IJCRR - 13(22), November, 2021
Pages: 94-99
Date of Publication: 20-Nov-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Nutritional Composition and Sensory Properties of Value-Added Health Mix for Undernutrition and Better Cognition
Author: Anitha R, PA Raajeswari
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The incidence of undernutrition among children is high in India, which will pave its way to the occurrence of frequent infection, reduced learning capacity, poor academic performance and cognitive deficit. The health mix is the most popular, convenient, easy to prepare and healthy dish for the children. Objective: To develop a cheaper and nutritious health mix for improving the nutritional status and cognitive function in children. Method: The raw ingredients were procured, processed, powdered and mixed into 5 variations of health mix. The developed health mixes were analysed for their nutritional and sensory qualities. Result: The results stated that the health mix 3 with the combination of multi-grain such as red rice (25g), Bajra (25g), Green gram (20g), Soybean (10g), Rice flakes (10g), Jaggery (8g) and Brahmi leaves (2g) received significantly higher scores and also selected as best in having a high amount of essential nutrients namely, protein (14.9 g), fat (1.68 g), iron (6.52 g), zinc (1.91 mg), selenium (445 mg) required for the improvement of nutritional status and cognitive function. Health 3 has got the highest rating in many sensory qualities and also the results were similar to the control sample. Conclusion: Our study indicates the importance of a healthy mix, prepared from the combination of multi-grains with Brahmi leaves, as one of the most convenient food formulas for supplementation to undernourished children. Future studies on such supplementation to improve the nutritional status and cognitive function of undernourished children is recommended.
Keywords: Undernutrition, Health mix, Nutritional quality, Sensory evaluation
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION
Undernutrition is a multidimensional issue holding back development with unacceptable human consequences. The burden of this across the world remains unacceptably high and progress unacceptably slow.1 In India, nearly every second young child is undernourished.2 National Family Health Survey 4 reported that both chronic and acute undernutrition was high in many states of India. Undernutrition weakens the immune system, putting children at higher risk of more severe, frequent and prolonged bouts of illness. It is also a consequence of repeated infections, which may further worsen the child’s nutritional status at a time of greater nutritional needs.1
Children who fail to grow optimally during this crucial period may not make up for the loss in growth even on an excellent diet in later life.3 Inadequate intake of nutrients leads to serious during periods of rapid growth, physical and cognitive development of children.4 The diets of children today increasingly reflect the global ‘nutrition transition’, which is seeing communities leave behind often more healthy, traditional diets in favour of modern diets often missing whole grains, fruits, nuts and seeds, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids.5,6 Foods that are nutritionally balanced, energy-dense, easily digestible, and have functional benefits, are needed for the food formulation.7
Cereals being the staple foods of the majority of the population in India, the combination of cereal with an appropriate proportion of pulses and oilseeds complement each other and result in improved nutritional qualities.8 bowls of cereal, millets and legumes also form a good source of macro and micronutrients, phytochemicals and prepare nutritionally balanced composites of high biological value.9 Nutrition can be redesigned to improve cognitive development, and micronutrient supplementation can help those at risk of cognitive impairment avoid deficiencies.10 Vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, B12, C, folic acid, and minerals like iron, iodine, and zinc are the micronutrients most closely linked to cognitive function.11,12
In addition to micronutrients, several plant-based extracts, particularly ‘Brahmi’ have recently been shown to improve cognition. It was proved that eight out of nine clinical double-blind, placebo-controlled Brahmi trials in humans demonstrated improvements in cognition.13 Hence, the present study was aimed to formulate a value-added nutritious health mix with the combination of cereals, millet, legumes and Brahmi leave to alleviate undernutrition and help to improve the cognitive function of school children.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Selection of ingredients
The ingredient cereals, millets and pulses such as Red rice, Wheat, Bajra, Thinnai and rice flakes, soya bean, green gram and roasted Bengal gram was chosen for their higher potential dietary sources and Brahmi leaves (Vallarai Keerai) were added for the enhancement of brain function and memory. Jaggery was used for its sweet taste, palatability and high amount of iron.
Procurement and processing of selected ingredients
Raw ingredients were procured from the local market. They were cleaned of impurities. Bajra, ragi, soya bean and green gram were washed and sprouted individually for 24 hours for the up-gradation of nutrients. Sprouted and non-sprouted ingredients were dried, roasted for moisture reduction and flavour enhancement. Roasted grains were milled into a fine powder separately. Vallarai Keerai was purchased from the local agricultural farm and the leaves were cut from thin branches. The good quality leaves were selected and washed thoroughly, blanched for 3 minutes to kill the microorganism on the surface and within the leaves and also to remove if there are any volatile compounds. Then they were shade dried by placing them in a white muslin cloth for five days. Dried leaves were powdered by using a mixer grinder and sieved to get a fine powder. All the ground ingredients were stored in an airtight container until used for formulation.
Development of health mix
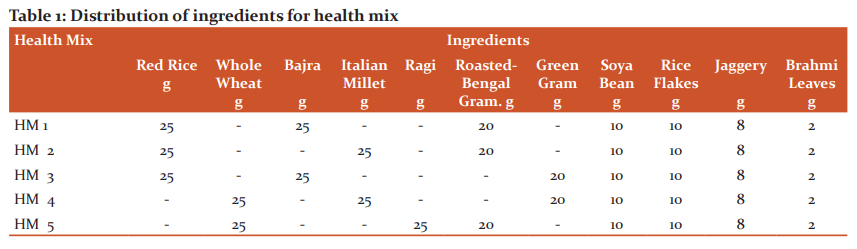
About five variations of health mix were developed by mixing the processed ground flours to select one best variation in sensory and nutritional quality. The proportions of the health mix are presented in Table 1.
Preparation of value-added Health Mix Ladoo (HML)
About six variations of health mix Ladoos were prepared by mixing 25 gm of each health mix variation with hot water. The control health mix porridge was prepared by using sathumavu provided by the Government of Tamilnadu through Anganwadi centres.
Organoleptic evaluation of the health mix Ladoo
Evaluation of sensory attributes is a science by using human senses for measuring appearance, flavour, colour, texture and taste.14 Acceptability testing was carried out by 20-panel members for the prepared health mix porridge using nine points hedonic rating scale with the highest score as liked extremely (9) to dislike extremely (1). The panel members were instructed about the evaluation procedure and score ratings were obtained in the sensory evaluation sheet.
Evaluation of nutritional qualities of the health mix
Nutrients such as calories, protein, fat, carbohydrate, ash, moisture, total fibre, iron, calcium, zinc and selenium were analyzed using standard procedure.15 Estimation of nutrients such as ash by the incineration method in a muffle furnace at 550oC, the moisture content in a hot air circulating oven, crude fat by soxhlet extractor, protein (N X 6.25) in Kjeldahl method, carbohydrate content by difference, crude fibre by digestion, minerals such as iron by calorimetrically, calcium by precipitation and titration against potassium permanganate, zinc and selenium were evaluated by atomic absorption spectrophotometer.16,17
Anti-nutritional content of the health mix
A highly accepted health mix was evaluated for anti-nutritional factors since they may hinder the absorption of some of the essential nutrients during metabolism. Secondary metabolites such as oxalic acid, tannins, phytic acid and alkaloids were evaluated.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Different health mix was prepared by combining raw ingredients in the proportion as 2 bowls of cereal, 1 millet, 2 legumes and 1 green and they were tested for nutritional qualities and sensory acceptability.
Nutritional qualities of the developed health mix
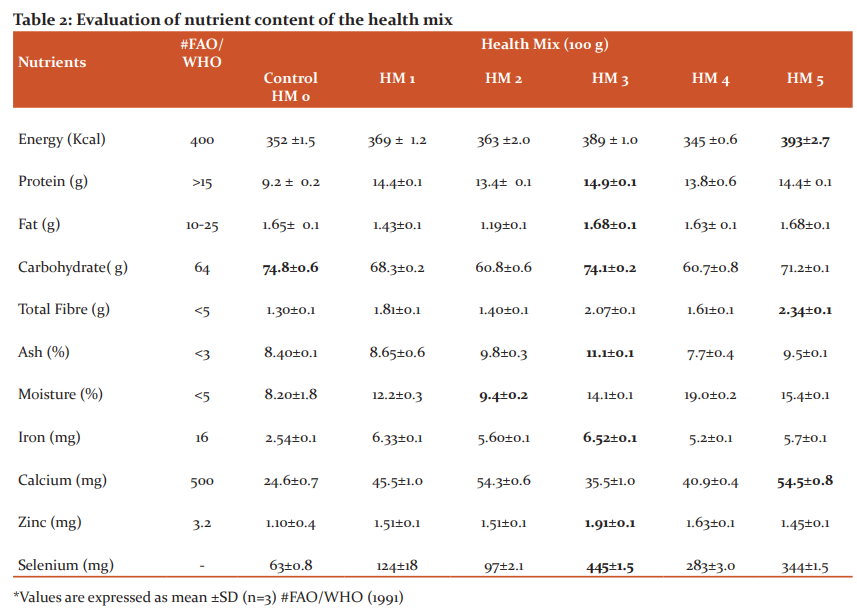
The mean and standard deviation value derived from the triplicate analysis of nutrients such as energy, protein, fat, total fibres, ash, moisture, iron, zinc, calcium, selenium present in various combinations of composite flour is displayed in Table. 2
The prepared health mixes were nutritionally adequate and comparable to standard recommended allowances. Health Mix 3 has got the highest in protein (14.89g) and fat (1.68g) carbohydrate (74.14g), iron (6.52mg), zinc (1.91mg) and selenium (444.7mg) when compared to other health mix variations. The calorie (393 kcal), fibre (2.34g) and calcium content were higher in health mix 5 since ragi was added one of the ingredients in the combination. Many nutrients are essential for brain development, particularly protein for cell proliferation and differentiation, synthesis of growth factors, the role of iron in myelination, essential fatty acids in synaptogenesis, and zinc for DNA synthesis. Dietary protein is providing an amino acid source for neurotransmitter production, namely, serotonin and catecholamines.19
Consumption of carbohydrates is necessary and at least 130 grams of carbohydrates per day is required to keep the blood glucose at a balanced level and adequate carbohydrates should be taken regularly for better cognitive functions.20 Though health mix 1,2,4,5 was adequate in some nutrients, HM 3 has been selected as best due to its superior quality of many important nutrients, namely protein, fat, carbohydrate, iron, zinc and selenium for the improvement of undernutrition and cognition.
Anti-nutritional contents of the health mix
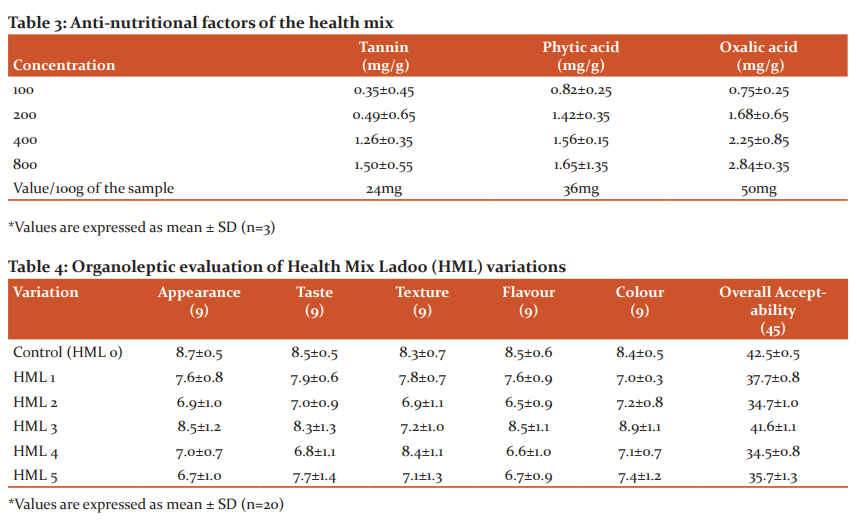
Table.3 represents the quantitative determination of anti-nutritional content, namely, tannins, phytic acid and oxalic acid in the developed health mix. A gradual rise in the result of the sample when increasing concentration indicates a better outcome of the study. Mean tannin, phytic acid and oxalic acid content of the processed and developed health mix was 24mg, 36mg and 50 mg respectively. One of the major problems of plant-based flours is the presence of anti-nutritional contents such as phytate, oxalate, and tannin may usually have a negative effect on protein digestibility and other nutrient availability.21 The anti-nutritional contents of the current sample were within an acceptable limit and did not have an adverse effect on health. This shows that the developed health mix could be used extensively since it possesses very limited anti-nutritional factors and there would not be any interference with other nutrient bioavailability. Many researchers have reported that processing methods improved the nutritional quality of foods prepared from legumes and cereals by a reduction in their anti-nutritional factors.22
Organoleptic evaluation of the prepared Health Mix Ladoo (HML)
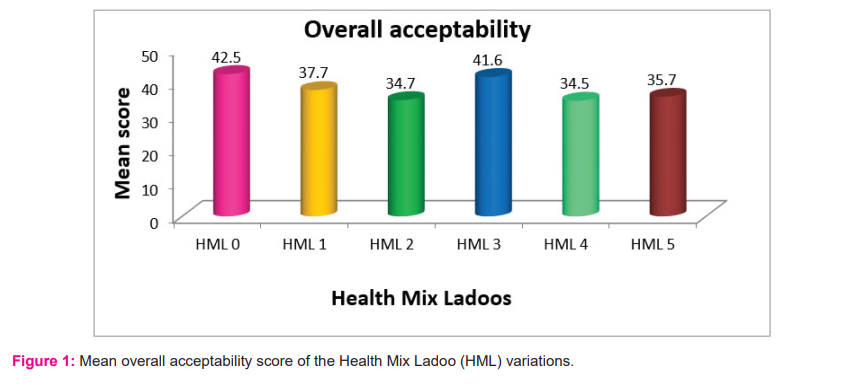
The mean scores of five variations of health mix Ladoo in appearance, flavour, taste, texture, colour and overall acceptability are presented in Table 4. The comparison of sensory attributes between different health mixes. The results showed that HML 3 has reached the maximum scores in many sensory qualities and also it was almost similar to that of the control sample (HML 0). The HML 3 has secured the highest in flavour (8.5±1.1) and colour (8.9±1.1) when compared to other variations. The mean score of appearance (8.5±1.2) and taste (8.3±1.3) of HML 3 was very nearer to the mean score of the control sample. The mean score of texture was maximum in HML 4 (8.4) due to the combination of ingredients, namely, wheat, Italian millet and green gram since these ingredients give the coarse structure. It was observed during sensory evaluation that the flavour of the Health Mix Ladoo-3 (HML 3), Health Mix Ladoo-1 (HML 1) and control sample [Health Mix Ladoo-0 (HML 0)] were very good and highly appreciable when compared to other variations. Health Mix Ladoo 4 has obtained the lowest in overall acceptability scoring than others. Figure 1 stated the results of mean scores of overall acceptability of all variations of the prepared health mix. Though all variations of the developed health mixes were accepted by the panel members one has to be selected for further processes. However, HML 3 was being selected as best based on the overall rating for further supplementation to improve the nutritional status and cognitive function of the children. Many researchers prepared health mix by using multiple ingredients with the combination of roasted flours of wheat, soybean and chickpea flour, and with malted and roasted grains of wheat, barley, green gram and jaggery.23,24
CONCLUSION
Health mix, prepared from the combination of different multigrain added to Brahmi leaves was one of the versatile and most convenient food formulas for supplementation to the undernourished children. It can be concluded from the results that the nutritional content and sensory qualities of health mix 3 was superior. Hence, considering the nutritional analysis and sensory acceptability trail, it is strongly recommended that the health mix 3 can be considered optimal for further future studies as supplementation to improve the nutritional status and cognitive function of the undernourished children.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors are thankful to all the study participants for their kind cooperation. Authors are also grateful to authors/ publishers of all those articles from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict(s) of Interest: Nil
Source(s) of funding: Nil
Ethical consideration: The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of The Human Ethical Committee, Avinashilingam Institute for Home Science and Higher Education for Women, Coimbatore (AUW/IHEC-18-19/FSN/FHP-07).
References:
-
UNICEF. Levels and trends in child malnutrition UNICEF-WHO-World Bank Group joint child malnutrition estimate key findings of the 2015 edition. New York: UNICEF, WHO, World Bank Group. 2015.
-
Initiatives D. Global Nutrition Report 2018: Shining a light to spur action on nutrition. Retrieved from Bristol. The UK. Available online at https://globalnutritionreport. org/reports/global-nutrition-report-2018.
-
Kamath SM, Venkatappa KG, Sparshadeep EM. Impact of nutritional status on cognition in institutionalized orphans: a pilot study. JCDR. 2017 Mar; 11 (3): CC01.
-
UNICEF. The progress of nations. UNICEF; 1998.
-
World Health Organization. The state of food security and nutrition in the world 2019: safeguarding against economic slowdowns and downturns. Food Agric Org. 2019 Jul 15.
-
Afshin A, Sur PJ, Fay KA, Cornaby L, Ferrara G, et al. Health effects of dietary risks in 195 countries, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. The Lancet. 2019 May 11; 393(10184):1958-72.
-
Murugkar DA, Gulati P, Gupta C. Effect of sprouting on physical properties and functional and nutritional components of multi-nutrient mixes. Int J Food Nut Sci. 2013 Apr 1; 2(2):8.
-
Shilpa G, Pushpa B. Formulation and evaluation of cereal based health mix for preschool children. Asian J Home Sci. 2014; 9(1):44-9.
-
Gorinstein S, Pawelzik E, Delgado?Licon E, Haruenkit R, Weisz M, et al. Characterisation of pseudocereal and cereal proteins by protein and amino acid analyses. J Sci Food Agri. 2002 Jun; 82(8):886-91.
-
Bryan J, Osendarp S, Hughes D, Calvaresi E, Baghurst K, et al. Nutrients for cognitive development in school-aged children. Nutri Rev. 2004 Aug 1; 62 (8):295-306.
-
Huskisson E, Maggini S, Ruf M. The influence of micronutrients on cognitive function and performance. J Int Med Res. 2007 Jan; 35(1):1-9.
-
Lam LF, Lawlis TR. Feeding the brain–The effects of micronutrient interventions on cognitive performance among school-aged children: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Clin Nutr. 2017 Aug 1; 36(4):1007-14.
-
Pase MP, Kean J, Sarris J, Neale C, Scholey AB, et al. The cognitive-enhancing effects of Bacopa monnieri: A systematic review of randomized, controlled human clinical trials. The J Alt Comple Med. 2012 Jul 1; 18(7):647-52.
-
Srilakshmi B. Evaluation of Food Quality. Food Sci. 2010;3(5): 376-380.
-
AOAC. Official methods of the association of official agricultural chemist, Washington. D.C. 11th edition. 2000.
-
Official AO. Methods of analysis of AOAC International. AOAC International, Maryland, USA. 2005.
-
AOAC. Official methods of the association of official agricultural chemist, Washington. D.C. 20th edition. 2016.
-
Black MM, Walker SP, Fernald LC, Andersen CT, DiGirolamo AM, et al. Early childhood development coming of age: science through the life course. The Lancet. 2017 Jan 7; 389 (10064):77-90.
-
Brunger AT, Choi UB, Lai Y, Leitz J, Zhou Q. Molecular mechanisms of fast neurotransmitter release. Ann Rev Biophys. 2018 May 20; 47:469-97.
-
Beilharz JE, Maniam J, Morris MJ. Diet-induced cognitive deficits: the role of fat and sugar, potential mechanisms and nutritional interventions. Nutr. 2015 Aug; 7(8):6719-38.
-
Reda TH, Atsbha MK. Nutritional composition, anti-nutritional factors, antioxidant activities, functional properties, and sensory evaluation of cactus pear (Opuntia ficus-indica) seeds grown in the Tigray region, Ethiopia. Int J Food Sci. 2019;5 (2): 391-394.
-
Ochanda SO, Akoth OC, Mwasaru AM, Kagwiria OJ, Mathooko FM. Effects of malting and fermentation treatments on group B-vitamins of red sorghum, white sorghum and pearl millets in Kenya. ). J Food Proc Tech .2010; 2(2): 182-184
-
Salve RV, Mehrajfatema ZM, Kadam ML, More SG. Formulation, nutritional evaluation and storage study of supplementary food (Panjiri). J Food Proc Tech. 2011; 5(6): 492-495.
-
Gahlawat P, Sehgal S. Anti-nutritional content of developed weaning foods as affected by domestic processing. Food Chem. 1993 Jan 1; 47(4):333-6.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License