IJCRR - 14(1), January, 2022
Pages: 57-63
Date of Publication: 03-Jan-2022
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
An Empirical Study of Procrastination Practices at Workplace and their Associated Factors across Institutions: Case of Healthcare Administrative Professionals
Author: Mohamed Khedhiri, Hanan Althagafi
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Little research has explored procrastination in Healthcare Institutions rather than business settings, especially in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia where the healthcare sector is growing rapidly. Objective: To perform an empirical study of procrastination practices at workplace and their associated factors across institutions in a cross-sectional data setting when the target population is healthcare administrative professionals. Method: A specific questionnaire was prepared to address the stated objective. Two estimation procedures were performed: (i) seemingly unrelated regression was used to determine the effect of routine procrastination practices on project management procrastination; (ii) White's heteroscedasticity consistent covariance estimator is used to estimate a single model. Results: The main finding is that the routine procrastination practices have a positive impact on project management procrastination 1% level, there is sufficient evidence to support the claim that neuroticism and project procrastination are not related, indicating that people have rational choices and obey to the time-consistent preferences. In addition, we found that people working at the Ministry of Health and University Hospitals were more likely to procrastinate at workplace than any other healthcare institutions. A further finding highlights a more general issue: respondents' bad habit is an important factor for people to procrastinate at workplace. Conclusion: This paper contributes to past procrastination in project studies; estimating each model separately and ignoring the inter-relation between these models provide biased results, and hence wrong policy decision makings.
Keywords: Procrastination, Project, Healthcare, Habits, Neuroticism, Questionnaire
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
There is a growing literature on procrastination over the past decades. Only few studies have explored procrastination from a management perspective over employees,1 and little research has explored procrastination in Healthcare Institutions rather than business settings, especially in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) where the healthcare sector is growing rapidly. The Kingdom increased the budget of the Ministry of Health by 7.40% during the fiscal year of 2020, the highest increase in more than a decade despite a government deficit of SAR186, 935million, and the highest percentage of the Kingdom’s GDP on healthcare among the GCC countries. The main goal of this increase is to support its healthcare transformation strategy (HTS) proposed in the vision 2030 of the Kingdom. 2 The HTS is the first of three five–year phases. Each phase will put the Kingdom on track to reach the ultimate goals of its vision.2,3
Motivated by the HTS, the focus of this paper is on the negative form of procrastination practices at workplace, when the target population is healthcare administrative professionals working in the Kingdom; that means the irrational delay of behavior.4
Therefore, the goal of this paper is twofold. The first goal is to perform an empirical study of procrastination practices at workplace and their associated factors across healthcare institutions in a cross-sectional data setting. The collection of the data was performed through a survey that was supervised by the principal investigator to ensure the best procedures were adopted. The second goal is to determine the impact of routine procrastination practices on project procrastination practices. This latter is subsequently tested, and the results are compared to a broad single equation model.
Literature review
Langton5 suggests that procrastination is the process of doing more pleasurable things in place of less pleasurable ones, thus delaying tasks to later time. A more in-depth analysis of procrastination defines procrastination as a voluntary delay of an intended course because of, (i) fear of success6 or failure,7 or (ii) fear of being alone or dependent. 8Procrastination may cost employers about $10,000 per employee per year9 and reduce earnings by approximately 30%. 10
There are many types of procrastination: (i) academic procrastination, defined as putting academic assignments until the last minute if at all;11 (ii) life routine procrastination, defined as difficulty in scheduling when to do the many recurring life routines and doing them on schedule12and in some studies they called it ‘Trait Procrastination;’8 (iii)decisional procrastination, defined as the inability to make timely decisions in minor matters13, 14 and in major ones;15and (iv) compulsive procrastination defined as decisional and task procrastination in the same person.
A variety of other studies suggested that all procrastinators lack high action identities. 16, 17The generality of the action identity will be referred to as the level of the action identity. 18, 19 On the Decisional Procrastination side, indecisiveness has been defined20 as a trait-related general tendency to experience decision difficulties across a variety of situations, leading to decision delay, worry, and regret. Indecisive individuals not only show uniformly increased delay relative to others, but rather that their delay behavior may be more striking in its unresponsiveness to risk. 21In another study,22 it has been confirmed that there is strong evidence for that indecisive individual in changed shift behavior from the first to the second half of the task. Anticipated regret and perceived fairness were mentioned as possible mediating processes. 23 An experimental study in a bank in Colombia aimed to send reminders about goal achievements with small in-kind prizes every week to remind employees of their goal achievements found effective for fighting procrastination in the workplace. 24
Projects are aspirational efforts using significant resources to reach a better future state by achieving tangible goals. 25 The value of these projects is very known in the literature by studying cost-benefit analysis approach in a broad sense. 26, 27, 28, 29Recent research indicates30 that projects contribute to approximately one-third of the gross domestic product (GDP) in a typical Western economy transitioning from an industrial to a post-industrial setting.
Past research on project procrastination has shown people are most prone to procrastinate on the highest cost of the project stage. 31 If the cost structure is endogenous, people are prone to choose cost structures that lead them to start but not finish projects.32
A meta-analysis33 contains the correlations of 121 studies examining the relation between procrastination and personality variables (motives, affect, and performance), resulted in a negative effect found in relation to conscientiousness and self-efficacy, and a positive relation was found with self-handicapping. Affect was moderately related, as well as performance outcomes, and motives were weakly correlated.
In the next section, we examine the methods used to perform the analysis of this study. Then, the results are reported and discussed. And finally, the paper concludes with some remarks that may refine and improve the validation of our results.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design and sampling techniques: The target population for this study was the administrative professionals who worked in the healthcare facilities located in Riyadh city, Saudi Arabia. The term “healthcare facility” includes Ministry of Health (MOH) hospitals, private hospitals, military hospitals, and academic hospitals.
A cross-sectional study was conducted based on the following criteria: (i) Individuals who are working at administrative departments in the hospitals; (ii) A minimum of bachelor’s degree diploma and three years of experience in the field; (iii) Saudi citizen or non-Saudi citizen; (iv)English or Arabic as a native or second language.
A subset of the population working in this area was surveyed by using a self-administered questionnaire. Based on MOH, 2019, the total number of health administrators is 3920, with a margin of error of 5%, a confidence level of 95%, and a response distribution of 50%, the estimated sample size was 350. Trained research coordinators at King Abdulaziz Medical City conducted the interviews. The collection of the data was supervised by the principal investigator to ensure the best procedures were adopted. After cleaning and editing the data set, only 245 responses were retained and used for this study (response rate = 70%).
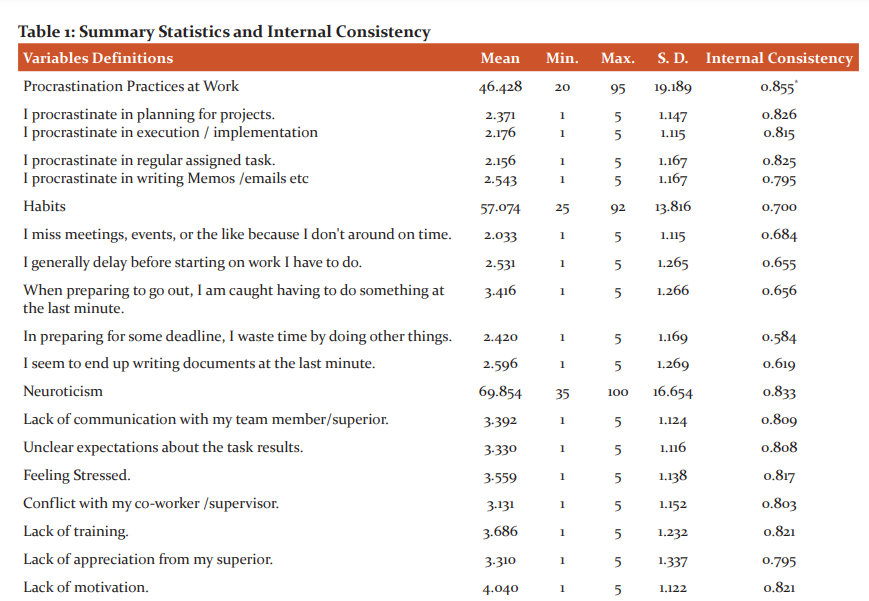
Interview questionnaire: A specific questionnaire was prepared in 2020 that addressed the aims of this study. To best of our knowledge, no existing questionnaire has been found that cover this type of analysis. In this paper, we have three continuous dependent variables (Table 1): The first dependent variable is project management procrastination (item 1 and 2), the second dependent variable is routine procrastination practices (item 3 and 4), and lastly, the procrastination practice at work (items 1, 2, 3,4) which includes project management procrastination and routine procrastination practices as well.
The exogenous variables can be classified in two categories. The first category includes two continuous variables: procrastination habits (5 items) and neuroticism (7 items).
In all these items, employees are asked to rate their responses in – Likert response categories – ranging from 1 “strongly disagree” to 5 “strongly agree”. For each variable, items are summed and converted on to a scale of 100 to minimize measurement errors encountered in this type of analysis. The second category includes respondent's personal characteristics such as sex, nationality, age, and experience. 32
Statistical analysis: SAS 9.2 version33was used for data analysis. The internal consistency 34 of each dimension was checked via Cronbach coefficient “alpha >0.70.”
The Kruskal-Wallis 35 test was used to compare the homogeneity among groups. Two estimation procedures were performed: (i) seemingly unrelated regression36 was used to determine the effect of routine procrastination practices on project management procrastination; (ii) White’s heteroskedasticity consistent covariance estimator37 is used to estimate a single model. And finally, our analyses present test of significance of some important factors affecting procrastination at workplace by using an F-test.
RESULTS
The summary statistics and internal consistency were provided by Table 1. The study sample was comprised of 71% men and 29% women. 79.6% of respondents are Saudi while 20.4% are non-Saudi. Project management procrastination (PMP), routine procrastination practices (RPP), and procrastination practices at workplace (PPW) represented average below 50% (45.5%, 47.4%, and 46.4% respectively), while habits and neuroticism represented average above 50% (51.9% and 69.8% respectively). Finally, experience had standard deviation 74% half the size of the mean, indicating a wide range of experience across the sample.
The reliability of all variables was determined by using Cronbach’s alpha method. In all dimensions, the overall alpha scale was, at least, equal to or greater than 70%, suggesting that all variables exhibit internal consistency at subscale levels.
The validity of instruments was conceptually difficult to prove quantitatively without a standard. However, some evidence may be built over time. One method is to check construct validity. The construct validity was supported by two evidences: (i) the high internal consistency mentioned above; (ii) the quantitative analysis that will be discussed later in this section.
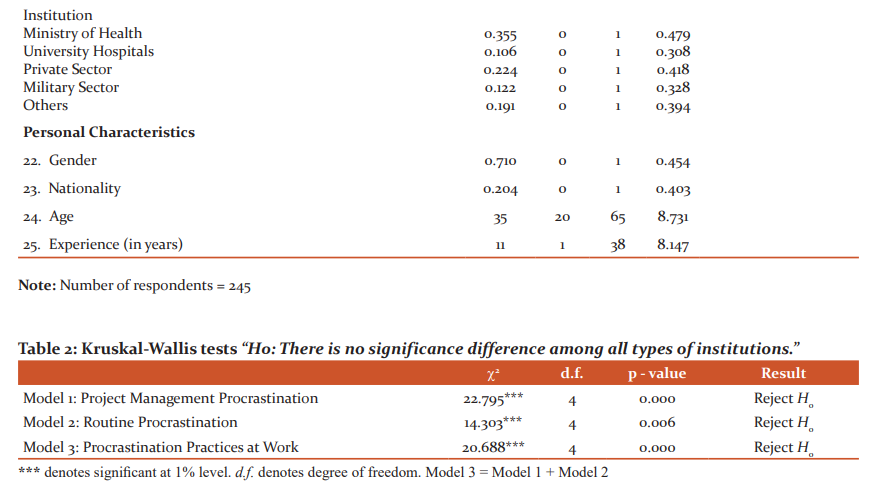
We used Kruskal – Wallis procedure to test whether healthcare institutions differ significantly among these groups. Table 2 provides the results of this test for PMP, RPP, and PPW. Under the null hypothesis that there is no significant difference among all types of healthcare institutions is rejected for all types of practice. For this reason, we generated four dummy variables that considered this difference (Table 1).
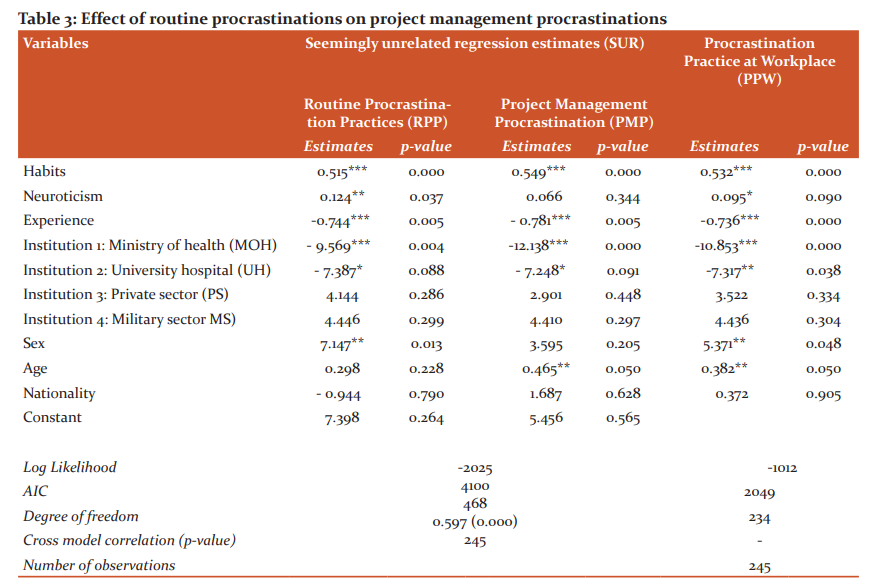
Table 3 shows the parameter estimates of the statistical models. The effect of routine procrastination practices on project procrastination practices is showed by cross model correlation estimates (estimates= 0.597, p-value = 0.000), and deemed to have significant positive impact at 1% level. Thus, the estimates of the procrastination practice at workplace model are reported in the last column for comparative purposes only.
In a statistical context, and not surprisingly, the RPP estimates show that habits and neuroticism increase procrastination (estimates are 0.515 and 0.124 respectively). These suggest that habits and, with less degree neuroticism, are important factors that enhance procrastination tendencies. Moreover, and across institutions, we found that professionals working at the Ministry of Health and University Hospitals were more likely to procrastinate at workplace, while Military sector and Private sector did not provide us any effects.
Regarding the PMP estimates, we found similar pattern in terms of sign and significance, except that neuroticism has no significant impact on PMP (the past study also indicates that neuroticism has no direct link to procrastination),38 and the magnitude of the parameters estimates in the PMP model are greater than that of RPP model.
In terms of respondent personal characteristics, we investigated four factors associated with procrastination. These include respondents' sex, age, experience, and nationality. These factors deemed to be related to procrastination but in more diffuse and nonspecific pattern. Professionals' people with long experience have less procrastination practice for both RPP and PMP models, suggesting people with long experience are more organized in setting their goals. For the RPP model, male professionals tend to procrastinate more than female, while age has no significant effect. The opposite pattern holds for the PMP model, that is mean, older professionals procrastinate more than younger professionals, while sex has no significant effect. Finally, the nationality of professional workers has no
significant effect on both models. To better understand the above findings, we conducted several tests of the most important factors, cross the models, that may affect procrastination, and which are then compared to a single equation estimation model (model PPW, last two columns of Table 3). Table 4 contains the results of these tests. Test 1, states that there is no relationship between procrastination and neuroticism; Test 2, states that healthcare administrative professionals working at the Ministry of Health and University Hospitals do procrastinate; and finally, Test 3, states that respondent’s sex and age affect, indeed, procrastination.
Results show, also, that neuroticism cannot affect healthcare administrative professionals to procrastinate when managing projects (p-value = 0.142). This result is a little bit different from the PPW model where neuroticism is significant at 10%. Hence, using a single equation estimation may lead to the wrong result. However, Tests 2 and 3 are rejected by SUR procedure, indicating that healthcare administrative professionals working at the Ministry of Health and University Hospitals do not procrastinate and that sex and age, in general, have a positive effect on procrastination.
DISCUSSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS
Our empirical analysis identifies several results about procrastination practices at workplace when the target population is healthcare administrative professionals. The key intuition that drives our results is that by just estimating the PPW model as a single equation and ignoring the impact of RPP on PMP, the non-significance of neuroticism cannot be detected. The first reason of the absence of neuroticism is that Healthcare Administration requires effective leadership and business expertise in addition to strong analytical and communication skills. A second reason is that healthcare administrative professionals deemed to be rational in their decision makings and they obey to the time-consistent preferences.39Thus, it is possible to state that neuroticism cannot affect healthcare administrative professionals to procrastinate when managing projects. Another finding of the study that deserves to be mentioned is that healthcare administrative professionals working at the Ministry of Health and University Hospitals procrastinate more than any other healthcare institution, although the former is more significant than the latter, in a statistical context.
The results in this study highlight a more general issue: respondents’ habit or the environmental cultural is an important factor for people to procrastinate at workplace. Habit is a very complex dimension to measure and evaluate since some of the habit's components are associated with heredity, 40 teamwork activity, friends, etc. One possible solution for policy decision makings is to implement incentives to combat bad habits at workplace. These incentives may include a significant improvement of the institution's environmental culture by providing people adequate training, a meaningful and challenging workplace, and especially, competency-based performance systems. 41, 42, 43
CONCLUSION
This paper focused on performing an empirical study of procrastination practices at workplace and their associated factors across institutions in a cross-sectional data setting. The target population was healthcare administrative professionals in Saudi Arabia. It is important to openly acknowledge the limitation of the data and the potential bias encountered in cross-sectional data. 44
Three models were developed that distinguish among routine procrastination practices (RPP), project management procrastination (PMP), and procrastination practice at workplace (PPW). A seemingly unrelated regression estimation was used to capture the effect of RPP on PMP. Throughout our analysis, we proposed testable hypotheses across the models and their implications for policy decisions making process. The findings of this study indicate that the routine procrastination practices at workplace have, indeed, a positive impact on project procrastination. In addition, and across the models, neuroticism has no relationship with procrastination, and that age and sex have positive impact on procrastination. Furthermore, we found that professionals working at the Ministry of Health and University Hospitals were more likely to procrastinate at workplace, while Military sector and Private sector did not provide us any significant effects.
We suggest this paper contributes to past procrastination in project studies: estimating each model separately and ignoring the inter-relation between these models provide biased results, and hence wrong policy decision makings. In line with the recognition of the need for more studies on project procrastination in health care sector, we provided models that distinguish among different types of institution.
More research is needed to validate and refine the above findings. A possible strategy for healthcare institutions to curb procrastination would be to increase the sample size at the national level and test how robust the present findings are under different parameterizations and model specifications. We also see a new opportunity on model building on project values28 that allows a more comprehensive understanding of the strategic choices for each institution rather than using project as broad variable. Moreover, additional research on the genetic aspects of procrastination is required to better understand this phenomenon,45 and how these aspects differ across cultures.
Acknowledgement:
Authors acknowledge the support of NGHA for this research. Special thanks to respondents of the questionnaire who provided valuable and constructive information that greatly inspired the research and IJCRR comments on an earlier version of the manuscript.
Source of funding: None
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest
Authors’ Contribution:
Mohamed Khedhiri: Manuscript writing, submission, and revision.
Hanan Althagafi: Questionnaire design and literature review.

References:
-
Ferrari J.; Dovosko E.; and Joseph N. Procrastination in Corporate Settings: Sex, status, and geographic comparisons of arousal and avoidance types. Ind Diff Research, 2005; (3), 140-149.
-
Grand S. and Wolff K. Assessing Saudi Vision 2030: A 2020 Review. Retrieved from: https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/wpcontent/uploads/2020/06/Assessing-Saudi-Vision-2030-A-2020-review.pdf.
-
https://www.moh.gov.sa/en/Ministry/vro/Documents/Healthcare-Transformation-Strategy.pdf.
-
Akerlof, G. A. Procrastination and Obedience. American Eco Rev, 1991; 81 (2), pp. 1-19.
-
Langton. Procrastinating. J Th Soc Beh, 2016; 11, 207-221
-
Berg N. and Gigerenzer G. As-if behavioral economics: Neoclassical economics in disguise? Hist Econ Ideas, 2010;(18), 133–165.
-
Steel, P. Arousal, avoidant, and decisional procrastinators: Do they exist? Pers&Ind Diff, 2010;(48), 926–934.
-
Steel, P. The Nature of Procrastination: A Meta-Analytic and Theoretical Review of Quintessential Self-Regulatory Failure. Psy Bulletin, 2007;(133), 65-94.
-
D’Abate C., and Eddy E. Engaging in personal business on the job: Extending the presenteeism construct. H Res Dev Quarterly, 2007;(18), 361–383.
-
Fletcher, J. The effects of childhood ADHD on adult labor market outcomes (Working Paper 18689). Available National Bureau of Economic Research at: http://www.nber.org/papers/w18689.
-
Solomon L. and Rothblum, E. Academic Procrastination: Frequency and cognitive-behavioral correlates. J Couns Psy, 1984; (31), 503-509.
-
Milgram, N. (1988). Procrastination in Daily Living. Psych Reports, 1988;(63):752-754.
-
Effert R. and Ferrari J. Decisional Procrastination: Examining personality correlates. J Soc Beh& Pers, 1989; (4), 151-156.
-
Janis I. and Mann L. Decision-making: A Psychological Analysis of Conflict, Choice, and Commitment, 1977. Free Press: New York.
-
Ellis A. and Knaus W. Overcoming Procrastination. Institute for Rational Living, 1979: New York.
-
Dewitte S and Lens W. Psychology and Economics; Evidence from the Field. JEco Lit, 2010;(47); 315-37.
-
Dewitte S. and Lens W. Procrastinators Lack a Broad Action Perspective. Europ J Pers, 2000; (14), 121–140.
-
Vallacher R. and Wegner D. A Theory of Action Identification. Erlbaum, 1985: Hillsdale, NJ.
-
Vallacher R. and Wegner D. What Do People Think They're Doing? Action Identification and Human Behavior. Psyc Rev, 1987; (94), 3-15.
-
Patalano A and Wengrovitz S. Indecisiveness and Response to Risk in Deciding When to Decide. J Beh& Dec Making, 2007; (20), 405–424.
-
Patalano A.; Juhasz B.; and Dicke J. The Relationship between Indecisiveness and Eye Movement Patterns in a Decision-Making Informational Search Task. J Beh & Dec Making, 2010; (23),353–368.
-
Pittman T..; Tykocinski O.; Sandman-Keinan R.; and Matthews P. When Bonuses Backfire: An Inaction Inertia Analysis of Procrastination Induced by a Missed Opportunity. J Beh&Dec Making, 2008; (21), 139–150.
-
Cadena, OX. and National Bureau of Economic Research. Fighting Procrastination in the Workplace: An Experiment. Cambridge, Mass: Nat Bur Econ Res, 2011.
-
Winch G. (2015). Project organizing as a problem in information. Construction Mgmt &Econ, 2015;(33), 106–116.
-
Laursen M. and Svejvig P. Taking stock of project value creation: A structured literature review with future directions for research and practice. Int JProj Mgmt, 2016; (34), 736–747.
-
Martinsuo M. The management of values in project business: Adjusting beliefs to transform project practices and outcomes. Proj Mgmt J, 2020;(51), 389–399.
-
Martinsuo M., Klakegg, O., and Van Marrewijk A. Editorial: Delivering value in projects and project-based business. Int J Proj Mgmt, 2019; (37), 631–635.
-
Zerjav V. Why Do Business Organizations Participate in Projects? Toward a Typology of Project Value Domains. Proj Mgmt J, 2021; (52), 287–297.
-
Schoper Y., Wald, A., Ingason, H., and Fridgeirsson, T. Projectification in Western economies: A comparative study of Germany, Norway, and Iceland. Int J Proj Mgmt, 2018; (36), 71–82.
-
O’Donoghue T. and Rabin M. Procrastination on Long-term Projects. J Econ Beh& Org, 2008;(66),161-175.
-
O’Donoghue T. and Rabin M. Doing it now or later. A Econ Rev, 1999; (89), 103-124.
-
Wendelien V. A meta-analytically Derived Nomological Network of Procrastination.Pers& Ind Dif, 2003; (35), 1401-1418.
-
Lonergan M. and Maher J. The Relationship between Job Characteristics and Workplace Procrastination as Moderated by Locus of Control. J Soc Beh&Pers, 2000;(15), 213-224.
-
SAS/SAT 9.2 User’s Guide,2007. SAS Institute, Cary, North Carolina.
-
Cronbach, Lee J. (1951). "Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests". Psychometrika. (16), 297–334.
-
Kruskal; Wallis (1952). "Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis". J A Stat Ass. 47 (260), 583–621.
-
Greene, WH. Econometric Analysis. Third Edition, 1997. Prentice hall, Engel Wood Cliffs.
-
White, H. A Heteroskedasticity-Consistent Covariance Matrix Estimator and a Direct Test for Heteroskedasticity. Econometrica, 1980;(48), 817–838.
-
Lee DG.; Kelly KR.; and Edwards, JK. A Closer Look at the Relationship Among Traits Procrastination, Neuroticism, and Conscientiousness. Pers & Ind Dif,2006; (40), 27 – 37.
-
Plomin R. and Caspi A. Behavioral Genetics and Personality. In Pervin, L.A. and John, O., Handbook of personality: Theory and research, 1999 (251-277). New York: Guilford Press.
-
Boyatzis R. Using Tipping Points of Emotional Intelligence and Cognitive Competencies to Predict Financial Performance of Leaders. Psicothemia, 2006;(18), 124-132.
-
Calhoun J., Vincent, E., Calhoun, G., and Brandsen L. Why Competencies in Graduate Health Management and Policy Education? J H Ad Ed, 2008; (1),17-36.
-
Ulrich D., Zenger J., and Smallwood N. Building your Leadership Brand. Leader to Leader, 2000; 40-46.
-
Bland M. An Introduction to Medical Statistics. 3rd Edition: Oxford University Press, 2002; 27-31.
-
Gustavson D., Miyake A., Hewitt J., and Friedman N. Genetic Relations Among Procrastination, Impulsivity, and Goal Management Ability: Implications for the Evolutionary Origin of Procrastination. Psy Sci;2014;(25), 1178–1188
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License