, Singh M, Asghar S. Comparison of Rapid Immuno- Chromatographic Card Test with ELISA in Diagnosis of Dengue Fever at Tertiary Care Centre. Indian J Microbiol Res. 2018;5(2):284-287.
11. Gill M, Kaur A, Kukreja S, Chhabra N. Comparative Evaluation of a Rapid Test with ELISA for the Detection of Dengue Infection. Indian J Microbiol Res. 2016;3(4):405-407.
12. Yow K, Aik J, Tan E, Ng L, Lai Y. Rapid Diagnostic Tests for the Detection of Recent Dengue Infections: An Evaluation of Six Kits on Clinical Specimens. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(4):1-11.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License