IJCRR - 13(22), November, 2021
Pages: 80-85
Date of Publication: 20-Nov-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Influence of Low Birth Weight and Preterm Birth on Morbidity, Mortality and Medication Use among Neonates in Resource-Limited Settings: A Prospective Observational Study
Author: Pradeepkumar Bhupalam, Sowjanya Nalampati, CB. Jyostna Angiel, T. Gowthami, Goruntla Narayana, Kanala Somasekhar Reddy, Chintaginjala Haranath, MV. Sunil Kumar, Abdul Ahad
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: The birth rate in India is estimated to be 26,932,586 per year. Of these 27 million babies born each year, 1 million babies die before the age of 1 month; India carries the highest share with 30% of global neonatal mortality. Three neonates are dying every minute in India and every fourth baby born has a low birth weight. Low birth weight directly or indirectly contributes to 60- 80% of all neonatal death. Aim: We aimed to assess the impact of preterm birth and low birth weight on medical conditions, medications use and mortality among neonates in a resource-limited setting. Methodology: A prospective observational study was conducted at the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) over 6 months. Neonates of either sex admitted to NICU and who received at least one medication were enrolled in the study. Perinatal and demographic data, reasons for NICU admission, medications prescribed, and discharge status were documented and analysed. Result: Four hundred and four neonates were included in the study: 61.1% were boys, 38.9% were girls. Respiratory distress syndrome (n=120, 29.7%), neonatal jaundice (60, 14.85%), and sepsis (44, 10.9%) were the most commonly observed conditions and were significantly more common among preterm and low birth weight neonates. Nearly half of the medications prescribed were antibiotics (n=1113, 49.6%). The mean number of medications prescribed to each neonate is 5.5. The mortality rate was significantly higher in extremely preterm and very preterm when compared to term neonates. Conclusion: Medical conditions, medications prescribed and the mortality rate was significantly higher among preterm and low birth weight neonates admitted in the NICU that are included in the study.
Keywords: Low birth weight, Preterm birth, Mortality, Medication use, Neonates, Resource limited setting
Full Text:
Introduction
As per WHO, birth before 37 weeks of gestation is defined as preterm birth (PTB) and less than 2500 grams of body weight as low birth weight (LBW). PTB and LBW babies are more prone to severe morbidity and mortality in the neonatal stage.1As per WHO estimate globally, 15 million preterm births per year, and India ranked with the highest number of preterm births of 3.5 million approximately.1,2As per UNICEF estimate globally 3.9 million infant deaths per year, 1 million deaths (Approximately 25.6%) carried by India.3,4Preterm birth complications are the leading cause of death among children under 5 years of age, responsible for nearly one million deaths in 2015. Three neonates are dying every minute in India and every fourth baby born has a low birth weight.5directly or indirectly contributes 60–80% of all neonatal deaths. On average, 12% of babies are born preterm in low-income countries compared to 9% in high-income countries. WHO identified that half of the babies born at or below 32 weeks (2 months early) die due to a lack of feasible and cost-effective care in low-income countries, such as warmth, breastfeeding support, and basic care for infections and breathing difficulties.2There is a scantiness of research on outcomes of PTB and LBW in India and no studies in rural recourse limited settings of India. In this context, this study was conducted with an aim to assess the impact of PTB and LBW on morbidity, drug usage, and mortality among neonates in a rural resource-limited setting.
Methods
A prospective observational study was conducted in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) at a rural recourse limited setting of Anantapur district, Andhra Pradesh, India over six months from April 2019 to September 2019. The study was initiated after clearance from the ethics committee (Approval No: RIPER/IRB/PP/2019/06). Irrespective of gender, neonates admitted in NICU were included in the study after taking consent from guardian/parent. Neonates under observation, fluid replacement, nutritional supplements, vaccination and phototherapy without one or more medication use were excluded from the study. The sample size was calculated as 404 using Epi-info 7 das software version 7.2.3.1 (CDSCO, Atlanta, USA) with the assumption of 50% probability, design effect 1, error 5%, CI 95% and 5% non-response rate. Study participants were categorised based on gestational age (GA) as extremely preterm (EPT: Less than 28 weeks), very preterm (VPT: 28-32 weeks), moderate to late preterm (MLPT: 33-37 weeks) and term (More than 37 weeks). Study participants were classified based on birth weight as extremely low birth weight (ELBW: Less than 1000 Grams), very low birth weight (VLBW: 1000-1499 Grams), low birth weight (LBW: 1500-2499 Grams) and normal birth weight (NBW: Equal or more than 2500 Grams). All required data was collected by using a data collection form which consists of demographic details which include name, age, gender, patient ID, birth weight, gestational age, medical condition, medications prescribed including dose, frequency, duration of therapy, route of administration and discharge status of the patient. Graph Pad Prism 3.0 software (San Diego, California, USA) software was used for the statistical analysis. Descriptive statistical analysis for categorical variables was performed by calculating the frequencies and percentages; the chi-square test was used to compare categorical variables. An unpaired t-test was used to compare continuous variables. p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
A total of 404 neonates were included in the study with a mean (SD) age of 8.06 (7.46) days and a median of 6 days. 66.1% were boys, preterm 35.15 %, and 40.1 % were underweight as shown in Table 1.
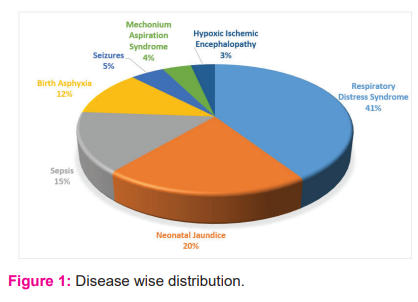
A major reason for NICU admission was respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) 29.7%, neonatal jaundice 14.85%, sepsis 10.9%, and birth asphyxia 8.4% as shown in Table 2.
Compared to term neonates, RDS and birth asphyxia were significantly higher in very preterm and moderate to late preterm neonates. Compared to normal birth weight neonates, RDS and seizures were significantly higher in very low birth weight and low birth weight, birth asphyxia was significantly higher in very low birth weight neonates as shown in Table 3.
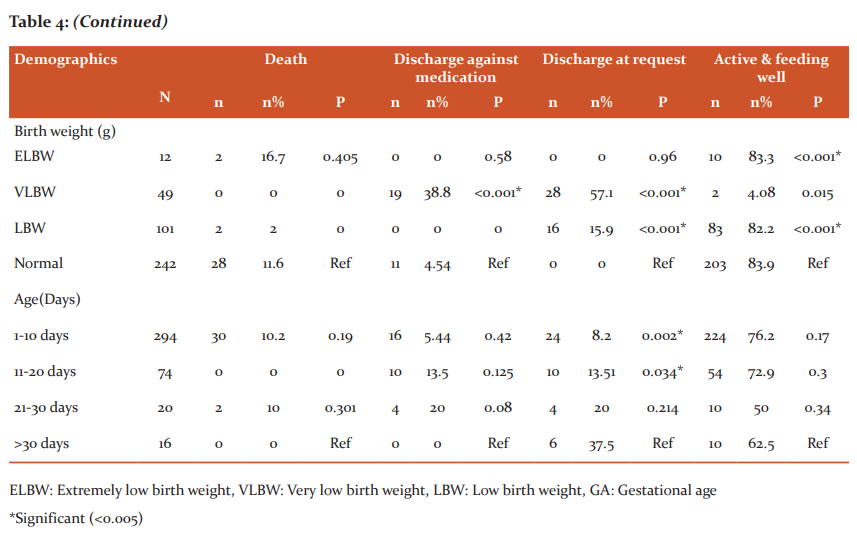
At the time of discharge, out of 404 participants included in study 298 (73.8%) were clinically active and feeding well. The mortality rate was 32 (7.92%), 30 (7.4%) of neonates were discharged against medication and 44 (10.9%) neonates were discharged at a request. Overall death rates in extremely preterm (16.7%) and very preterm (4.34%) were significantly higher compared to term (10.7%) neonates as shown in Table 4.
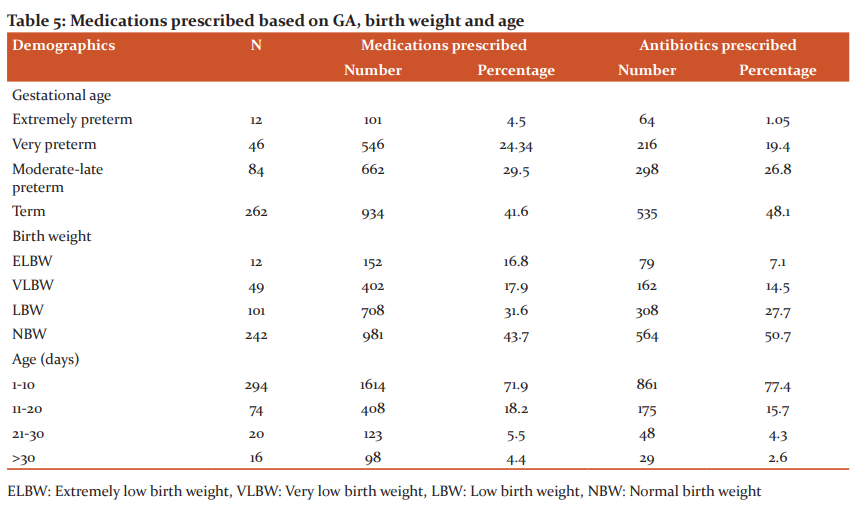
A total of 2,243 medications were prescribed to all neonates included in the study, on average, each neonate has prescribed 5.5 medications. Of all the medications prescribed 1113 (49.6%) were antibiotics and the remaining 1130 (50.4 %) were non- antibiotics as shown in Table 5. According to the ATC classification system, most of the antibiotics were prescribed for systemic use followed by oral and topical use. Analysis based on the WHO core indicators revealed that an average of 5.5 medications was prescribed per encounter. Among all the medications prescribed 90% of medications were prescribed by generic name and all the medications prescribed among all the neonates included in the study were on the National essential medication list and on the WHO essential medicines list for children.
.png)
SD: Standard deviation, LBW: Low birth weight VLBW: Very low birth weight, ELBW: Extremely low birth weight.
.png)
.png)
.png)
Discussion
The main objective of this study is to assess the impact of preterm birth and low birth weight on medical conditions, medications use and mortality among neonates. Our study revealed that out of 404 patient’s majority of them are baby boys 247(61.1%) and baby girls157 (38.9%). A similar pattern was observed in studies conducted in Central India (59.3%) baby boys and East India (62.5%) baby boys.[5,6] The prevalence of preterm (35.1%) and low birth weight (40.1%) babies in our study were lower compared to a study conducted in Central India (54.8% and 73%, respectively) and higher compared to a study conducted in east India.5,6
The most common condition for NICU admission was RDS (Respiratory distress syndrome), followed by sepsis and neonatal jaundice and the most reason was Tachypnoea. RDS was the commonly observed condition among all categories of neonates according to the GA and birth weight.
The majority of neonates in extremely preterm, very preterm and moderate to late preterm categories experience RDS and neonatal jaundice.
The mean number of medications prescribed to neonates in our study was 5.5 medications per neonate and was consistent with published data between 3.7 and 8.6 medications per neonate.7,8 Majority of the medications prescribed to neonates included in our study were antibiotics. Gentamycin was the most commonly prescribed antibiotic among neonates and a similar pattern was observed in previous studies conducted in the UK, USA, Australia and Germany.7,9
The most commonly prescribed off-label drugs in NICU were Gentamycin, Ampicillin, Amikacin, Cefotaxime etc. was observed in our study is similar to the studies conducted in NICU, Iran 2019. The choice of antibiotic regimens varies to different hospitals according to their hospital policies.
The overall neonatal mortality rate in our study was 7.9% (32/404). The babies born extremely preterm had the highest mortality rate (16.7%) compared to others. Systematic analysis of Indian data identified that preterm birth complications cause 43.7% of neonatal deaths.10,11
The strengths of the present study include the systematic follow-up of neonates admitted in NICU to identify the medication utilization and to assess the prevalence and impact of preterm birth and low birth weight and medical conditions, medication use and neonatal mortality.12,13 Our study provides data about health outcomes and medication use among neonates in NICU in a secondary care hospital serving patients mainly of low socio-economic backgrounds. As this study is a single-centred study, our results may be different from outcomes at other hospitals of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana 8,14,15.
Conclusion: Respiratory distress syndrome was the most commonly observed medical condition among neonates and associated with the prescribing of more medications especially antibiotics. The mortality rate was higher in birth asphyxia. Medical conditions, medications prescribed and the mortality rate was significantly higher among preterm and low birth weight neonates compared to term and normal weight neonates.
Acknowledgement: Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
Conflict of Interest: Nil
References:
-
WHO.Pretermbirth.https://www.who.int/news-room/fact/sheets/detail/preterm-birth. [Last accessed 2018 December 11].
-
Krishna U, Bashar TSM, Parthasarathi G, Srinivasa MD. Impact of preterm birth and low birth weight on medical conditions, medication use, and mortality among neonates: A prospective observational study.World J Pediatr. 2019;15(3):281-8.
-
The World Counts. How many babies are born each day? http://www.the world Counts.Com/Stories/How-Many-Babies-Are-Born-Each-Day. [Last accessed 2018 December 11].
-
Med India. Indian population clock. https://www.medindia.net/patients/calculators/pop_clock.asp. [Last accessed 2018 December 11].
-
Chatterjee S, Mandal ALN, Mukherjee S, Singh AK. Drug Utilisation study in a neonatology unit of a tertiary care hospital in eastern India. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug is safe. 2007; 16: 1141-5.
-
Chautankar SA, Marathe PA, Potey AV, Nanavathi RN. Drug utilization in neonatal intensive care unit of a tertiary–care hospital in Mumbai, India. Indian paediatrics. 2017:54:931- 4.
-
Donnell CPF, Stone RJ, Morley CJ. Unlicensed off-label drug use in Australian intensive care unit. Pediatrics 2002; 110:52.
-
Kieran EA, Callaghan N, Connell CPF. Unlicensed and off-label drug use in an Irish neonatal intensive care unit: a prospective cohort study. Acta Paediatr. 2014:103;139-42.
-
Neubert A, Lukas K, Leis T, Dormann H, Brune K, Rascher W. Drug utilization on a preterm and neonatal intensive care unit in Germany: A prospective, cohort-based analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2010;66:87-95.
-
Sankar MA, Neogi SP, Sharma J, Chauhan M, Srivastava R, Prabhakar PK, et al . State of newborn health in India. J perinatal. 2016; 36:3-8.
-
Vladislava Z, Megan RS, Kyungjoon L, Lina G, Monika AZ, Black MJ. Low Birth Weight due to Intrauterine Growth Restriction and/or Preterm Birth: Effects on Nephron Number and Long-Term Renal Health. Int. J. Nephr.2012;12: 1-13.
-
Cunha GS,Mezzacappa F,Riberiro JD.Maternal and neonatal factors affecting the incidence of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in very birth weight newborns.J Pediatr.2003:79:550-6.
-
Bhupalam P, Tawfeek A, Goruntla N, Reddy YP and Jinka D Assessment of antibiotic prescribing pattern in pediatric patients: A cross-sectional hospital-based survey. CHRISMED J Health Res. 2017;4:235-7.Citation metadata
-
Laforgia N. Nuccio MM, Schettini F, Dell’ Area M, Gasbarro AR, Dell’ Erba A, et al. Off-label and unlicensed drug use among neonatal intensive care unit in Southeren Italy. Pediatr Int. 2014; 56:7-9.
-
Warrier I, Du W, Natarajan G,SalariV,ArandaJ.Patterns of drug utilization in a neonatal intensive unit. J Clin Pharmacol.2006; 46:612-20.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License