IJCRR - 13(22), November, 2021
Pages: 115-120
Date of Publication: 20-Nov-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Prevalence and Risk Factors for Malnutrition among Rural School Children in Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh, India
Author: Goruntla Narayana, Dudekula Ruha Thasmiya, Poluru Prasuna Chowdary, Kasturi Vishwanathasetty Veerabhadrappa, Madhale Milka D, Kandula Usharani, Murugesan Reetha
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: There was a scarcity of evidence on malnutrition-related factors among school-going children ≥ 5 years in rural India. Objective: To assess the prevalence of stunting, underweight, wasting, and associated factors in school children of Anantapur district. Methods: This was a cross-sectional study conducted in a primary and secondary school located in rural settings of Anantapur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. A multi-stage random sampling technique was used to select the children for our study. The study was approved by the institutional review board and registered in the clinical trial registry of India. A suitable data collection form was used to collect information about socio-demographics, utilization of government nutritional programs, physical activity, and WHO anthropometric parameters. Chi-square Fisher exact test was used to associate predictors with malnutrition measures. The height-for-age z-score for stunting, weight-for-age z-score for undernutrition, and weight-for-height z-score for wasting were computed in WHO anthroplus software. Results: A total of 390 children have participated in the study with a mean age of 11.8\?2.4. The prevalence of stunting, underweight, and wasting among school children was 25.4%, 11.5%, and 17.7%, respectively. There was no significant difference in the nutritional measures among male and female children. Predictors like illiteracy of parents, joint family, and non-healthcare occupations were significantly associated with malnutrition characteristics among school-going children. Conclusion: The study concludes that the prevalence of stunting, underweight, wasting was existing among rural school-going children. Even government provides nutritional schemes to overcome malnutrition disorders in school children, there was still a gap to prevent nutritional disorders. Targeted educational programs on the importance of child nutrition and malnutrition complications towards mothers are required to improve nutritional status among school-going children
Keywords: Anthropometry, Children, Nutrition, Stunting, Under-weight, Wasting
Full Text:
Introduction
Globally, including in India, health complications associated with undernutrition and deficiency of vitamins is a significant public health problem.1 Nutritional status during school age is a major predictor of nutritional and health status in adult life. The quality of life of the children residing in rural settings is inferior compared to the urban settings of India.2
School-age is the dynamic period for the physical growth and mental development of the child. Evidence shows that poor nutritional status is the primary cause of low school enrolment, absenteeism, early dropouts, and low performance.3 In the current scenario, the nutritional status of children was very unsatisfactory in India. According to the National Family Health Survey (NFHS) report, about 45.5% of children are suffering from disorders associated with malnutrition in India.4 Even though India has a higher Gross National per capita income (US$1070) than other Asian countries (Bangladesh=US$570; Nepal=US$400), yet undernutrition is high in India compared to these countries.5 Therefore, poverty alone does not entirely explain the burden of undernutrition, but it also relates to parental education, awareness, lack of sanitation, low food intake, family size, suffering from infectious diseases, social, cultural, and political aspects regarding nutrition recommendations.6
There was less attention among health providers/policymakers towards evaluating the nutritional needs of school-age children than under-five age groups.7 Most of the time, maternal and child health programs/schemes cover nutritional requirements of children under five years of age only.8 School age is also very crucial to identify health problems associated with undernutrition and treat them early. So, our study aims to assess the prevalence of stunting, underweight and wasting, and associated factors among school-going children in rural school settings of Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Materials and Methods
A cross-sectional, descriptive-analytical study was conducted in primary and secondary schools located in rural settings of Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh, India. The study was conducted for a period of six months, from April 2019 to September 2019.
Study criteria
Children aged more than or equal to five years and less than are equal 15 years, irrespective of gender, and who attended school at the survey time were included in the study. The physically challenged children and having spinal deformities were excluded from our study due to difficulty in measuring the anthropometric parameters. Also, children suffering from any chronic disorders are not considered for inclusion in our study.
Registration and Ethical considerations
The trial was registered in the Clinical Trial Registry of India (CTRI/2019/11/022144) before enrolment of the participants. The study was conducted after getting ethical clearance from Institutional Review Board (RIPER/IRB/PP/2019/009). Verbal and written consent was taken from the parents or guardians to enrol their children in our study. Confidentiality of the data and anonymity of the participants was maintained during and after completion of the study.
Sample size and sampling technique
The sample size was calculated using Epi-Info 7 statistical software given by the Centre for Disease Control, USA. The sample size was determined by considering the proportions of underweight, stunting, and wasting reported by Srivastava et al. study in Uttar Pradesh, India. (1) The parameters used in sample size determination, calculated sample size, and the final sample size was represented in Table 1.
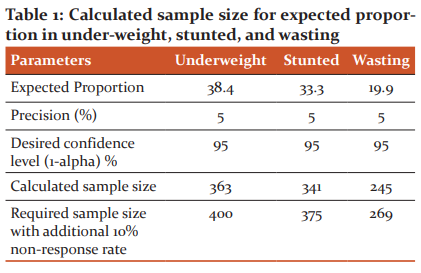
By considering the expected proportion of 38.4%, precision 5%, confidence level 95%, and non-response rate of 10%, the final sample size was determined as 400.
A simple random sampling technique was used to select the required number of children from the selected two primary and two secondary schools present in rural settings of Anantapur District. From each school, 100 children were selected randomly from the total school strength using a table of random numbers. Children who satisfy the study criteria were subjected to collect data about demographics and anthropometric parameters.
Data collection
A total of 390 children and their parents or caregiver were enrolled in our study after getting oral and written informed consent. All parents or caregivers were explained about study objectives and protocol in the local language before getting informed consent. A suitable data collection form was used to collect the socio-demographic and anthropometric parameters of the study participants.
Socio-demographic details like children's age, gender, parents’ education, religion, type of family, socio-economic status, physical activity, utilization of government nutrition programs, and parents belonging to healthcare jobs were collected from the parents by face-to-face interviews and medical records. The socio-economic status of the family was assessed by using a modified Kuppuswamy classification.
Anthropometric measurements (weight and height) for all children aged between five and 15 years were assessed using standard equipment for height and weight. Nutritional assessment was carried out by using World Health Organization (WHO) 2006 child growth standards. height-for-age z-score for stunting, weight-for-age z-score for underweight, and weight-for-height z-score for wasting were computed in WHO anthroplus software. The threshold points for the determination of undernutrition measures were given below;
Underweight: weight-for-age z-score ≤ 2 standard deviations (SD) of the WHO child growth standards median.
Stunting: height-for-age z-score ≤ 2 standard deviations (SD) of the WHO child growth standards median.
Wasting: weight-for-height z-score ≤ 2 standard deviations (SD) of the WHO child growth standards median.
Statistical Analysis
Data analysis was performed by using Epi-Info 7 statistical software given by the Centre for Disease Control, USA. Descriptive statistics like proportion, frequency, mean, and standard deviation were used to represent the socio-demographic and anthropometric parameters of the study participants. Inferential statistics like the Chi-square test was used to associate the socio-demographics with stunting, underweight, and wasting. P< 0.05 was considered as a statistically significant value.
Ethical clearance: The study was conducted after getting ethical clearance from Institutional Review Board (RIPER/IRB/PP/2019/009).
Results
A total of 390 children (male=59; female=231) have participated in the study with a mean age of 11.8±2.4 years. The majority of the children were physically active (357; 91.5%), Hindus (354; 90.7%), lower socio-economic family group (213; 54.6%), and utilizing government nutritional scheme (390; 100%). The majority of the parents were non-healthcare jobs (345; 88.5%), and illiterates (77.2% of Mothers and 50.3% of Fathers) as represented in Table 2.
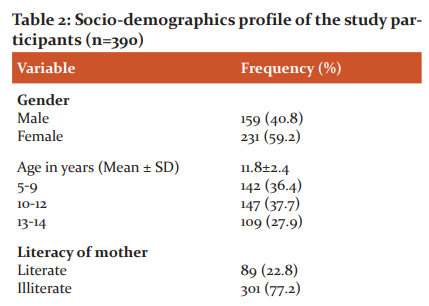
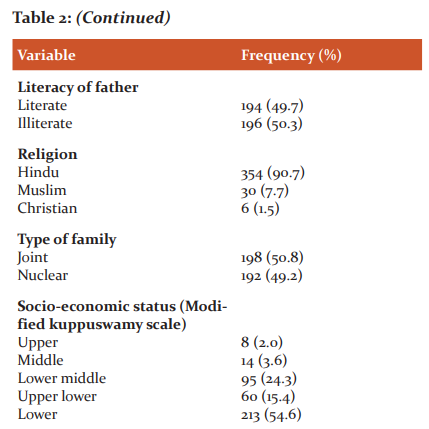
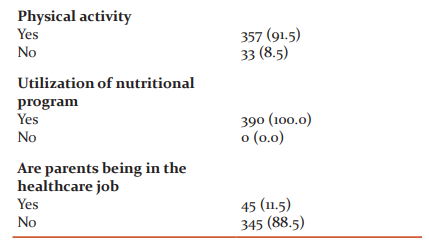
The study findings revealed that the prevalence of stunting, underweight, and wasting were found to be 25.4%, 11.5%, and 17.7%, respectively. There was no significant difference among male and female children concerning undernutrition measures. Undernutrition measures associated with age and gender were represented in Table 3.
Above 10 years of age, many children experience the pubertal growth spurt and appear to have more weight concerning the weight-for-age score. They have not achieved weight requirements as per age. The weight-for-age indicator does not differentiate height and body mass in children above 10 years.
Weight-for-age reference data are not available beyond age 10 because this indicator does not distinguish between height and body mass in an ageing period where many children are experiencing the pubertal growth spurt and may appear as having excess weight (by weight-for-age) when in fact they are just tall.
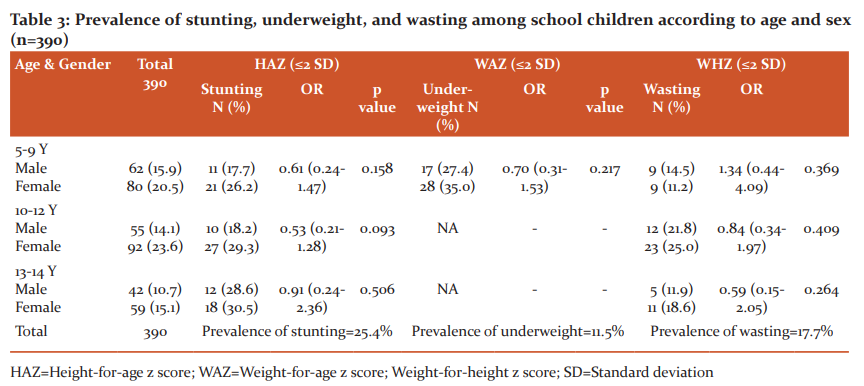
HAZ=Height-for-age z score; WAZ=Weight-for-age z score; Weight-for-height z score; SD=Standard deviation
Predictors like illiteracy of parents, the joint family were significantly associated with undernutrition characteristics like stunting, underweight, and wasting. Parents' non-healthcare occupation was significantly associated with stunting. All predictors associated with undernutrition measures were represented in Table 4.


Discussion
Children in the age group between 5 and 15 years were considered as school age. This age is a very crucial period for physical growth, mental development, and social changes. The present study provides insights for the planning and development of educational programs based on socio-demographic correlates of undernutrition in rural school children.
The current study revealed a nutrition lag in terms of height and weight compared to the reference standards laid down by the WHO. In developing countries, including India, most children fail to grow in length and weight as per the age-specific pattern; there was a vast difference in the prevalence of low weight for age and height for age between the regions. Our study findings show that the prevalence of stunting, underweight, and wasting among rural school children was 25.4%, 11.5%, and 17.7%, respectively. Our study showed a low prevalence of underweight and wasting compared to the studies conducted in the Uttar Pradesh (2010) and Telangana (2016) states of India. It might be due to; improvements in the government nutritional schemes for school children in recent years. Even though there was a reduction in under-nutrition status in our study compared to the previous studies in India, there was still a need to address and educate the importance of nutrition and health among parents and children. The prevalence of under-nutrition status was low in India compared to other developing countries like Ethiopia, and Egypt.2,3,8,9
The study results show that there was no statistically significant difference in stunting, underweight, and wasting among male and female rural children. However, the proportion of under-nutrition status was high among female children. Our findings are contrary to the findings of other studies conducted in India, where the prevalence of under-nutrition was significantly high among girl children.10–12 Our study also supports these findings because the sample size is less compared to other studies in our study.
Predictors like illiteracy of parents, joint family, and non-healthcare occupation of the parents were significantly associated with malnutrition characteristics among school-going children in our study. These predictors are reported in various studies conducted in school-going children of India and other countries.3,9–11 Nutrition educational programs targeting children and parents will bring down the burden of under-nutrition in specific to rural school-going children.13,14 Finally, the study shows that maternal education, maternal working status, and family type are core determinants of child nutrition and health.15 Strategies focused on improving female literacy, women empowerment, and restricted family size will positively affect child nutrition and health.
Strengths and limitations
The study provides insights into the development of nutritional schemes or programs for school-going children in rural settings of the Anantapur district. The study was conducted in government schools located in rural areas of the Anantapur district. So, these findings may not apply to private schools and schools located in urban settings of the district.
Conclusion
The study concludes that the prevalence of stunting, underweight, and wasting was existing among rural school-going children. Even government provides nutritional schemes to overcome malnutrition disorders in school children, there was still a gap to prevent nutritional disorders. Targeted educational programs on the importance of child nutrition and malnutrition complications towards mothers are required to improve nutritional status among school-going children.
Acknowledgement
All authors would like to thank school management, children, and parents who spend their time providing valuable data to complete the study successfully.
Conflict of interest: Nil
Ethical clearance number: RIPER/IRB/PP/2019/009
Source of funding: Nil
Author’s contribution
This work was carried out in collaboration among all authors. Author GN designed the study, performed the statistical analysis, wrote the protocol, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Author RT, PC, KVV, MDM, UK, and MR helps in hypothesis framing, literature review, design, data collection, data entry, and managed the analyses of the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
References:
1. Srivastava A, Mahmood SE, Srivastava PM, Shrotriya VP, Kumar B. Nutritional status of school-age children - A scenario of urban slums in India. Arch Public Health. 2012 Dec;70(1):8.
2. Aurino E, Schott W, Behrman JR, Penny M. Nutritional Status from 1 to 15 Years and Adolescent Learning for Boys and Girls in Ethiopia, India, Peru, and Vietnam. Popul Res Policy Rev. 2019 Dec;38(6):899–931.
3. Ayalew M, Bayley A, Bekele A, Handebo S. Nutritional Status and Educational Performance of School-Aged Children in Lalibela Town Primary Schools, Northern Ethiopia. Int J Pediatr. 2020;20(1):1-9.
4. Kamran Shaikh M, Kamble N, Bhawani D, Bele S, Sita RR. Assessment of nutritional status among school children of Karimnagar, Telangana, India. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016;4(1):4611–7.
5. Kanjilal B, Mazumdar P, Mukherjee M, Rahman MH. Nutritional status of children in India: household socio-economic condition as the contextual determinant. Int J Equity Health. 2010;9(1):19.
6. Murarkar S, Gothankar J, Doke P, Pore P, Lalwani S, Dhumale G, et al. Prevalence and determinants of undernutrition among under-five children residing in urban slums and rural area, Maharashtra, India: a community-based cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2020 Dec;20(1):1559.
7. Srivastava A, Mahmood SE, Srivastava PM, Shrotriya VP, Kumar B. Nutritional status of school-age children - A scenario of urban slums in India. Arch Public Health. 2012 Dec;70(1):8.
8. Abdel Wahed WY, Hassan SK, Eldessouki R. Malnutrition and Its Associated Factors among Rural School Children in Fayoum Governorate, Egypt. J Environ Public Health. 2017;2017(1):1–9.
9. Girma A, Woldie H, Mekonnen FA, Gonete KA, Sisay M. Undernutrition and associated factors among urban children aged 24–59 months in Northwest Ethiopia: a community based cross-sectional study. BMC Pediatr. 2019 Dec;19(1):214.
10. Patel PP, Patel PA, Chiplonkar SA, Khadilkar AV, Patel AD. Effect of mid-day meal on nutritional status of adolescents: a cross-sectional study from Gujarat. Indian J Child Health. 2016 Sep 25;03(03):203–7.
11. Sharma M, Watode B, Srivastava A. Nutritional Status of Primary School Children through Anthropometric Assessment in Rural Areas of Moradabad. Ann Int Med Dent Res [Internet]. 2017;4(2):1-10
12. Rema N. Prevalence of nutritional and lifestyle disorders among school-going children in urban and rural areas of Coimbatore in Tamil Nadu, India. Indian J Sci Technol. 2011 Feb 20;4(2):131–40.
13. Mwaniki EW, Makokha AN. Nutrition status and associated factors among children in public primary schools in Dagoretti, Nairobi, Kenya. Afr Health Sci. 2013 Mar;13(1):39–46.
14. Agia H, Abe K, Andrianome VN, Randriamampionona E, Razafinombana AR, Murai T, et al. Risk factors for malnutrition among school-aged children: a cross-sectional study in rural Madagascar. BMC Public Health. 2019 Dec;19(1):773.
15. Rahaman SN, Das S, Dash SK, Giri B, Ali KM. Nutritional Status of Primary School Children in Different Parts of India: A Review. IJCRR. 2019;11(07):01–4.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License