IJCRR - 13(21), November, 2021
Pages: 34-38
Date of Publication: 09-Nov-2021
Print Article
Download XML Download PDF
Pattern of the Angle between Axial and Digital Triradius of the Dermatoglyphic Trait Among Type Two Diabetes Mellitus Patients in the Eastern Region of India: A Case-Control Study
Author: Sarkar Satabdi, Sarkar Tanmay, Basak Samanwita, Sarkar Arpita, Saha Pallab Kumar, Kundu Banani
Category: Healthcare
Abstract:Introduction: Dermatoglyphics is the study of epidermal ridge patterns on the fingers, palms, and soles. The correlation of dermatoglyphic patterns with many chromosomal abnormalities and genetic diseases is evidenced by many researchers in the world. As type two diabetes mellitus (DM) has the strong genetic background, the dermatoglyphic study can be useful as a screening tool in early diagnosis and to find out the persons are at risk. Aims: To compare the angle between axial and digital triradius (and angle-angle between line drawn from axial triradius t at base of palm between the thenar and hypothenar eminences to triradius 'a'- at base of index finger and to -triradius at base of little finger) between type 2 DM patient and sex-matched control group. Case Report: A case-control study was done among 200 types two DM patients of 40-60 years of age as case and 200 sex�matched control groups. The palmar prints were collected by ink method and at angles of each print were measured. Data were analyzed revealing mean and standard deviation and tested by student's t-test, taking p-value < 0.05 as statistically significant. Discussion: Statistically significant changes are observed in the mean atd angle of the left hand of a type 2 diabetes patient (42.62\?0.206 with S.D 2.91) compared to control (42.13\?0.20 with S.D 2.83). CONCLUSIONS: Increased atd angle of the left hand in presence of risk factors for the development of type two diabetes mellitus is a strong predilection for the development of the disease
Keywords: Dermatoglyphics study, Axial triradius, Digital triradius, ATD angle, Type two diabetes mellitus, Ink method
Full Text:
INTRODUCTION:
Dermatoglyphics is the study of the epidermal ridge pattern of the skin of the fingers, palms, toes, and soles. These features are produced under genetic control but may be affected by environmental factors during early intrauterine life. Harold Cummins illustrated the term ‘Dermatoglyphics’ in 1926 (Greek derma-skin, Greek Glyphein- to carve).1
The epidermal ridge patterns once established do not change after 21 weeks of intrauterine life. The specific features of dermatoglyphic traits were ascertained to be inherited as dominant, incompletely dominant recessive, a single gene, or polygenic with complete or incomplete penetrance.2 It is also considered as a variable expression of genes. The large number of chromosomal and developmental defects like mongolism, Turner’s syndrome, cardiovascular disease, bronchial asthma, schizophrenia, and hypertension had shown an association with dermatoglyphic feature changes.3,4,5,6 The epidermal ridge pattern analysis in the dermatoglyphic study can be considered as a diagnostic as well as screening tool as it is based on genetic background, easily accomplished task, and cost-effective.
Diabetes mellitus (DM), a non-communicable disease poses a significant public health problem in India and is one of the most studied metabolic diseases in the world. The occurrence of type two diabetes mellitus has strong interaction between genetic and environmental factors. Family history is a strong risk factor and it indicates genetic predisposition.7 As epidermal ridge patterns are genetically determined, the dermatoglyphic prints represent a non-invasive anatomical marker of type two diabetes mellitus. Thus, it will help in early detection. Early treatment of the disease cause delaying in the development of microvascular and macrovascular complications.
So far, very little information is obtained about the dermatoglyphic features of type 2 DM patients in many regions of India. From the eastern part of India, the data on the angle between axial and digital triradius (atd angle) of dermatoglyphic study of type 2 DM patients is insubstantial, though the disease burden is gradually increasing in comparison to the many other regions of India.8 Hence the purpose of our study was to collect and analyze the data of atd angle in type two DM patients and compared that data with non-diabetic patients (controls) and tried to reach conclusions that those data can be useful as a screening tool in the diagnosis of type 2 DM.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
The study was conducted after taking permission from the institutional ethical committee and review Board. The study was conducted on 200 (100 male and 100 female) clinically diagnosed type two DM patients (confirmed by fasting blood glucose more than 126 mg/dl and post-prandial blood glucose equal to or more than 200 mg %)9, of the age group of 40-60 years who attended the OPD between January 2011 to August 2012. 200 sex-matched controls of same age group and the same demographic profile were selected among the staff members, the paramedical staff, and accompanier of non-diabetic patients (those who did not have any symptoms which were related to type 2 DM and random blood sugar level is <200mg/dl) after taking their informed consent.
Deformity of hand, ridges obscured by injury to hand, ridge aplasia, ridge hypoplasia, presence of diseases like hypertension, congenital anomalies, carcinomas, psychiatric diseases, bronchial asthma were taken as exclusion criteria for both patient and control group.
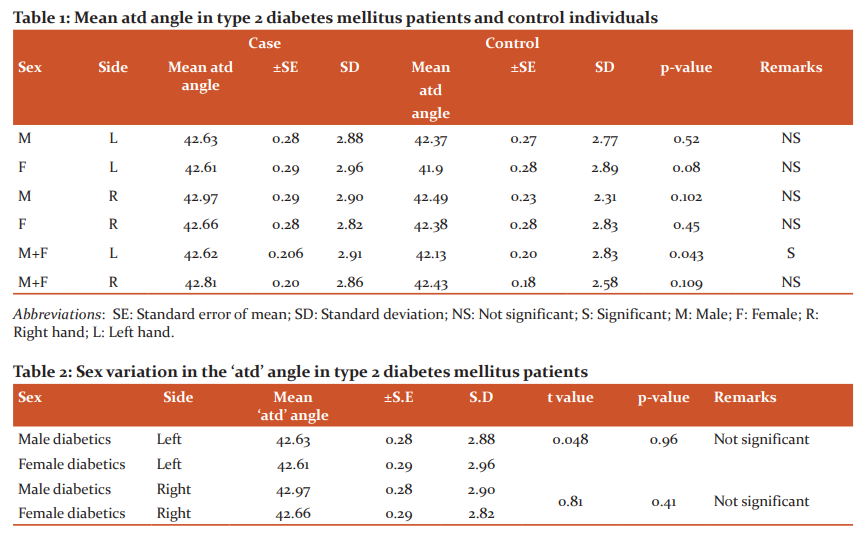
In the present study, the dermatoglyphic prints had taken by the Ink method.10 The palmar prints were taken on slightly glazed good quality paper by applying Kores black duplicating ink on the palmar surface of the hand of the subject [FIGURE 1]. After taking proper consent and explaining the process, study participants were asked to wash their hands with soap and water. For applying the ink to the subject’s hand, a small amount of ink was poured on the slab and made a thin, even smear with the help of a roller. The area of the palm to be printed was pressed upon the slab gently. After that, the inked area of the palm was placed on the paper. To get a proper palmar print the paper was placed on a sponge rubber pad. With the help of magnifying glass, we identified the axial and digital triradius in palmar print of the study subjects.
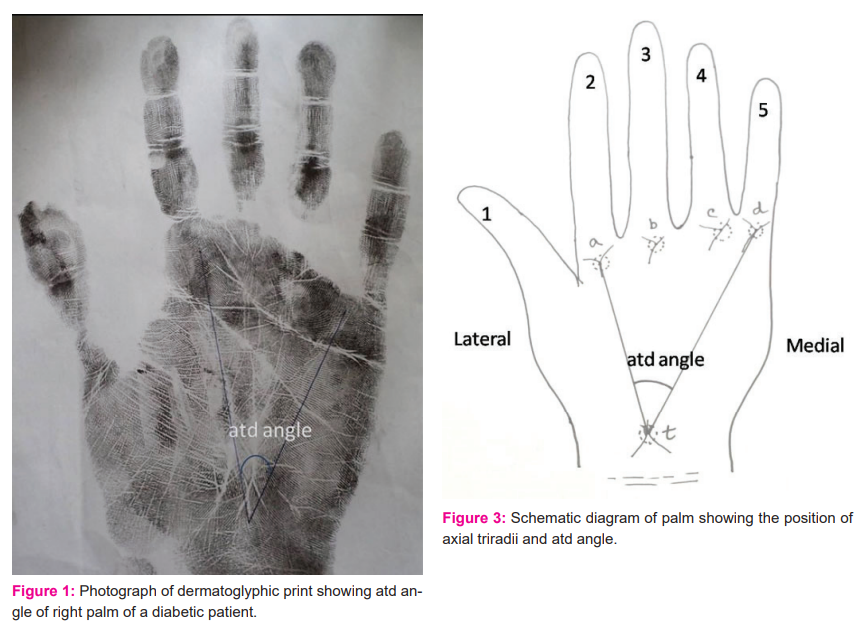
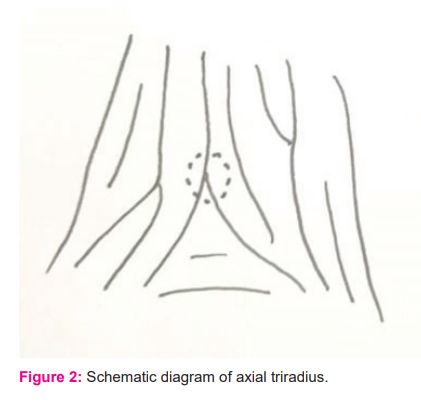
On the palm, the directions of dermal ridges are characteristically different in various areas. In the thenar area, the ridges are longitudinally oriented while in the hypothenar area it is characteristically oblique or transverse. Three ridge systems meet to form a triradiate structure, the triradius [FIGURE 2]. The triradius is found at the base of each finger except the thumb and they are designated as a, b, c, d digital triradii in order from index to little finger. Another triradius is usually found at the base of the palm between the thenar and hypothenar eminences and it is called axial triradius t. Depending upon the position, the axial triradius is termed as t, or t”. When an axial triradius is seen near the center of the palm, it is called the t”. While one is situated in the midway between the t and t” it is called as t’. The angle between a line drawn from t to a and t to d is atd angle.9 [FIGURE 3].
After collecting the data from cases and controls, it was tabulated in Microsoft excel datasheet 2007. By applying principles of descriptive studies data was arranged and statistical analysis of data was done by GraphPad Prism software version 6.0. Continuous data were analyzed revealing mean and standard deviation and tested by student’s t-test. p-value was calculated from statistical analysis (If the p-value is <0.05 then the difference is statistically significant).
RESULT:
In this study, we measured the atd angle of both hands of 200 types two diabetes mellitus patients and 200 controls. All data were tabulated, compared, and analyzed. We got statistically significant data only in the study of atd angle of the left hand as the mean ‘atd’ angle in control individual is 42.13±0.20 with standard deviation (SD) 2.83 and in type 2 DM patient it is 42.62±0.206 with SD 2.91, the two-tailed p-value is 0.043 [TABLE 1]. The mean atd angle of male diabetes mellitus patients of the left hand and right hand were more compared to female diabetes patients but the difference in values was not statistically significant [TABLE 2].
DISCUSSION:
Changes in atd angle of type 2 diabetes mellitus subjects had studied by Gabriel Oladipo G, Ogunnowo BM,1 RajnigandhaV et al. (2006),12Padmini MP, Rao NB, MalleswariB (2011)13 and Sharma MK ,14 and Peter D,1 Trivedi P. et al.,16Pathan FJ, Hashmi RN,17Rakate NS, ZambareBR(2013),18Srivastava S, Rajasekar S(2014)19 and all these studies were done in western and southern parts of India and Nigeria. Our study was conducted in the eastern part of India. From this region of India, no substantial data were published regarding the atd angle among diabetes individuals. Sex-wise variations of data of atd angle among diabetes individuals were not mentioned by any of the researchers.
In the present study, we found that atd angle significantly increased in the left hand of type 2 DM taking collectively both sexes in consideration which is similar to the findings of Rajnigandha V et al.12 and Eberechi, Dike, Gabriel O, Peter D.(2012).15
In case of the right hand in both sexes, we got increased value in atd angle in type 2 DM patients but it was not statistically significant. Whereas RajnigandhaV et al.,12 Padmini MP, Rao NB, Malleswari B,13Sharma MK and H14and Trivedi P. et al. (2013)16 had found significantly increased atd angle in the right hand.
In male cases, we got increased atd angle than controls which simulated with the findings of Padmini MP, Rao NB, Malleswari B, et. al.,13 Rakate N S, Zambre B R 18 and Trivedi P. et al. (2013)16 in case of the left hand, But these findings were not statistically significant.
In case of mean atd angle of the right hand of male diabetics was higher than controls which were similar with the findings of Sharma MK and H 14 and Rakate N S &Zambre B R.18 In the present study and the study by Malleswari B et al. 13 the findings were not statistically significant.
Whereas statistically significant changes of mean atd angle of male diabetics were observed in the studies of Gabriel Oladipo G, Ogunnowo BM,11Rajnigandha V et al. 12 and Trivedi P et al.16 (only in Right hand).
In the case of female diabetics mean atd angle of the right hand was higher (statistically insignificant) compare to the control in our study which was similar to the study of Malleswari B et al. 13 and Sharma MK and H.14 Though statistically significant variation of mean atd angle in female diabetics were seen by Gabriel SO et al.11, Rajnigandha V et al.,12Malleswari B 13 (in left hand), Sharma MK and H 14(left hand).
In the present study, mean atd angle of male diabetic were more in both hands in comparison to the female diabetics though these values were not statistically significant. Other researchers did not study sex-wise variation of ‘atd’ angle.
Strength & weakness of study:
For this study, we considered only the ‘atd’ angle of dermatoglyphic trait, as this is the most widely used method, cost-effective, and less time-consuming. The collective data on other parameters of dermatoglyphic traits will enhance the possibilities of consideration of the dermatoglyphic study as a screening tool or diagnosis of type two diabetes mellitus more. In this study, we collected data from the patients visiting the various medical colleges of Kolkata and the surrounding region of the state of West Bengal. Conducting the study in different geographical populations and different ethnicities will provide a more clear idea about the usefulness of dermatoglyphic study as a screening tool.
Conclusion: We can conclude from the above result and discussion that increased atd angle of the left hand in presence of the family history of DM with or without having other risk factors, is a strong predilection for the development of the disease. These groups of people can be advised to adopt preventive measures like lifestyle modification and frequent blood glucose estimation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT:
The authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors / editors / publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
FUNDING: NIL
CONTRIBUTIONS BY AUTHORS
Concept Design: Sarkar Satabdi
Definition of intellectual content: Sarkar Satabdi
Literature search: Sarkar Satabdi, Sarkar Tanmay
Data acquisition: Sarkar Satabdi, Sarkar Arpita, Saha Pallab Kumar, Basak Samanwita
Data analysis: Sarkar Satabdi, Sarkar Arpita, Kundu Banani
Statistical Analysis: Sarkar Satabdi,Sarkar Tanmay,
Manuscript Preparation: Sarkar Satabdi, Sarkar Arpita
Manuscript editing: Sarkar Satabdi, Sarkar Arpita, Sarkar Tanmay, Basak Samanwita
Manuscript review: Sarkar Satabdi, Sarkar Tanmay, Sarkar Arpita, Basak Samanwita, Saha Pallab Kumar, Kundu Banani
References:
1. Cummins H, Midlo, C. Palmar and plantar epidermal ridge configurations (dermatoglyphics) in European Americans. Am. J. Phy. Anthropol1926; 9: 471-502
2. Meier RJ. Anthropological Dermatoglyphics: A Review. Yearbook of Physical Anthropology 1980; 23:147-178
3. Blanka S, Milton A. Dermatoglyphics in medical disorders. New York: Heidelberg Berlin: Springer – Verlag1976.
4. Rashad MN, Mi MP. Dermatoglyphic traits in patients with cardiovascular disorders. Am J Phy Anthropol. 1975;42(2):281-3
5. Pakhale S V, BoroleS B, Doshi M A, More P V. Study of the fingertip pattern as a tool for the identification of the dermatoglyphic trait in bronchial asthma. JCDR2012;6(8): 1397–1400
6. Hirmath R, Nuchhi A, Gosavi A, Mugadlimath A . Comparative Study of Dermatoglyphic Patterns of Schizophrenic Patients with Control Population Int J of Anat Rad and Sur 2017;6(4):26-30
7. Verbov J. Clinical significance and genetics of epidermal ridges-a review of dermatoglyphics. J Invest Dermatol 1970; 54:261-271.
8. Pradhan R, Kumar D B, Mitra A. Some Salient Points in Type 2 Diabetes Prevalence in Rural Bengal, Studies on Ethno-Medicine 2009; 3:2: 127-131
9. Kasper DL. Harrison's principles of the internal medicine.19th edition. New York.McGraw Hill Education Medical2015; 2:2399-2400
10. Singh IP and Bhasin MK. Dermatoglyphics. A manual of biological anthropology. New Delhi.Kamla-Raj Enterprises2004: 317-84
11. Oladipo G, Ogunnowo B. M. Dermatoglyphic patterns in diabetes mellitus in a southeastern Nigerian population. Afr. J. of Appl.Zool& Environ. Biol 2004; 6: 6-8.
12. Rajnigandha V, Mangala P, Latha P, Vasudha S. Thedigito-palmar complex in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Turk. J. Med. Sci 2006;36(6):353-55.
13. Padmini MP, Rao NB, MalleswariB. The Study of Dermatoglyphics in Diabetics of North Coastal Andhra Pradesh Population, Ind J. Fundamental. Appl. Life Sci 2011; 1: 75-80.
14. Sharma MK, Sharma H . Dermatoglyphics: A diagnostic tool to predict diabetes. J. Clin. Diagnostic Res 2012; 6(3): 327-332.
15. Eberechi D, Gabriel O, Peter D. A comparative study of the digital pattern, position of triradii, b-c and a-d palmar distances of diabetic subjects and essential hypertensive individuals in river state.Int. J. Adv.Biotechnol. Res 2012; 3(2): 615-620
16. Trivedi P, Singel T, Kukadiya U, Satapara V, Raghava J, Patel M, et al. Correlation of atd angle with NonInsulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus in Gujarati population. J. Res. Med. Dent. Sci 2012; 2(2): 47-51.
17. Pathan FJ, Hashmi RN. Variations of Dermatoglyphics Features in Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Recent Trends Sci Technol. 2013; 8(1): 16-19.
18. Rakate NS, Zambare BR.Comparative study of the dermatoglyphic patterns in type II diabetes mellitus patients with non-diabetics.Int J Med Res Health Sci 2013;2(4): 955-959
19. Srivastava S, Rajasekar S. Comparison of Digital and Palmar Dermatoglyphics Patterns in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic individuals. IOSR-JDMS 2014; 13:93-95.
|






 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License