IJCRR - 13(22), November, 2021
Pages: 100-104
Date of Publication: 20-Nov-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Alloxan-induced diabetes, Prenalon, Small intestine, Sucrase, Lactase, Maltase, Glucose levels
Author: Karimova II, Kuchkarova LS, Ergashev NA, Tursunboeva HO, Rakhmatova MJ, Khidirova NK
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: It is known that the activity of intestinal enzymes involved in the digestion of carbohydrates increases in diabetes mellitus. An increase of intestinal brush bolder maltase, sucrase, and lactase activity was shown in experimental diabetes and hyperglycemia. To reduce the activity of intestinal carbohydrates various herbal preparations are used. Objective: This work aims to study the effect of prenatal on the activity of intestinal disaccharidases in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Material and Methods: White outbred rats were divided into the control and experimental groups to receive a single injection of saline, or alloxan monohydrate (150 mg/kg) (intraperitoneal) respectively. Further, experimental animals with high glucose levels were divided into the experiment I and experiment II groups. Control and experiment 1 group rats were injected with saline. Experiment 2 group rats were injected with prenatal (5mg/kg/24 h) for 30 days. The glucose level and intestinal disaccharidases activity were determined by using a glucometer and special kits (Human, Germany) respectively. Results: It was found that in experimental diabetes, the activity of the small intestine carbohydrates sharply increased. Injection of prenalon to alloxan-induced diabetic rats resulted in stabilizes of glucose level and normalizing of the activities of intestinal sucrase, maltase, and lactase. Conclusion: Administration of prenatal to the alloxan-induced diabetic rats led to the restoration of blood glucose levels and the activity of intestinal disaccharidases.
Keywords: Alloxan-induced diabetes, Prenalon, Small intestine, Sucrase, Lactase, Maltase, Glucose levels
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common metabolic diseases, characterized by increased glucose levels, insulin deficiency, or low insulin sensitivity. A diabetic syndrome is also expressed changes in the activity of lipid, protein, and carbohydrate enzymes metabolism.1,2,3An increase of pancreatic and intestinal carbohydrases activity was shown in alloxan-induced4,5and in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.6,7
Currently, harmless plant substances which affect the activity of enzymes of glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, lipid peroxidation, and carbohydrate assimilation attract the attention as antidiabetic preparations.8,9,10To reduce the causing hyperglycemia activity of digestive carbohydrasesturkesteron4,5, acarbose6, quercetin7, black chokeberry extract11 and other preparation were used. Antidiabetic and hypoglycemic properties were also shown for a complex of substances from Alcea rosea. seed extract.12It has been suggested that obtained from the leaves of A. nudiflora prenalon, including various biologically active compounds with high activity13, might be effective for diabetes treatment.
This work aims to study the effect of prenalon on the activity of intestinal disaccharidases in alloxan-induced diabetic rats.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals
In the experiments, white outbred laboratory male rats weighing 200-220 g were used. Animal procedures were performed according to Helsinki Declaration of the World Medical Association (WMA) "Ethical Principles for Medical Research with Human Participation as Research Subjects", adopted at the 18th WMA General Assembly in June 1964, and revised at the 64th WMA General Assembly in 2013 The rats were kept in well-ventilated, clean and bright rooms in separate plastic cages 50×30×28 cm3in size 4 animals in each. The room temperature was 22-24 °?, the relative air humidity was 40-60%. Access to food and drinking water was not restricted. The rat’s diet was included the following components: grain feed, sunflower seeds, milk, meat, wheat bread, vegetables, dry soups.
Experimental design
At the first stage of the observation, the animals were divided into control and experimental groups. Before modelling diabetes rats of experimental groups have been fasting for two days with unlimited access to water. Then the animals of the experimental group were injected intraperitoneally with a solution of alloxan monohydrate (DIAEM, OOO, Russia, 150 mg/kg) and the animals of the control group were injected with an equal volume of saline at the same time in the same manner. On the 12th day of observation, blood from the tails was analyzed for glucose levels in all animals. Only experimental rats with a blood glucose level of around 200 mg% were taken for the next stage of observation. Further, animals with high glucose levels were evenly divided into two groups (experiment I and experiment II). During 30 days the control and alloxan-induced diabetic rats of the first experimental group (experiment I) were injected subcutaneously with saline. The alloxan-induced diabetic rats of the 2nd experimental group (experiment II) were also injected subcutaneously with the same volume of prenalon solution (5.0 mg/kg/24 h) in the morning between 8-10 hours for 30 days. The day when the rats began to receive prenalon was accepted as the 0th day of the experiment. Animals were sacrificed by decapitation in the morning between 8 and 10 o'clock on 5th, 10ht, 20th, and 30th days after prenalon administration. Before sacrification, the animals were starved for 24 hours. Immediately after decapitation and opening of the abdominal cavity, the small intestine was removed, cleaned from the mesentery, and washed with 20-30 ml of Ringer's solution (pH-7.4). Then, the intestine was cut open and the mucosa was separated with a plastic spatula and placed in the tube. Ringer's solution was poured into each containing mucosa tube in a ratio of 1:9. Obtained samples were homogenized using a Teflon/glass homogenizer within 1 minute at 300 rpm. All processes were performed in cold conditions.
Biochemical analysis
The blood glucose level was determined using a glucometer (Accu-Chek active (Roche Diagnostics, Switzerland).
To determine the activity of intestinal enzymes, 2% solutions of lactose, sucrose, and maltose (Reagent, Sigma) were used as a substrate. The activities of lactase (EC 3.2.1.23), sucrase (EC 3.2.1.48), and maltase (EC 3.2.1.20) of the small intestine were determined using a complex of reagents (Human, Germany) by the glucose oxidase method.14 The enzyme activity was calculated per gram of tissue concerning the amount of reducing glucose (µmol) for 1 minute.
Statistical Analysis
The arithmetic mean (M), standard error (m), t coefficient, and statistical significance value (P) were determined. If the P-value was less than 0.05, the difference between the two groups was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Glucose level
It is turned out that the level of glucose in the rat blood was increased 3.5, 3.3, 4.1and 3.1-fold on the 5th, 10th, 29th, and 30th days observation respectively in alloxan-induced diabetic rats compared with the non-diabetic rats. Administration to alloxan-induced diabetic animals prenalon (5.0 mg/kg/24 h) led to a markedly decrease of blood glucose level although it remained above the control values. However, in the experiment I group of rats, the blood glucose level was decreased by 45.1% on the 5th day, by 62.6% on the 10th day, by 64, 6% on the 20th, and by 53.8% on the 30th day of observation compared to the experiment I group (Table 1).
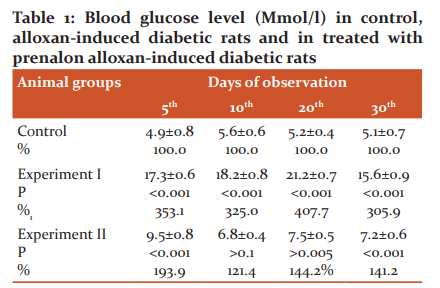
Experiment I - alloxan diabetes group; Experiment II - alloxan diabetes + prenalon group, P - statistical significance between control and experimental groups.
Maltase activity
In alloxan-induced diabetic rats maltase activity was increased by 32.6%, 95.3%, 81.2%, and 68.0% on the 5th, 10th, 20th, and 30th days of the experiment, respectively, compared to the control group. Administration of prenalon to alloxan-induced diabetic rats led to a normalization of the enzyme activity by the end of the experiment. The decrease of the intestinal maltase activity in the experiment II group on the 5th, 10th, 20th 30th days of the treatment with prenalon was 4.1%, 16.5%, 24.6%, and 35.5% respectively compared to the experiment I group (Table 2).
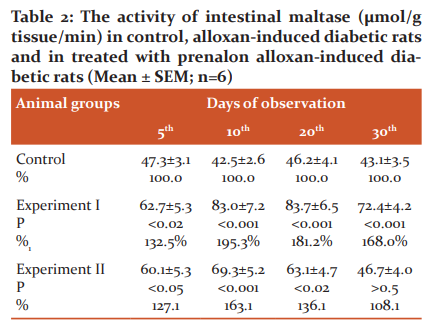
Experiment I - alloxan diabetes group; Experiment II - alloxan diabetes + prenalon group, P - statistical significance between control and experimental groups.
Sucrase activity
It was noted that the intestinal sucrase activity in the 1stexperimental group animals significantly increased in comparison with control animals. Increase of sucrase activity in alloxan-induced diabetic rats was 31.7% on the 5th day, 39.3% on the 10th day, 42.2% on the 20th day, and 40.6% on the 30th day of the experiment in comparison with control. Administration of prenalon resulted in a gradual approximation of sucrase activity to control value. On the 30th day of the experiment, the sucrase activity in diabetic rats treated with prenalon was identical to those in the control one. In the experiment II group rats, a decrease of intestinal sucrase activity compared to the experiment I group was statistically significant on the 20th and 30th days of the experiment (Table 3).
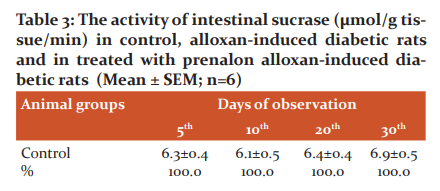
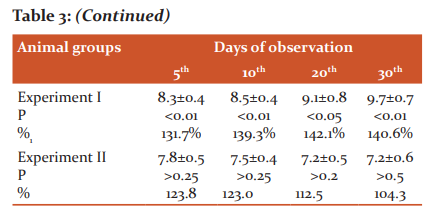
Experiment I - alloxan diabetes group; Experiment II - alloxan diabetes + prenalon group, P - statistical significance between control and experimental groups
Lactase activity
Small intestine lactase activity in alloxan-diabetic animals was increased by 45.6%, 87.7%, 62.7%, and 55.6%, respectively, on the 5th, 10th, 20th, and 30th days of the experiment compared to the control group (Table 4). Treatment of diabetic rats with prenalon also led to a gradual decrease of enzyme activity which was reached the control value by the end of observation. After administration of prenalon to the 2nd experimental group rats, the lactase activity was decreased by 14.1% on the 5th day, by 18.0% on the 10th day, by 14.6% on the 20th day, and by 23.5% on the 30th day of observation compared to the experiment I group rats (4).
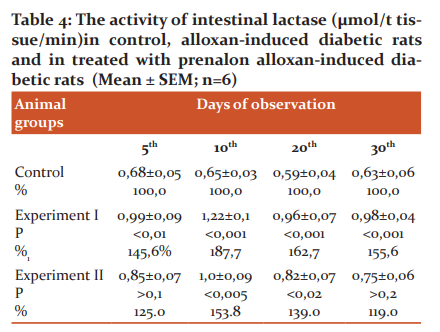
Experiment I - alloxan diabetes group; Experiment II - alloxan diabetes + prenalon group, P - statistical significance between control and experimental groups
So, by the end of the experiment, the activity of all brush border disaccharidases was significantly decreased in treated with prenalon diabetic rats compared with untreated diabetic rats.
DISCUSSION
In this study, the possibility of the correcting effect of prenalon on the activity of intestinal enzymes involved in the final stage of carbohydrate digestion in alloxan diabetes of male adult rats was studied. Obtained data show an increase in blood glucose level as well as activity of intestine disaccharidases in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Simultaneous changes of both blood glucose level and intestinal disaccharidase activity supposed, the increase of disaccharidases activity is contributing to the hyperglycemia in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. An increase in the activity of enteral disaccharidases in experimental diabetes was also identified in streptozotocin-induced diabetes.7 However, the authors did not describe the possible mechanisms of enteral disaccharidases activity induction in diabetes or hyperglycemia. In diabetes despite the increased glucose level in the blood, its level is lowered in other body tissues.15 Probably glucose hunger of the major body cells leads to an increase in the activities of intestinal disaccharidases through a nervous and humoral feedback mechanism. However, this assumption requires additional experimental researches. An endocrine system including the hypothalamus, pituitary, adrenal, thyroid, parathyroid, and other glands is impaired in diabetes mellitus.16Diabetes-related deficiency of thyroid-stimulating and/or thyroid hormones could also lead to an increase in intestinal lactase activity.17,18. The change in the hydrolytic activity of brush bolder disaccharidases could be also due to structural disorders in the mucous membrane of the small intestine in alloxan-induced diabetes rats.8,19Many plant compounds attract the attention of specialists because concerning the human or animal organism they have a wide spectrum of biological activity, due to the diversity of their chemical structure3,8,20. Medicinal plants which possess antioxidants activity usually has hypoglycemic activity because oxidative stress plays a major part in diabetes development and treatment.4-13,20Taken from A. nudiflora leaves prenalon includes polyphenols, tocopherols, carotenoids, sterols, terpenoids, and other substances with pharmacological effects on the metabolic processes.13According to the obtaining results prenalon has a certain corrective effect on the reduction of blood glucose level and activities of intestinal disaccharidases in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Taking all these data together, it is suggested that the prenalon could be a potential therapeutic agent for a decrease of glucose level and disaccharidases activity against diabetes.
CONCLUSION
Association between increase of blood glucose level and activity of intestinal disaccharidases in diabetic rats shows the efficiency of sugar hydrolysis in the small intestine contributes to the increase of blood glucose level. Administration of prenalon to alloxan-induced diabetic rats results in a decrease in both blood glucose level and intestinal disaccharidases activity. It also confirms the regular functional relationships between blood glucose level and the ability of the small intestine to assimilate carbohydrates. In addition, these data indicate that prenalon could be a candidate for a decrease of blood glucose level and/or enteral disaccharidases activity.
These positive results were obtained in animal studies. Therefore, further research is needed to identify the mechanisms through which prenalon works to acceptably address safety concerns. It is hoped that this study will revive interest in the hypoglycemic properties of prenalon and serve as an impetus for broader research.
Authors’ Contribution
Karimova II, Tursunboeva HO conceived, planned, and carried out the experiments. Kuchkarova LS and Ergashev NA analyzed data and wrote the manuscript. Akhmatova MJ, Khidirova NK got the prenalon preparation from extract A. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in the references of the manuscript. The authors are also grateful to the authors/editors, publishers of all those articles and journals where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of interest: There is no conflict of interest associated with this article.
Source of funding: There is no external funding agency associated with this article.
References:
-
Kharroubi AT, Darwish H M. Diabetes mellitus: The epidemic of the century. World J Diabetes 2015;6(6):850-67.
-
Khawandanah J. Double or hybrid diabetes: A systematic review on disease prevalence, characteristics and risk factors. Nutr Diabetes. 2019;4;9(1):33.
-
Hamden K, Mnafgui K, Amri Z, Aloulou A, Elfeki A. Inhibition of key digestive enzymes related to diabetes and hyperlipidemia and protection of liver-kidney functions by trigonelline in diabetic rats. Sci Pharm 2013;81(1):233-46.
-
Kuchkarova LS, Rokhimova SO, Syrov VN. Effect of Turkesterone on the Pancreas Histology and Function in Diabetic Rats. Inter J Cur Res Review 2020;12 (21):1-5.
-
Kuchkarova LS, Rokhimova SO. Intestinal carbohydrate digestion in rat alloxan diabetes. Scientific review.Biological sciences 2020; 3:56-60 (in Russian).
-
Jureti? D, Bernik S., Cop L, Hadzija M, Petlevski R, Lukac-Bajalo J. Short-term effect of acarbose on specific intestinal disaccharidase activities and hyperglycemia in CBA diabetic mice. Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 2003;87(7-8): 263-8.
-
Ramachandra R, Shetty AK, Salimath PV. Quercetin alleviates activities of intestinal and renal disaccharidases in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2005; 49(4):355-60.
-
Giacco F, Brownlee M. Oxidative stress and diabetic complications. Circ Res 2010;107(9):1058-70.
-
El-Salam NA, Radwan MM, Wanas AS, Shenouda ML, Sallam SM, Piacente S, Ghazy NA. Phytochemical and Biological Evaluation of Alcea Rosea L. Growing In Egypt. Planta Med 2016;82(5):83.
-
Rajendiran D, Packirisamy S, Gunasekaran K. A review on the role of antioxidants in diabetes. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 2018;11(2):223-41.
-
Jurgo?ski A, Ju?kiewicz J, Zdu?czyk Z. Ingestion of black chokeberry fruit extract leads to intestinal and systemic changes in a rat model of prediabetes and hyperlipidemia. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 2008;63(4):176-82.
-
Dar PA, Ali F, Sheikh IA, Ganie SA, Dar TA. Amelioration of hyperglycemia and modulation of antioxidant status by Alcea rosea seeds in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Pharm Biol 2017;55(1)1849-55.
-
Rakhmatova MZ, Karimova II, Gayibov UG, Khidyrova NK. Polyprenolsthe leaves of the plant alceaenudifloral and their antioxidant activity. East Eur Sci J 2020; 6(58):53-6.
-
Dahlqvist A. Assay of intestinal disaccharidases. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 1984;44(2):884–92.
-
Holst JJ, Gribble F, Horowitz M, Rayner CK. Roles of the gut in glucose homeostasis. Diabetes care 2016;39:884–92
-
Alrefai H, Allababidi H, Levy S, Levy J. The Endocrine System in Diabetes Mellitus. Endocrine 2002;18(2):05-119.
-
Schlienger JL, Anceau A, Chabrier G, North ML, Stephan F. Effect of Diabetic Control on the Level of Circulating Thyroid Hormones. Diabetologia 1982; 22(6):486-8.
-
Hewitt JE, Smith MW. Thyroid hormone effects on lactase expression by rat enterocytes. J Physiol 1986;376(6): 253–65.
-
Zhao M, Liao D, Zhao J. Diabetes-induced mechano-physiological changes in the small intestine and colon. Diabetes 2017;8(6):249-69.
-
Firdous SM. Phytochemicals for treatment of diabetes. Expt J. 2014;13:451-3.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License